digestion and absorption of lipids
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
summarise the process of lipid digestion:
starts in mouth and stomach, but most takes place in duodenum and ileum
bile salts (not an enzyme!) emulsify lipids
then lipase hydrolyses ester bonds
describe the digestion of lipids:
bile salts neutralise stomach acid and emulsify large lipid globules → smaller lipid droplets
this increases SA for lipase to act on - triglycerides → fatty acids and monoglycerides
bile salts surround FA chains and monoglycerides to form micelles, making the FA chains more water soluble
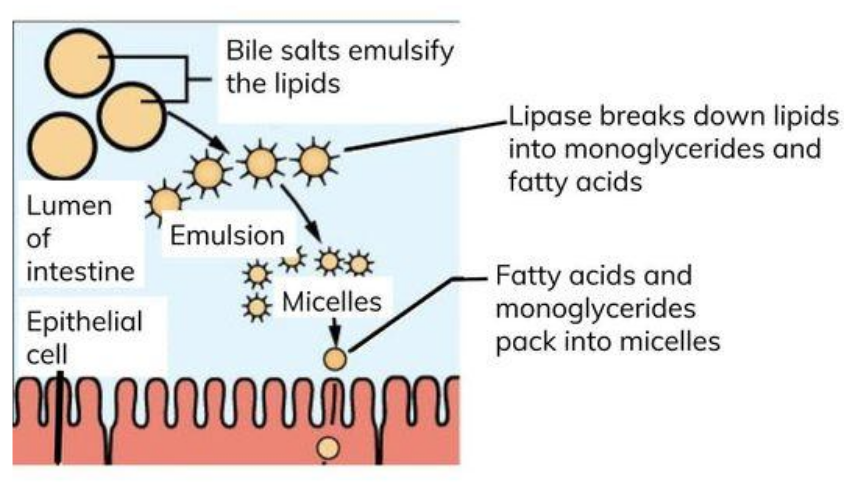
describe the process of absorption of triglycerides:
micelles contain bile salts, fatty acids and triglycerides
micelles make fatty acids more water soluble and carry fatty acids to epithelial lining of ileum
micelles are broken down to release fatty acids and monoglycerides
micelles maintain a higher concentration of fatty acids to the lining of the ileum
fatty acids and monoglycerides diffuse into the epithelial cells that line the ileum
triglycerides reform inside the cell’s ER
triglycerides are packaged in the Golgi w/ cholesterol and proteins to form chylomicrons for transport
chylomicrons are released from the epithelial cells by exocytosis into lacteals (lymphatic vessels in the villi)
chylomicrons are transported via lymph vessels in the lymphatic system to the blood
where is lipase produced?
pancreas
where are bile salts produced and stored? how are they secreted into the duodenum and ileum?
produced in liver, stored in gall bladder
secreted into duodenum and ileum via bile duct
why can fatty acids diffuse across the epithelial lining?
non charged/non polar
explain the advantages of lipid droplet and micelle formation:
droplets increase SA for lipase action
∴ faster hydrolysis of triglycerides
micelles carry fatty acids and glycerol to intestinal epithelial cell