current electricity
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
potential difference (voltage)
-In a battery, a series of chemical reactions occur in which electrons are TRANSFERRED from one terminal to another. What is BETWEEN the poles?
-where the charge begins to where it ends
electromotive force or (EMF)
-The MAXIUMUM potential difference a power source can have
-isn't actually a force, simply the amount of energy per charge
-(J/C or V)
push and pull
When a wire connects the terminals of a battery or generators, the voltage will __ and ___ electrons through a conductor.
negative, positive
Electrons in the wire are PUSHED by the ____ terminal and PULLED by the ____ terminal through the wire.
voltage
electrical PRESSURE that pushes and pulls charges
A source of energy
A closed path
A device which uses the energy
All electric circuits have three main parts:
fluids
Electricity can be symbolic of ____
2
A circuit works on _ IMPORTANT PRINCIPLES
electric current
The amount of CHARGE that flows PER SECOND
-the rate at which charge FLOWS through a surface
conventional current
-The current is in the same direction as the flow of positive charge
-the flow of current from the positive terminal of a power source to the negative terminal
direct and alternating
2 types of Current
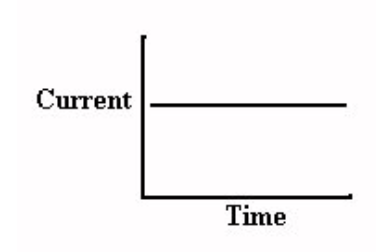
Direct Current
-current flows in one direction
-Example: Battery
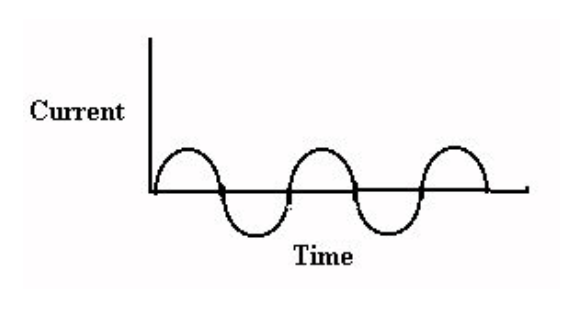
Alternating Current
-current reverses direction many times per second.
-This suggests that AC devices turn OFF and ON.
-Example: Wall outlet (progress energy)
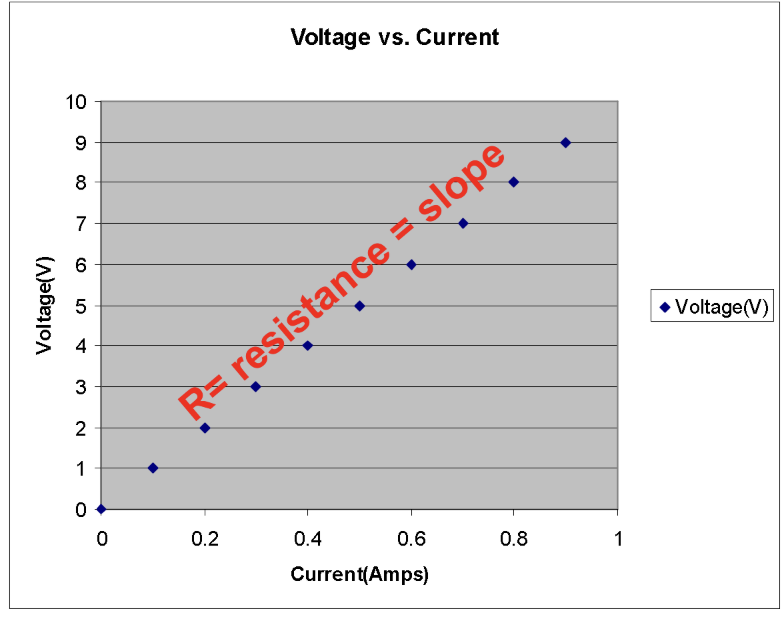
Ohm’s Law
The current in a circuit is:
directly proportional to voltage
inversely proportional to the resistance
I=V/R or V=IR
voltage vs current graph
resistence = slope
Electrical Resistance (R)
the ability of a material to resist the flow of charge (ohms)
-Changes electrical energy into thermal energy and light
-Ex: lightbulb filament
1) Voltage provided by source
2) Electric resistance of the conductor
The amount of charge that flows through a circuit depends on two things:
Resistor
A circuit device that is designed specifically to limit current flow.
any
___ device can be modeled with a resistor.
larger, smaller
The ____ the resistor/resistance the ___ the current that flows through them
lost
Voltage (Potential Difference) is ____ through resistors.
wire
The medium through which charges flow.
long
thin
hot
what creates more resistance:
length
cross-sectional area
temperature
copper
aluminum
material that creates less resistance:
material that creates more resistance:
Kilowatt-Hour (kWh)
The amount of energy consumed in 1 hour at a rate of 1 kW
Power
“rate” in formula (W)
energy —> heat and light
energy conversion in an incandescent light bulb
energy —> heat + kinetic
energy conversion in a clothes dryer
energy —> sound + light
energy conversion in a digital clock radio
A= C/s
unit of electric charge in terms of MKS units
in series
How must an ammeter be connected in a circuit to correctly read the current?
in parallel
how must a voltmeter be connected to a resistor in order to read the potential difference across it?
battery
-a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy
-a source of electrical potential, essentially a voltage, that pushes electrons through a circuit
electric circuit
a closed path that allows electric current to flow continuously
conservation of charge
the net charge of an isolated system will always remain constant