HF/ Diuretics meds
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What are some commone causes of Heart failure?
Myocardial (myocardium) disease or damage.
cardiomyopathy
CAD
Ischemia
Systemic/Pulmonary hypertension
Valuar heart disease
If the heart can’t conctract properly is that Systolic or diastolic dysfunction? what if the heart can fill properly ?
Systolic dysfunction = the heart can't contract properly.
Diastolic dysfunction = the heart can't fill properly with blood
Define Pre and after load
Pre -> the vol. of BL received from the heart, and it deals with the stretch of the ventricle
After -> The pressure the heart has to overcome to pump (like squeezing a water hose half shut)
Since HF leads to ? CO, the body will activate neurohormonal mechanisms to ? the BP so all tissue will get that 4-6L/min of blood.
? activation (? and ?) & ? system active = ? BP
As workload ?, cardiac muscle fibers weaken and lose contractility. The heart tries to compensate by ? the heart muscle (?).
Since HF leads to Low CO, the body will activate neurohormonal mechanisms to increase the BP so all tissue will get that 4-6L/min of blood.
SNS activation (NoriEpi and EPI) & RAAS system active = increased BP
As workload increases, cardiac muscle fibers weaken and lose contractility. The heart tries to compensate by thickening the heart muscle (ventricular hypertrophy).
Left HF S/Sx: DO CHAP and how do you treat O?
Dyspnea
Orthopnea
Tx. with elevated head w/ pillow
Cough
Hemoptysis (blood sputum)
Adventitious Breathing sounds
Pulmonary congestion
Right HF S/Sx: AW HEAD
Anorexia and nausea
Weight gain
Hepatomegaly (Liver dysfxn)
Bipedal Edema
Ascites (edema in abdominal cavity)
Distended neck vein/JVD
What is ventricular remodeling?
Over time, angiotensin II and aldosterone (RAAS) lead to fibrosis (scarring) and ventricular hypertrophy known as ventricular remodeling, which worsens heart failure.
What are the 4 side effects of HF therapies (Diuretics)? Please provided a short description
Hypokalemia.
Excessive and repeated diuresis can lead to hypokalemia.
Hyperkalemia
may occur with the use of ACE inhibitors, ARBs, or spironolactone.
Hyponatremia
Prolonged diuretic therapy results in disorientation, fatigue, apprehension, weakness, and muscle cramps.
Dehydration and hypotension.
Volume depletion from excessive fluid loss may lead to dehydration and hypotension.
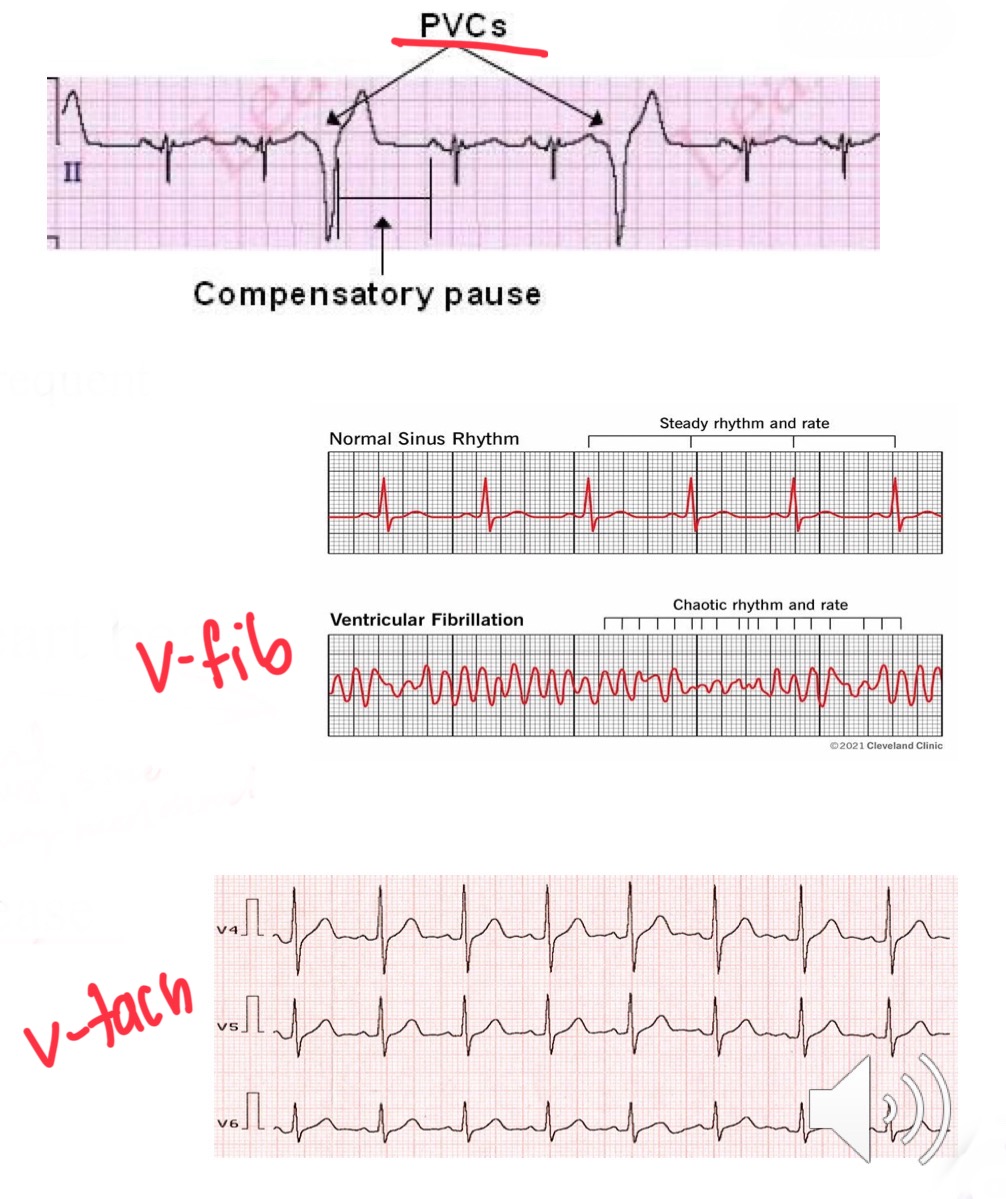
Define
PVCs (premature ventricular contractions)
Ventricular fibrillation(V fib)
Ventricular tachycardia (V tach)
PVCs (premature ventricular contractions) -> Common + no symptoms
Caused: Exercise, caffeine, anxiety...can cause cardiomyopathy if frequent
Ventricular fibrillation(V fib) -> Chaotic heart beats
Deadly + Most common cause sudden cardiac death
Ventricular tachycardia (V tach) -> HR> 120, starts in ventricles,
Caused: ischemic heart disease
What are the 3 causes of Edema? Please provided a short description
Heart Failure (HF)
Poor pumping → RAAS activated → Na⁺ and fluid retention → increased blood volume
Liver Cirrhosis
↓ Plasma proteins → ↓ oncotic pressure (can’t hold fluid in vessels)
Portal hypertension from blocked hepatic vessels → fluid backs up
Renal Disease
Damaged basement membrane in nephrons → loss of plasma proteins in urine → ↓ oncotic pressure
Define
Glaucoma
increased intraocular pressure (IOP) -> IOP can damage the optic nerve
S/Sx of dec K+ (7)
muscle cramps
muscle weakness to paralysis
hypotension
arrhythmias
polyuria
polydipsia
lightheaded → syncope
S/Sx of inc K+ (3)
Palpitations → chest pain
SOA
N&V
Class
Action
Tx
Adverse effects
D2D
Ivabradine
Class → Hyperpolarization-Activated Cyclic Nucleotide-Gated Channel (HCN) Blockers
Action → SA node blocked in repolarization phase, thus dec HR, inc ventricles fill time -> inc CO
Tx → chronic HF, age 6 months or older for stable HF, and decrease the risk of hospitalization
Adverse effects → bradycardia, HT, luminous phenomena
D2D → bradycardia with other negative chronotropic meds(beta blockers/meds slow HR)
Class
Action
Tx
Adverse effects
Contraindications
D2D
Digoxin
Class→ Cardiac Glycosides/ Pos inotropic
Action → Pos inotrpic -> inc CO and dec HR
Tx → HF -atrial flutter - A-Fib
Adverse effects:
HA, weakness, drowsiness
yellow halo around objects (xanthopsia) / altered colored vision
Digoxin toxicity: anorexia, N&V, malaise, irregular heart rhythm
Contraindications → Ventricular tachycardia/ fibrillation, acute MI
D2D:
Increased toxicity- Erythromycin, tetracycline
Antacids will decrease absorption
What is the antiodte to dogxin toxcity?
Digoxin immune fab
Class
Action
Tx
Adverse effects
Contraindications
D2D
Entresto [valsartan and sacubitril]
Class → Angiotensin Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitor (ARNI)
Action:
Blocks neprilysin ( lysis Na+) inc loss Na+Cl- and H2O
block angiotensin II -> inhibit RAAS. -> dec BP and blood volume
Tx → Symptomatic HF, dec hospitalizations
Adverse effects → hypotension, hyperkalemia
Contraindications → Angioedema
D2D → ACE inhibitors and Sparing Diuretics cause hyperkalemia
Entresto [valsartan (ARBs) and sacubitril (Neprilysin inhibitor)]
Class
Action (3)
Tx
Adverse effects
Contraindications
Milrinone
Class →Cardiotonic/ Inotropic
Action:
Blocks the enzyme phosphodiesterase
Inc Ca2+ lvl -> stronger contraction
prolong SNS stim -> inc HR
Tx:
short term HF if no response to (digoxin, vasodilators, diuretics)
Emergent situations
Adverse effects → ventricular arrhythmias, hypotension, thrombocytopenia.
Contraindications
Acute MI
Hypovolemia
Class
Action
Tx (3)
Adverse effects
D2D
Hydrochlorothiazide
Class → Thiazide/Thiazide-like diuretics
Action → xcretion of sodium chloride (NaCl) along with some potassium (K⁺) and bicarbonate (NaHCO₃).
Tx → essential HNT -Edema -Glaucoma
Adverse effects:
GI upset (fluid/electrolyte imbalance)
hypotension
Hypokalemia (muscle cramps, weakness)
Alkaline urine -> increases the chance of UTIs
D2D
Digoxin toxicity- due to change K+ levels - Watch blood K levels
Decrease the effect of antidiabetic agents
Class
Action
Tx
Adverse effects
Contraindications
D2D
Furosemide
Class → Loop diuretics (strong asf)
Action
block chloride pump ascending loop of Henle, thus dec Na+Cl- reabsorption
Tx → acute HF, pulmonary edema, severe edema, HT
Adverse effects
Hypokalemia
Hypotension (dizziness)
hyperglycemia
Contraindications → anuria , diabetes and gout
D2D → decrease anti-HT with salicylates/NSAIDs
Class
Action
Tx (4)
Adverse effects
Contraindications
D2D
Acetazolamide
Class → Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
Action → block carbonic anhydrase , inc H+ thus dec Na+ and HCO3 .
Tx → HNT - Edema - Glaucoma - HF
Adverse effects
acid-base imbalance results (metabolic acidosis)
hypotension, confusion, paresthesias
Contraindications
fluid and electrolyte imbalance
COPD
D2D
Watch with aspirin (ASA) -> Salicylate toxicity (metabolic acidosis)
Watch with K lowering agents
Class
Action
Tx
Adverse effects
Contraindications
D2D
Spironolactone
Class → Potassium Sparing
Action → aldosterone antagonist and blocks androgen production
Tx → hyperaldosteronism (inc Na+ and H20 retention, loss K+)
Adverse effects→ Hyperkalemia (SOA, chest pain, N&V, ataxia),
Contraindications→ anuria
D2D
Used in conjunction with/ Digoxin and Antiarrhythmic drugs for patients who are at risk of hypokalemia (increase the retention of K+)
decreased diuretic effect with salicylates
hypotension with other antiHT
Class
Action (2)
Tx
Adverse effects
Contraindications
Mannitol
Class → Osmotic Diuretics
Action
Pulls large amounts of fluid into urine by the osmotic pull of large sugar molecules
Fluid is pulled into the vascular system from extravascular spaces, thus decreasing IOP
Tx → glaucoma, ICP(inner cranial pressure), trauma, drug OD
Adverse effects
The increased fluid leads to HF, pulmonary edema
decrease fluid hypotension, dehydration, dizziness, HA
Contraindications
Auria and renal disease