Entomology - Morphology and Physiology
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
What is an exoskeleton
The external hardened, cuticular skeleton to which muscles are attached internally
What does integument mean
tough, outer protective layer
What does the exoskeleton do
Provides a barrier against desiccation
provides structure and support
surface for internal muscle attachment
protection from damage and infection
sensory interface with environment
What is the main challenge of having an exoskeleton
Growth
What is the structure of the exoskeleton (name the layers from the inside to the outside of the insect)
Basement membrane
Epidermis
Cuticle
procuticle
epicuticle
What is the function of the epicuticle
cement layer that protects from abrasion, and wax layer that creates a barrier to water movement (keeps water in)
What is the structure of the procuticle
chitin microfibers surrounded by matrix of protein
What is the structure of the epidermis
single-layer of secretory tissue
What does the epidermis do
produces cuticle layers (only living layer of the exoskeleton) using dermal glands
What is the function of the basement membrane
separates body cavity from integument
What is chitin
a nitrogen-containing polysaccharide
What makes up the polymer chitin and how are they grouped together
repeating units of monosaccharides to form chains, which are grouped into bundles that have strong hydrogen bonding
how are the bundles of monosaccharides put together
the bundles align parallel to form sheets
how are the sheets of polysaccharides in chitin arranged
they are deposited at different angles in a rotation to create a helical arrangement
What are the physical properties of chitin
pliable, resilient, and tough
What two layers can the procuticle be split into
The exocuticle (closer to epicuticle) and the endocuticle (closer to epidermis)
What is the exocuticle and it’s function
It is the sclerotized portion of the procuticle. It functions as a hard armor for the insect
What is sclerotization
this is the stiffening of the cuticle by cross-linkage of protein chains creating dark rigid plates
What is the advantage of unsclerotized membranes
it allows insects to move around and expand since it’s softer and more flexible
What is resilin
a rubber-like or elastic protein in some insect cuticle
What are two different types of cuticular extensions
Spines (multicellular) and Setae (single-cell and hair like)
What causes variation in the coloration of insect exoskeletons
both pigments (chemical) and structure (physical)
What is the Cyphochilius beetle known for, where is it native to
it’s known for being among the whitest insects in the world, due to it’s ability to reflect 99.6% of all light (chitin and air bubbles allow this). It’s native to Asia, and it has been important for product development because of it’s passive cooling abilities.
What is the Namib Desert darkling beetle known for, and how is it important for product development
The bumps on the insect attract water droplets that are maintained by it’s waxy exoskeleton. The insect can tip it’s backside up, allowing the water to gather around it’s mouth for drinking. This is important for product development because biotechnology has been able to mimic it in order to create a water reservoir for people living in the desert.
How do insects grow?
through molting
What is molting
a two-step process including the formation of new cuticle and shedding of old cuticle
Explain the first step of molting
The cuticle separates from the epidermis (apolysis), and the epidermal cells divide and secrete molting fluid into the apolysial space that is inactive at this point
Why is the molting fluid inactive in step 1 of molting
This is so that the enzymes in the molting fluid don’t digest any living cells
Explain step 2 of molting
Epidermal cells secrete new epicuticle and the enzymes in the molting fluid activate after the epicuticle is there to protect the epidermis from digestion
Explain step 3 of molting
The old endocuticle is digested and reabsorbed, and new, undifferentiated procuticle is formed
Explain step 4 of molting
The remnants of the old cuticle separate/open along the weak line (suture)
Explain step 5 of molting
The insect undergoes ecdysis, leaving the exuvium behind
What is ecdysis
escape from the old cuticle
what is the exuvium
the old cuticle remnant, includes the exocuticle and epicuticle
Explain step 6 of molting
The cells expand, new cuticle swells and expands as it is straightened out
Explain step 7 of molting
The procuticle differentiates in exocuticle and endocuticle, and then sclerotization of the exocuticle happens
What is a teneral adult
a newly molted insect before sclerotization
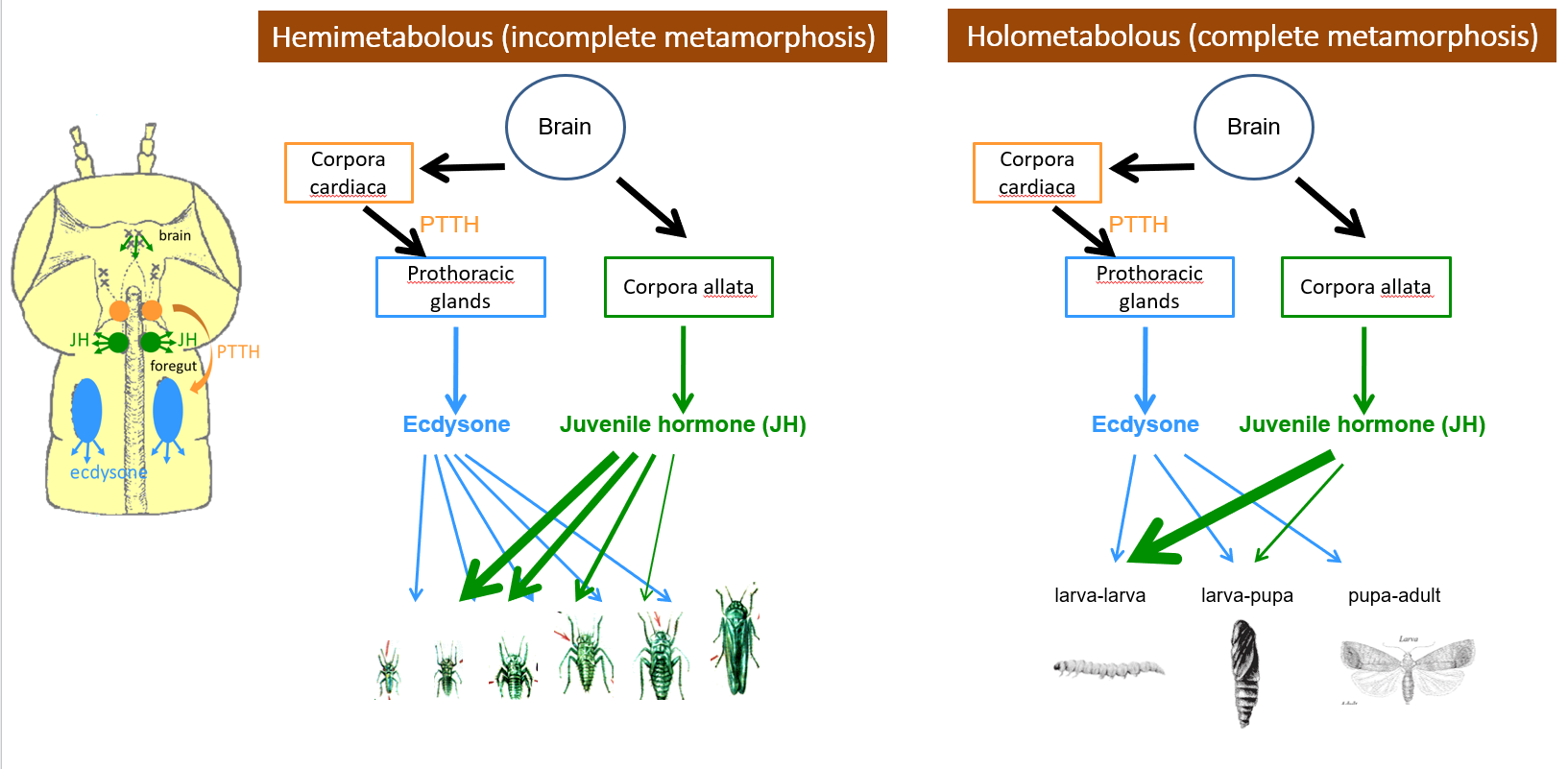
What is the function of PTTH (Prothoracicotropic hormone)
it starts the process of molting by activating the prothoracic glands to secrete ecdysone
What is ecdysone
it is the molting hormone, it initiates the growth and molting activities of the epidermis
What releases PTTH
Corpora cardiaca
What do the prothoracic glands do
they produce ecdysone after stimulated by PTTH
What is metamorphosis
The relatively abrupt change in body form and physiology between the immature and adult stages
What does hemimetabolous mean
incomplete metamorphosis - development in which the body form gradually changes at each molt
What does holometabolous mean
complete metamorphosis - development in which the body form abruptly changes at the pupal molt
What is determinate growth
means that there is a certain number of molts and the growth ends at the adult stage
immature hemimetabolous insects are called what
nymphs
How do the wings of hemimetabolous insects develop
externally (exopterygote)
immature holometabolous insects are called what
larvae
how do the wings of holometabolous insects develop
internally (endopterygote)
How do hemimetabolous insects differ from holometabolous insects
holo immatures are larvae and don’t resemble adults while hemi immatures are nymphs and resemble adults
holo wings develop internally while hemi wings develop externally
holo larvae and adults have different ecology while hemi nymphs and adults have similar ecology
how are hemimetabolous and holometabolous insects similar
both have determinate growth
Why is it a key innovation for larvae and adults to have different ecologies
this is because it led to an increase in diversity
T/F: All arthropods molt
false
T/F: All arthropods undergo metamorphosis
false
T/F: insects continue to molt as adults
False
What does ametabolous mean
means no metamorphosis, no change in body form during development, indeterminate growth
What is indeterminate growth
there’s no determinate number of molts, they continue molting even in adulthood (no terminal adult)
Which hexapods are ametabolous
non-insect hexapods and apterygote insects
What does juvenile hormone do
determines the body form/outcome of the molt by inhibiting development of adult characteristics before the final molt (suppressing hormone)
What produces juvenile hormone
corpora allata
For a particular pupating organism that normally has five instars, what would happen if the corpora allata was removed at the fourth instar
The insect would become an adult sooner, so it have a smaller pupa, and be a smaller adult
What would be the affect of inserting the corpora allata from a young larva into a 5th instar (last instar before pupation)
There would be an additional larval molt, causing the pupa and the resulting adult to be giant
draw out diagrams for hormones and hemi/holometabolous
What are IGRs
insect growth regulators - chemicals that disrupt normal insect growth and development
What are juvenile hormone mimics
IGRs that keep an insect from reaching adulthood
What are ecdysone receptor agonists (mimic)
IGRs that induce premature molts
What are chitin synthesis inhibitors
IGRs that inhibit cuticle formation
What are the applications of IGRs
they are useful in agriculture, horticulture, forestry, livestock, and households
What are the advantages of IGRs
specific to insects
harder for insects to evolve resistance to
What are disadvantages of IGRs
timing - they are only effective when immature insects are exposed
relatively slow process
What is example of a naturally occurring IGR
some plants produce an ecdysone mimic when they are fed on, causing the insect to molt prematurely and die
a specific example is in lettuce roots. Root herbivory by fungus gnats increases PE (ecdysone mimic) concentration in lettuce roots. The PE causes the gnats to die sooner and pupate too early
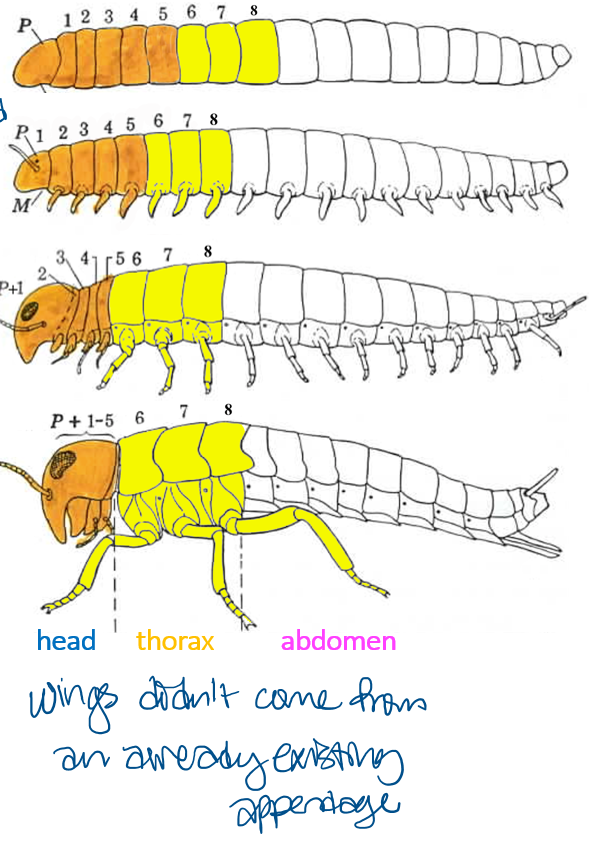
What are the three tagmata of insects specialized for
Head - sensory and ingestive
Thorax - locomotor
Abdomen - digestive and reproductive
Explain the evolution of insect tagmosis
a segmented, worm-like ancestor had 20 body segments
development of paired appendages on each segment happened
anterior (head end) segments begin to differentiate
6 segments (P +1-5) consolidated into a compound head, and the appendages form mouthparts and antennae
3 segments (6-8) become the thorax, and the appendages develop into jointed les for locomotion
the remaining 11 segments become the abdomen, and the segmented appendages disappear (except segments 8,9, and 11 of the abdominal region)
What is the function of antennae
smell
What is the function of compound eyes
vision
what are ocelli and their function
they are light-sensitive “simple” eyes that only help to sense light and dark
What is the sensory equipment located on the head (excluding mouthparts)
antennae
compound eyes
ocelli
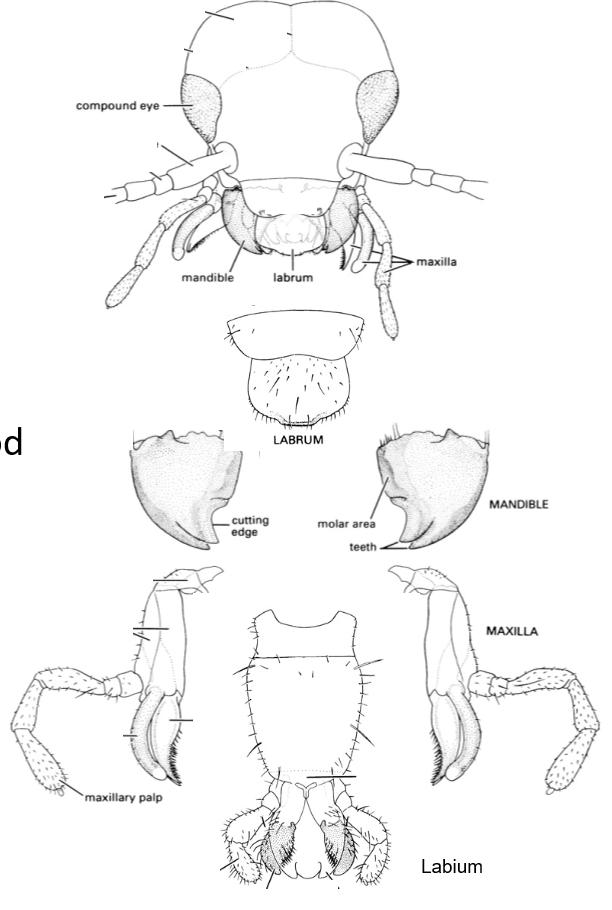
What are the mouthparts on the head
labrum
mandibles
maxillae
labium
palps
What is the labrum
upper lip
what are the mandibles
jaws, that cut and macerate (soften) food
What are the maxillae
accessory jaws that assist mandibles in processing food
what is the labium
lower lip
what are palps
sensory organs to sample food before ingestion
Recognize what all the organs on the head look like