BE 202- Chapter 1
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Introduction to Physiology and Homeostasis
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
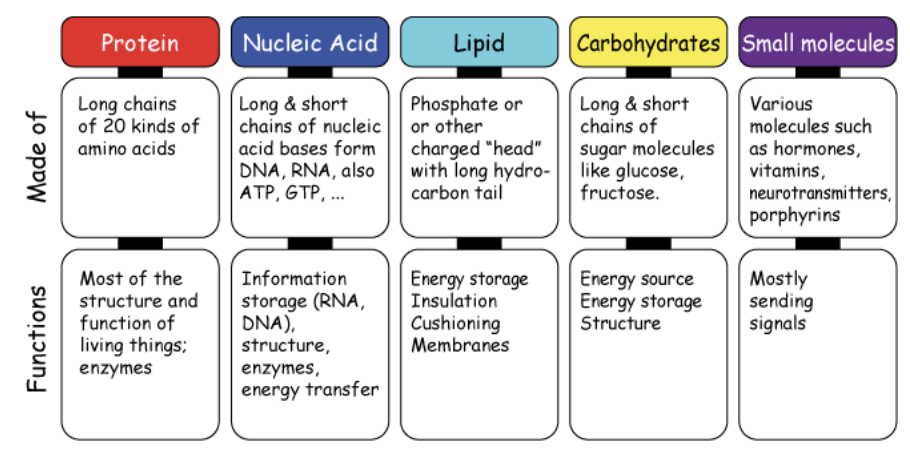
Physiology
the study of the functions of living thing
Levels of Organization in the Body
Chemical, Cellular, Tissue, Organ, Body system, Organism
Chemical Level
Various atoms and molecules make up the body
Cellular Level
Cells are the basic units of life
tissues, organs, body systems and the whole body body
Basic Cell Functions
Obtaining nutrients and O2
Performing chemical reactions
Elimination wastes
Synthesizing proteins and cell components
Moving materials throughout the cell
Responding to the environment
Reproducing
except nerve cells and muscle cells
Specialized Cell Functions: Digestive System
Gland cells secrete enzymes that break down ingested food
Specialized Cell Function: Kidneys
Epithelial cells selectively retain or eliminate substances
Specialized Cell Function: Muscle cell
produce muscle movement
Specialized Cell Function: Nerve cells
Generate and transmit electrical impulses that relay information
Tissue
groups of cells with similar structure and specialized function
4 types of Tissue
Muscle tissue, skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle
Muscle tissue
skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscle
Nervous tissue
initiate and transmit electrical impulses
Epithelial tissue
selective transfer material s between the cell and environment
Connective tissue
connects, supports, anchors various body parts
Two Types of Epithelial tissue
epithelial sheets and secretory glands
Two categories of secretory glands
exocrine and endocrine
Gland Formation
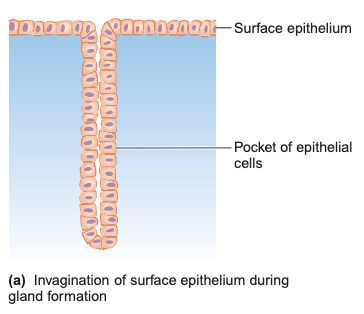
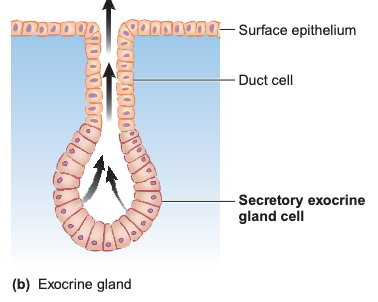
Example of Exocrine gland
Sweat gland, Salivary gland
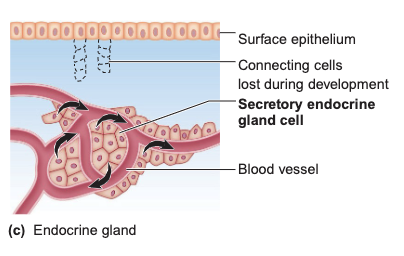
Example of endocrine gland
Pancreas
Organ Level
made up of several tissue types; consists of two or more primary tissue types organized to perform particular functions
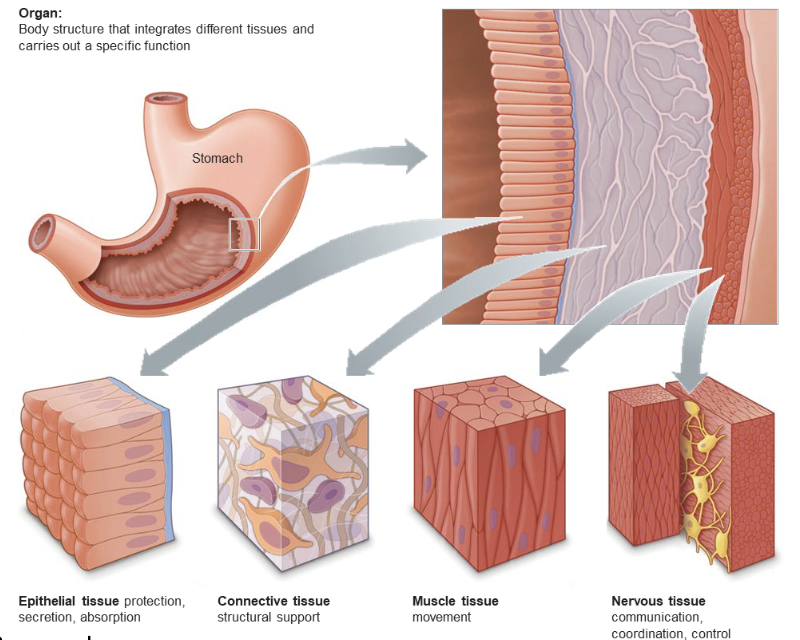
Body System
a collection of organs that performs related functions
11 body systems
Circulatory, Digestive, Respiratory, Urinary, Skeletal, Muscular, Integumentary, Immune, Nervous, Endocrine, Reproductive
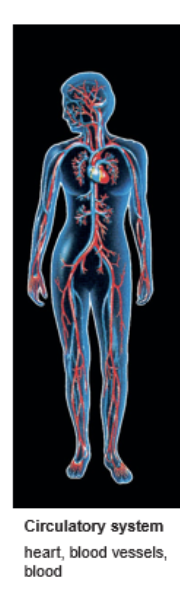
Circulatory System
heart, blood vessels, and blood
Transports nutrients, O2, CO2, waste, electrolytes and hormones throughout the body
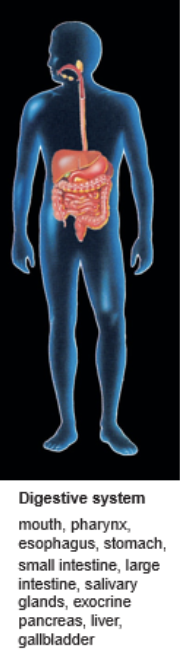
Digestive System
mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, intestines
breaks down food into small nutrient molecules and transfers them into the blood plasma
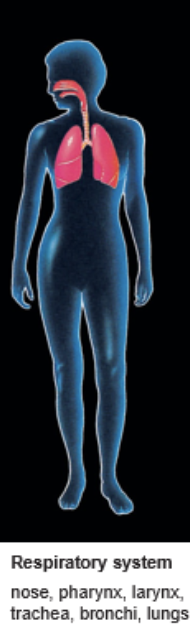
Respiratory System
Lungs and major airways
Receives O2 and eliminates CO2
Urinary System
Kidneys and associated structures
Kidneys filter wastes and extra water from blood and make urine
Urine travels from the kidneys through the ureters and fills the bladder
Muscular system and Skeletal system
Support and protect organs
allow body movement
Muscular System
generate heat and are important in maintaining body temperature
Skeletal Systems
storage reservoirs for calcium
Integumentary System
skin and related structures
the outer protective barrier
regulated body temperature

Immune System
white blood cell and lymphoid organs
defend Bacteria, Viruses
Help replace injured or worn-out cells
Nervous system
Brain, spinal cord, nerves and sense organs
controls and coordinates body activities
pathway for communication
Endocrine System
All hormone-secreting glands
Regulated activities that require duration rather than speed
Reproductive System
essential for perpetuating the species
not essential for homeostasis
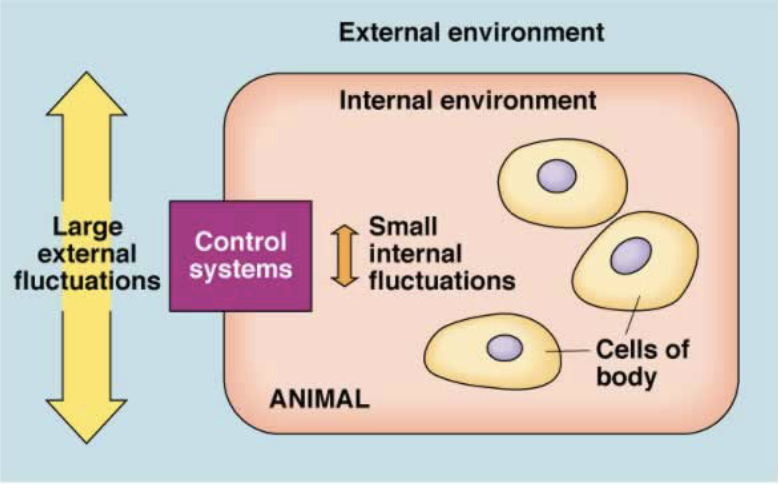
Homeostasis
dynamic steady state in the internal environment
Intracellular Fluid (ICF)
fluid contained within cells
Extracellular Fluid (ECF)
fluid outside the cells
Plasma
the fluid portion of blood
Interstitial fluid
surrounds the cells
Factors to maintain homeostasis
Concentration of nutrients
Concentration of O2 and (acid forming) CO2
Concentration of waste products