Regulating the cell cycle and cancer. Biology 1 Honors
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
Why is regulating cell division important?
To ensure organisms get the genetic information needed for survival; improper division can lead to cancer.
What is cancer?
Abnormal, uncontrolled cell division in multicellular organisms.
What is the lifespan of skin cells?
1-2 days and they can divide.
Why might neurons and white blood cells have longer lifespans?
They perform critical functions and need to be available for longer periods, despite not being able to divide.
How do receptor proteins affect cell division?
They communicate to prevent growth when cells touch each other.
What role do cyclins play in the cell cycle?
Proteins that regulate the timing of the cell cycle.
What are the symptoms of cancer?
Lumps, abnormal changes in skin, and changes in normal body functions.
What happens when cells do not respond to 'stop' signals?
They can form tumors that damage surrounding tissues.
What is the life span of red blood cells?
Less than 120 days and they cannot divide.
How do normal cells prevent overcrowding?
They have a 'stop' signal activated by sensors that detect nearby cells.
Metastasis
Spread of cancerous cells to other parts of the body
Mutations
A change in the DNA base sequence
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death; occurs during infant development
What causes cancer
Cancer results from a defect in genes that control cell growth and division.
Tumor
A mass of rapidly dividing cells; can be benign (non cancerous) or malignant (cancerous)
sister chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome attached by a centromere
Parent cell
original cell
Centrioles
Cell organelle that aids in cell division in animal cells only
daughter cells
new cells produced by cell division
Interphase
Period of time where a cell carries out cell processes and replicates DNA prior to cell division
Mitotic Phase
Second part of the cell cycle, where the cell divisions occurs.
Zygote
Diploid organism created by the fertilization and fusion of egg and sperm.
prophase
Chromatin condenses into chromosomes

metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
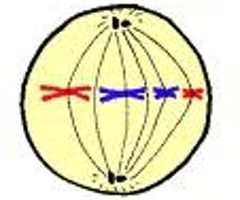
anaphase
Sister chromatids separate
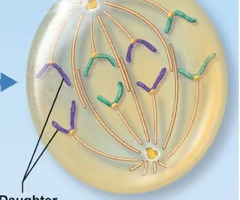
telophase
After the chromosome separates, the cell seals off, Final Phase of Mitosis.
chromatid
Each half of the chromosome
chromosome
A doubled rod of condensed chromatin; contains DNA that carries genetic information
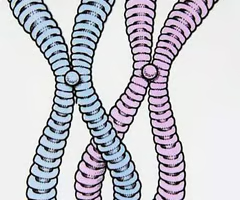
centromere
Area where the chromatids of a chromosome are attached
G1 phase
interphase stage of cell cycle where cell grows and carries out metabolic processes
G2 phase
interphase stage prepares to divide by copying organelles
S phase
interphase stage of cell cycle where cell replicates DNA
Spindle fiber
emerge from centrioles, attach to chromosomes to pull them apart during mitosis
Cleavage furrow
a pinching of the cell membrane that begins to form in telophase
Stem cell
unspecialized cell with no specific job
Diploid
cells have two sets of chromosomes (one from each parent, paired), found in most body (somatic) cells.
Haploid
cells have only one set, found in sex (gamete) cells like sperm and eggs, produced by meiosis for sexual reproduction.
Gametes
Sperm and Egg
Somatic cells are
differentiated cells that form the different types of body tissue that exist
Totipotent cells
can develop into all the cell types in a body, plus the extraembryonic, or placental cells.
Pluripotent cells
Cells can form any cell type.
multipotent cells
can develop into more than one cell type but are more limited in their repertoire than pluripotent cells
Stem cells can
differentiate into specialized cells or produce more stem cells.
CDK
Are enzymes that need a partner protein
Glans penis
Function: Aid in entry to female reproductive tract. Its the enlarged tip of penis covered by foreskin (Meatus)
Penis
Function: Penetrate and deposit sperm into female reproductive tract.
Prostate Gland
Function: Secretes a buffer (alkaline) that protects sperm in the acidic enviroment of the vagina.
Seminal Vesicles
Function: A mucus-like fluid containing fructose (for sperm nutrition) and prostaglandins to semen or seminal fluid. found at base of bladder.
Urethra
Function: Tube that carries urine and semen.
Vas Deferens
Function: Carries sperm from epididymis eventually to urethra. (receive mature sperm from Epididymis) Other: Prevents sperm and urine from being in the utrethra at same time
Epididymis
Function: Place in which sperm mature and become motile. Coiled tubule lying just outside each teste.
Other: Sperm will leave Epididymis, travel through ductus deferens, ejac duct, and leave penis
Scrotum
Function: Sac that holds Testes, found outside body
Other: Kept outside due to sperm not developing at body temp.
Testes
Funciton: Produce sperm, and testosterone.
Other: Primary reproductive organs or gonads responsible for gamete formation using MEIOSIS

the sensitive bulbous structure at the distal end of the human penis
Penis Glans
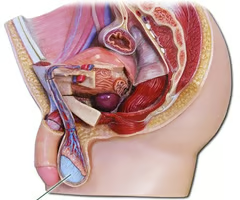
a typical paired male reproductive gland that produces sperm and secretes testosterone and that in most mammals is contained within the scrotum at sexual maturity
Testis
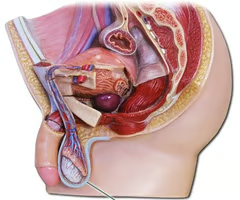
a pouch of skin containing the testicles.
Scrotum

a long, coiled tube that rests on the backside of each testicle. It transports and stores sperm cells that are produced in the testes
Epididymis
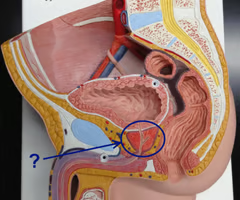
male reproductive organ whose main function is to secrete prostate fluid, one of the components of semen
Prostate gland

urethra
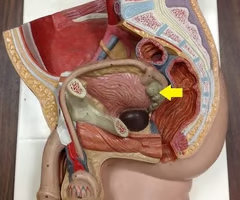
Seminal vesicle
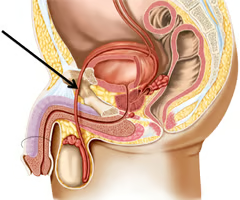
Vas deferens
Foreskin
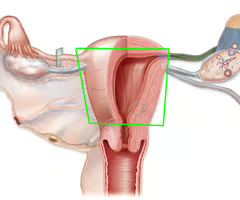
Hollow, flexible, muscular organ. Holds the fetus.
Uterus
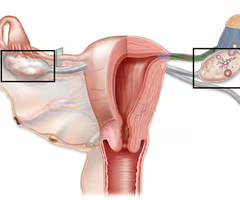
stores egg cells, produces hormones **Estrogen
ovary
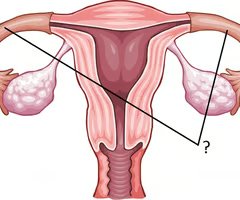
transports egg cell from ovary to uterus; this is where fertilization happens
fallopian tubes
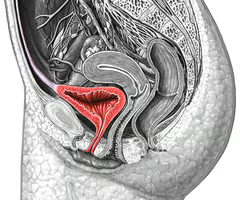
stores / holds liquid waste
Bladder
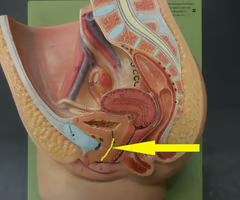
transports liquid waste from bladder to outside of the body
Urethra
transports solid waste from large intestine to outside of the body
Rectum
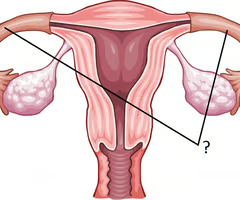
Takes place in the fallopian tubes
fertilization
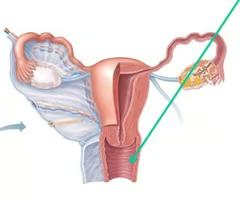
A muscular, elastic passageway that extends from the uterus to the outside of the body
Vagina

The opening to the uterus
Cervix
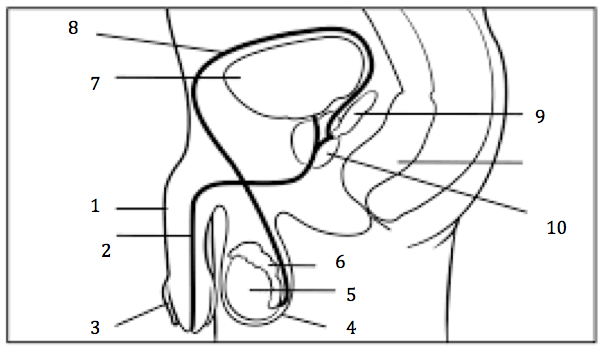
Number 2 on the diagram
Urethra
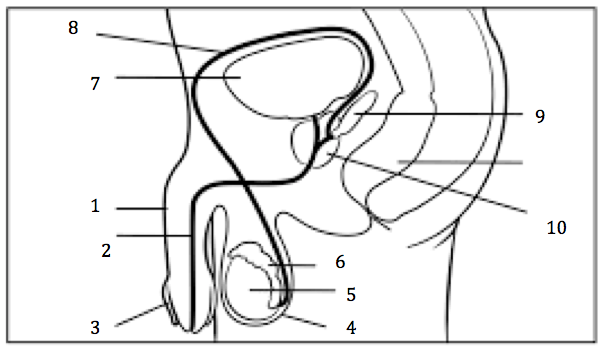
Number 3 on the diagram
Prepuce, or foreskin
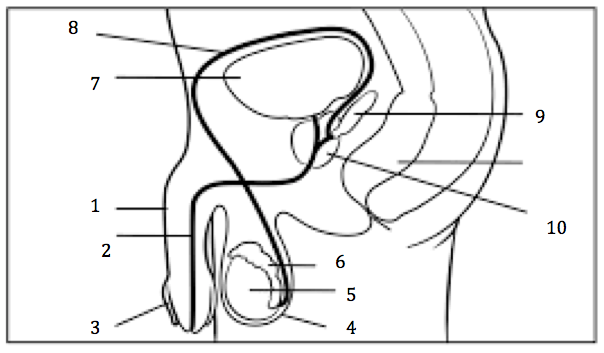
Number 4 on the diagram
Scrotum

Number 5 on the diagram
Testis
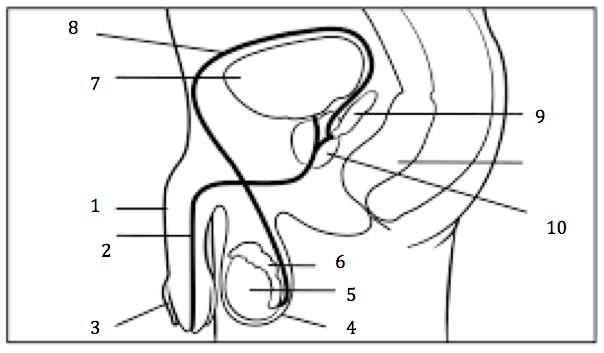
Number 6 on the diagram
Epididymis

Number 7 on the diagram
Urinary bladder
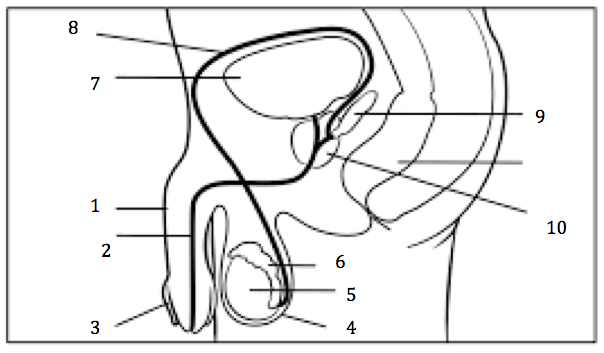
Number 8 on the diagram
Vas deferens
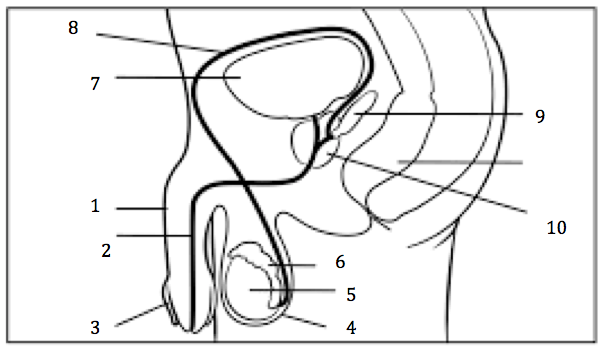
Number 9 on the diagram
Seminal vesicles
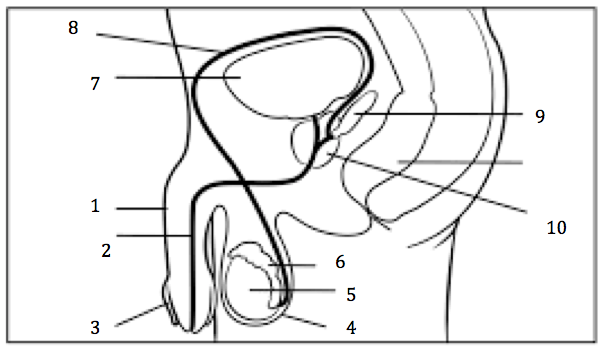
Number 10 on the diagram
Prostate gland
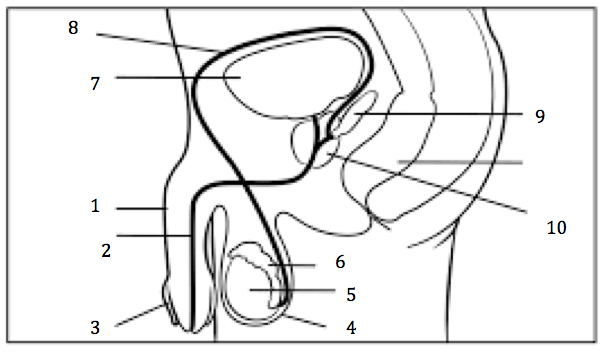
Number 1 on the diagram
penis
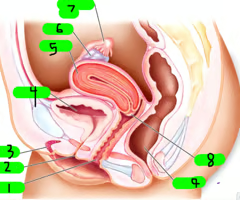
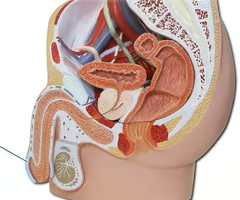
What is 1?
Vagina
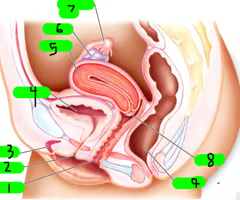
What is 2?
Urethra
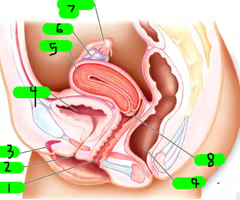
What is 3?
Clitoris
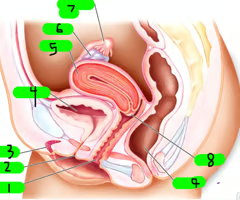
What is 4?
Bladder
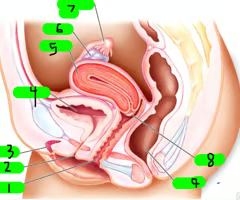
What is 5?
Uterus
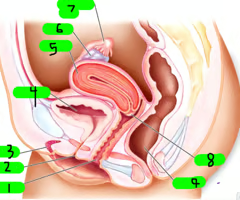
What is 6?
ovary
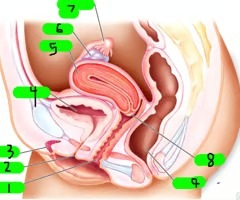
What is 7?
Fallopian tube
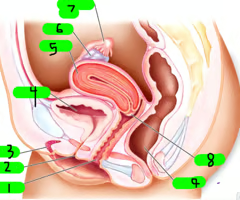
What is 8?
cervix
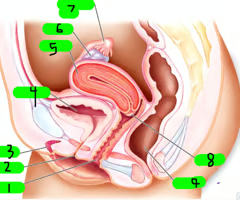
What is 9?
Rectum