Chemistry Regents - 2024 ⚗️🔬 (copy)
1/227
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Hey everyone, I've compiled some notes, topic lists, and study materials, along with flashcards from others. I hope this helps you out. Good luck with your regents! - Reed Tricky topics that don't work well on flashcards: - Calculating Hydrates and Anhydrates - Percent Composition - Half-lives - Gas Laws (especially Boyle's Law), including graphs and practical uses - Lewis Dot Diagrams and Formulas - Vapor Pressure - Naming Covalent and Ionic Compounds - Table J - Molarity - Shifts in Reactions - Titration - Organic Chemistry - Heat formulas Additional resources I recommend: - The Organic Chemistry Tutor on YouTube - HIGHLY RECOMMEND Mark Rosengarten on Youtube (Really good videos focuses on chem regents and has music videos!!!) - https://www.nysedregents.org/Chemistry/ - Full practice regents exam - https://web.bcsdny.org/flhs/science/chem/regentschem.htm - Practice regents questions by topic - Your teacher - Your old notes/past test - Check out note guides and flashcards on Knowt or Quizlet!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
228 Terms
Properties of Solids
Solids have a fixed shape and volume
They cannot be compressed
They have a high density
There is a very strong force of attraction between particles
There is negligible space between the particles
Properties of Liquids
Liquids are almost incompressible
Molecules in liquids are close to each other
Liquids have a fixed volume but no fixed shape
Liquids flow from higher to lower levels
Boiling points of liquids are above room temperature under normal conditions
Properties of Gasses
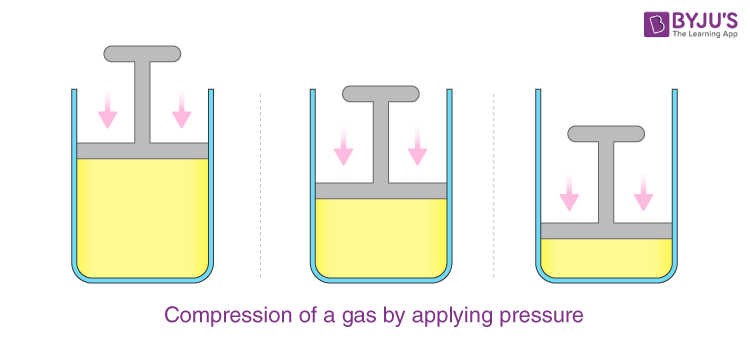
Compressibility: Gas particles have large intermolecular spaces.
Expansibility: Gas contracts under pressure.
Diffusibility: Gas molecules are in constant high-speed motion.
Low Density
Exertion of Pressure
Exothermic
- An exothermic process releases heat, causing the temperature of the immediate surroundings to rise.
- Melting, vaporization, and sublimation.
Endothermic
- Endothermic process: Absorbs heat, cools surroundings
This may seem weird, but if you’re struggling to remember, think of it this way: when you eat food (solid) and it turns into a gas (farts), and you're absorbing energy.
Dalton
Hard ball-like structure

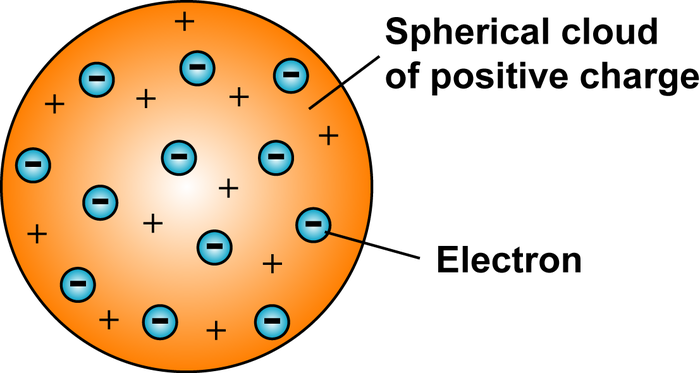
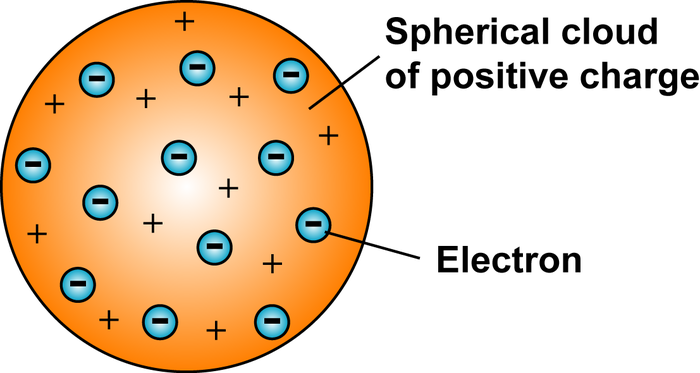
Thomson
Negatively charged atoms (electrons) in a positive soup
Rutherford
- Tiny, dense, positively charged core called nucleus
- Mass concentrated in the nucleus

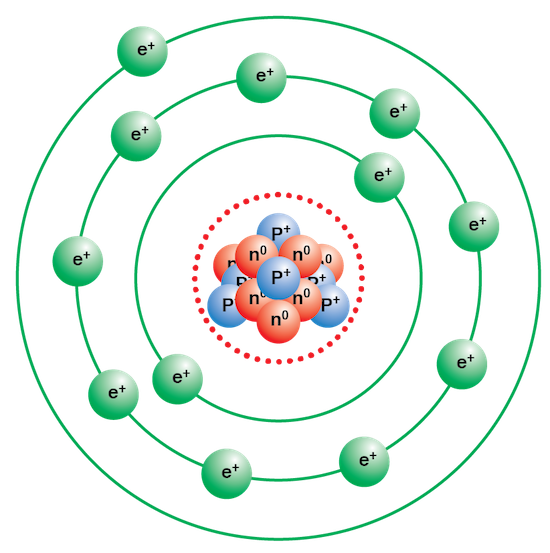
Bohr
Described electrons having orbitals (shells)
Name of Dalton’s model
Billiard Ball

Name of Thomson’s model
Plum Pudding
Name of Rutherford model
Nuclear model
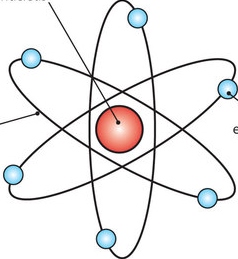
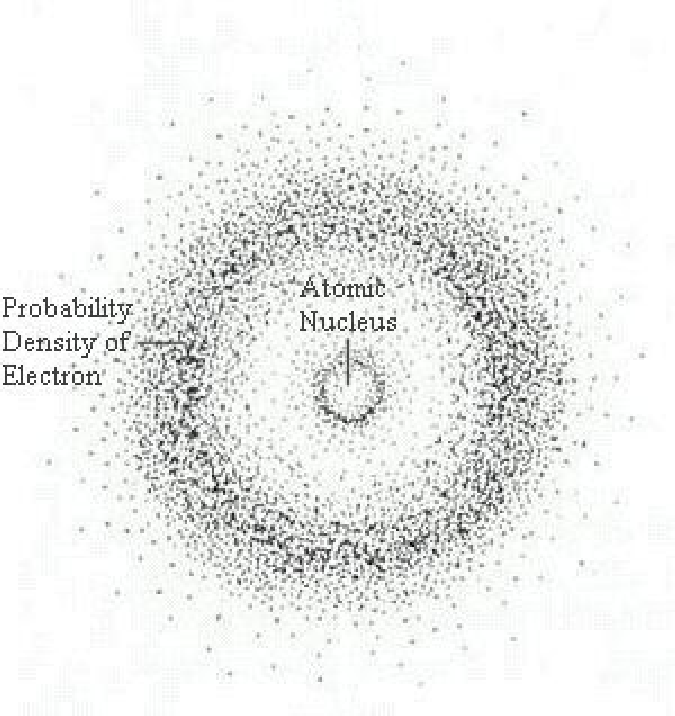
Schrödinger’s model
- Schrödinger model: Describes electron as a wave
- Defines regions in space, or orbitals, where electrons are likely to be found
Wave Mechanical Model

Atomic Number
- Atomic Number: Number of protons in the nucleus
- Determines the element's identity and position on the periodic table
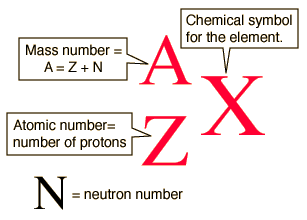
Mass Number
- The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus
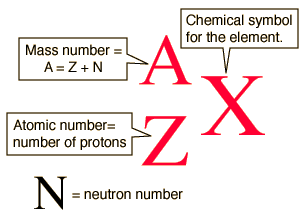
Isotopic Symbols
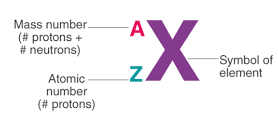
Average Atomic Mass Formulas
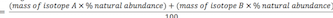
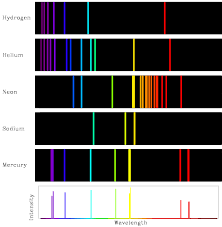
Emission Spectra
- Atoms or molecules emit light when they transition to lower energy states
- Each element has a unique emission spectrum based on its electron configuration
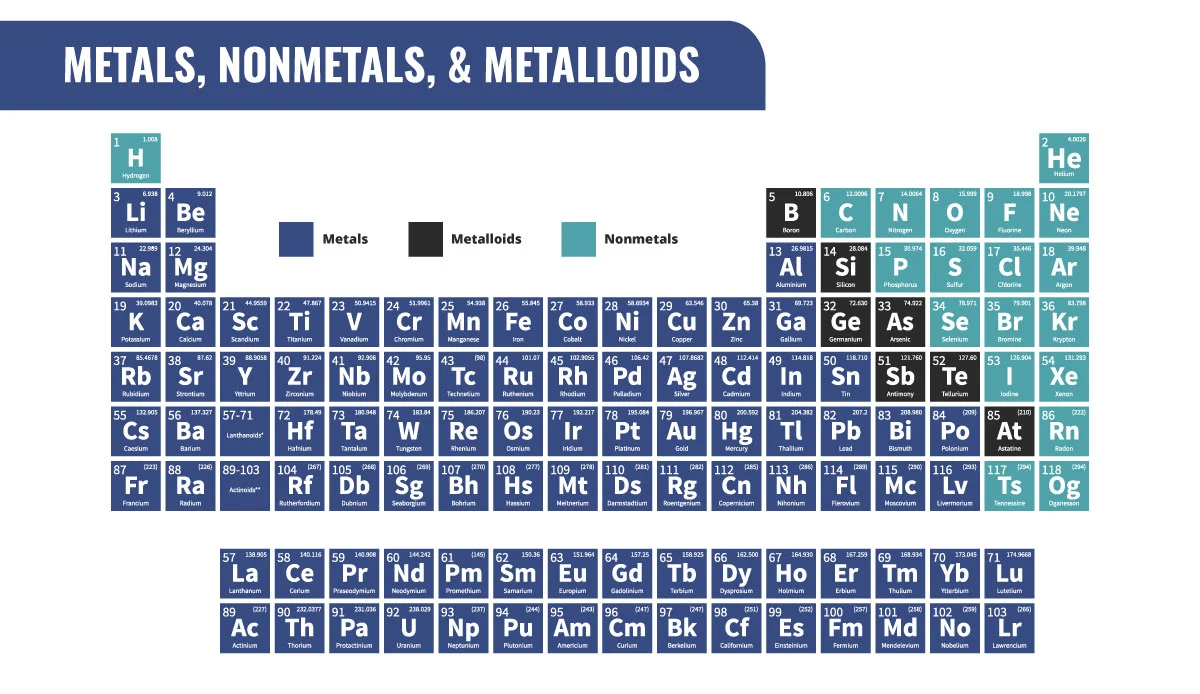
Metal’s Characteristics
Malleable
Good conductors
Ductile
Solid at room temp
Lustrous
High Boiling / Melting Points
High Density
Non-Metal’s Characteristics
Not Malleable
Not conductors
Not-Ductile
Solid at room temp*
Not-Lustrous
Low Boiling / Low Points
Low Density
Metalloid’s Characteristics
Brittle
Semiconductors
Not Ductile
Solid at room temp
Lustrous
High Boiling / Melting Points
Varied Density
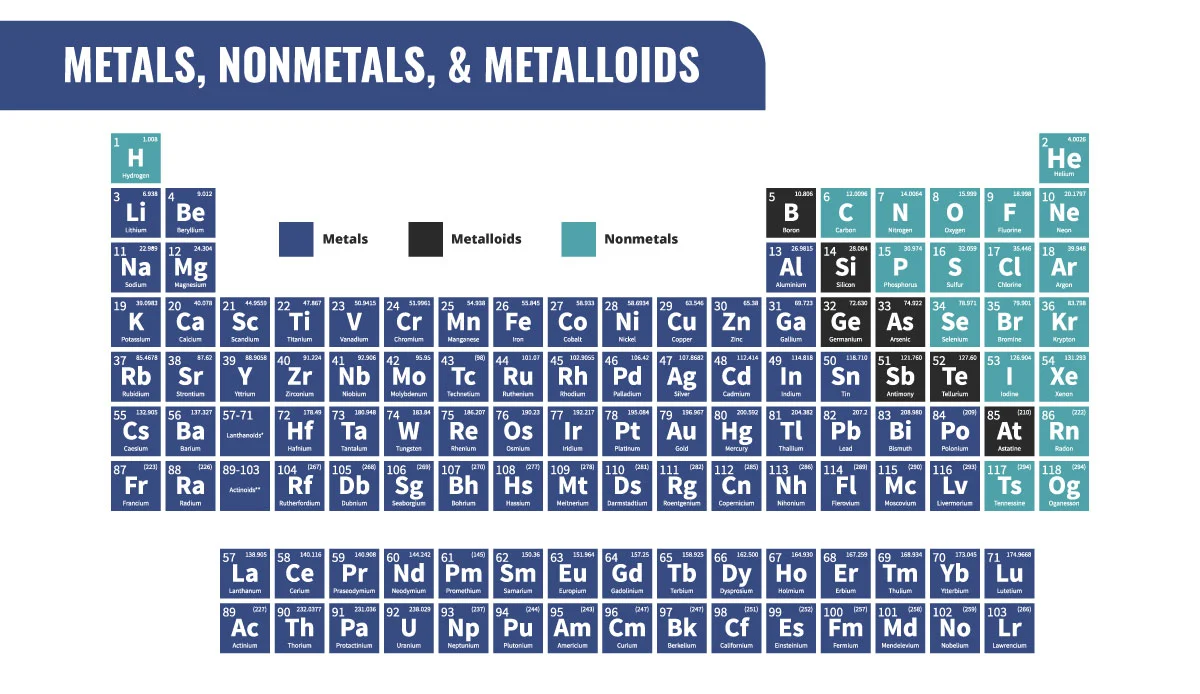
Alkali-Metal’s Characteristics
- Group 1 metals
- Low melting and boiling points
- Good conductors of heat and electricity
- React vigorously
- Easily lose their outermost electron to form a +1 ion
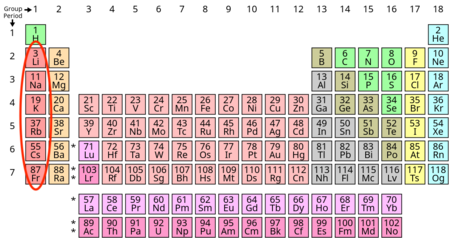
Alkaline Earth Metal’s Characteristics
- Good conductors
- Low ionization energy and low electronegativity
- High reactivity with 2 valence electrons
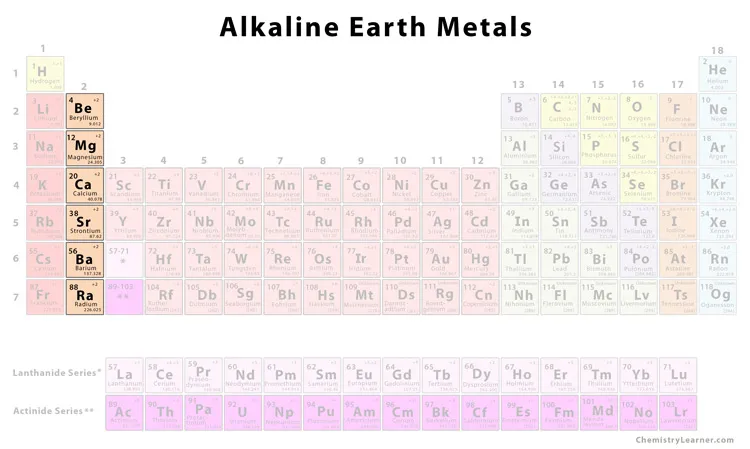
Halogen’s Characteristics
Highly reactive nonmetals
Exist in all three states of matter
Have seven valence electrons
High electronegativity
7 valence electrons
Noble Gases’s Characteristics
They are known for their low reactivity.
Noble gases have a full outer electron shell.
Noble gases are nonflammable.
They have low boiling and melting points.
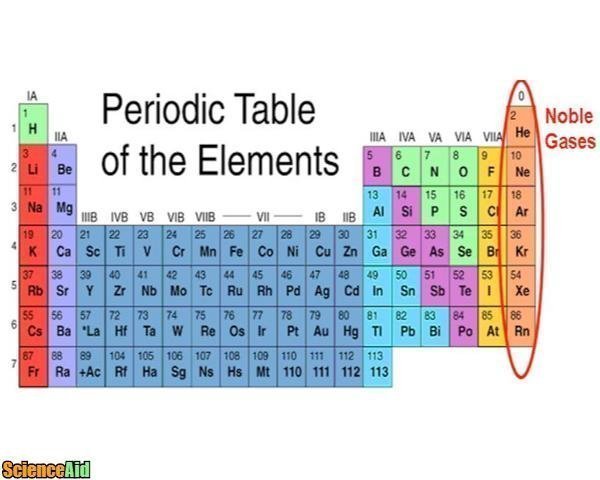
Electronegativity - Down a group
Decrease
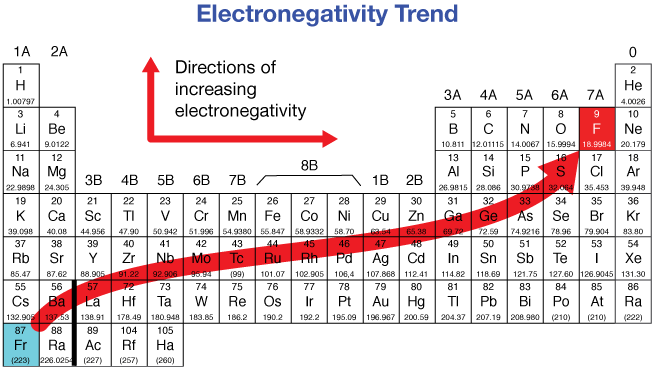
Atomic Radius - Down a group
Increases
Ionization energy - Across a period
Increases

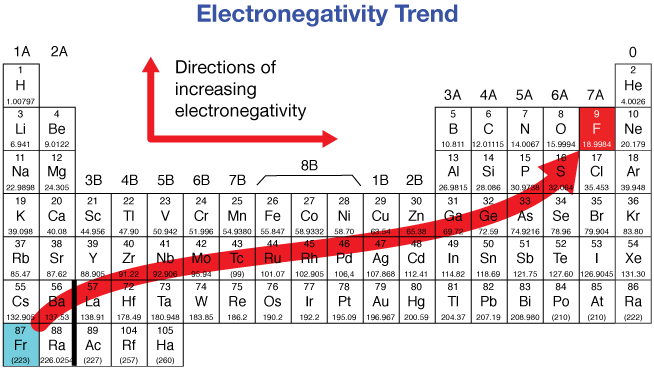
Electronegativity - Across a period
Increases
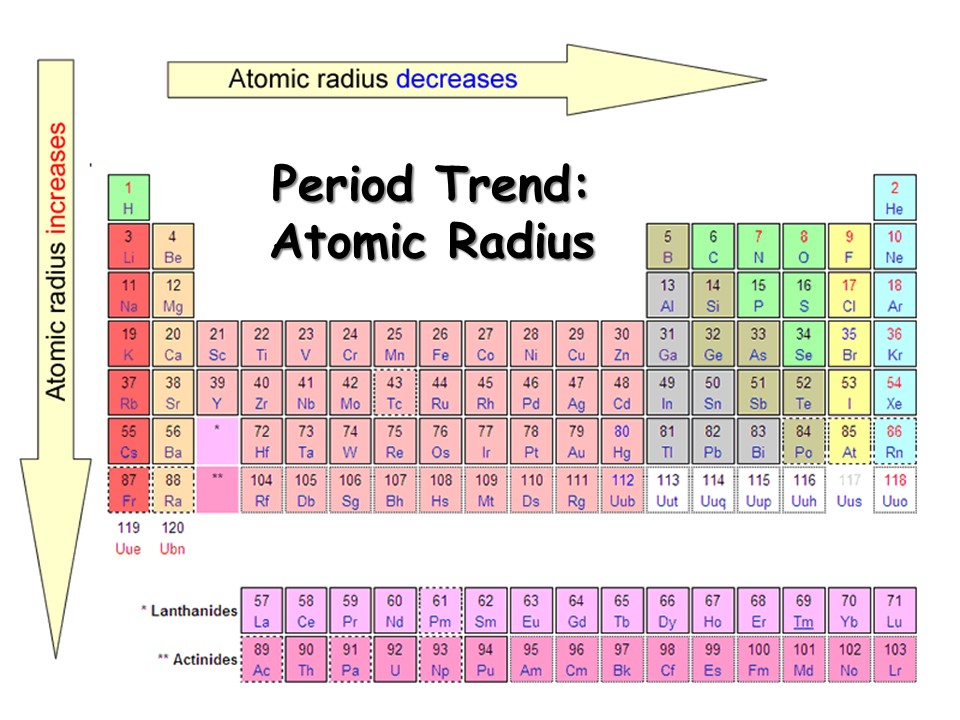
Atomic radius - Across a period
Decreases
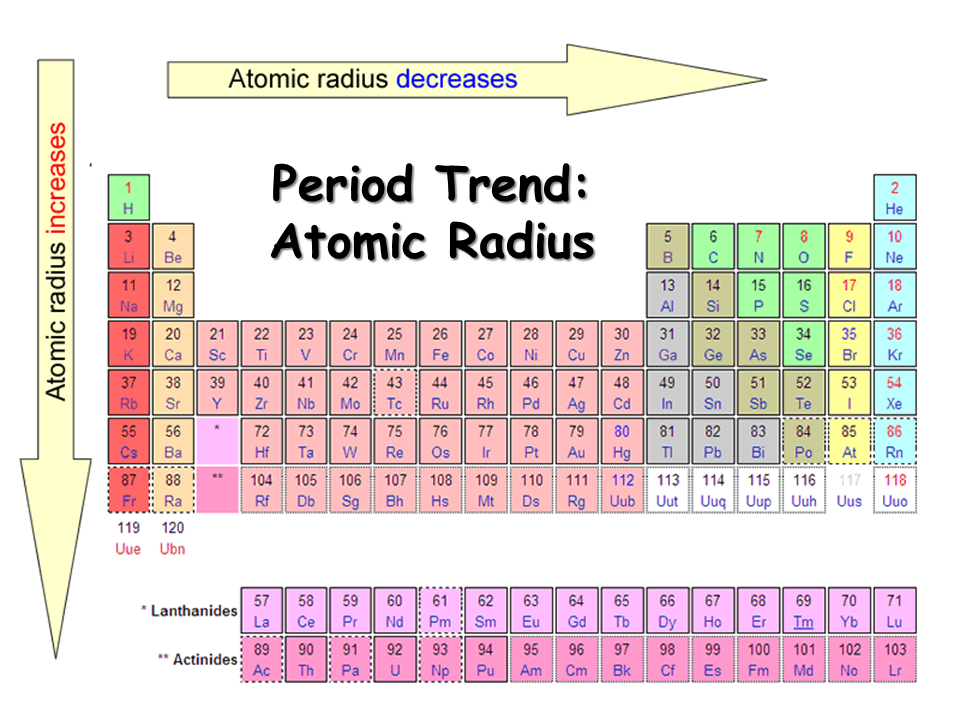
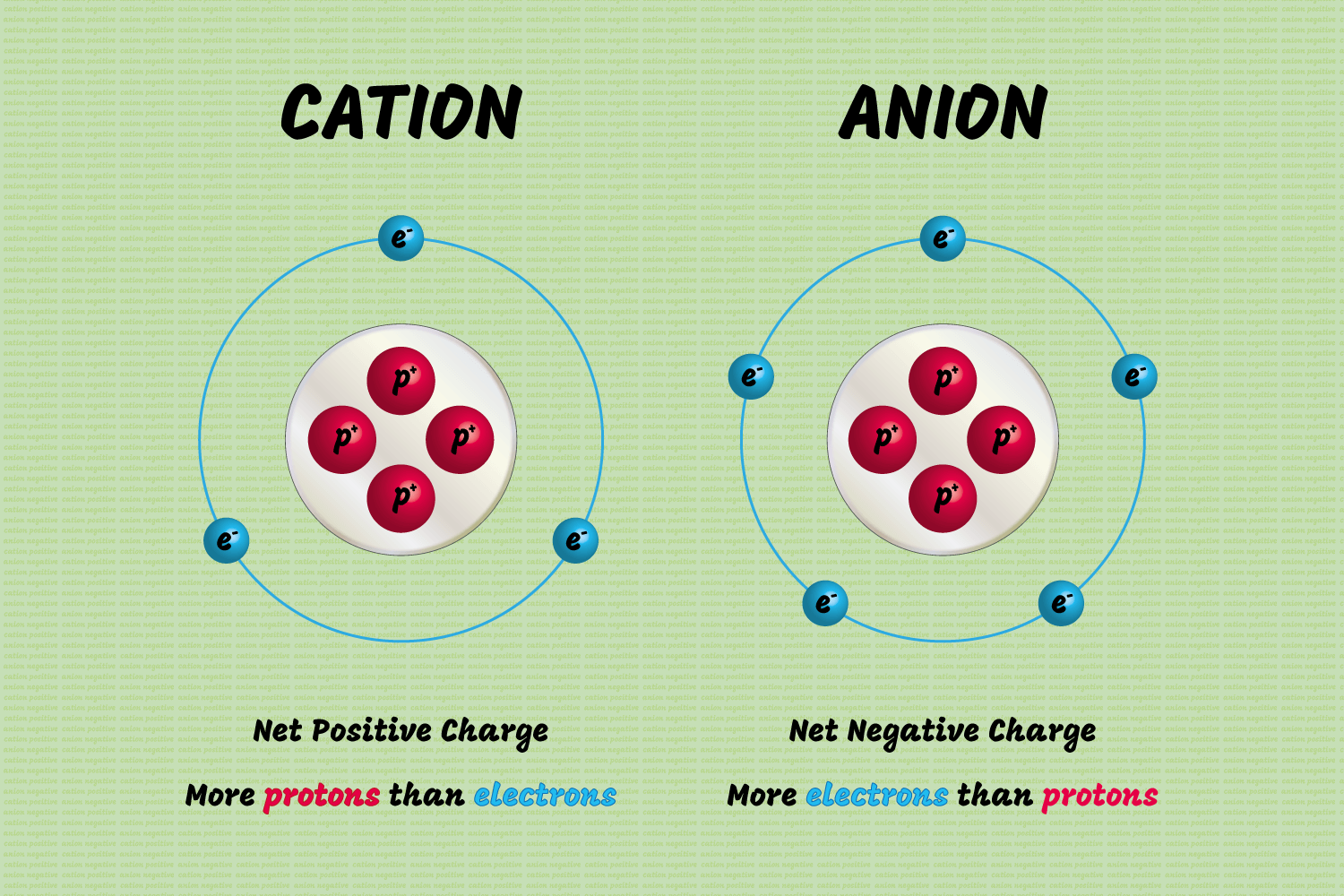
Anions (Can be polyatomic)
- "A negatively charged ion
- Attracted to the cathode"
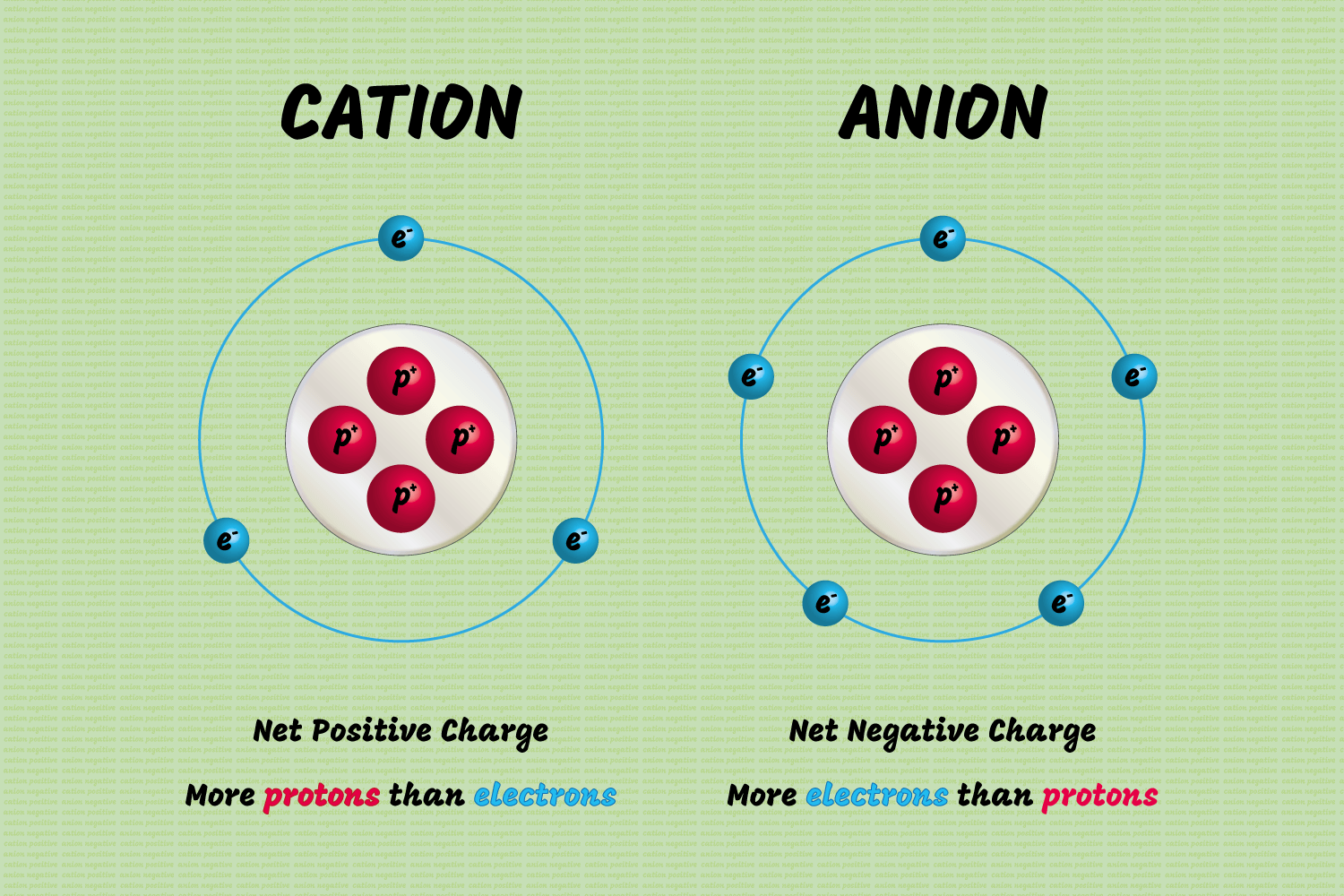
Ionic Lewis Dot Diagram
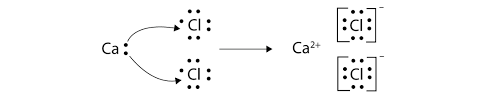
Covalent bonding diagram
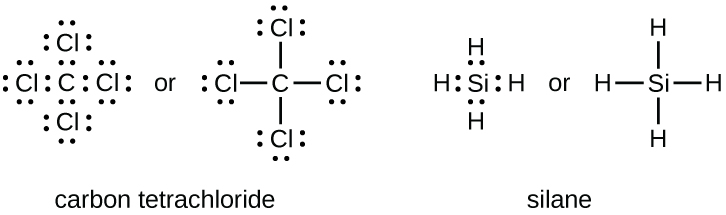
Covalent bonding formulas (written and non-written)

Ionic bonding formulas (written and non-written)
Don’t forget when you’re writing them to add the roman numeral*
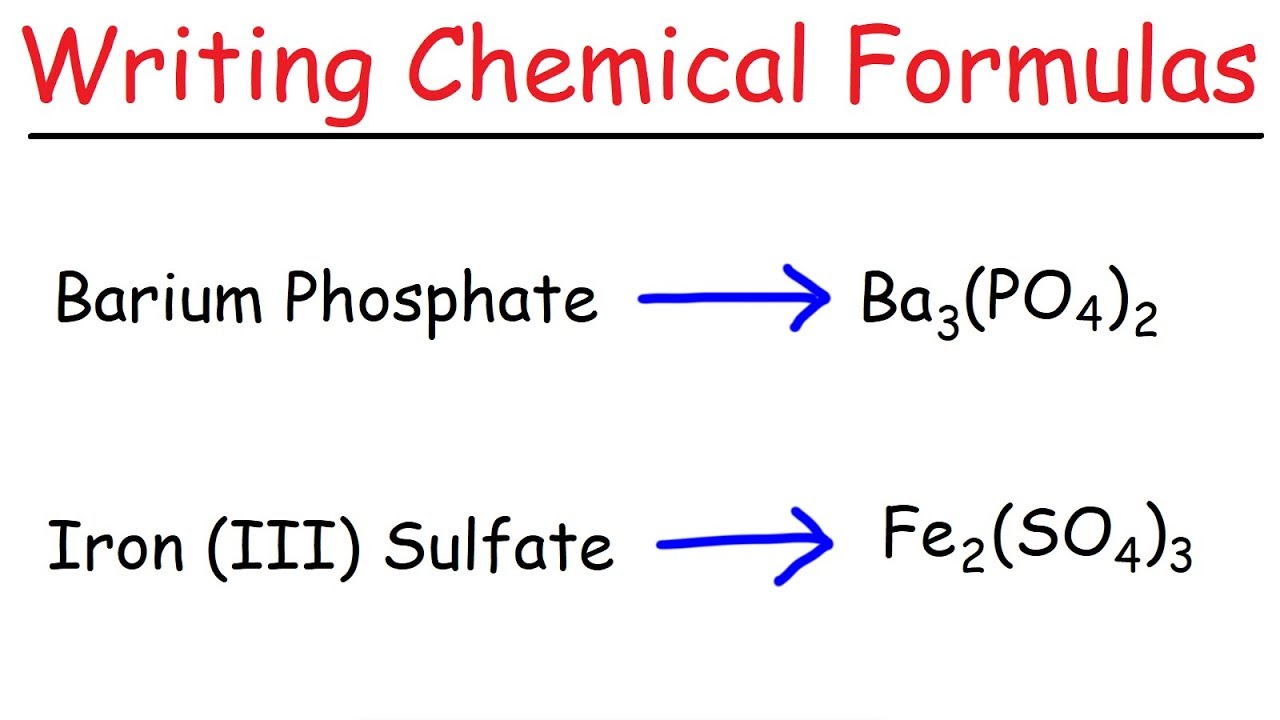
Ionic bonding characteristics
High Melting/ Boiling point
Good conductor when soluble/ aqueous
Brittle
Soluble in water
Covalent bonding characteristics
Low melting/ Boiling point
Insoluble
Bad conductors
Polar atoms characteristics
High Boiling Points
Good conductors
Non-Polar atom characteristics
Low Boiling Points
Bad conductors
Ways of separation
Filtration
By eye
Distillation
Chromatography
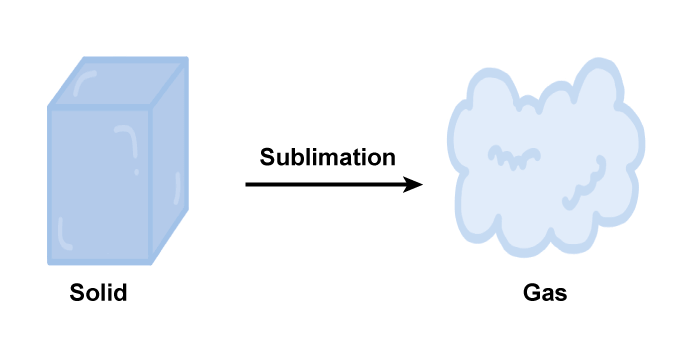
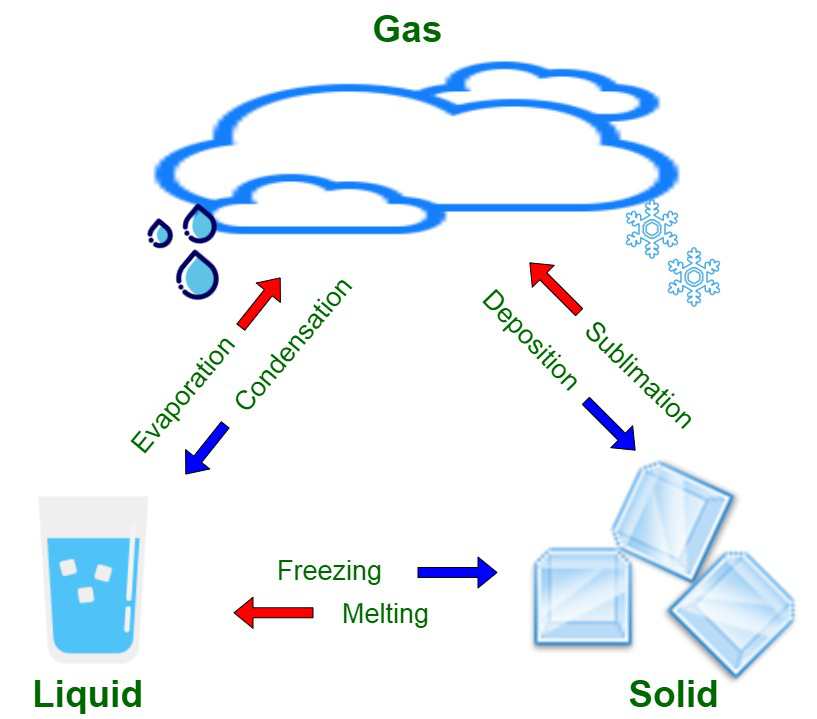
Sublimation
- Solid-to-gas phase transition
Vaporization
Water to gas phase transition
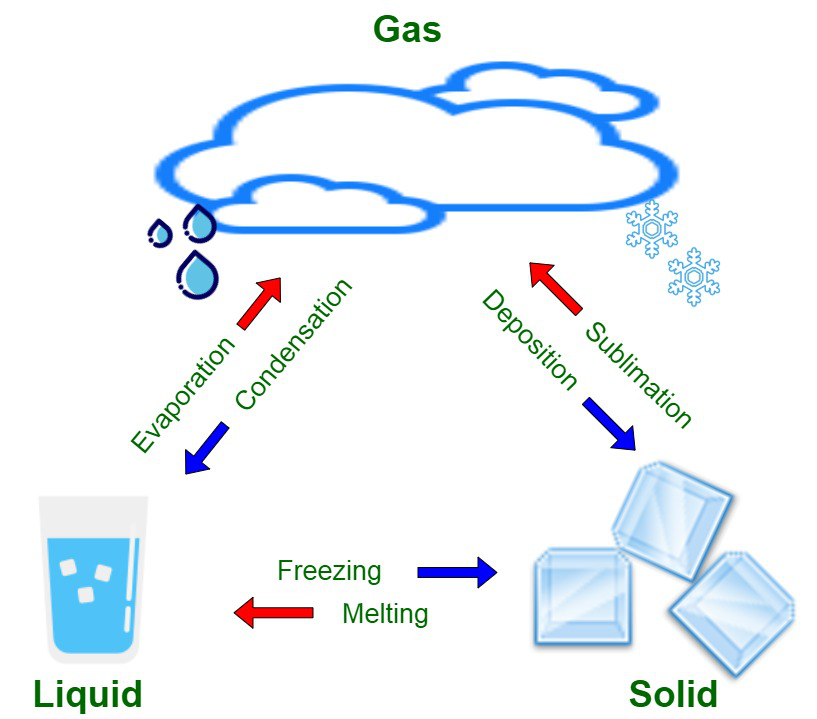
Condensation
Gas to liquid phase transition
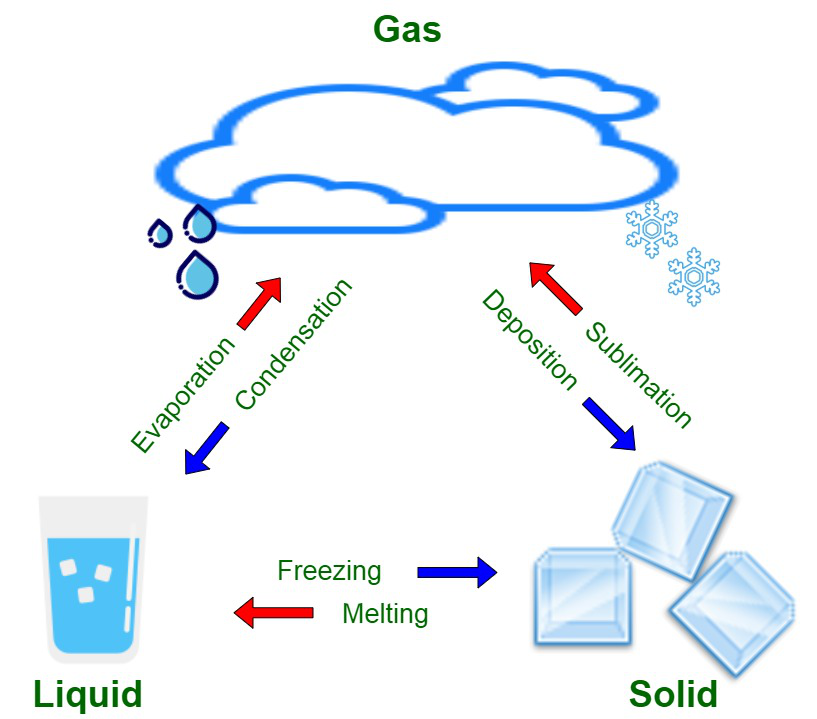
Deposition
Transition from a gas to a solid
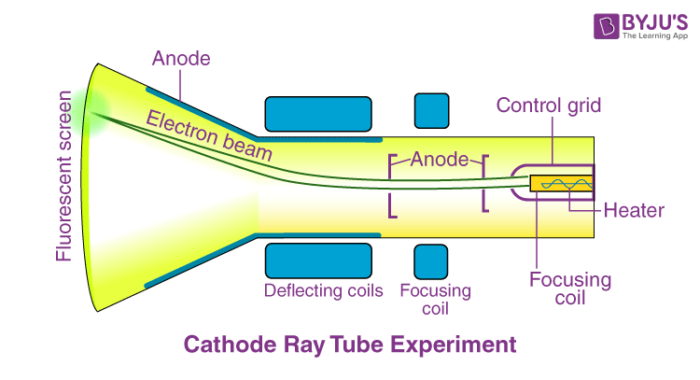
Cathode Ray Experiment
- Thomson placed two oppositely-charged electric plates around the cathode ray.
- The cathode ray was deflected away from the negatively-charged electric plate and towards the positively-charged plate, indicating that the cathode ray was composed of negatively charged particles.
meaning ELECTRONS EXIST (so cool)
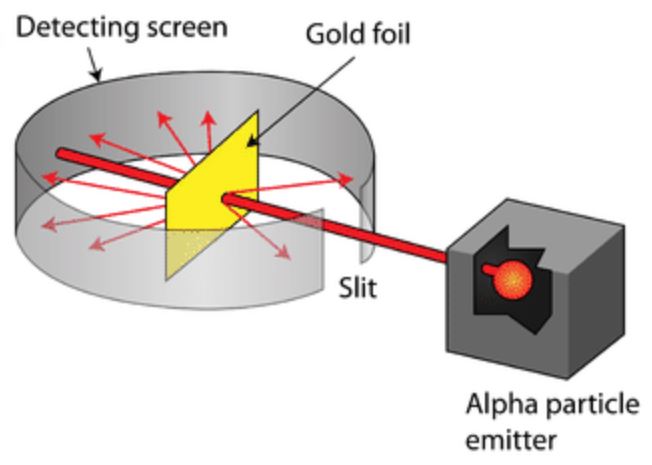
Gold Foil
- Alpha particles shot through gold foil: most pass through, but some bounce back.
- Concludes that atoms are mostly empty with a small, dense, positively charged nucleus.
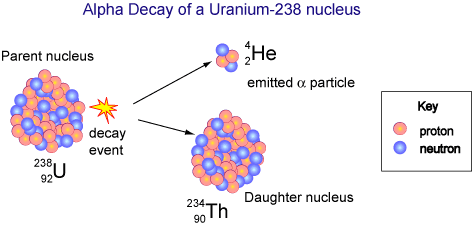
Radioactive Decay (Transmutation)
- Transmutation involves converting one chemical element into another.
Alpha particles
- α, +2 or He2+
- Composite particles of two protons and two neutrons
Weakest penetration power
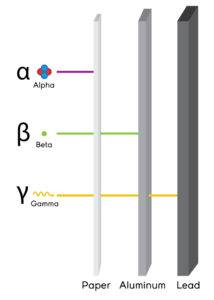
Beta particles
- They are negatively charged
with greater penetration than alpha particles, but less than gamma rays.
- Symbol: β or just as an electron.
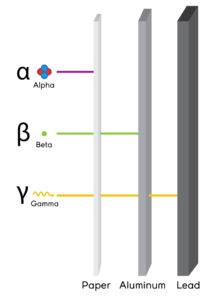
Gamma particles
- They have no mass or charge.
- Most penetrative
- Have the symbol γ.
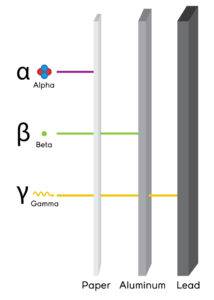
Positron particles (not that important)
- Particle with the same mass as an electron
- Has a positive charge
- Antiparticle of an electron
- Annihilates upon collision with an electron, releasing energy

Balanced Nuclear Equations
just balancing but use the charges of radiation particles ( In reference table )
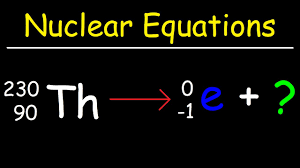
Fission
Splitting apart
Releases tons of energy
NUKES!!
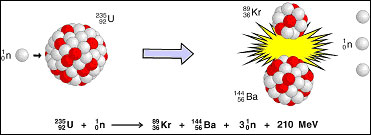
Fusion
Fusing together
Releases tons of energy
Nuclear power plants
Atomic Radius Down a Group
Increases

Atomic Radius Across a period
It decreases

Number of Valence Electron Change
Increases by one across a period
Number of Shell Change down a group
Increases by one down a group
Ide suffix
ide is used to describe non-metallic ions
chloride, sulfide, nitride, phosphide
Combustion reactions
- Reactants: hydrocarbon, oxygen
- Products: carbon dioxide, water
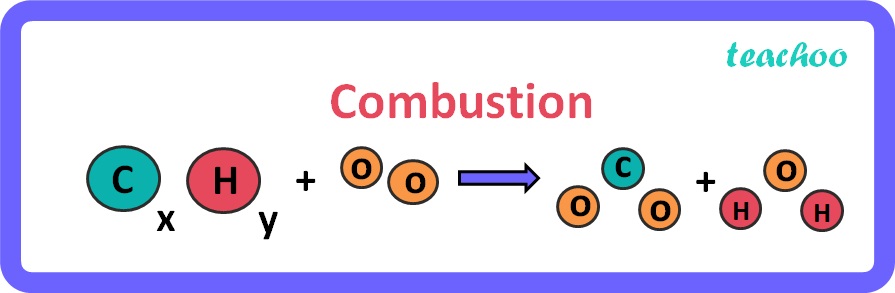
Molecular bonds
Covalent bonds
Is (NH4+) Ionic or Covalent when bonded with other stuff
Ionic
Soluble
Dissolves in water
Non-Polar vs Polar Covalent Bonds
- Polar covalent bonds: Electrons are unequally shared between atoms due to differences in electronegativities.
- Nonpolar covalent bonds: Electrons are more equally shared between atoms.
Electronegativity For Polar and Non-Polar
.5 is a polar covalent
1.8 - 2.0 electronegativity is ionic polar
Subtract the smaller electronegativity from the larger one to find the difference.
For example, if we're looking at the molecule HF, we would subtract the electronegativity of hydrogen (2.1) from fluorine (4.0). 4.0 - 2.1 = 1.9.
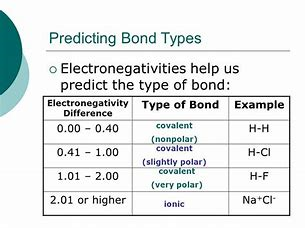
Intermolecular forces
Forces of attraction and repulsion between atoms
Electron Configuration in Excited States
Valence electrons move up energy shells, higher shells have more energy
Substances definition
Compounds or elements, definite composition
What type of change is an aqueous solution
Physical
Ductile
Can be made into wire
STP
Standard temperature and pressure
Inner Transition Metals
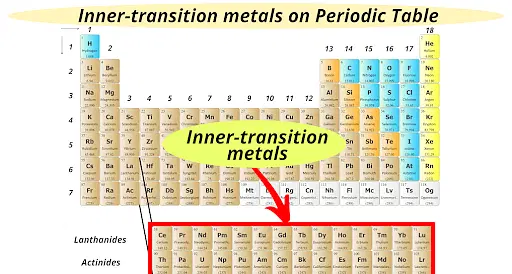
Oxidation #
- Oxidation number: total number of electrons gained or lost to form a chemical bond
Vibrating Particles in Regular Fixed Positions
Solid
Solution definition
A mixture of two or more substances that stays evenly mixed
Prefixes to memorize
Mono - 1
Di - 2
Tri - 3
Tetra - 4
Penta - 5
Hexa - 6
Hepta - 7
Octa - 8
Nona - 9
Deca - 10
Carbon - 14 ←
Element - Mass number (n + p)
Ionization Energy Down a Group
Decrease

Definition Cation (can be polyatomic)
- A positively charged ion is formed when a metal loses an electron.
- This ion is attracted to the anode.
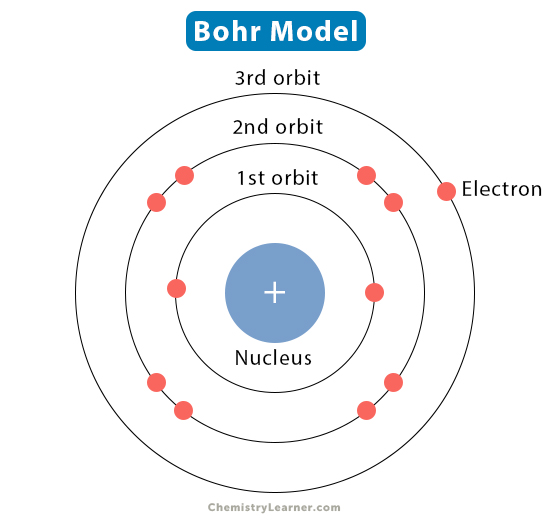
Bohr’s model name
Planetary model
Does Hydrogen act like a metal or nonmetal?
- Hydrogen technically is a non-metal
- Acts like an alkali metal
- Forms cations and covalent bonds
What are isotopes?
An atom with a different number of neutrons, but the same number of electrons and protons
Ion definition
Any charged particle that has lost or gained electrons
Properties of substance when mixed
The substances characteristics remain the same
Mixtures can be seperated by physical or chemical means?
Physical means
In phase change the flat parts represent?
Potential energy increasing, while kinetic energy staying the same
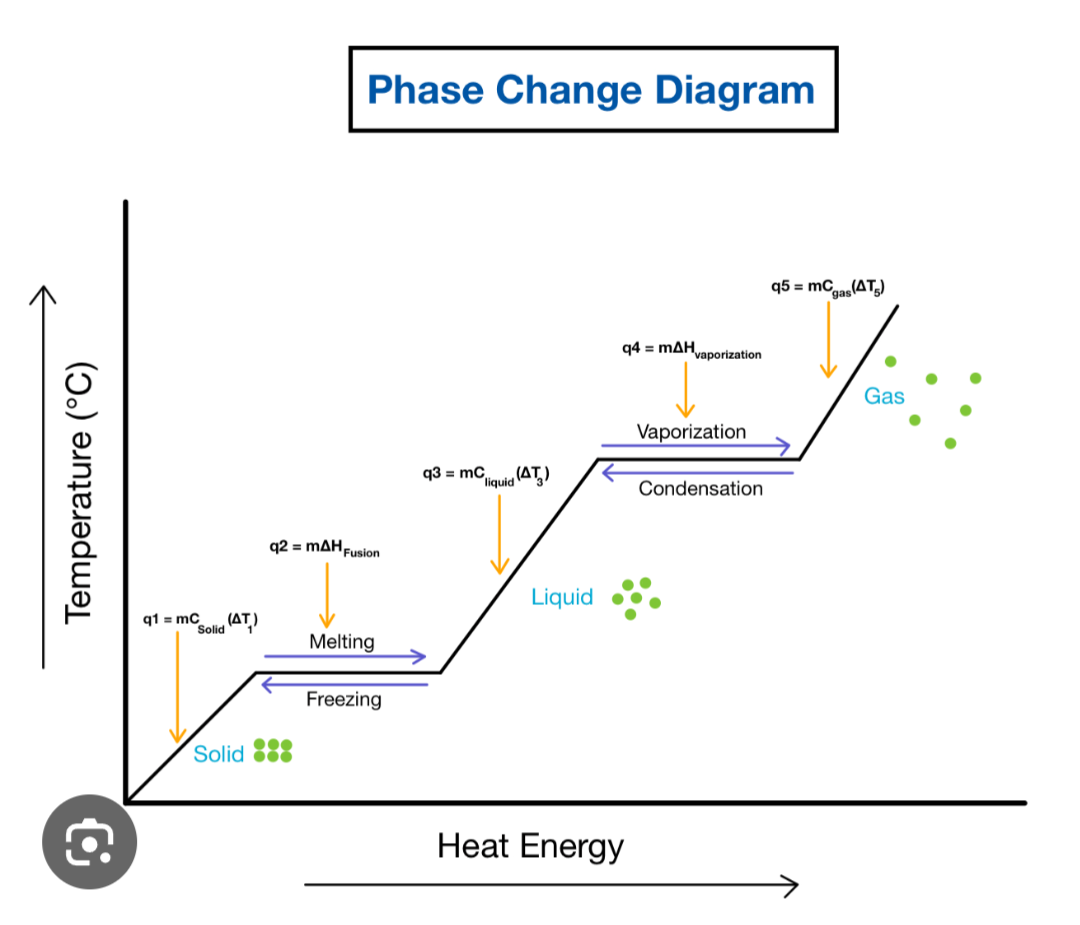
Potential energy definition
The amount of stored energy an object possess
Chromatography definition
Method of separation using solubility and polarity
Chemical change definition
The results in the formation of a difference substance (example: burning)
Physical change definition
Does not form new compounds, instead it can change appearance
In a phase change diagram what do the slopes represent in terms of kinetic energy and potential energy.
On the sloped lines the substances is heating (or cooling), and the potential energy remains the same while kinetic energy increases.
0 ° C = ___ °K
273°K
Heat of fusion definition
(heat it takes to melt a substance) Heat for one gram of the substance to turn it from solid to liquid
STP
(Standard Temperature and Pressure) on table A (273 K and 1 atm or 101.3 kPa and 0C)
Pressure and temperature have what relationship?
Direct, (as pressure increases, temperature increases)
CONDITIONS FOR IDEAL GASSES
low pressure
high temperature
move in constant random straight lines
and are separated by great distances compared to their size
Gases have no attractive forces, weaker IMF

Mendeleev
Russian periodic table guy, organized elements by atomic mass
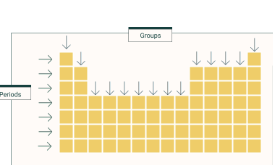
Groups direction
Vertical
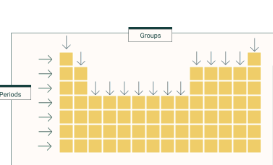
Period direction
horizontal
Ionization energy definition
the amount of energy required to remove an electron from an isolated atom or molecule