OPT 116 Energy Production : Glucose Metabolism
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
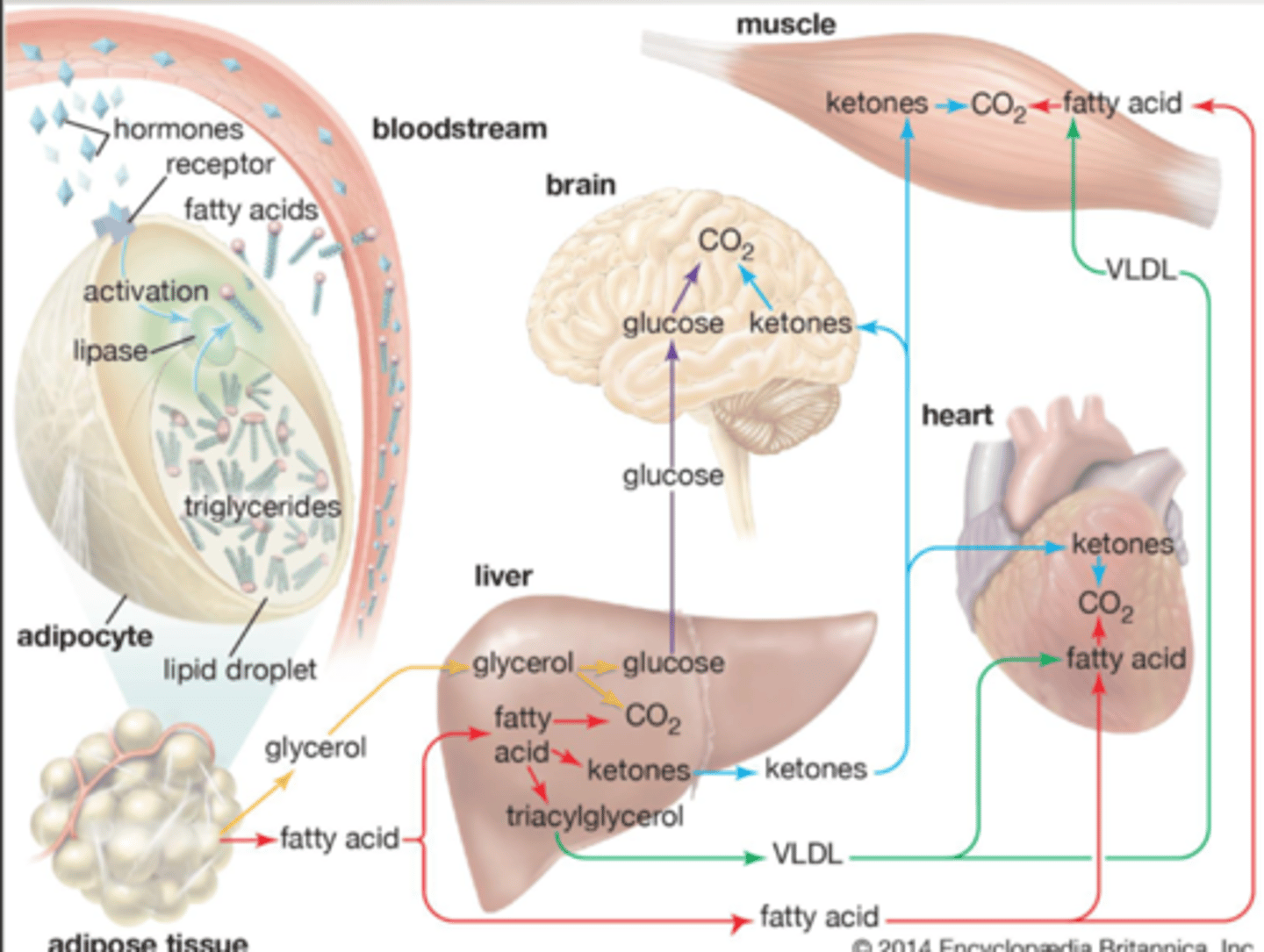
What can be used to produce energy?
glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids
After a carbohydrate rich meal, what is the primary source of energy?
glucose
during fasting, what is the primary source of energy?
fatty acids
After a protein rich meal, what is the primary source of energ?
amino acids
What cells rely solely on glucose for energy?
RBC: does not contain organelle to metabolize fatty acids
brain: has a barrier preventing fatty acids from entering
What types of cells rely primary on fatty acids for energy (even when glucose is present)?
liver cells, heart, and resting skeletal muscle
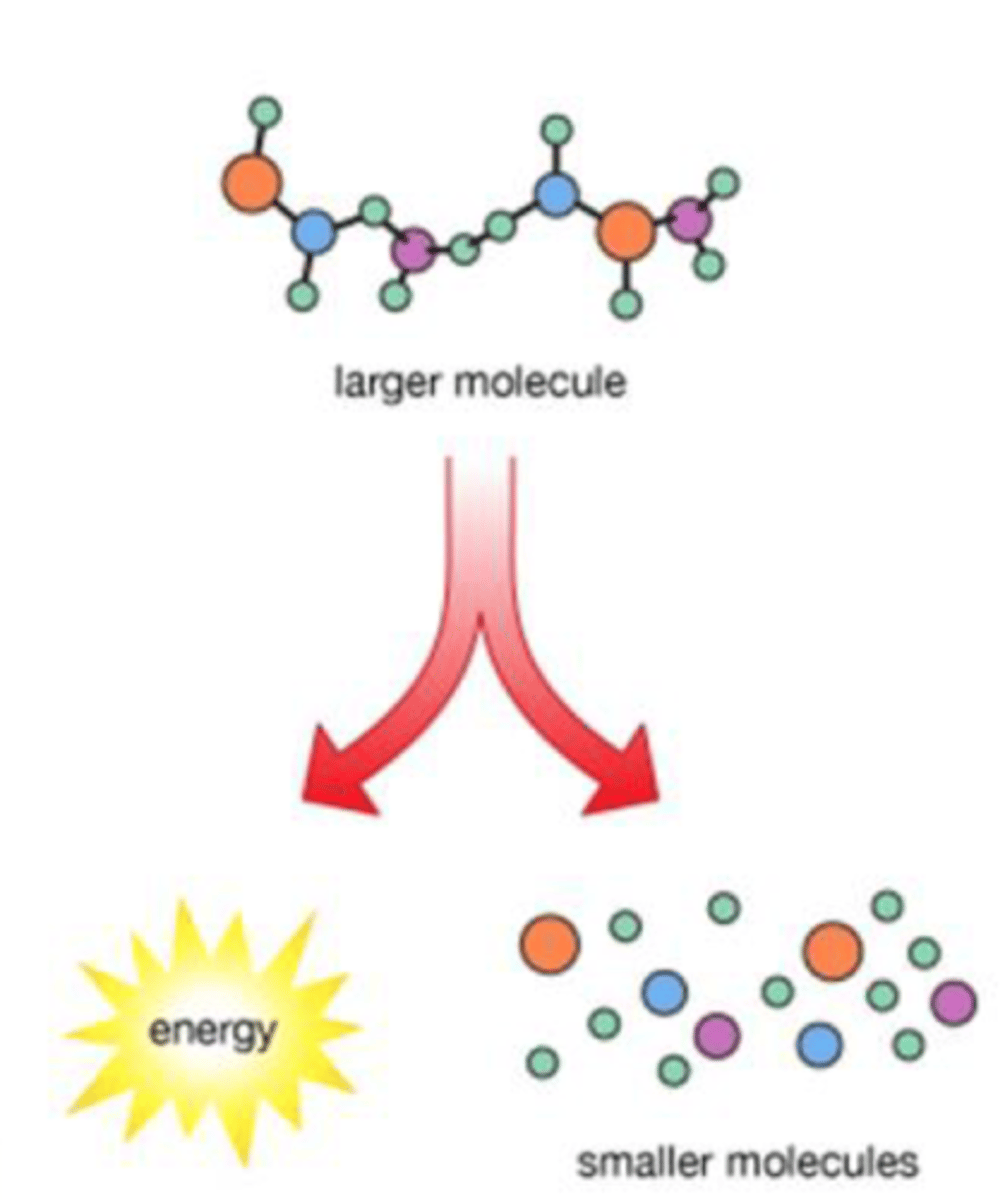
catabolism involves the transfer of electrons meaning
one molecule loses and electron while the other gains
catabolism
molecules are broken down into smaller ones
oxidation
when a substance loses an electron or hydrogen but gains oxygen
reduction
when a substance gains and electron or hydrogen but loses oxygen
What molecules are oxidized (loss) during energy production ?
glucose, fatty acids, amino acids
What molecules are reduced (gain) during energy production ?
NAD+ (accepts 2 e- and 1 proton to become NADH)
FAD (accepts 2 e- and 2 protons to become FADH2)
cellular respiration
Process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen
The process of cellular respiration
generates ATP by oxidative phosphorylation -- most efficient method of ATP production
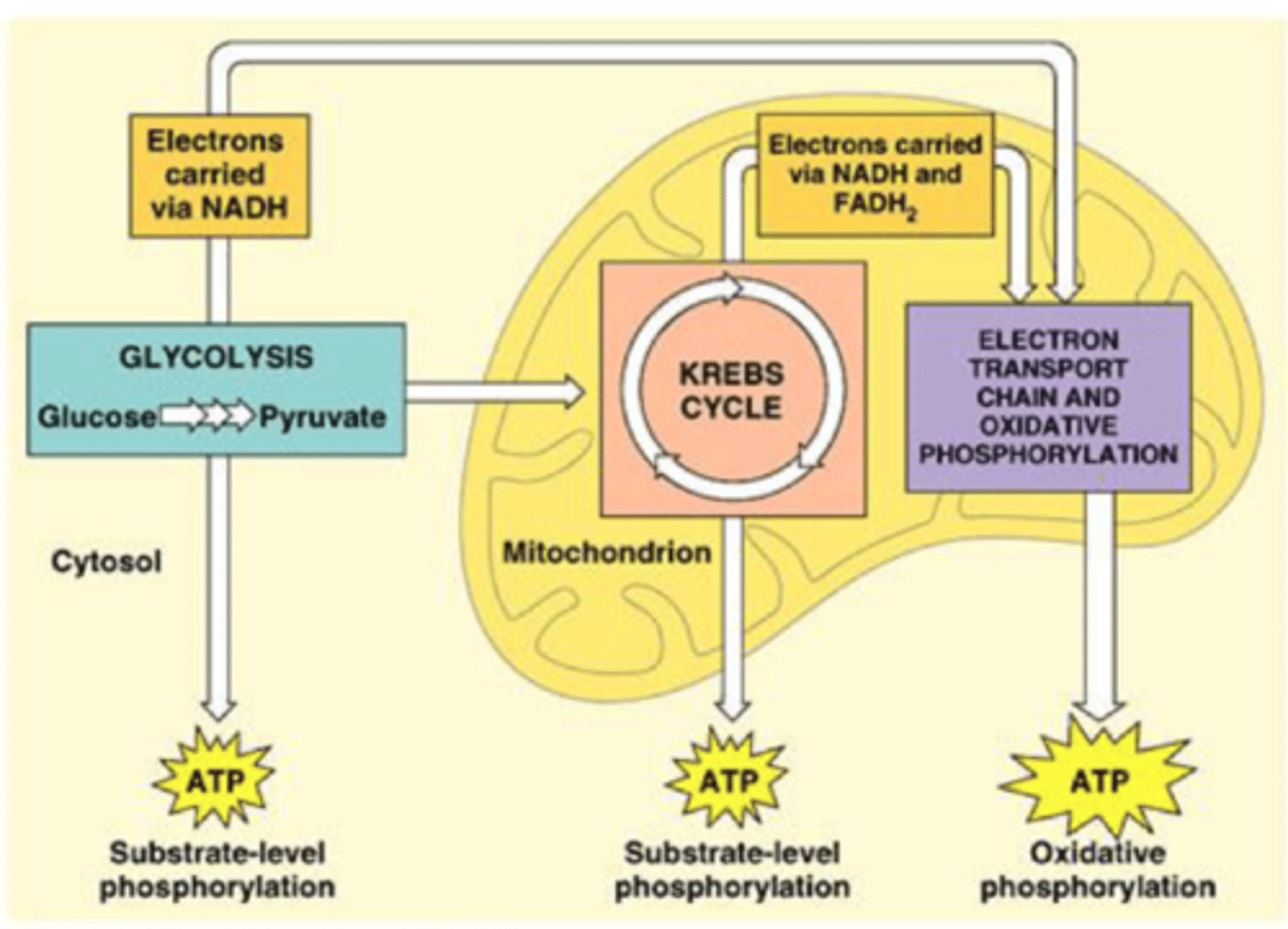
What is the final electron acceptor?
Oxygen
Fermentation
generates ATP by substrate level phosphorylation (less efficient) results in lactic acid production
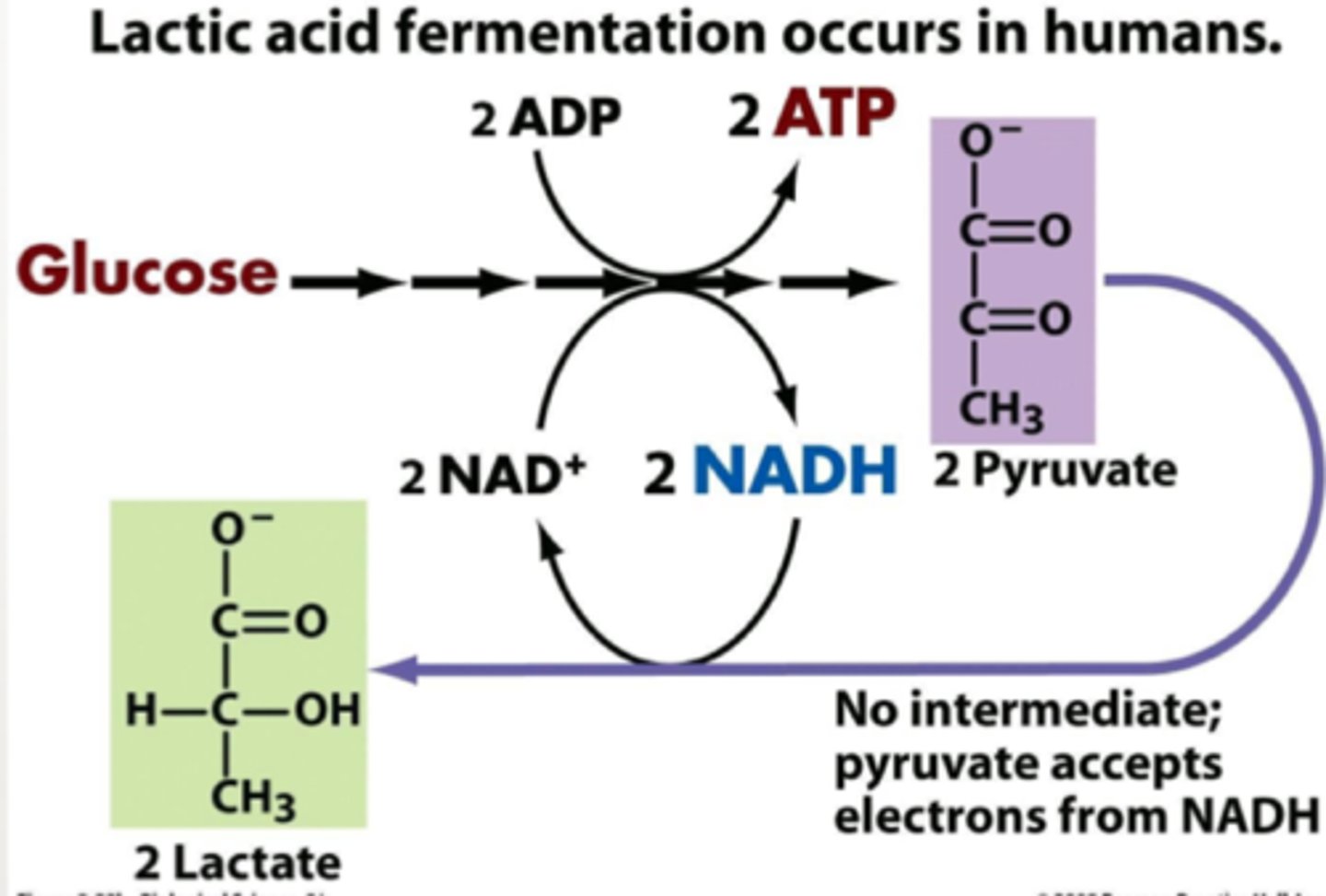
what is the final electron acceptor in fermentation?
organic molecule rather than oxygen serves as a final electron acceptor
what are the steps of cellular respiration?
1. Glycolysis
2. Transition Reaction
3. Citric Acid Cycle (krebs)
4. Electron Transport Chain
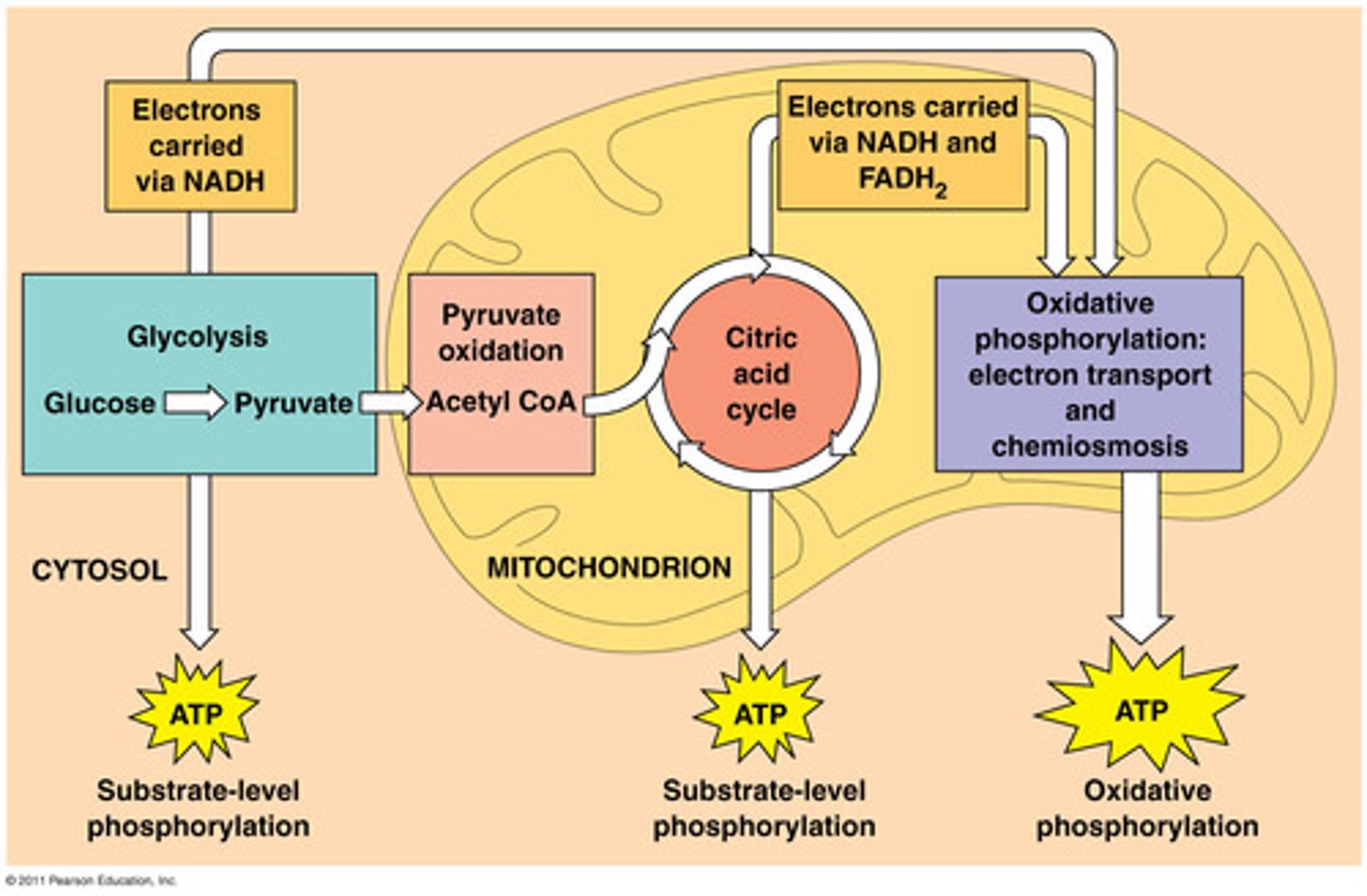
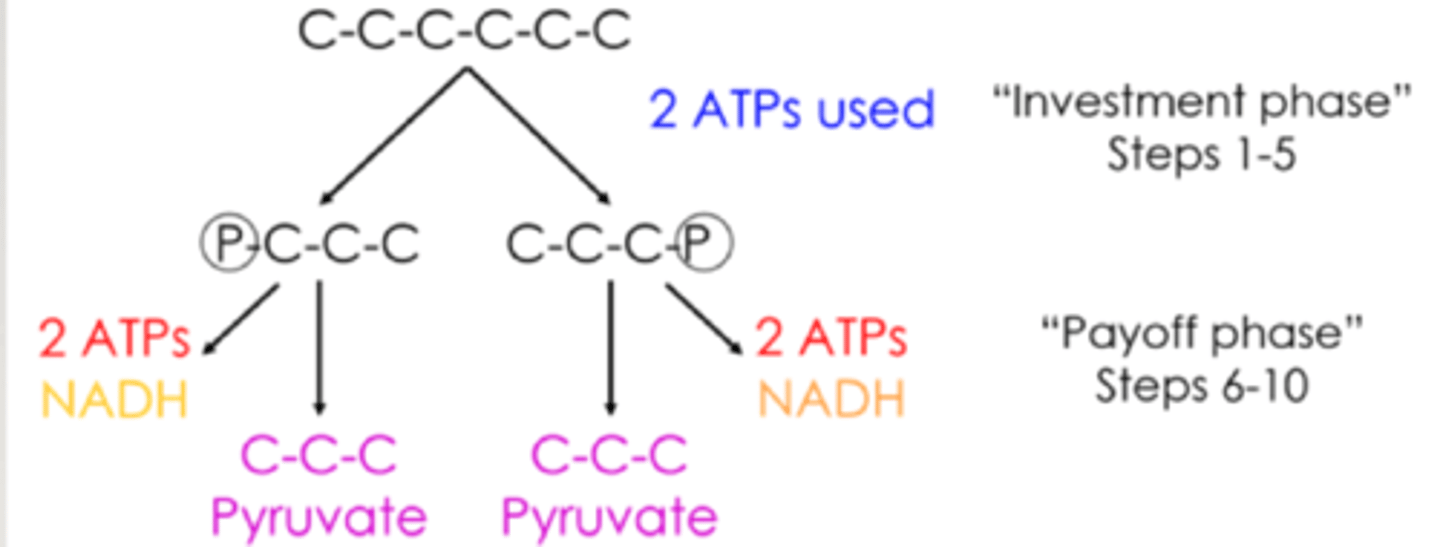
glycolysis
oxidizes glucose to pyruvate (splitting of glucose)
Glycolysis yields
2 pyruvate, 2 ATP, 2 NADH
how many steps are there in glycolysis?
- investment phase (1-5)
-Payoff phase (6-10)
investment phase of glycolysis
uses 2 ATP to split glucose into two molecules
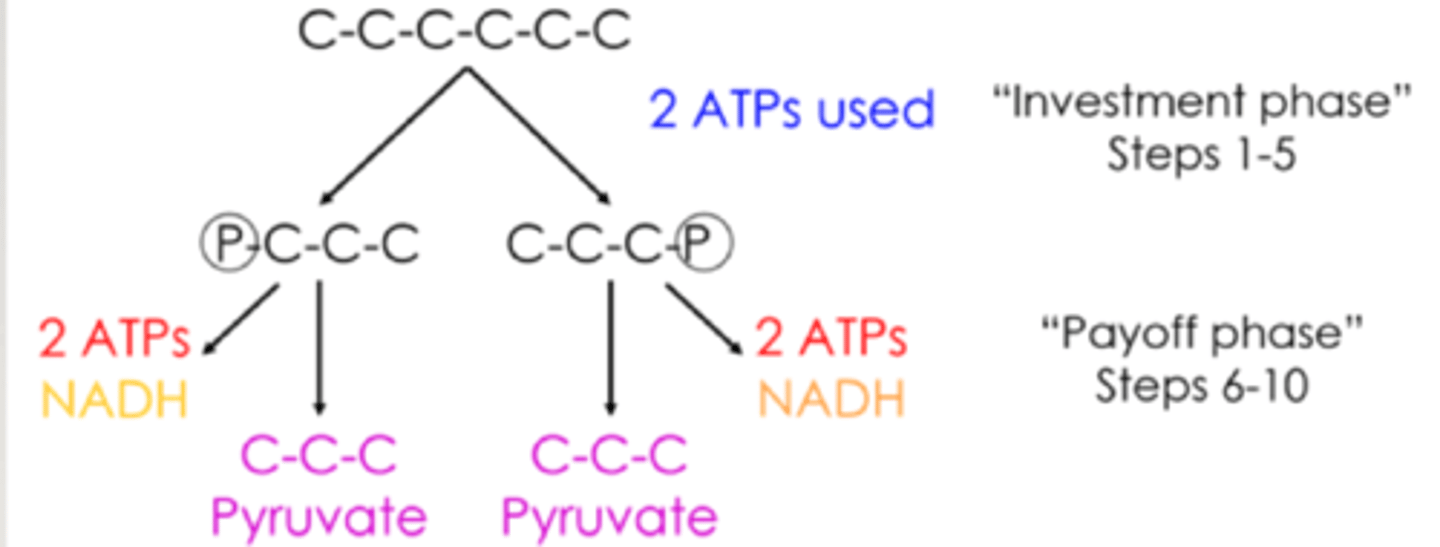
payoff phase of glycolysis
2 NAD+ are reduced to NADH, produces 4 ATP through substrate level phosphorylation
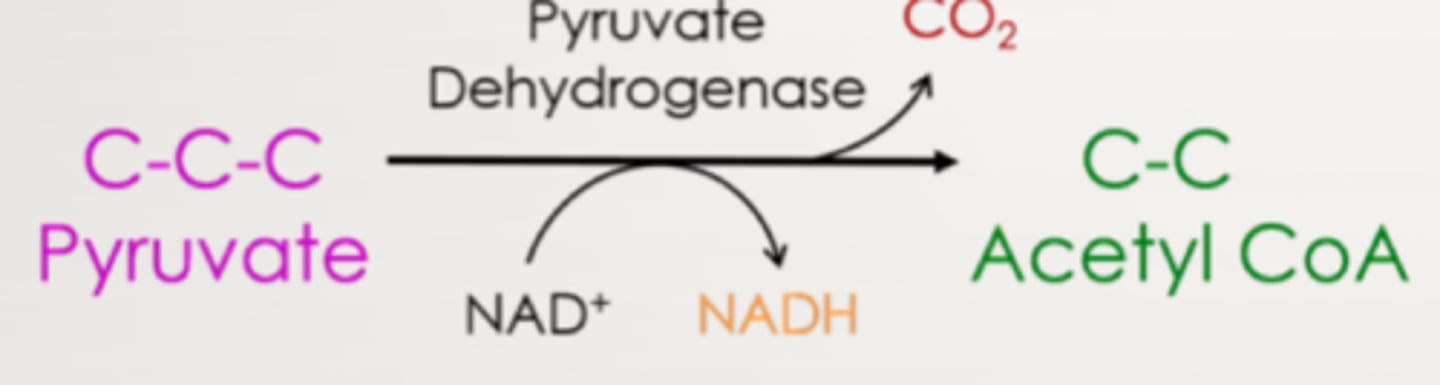
Transition reaction
pyruvate is shuttled into the mitochondria and converted into Acetyl CoA
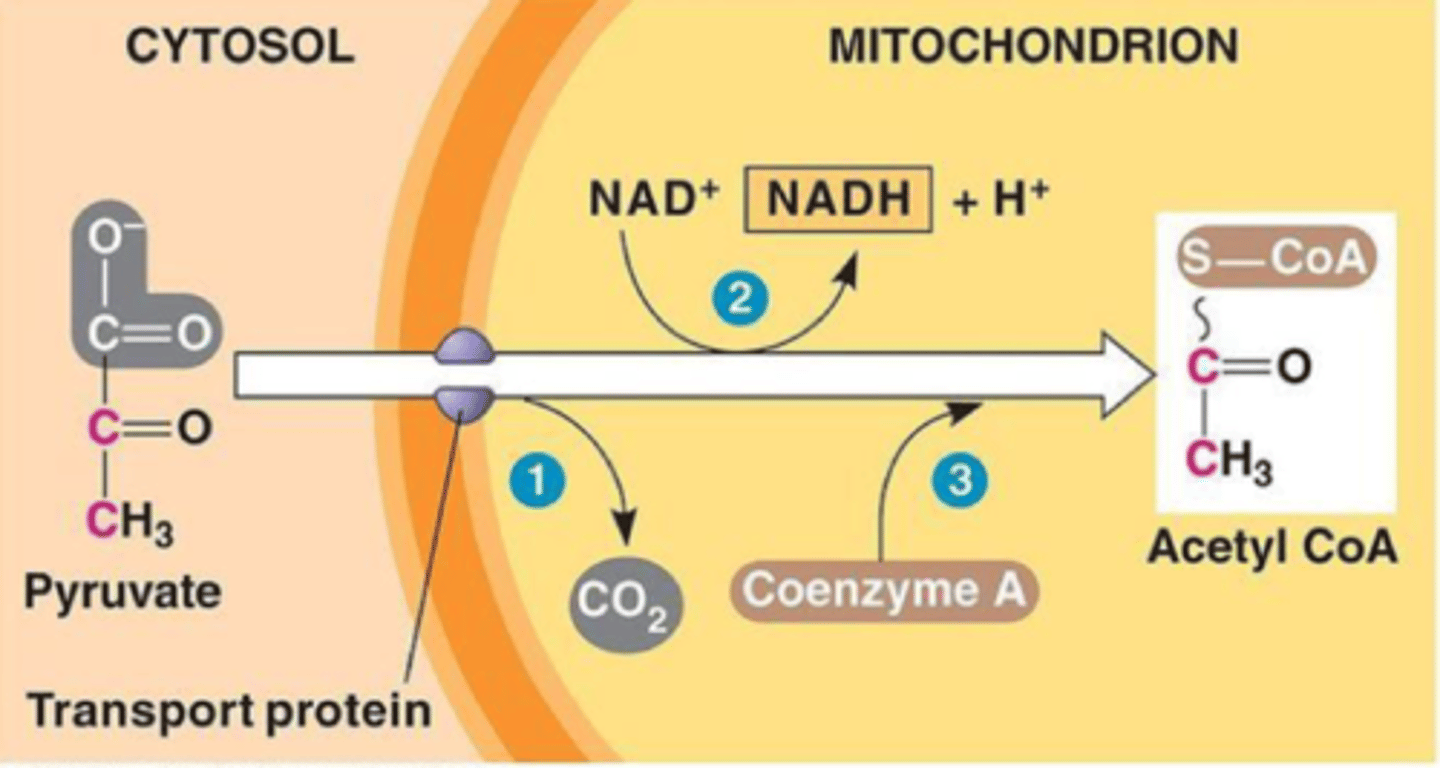
What does the transition reaction produce?
CO2
1 NAD+ is reduced to 1 NADH
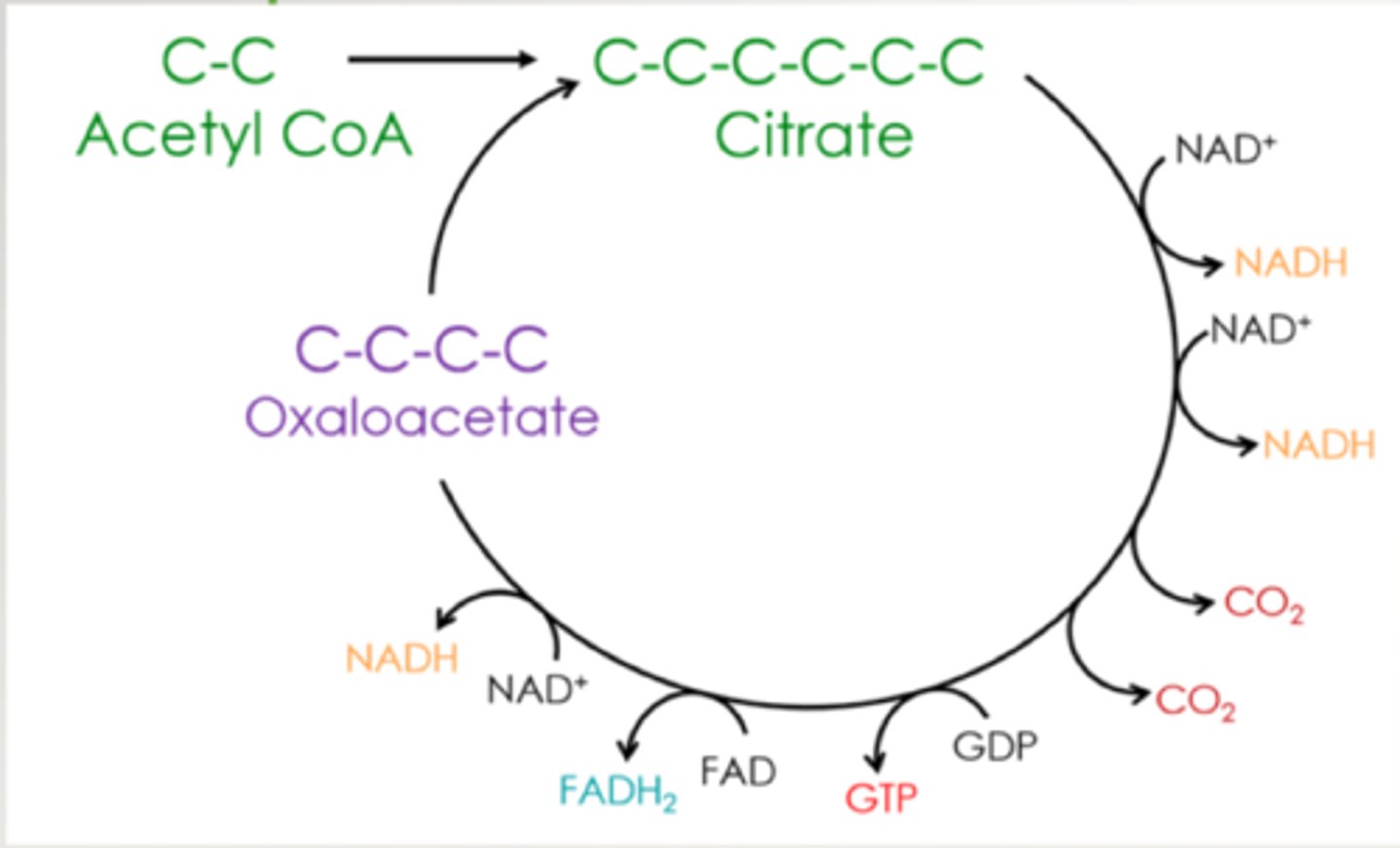
Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
metabolic process that oxidizes citrate to oxaloacetate
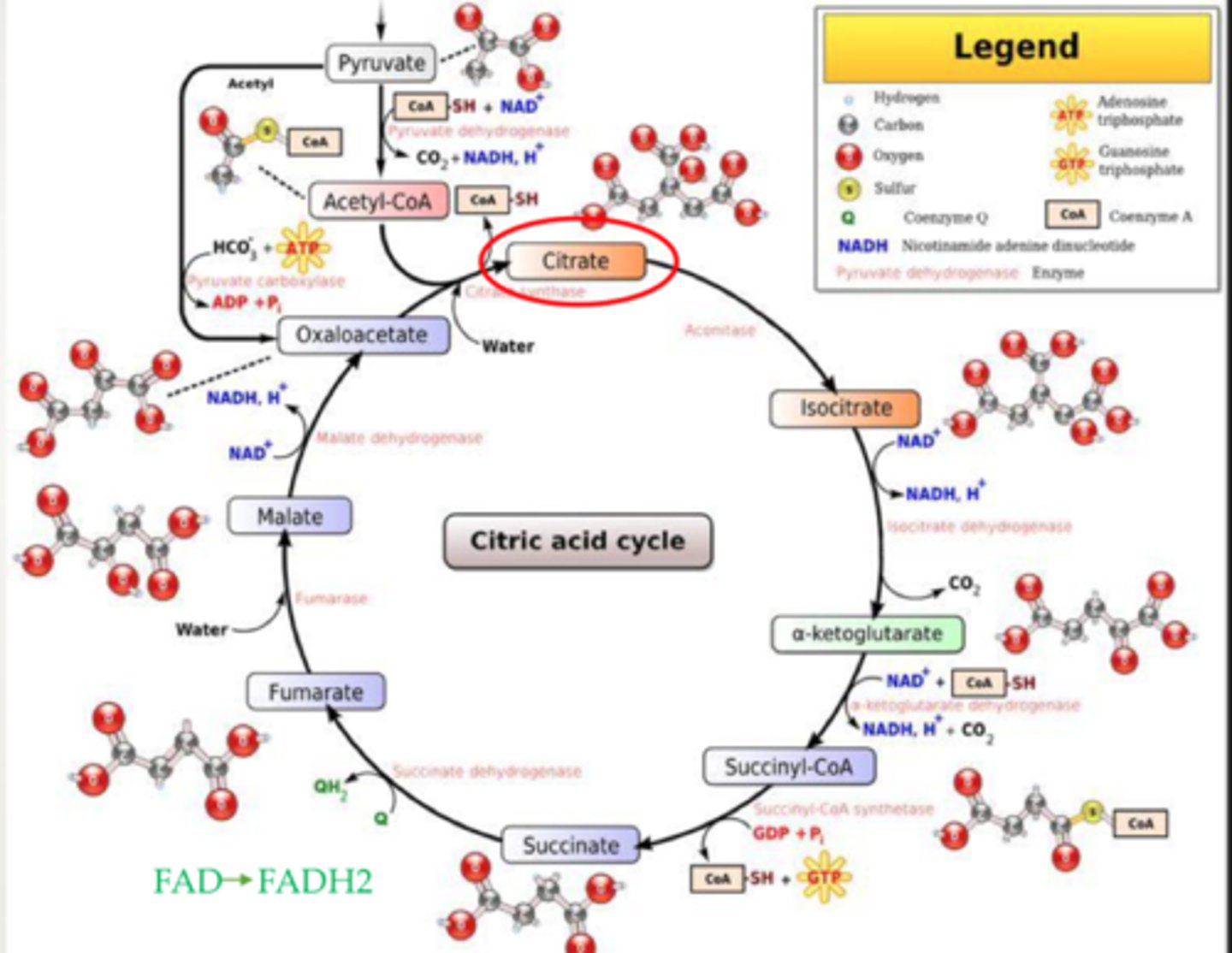
what does the krebs cycle produce?
1 oxaloacetate
3 NADH
1 FADH2
1 GTP
2 CO2
How is citrate formed?
by combining acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate
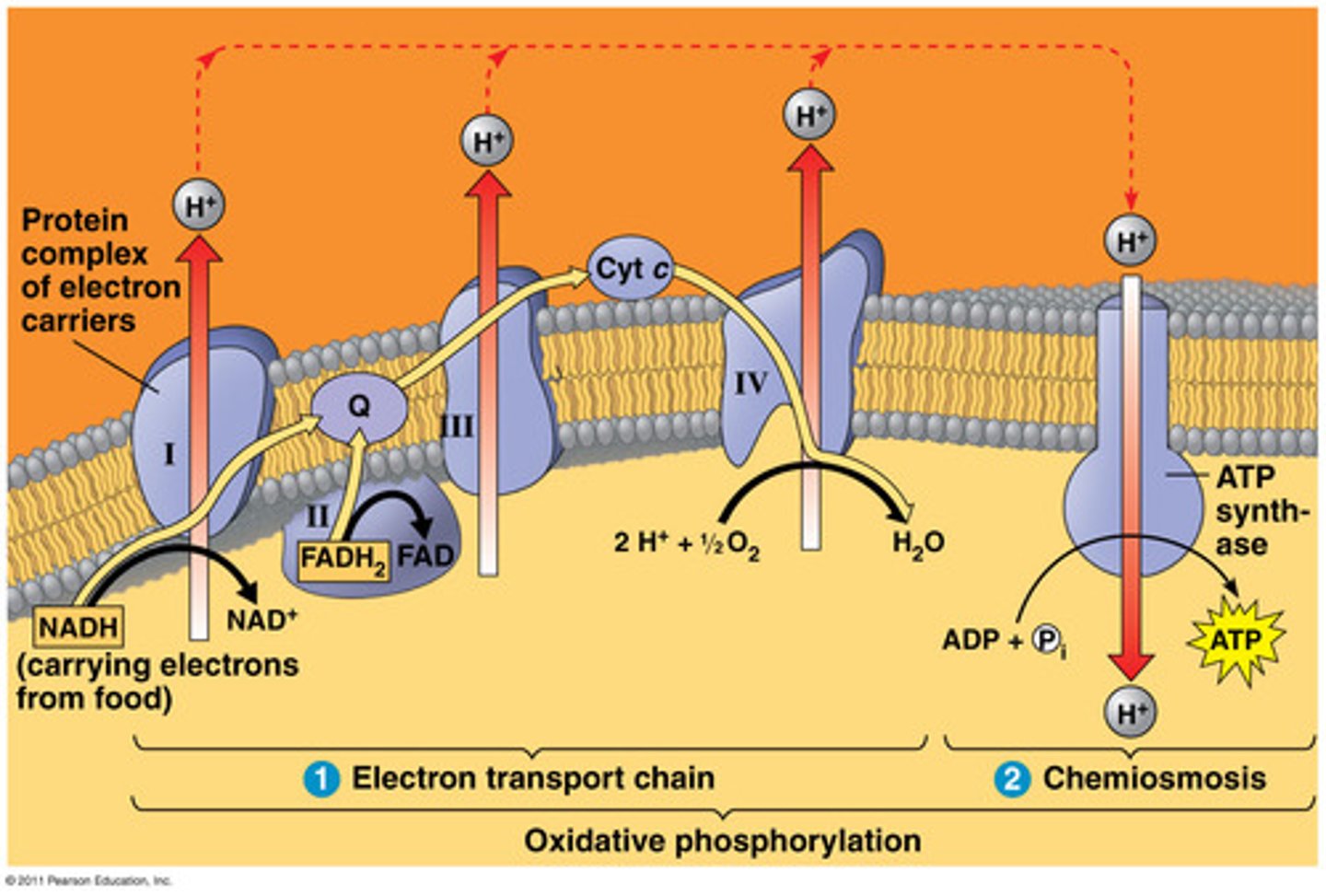
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
series of electron carrier proteins that shuttle high-energy electrons during ATP-generating reactions
Where does ETC occur?
inner membrane of mitochondria
About the electron transport chain
- 4 large complexes I-IV
- last component is oxygen
- each component of the chain is more electronegative than the last
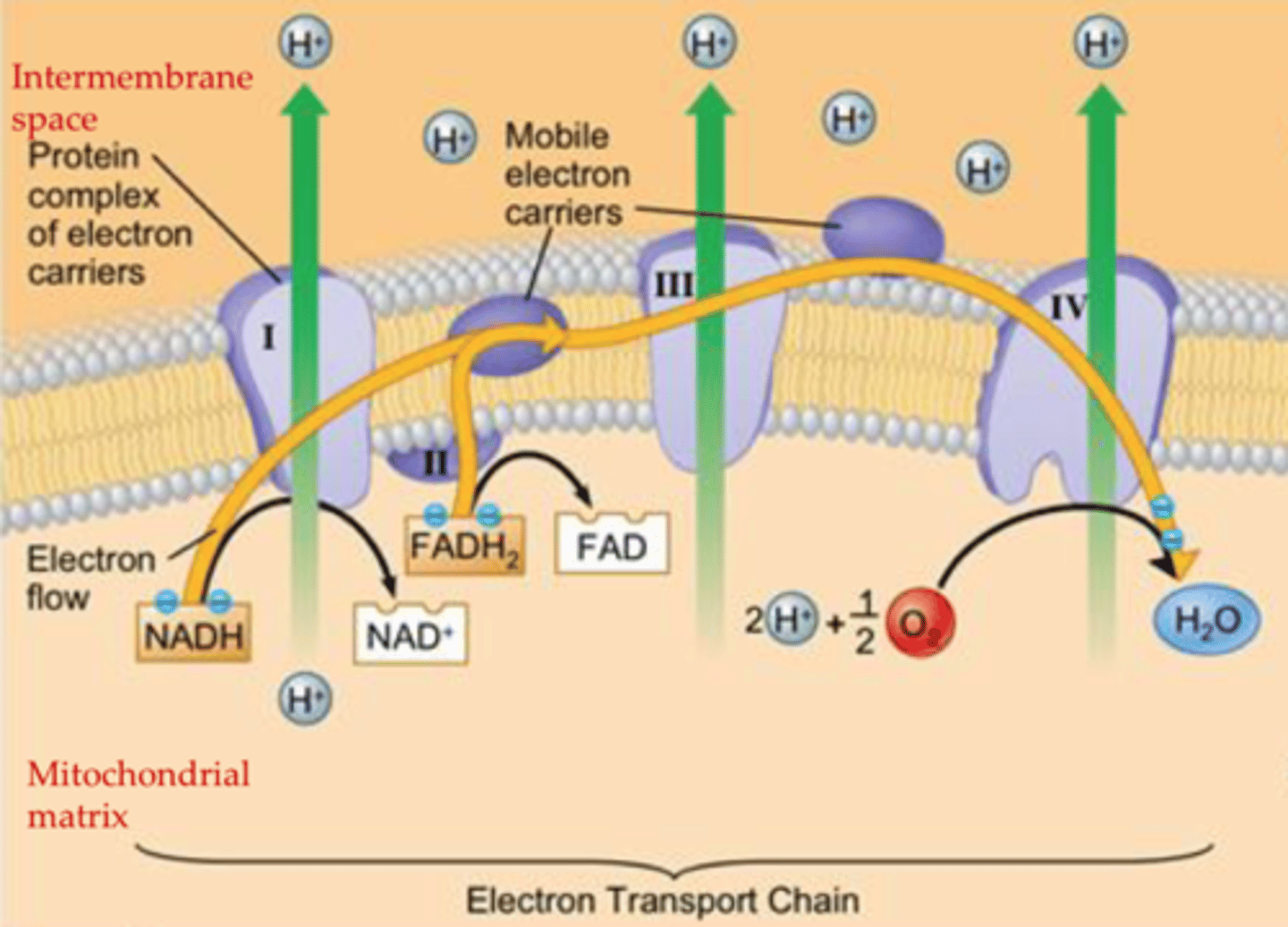
What do NADH and FADH2 do?
they pass on their electrons down the ETC
Where does NADH start in ETC?
Complex I
where does FADH2 start in ETC?
Complex II
what is the purpose of the electron transport chain?
pump H+ from the mitochondrial matrix to the inter membrane space , creating an electrochemical gradient
chemiosmosis
H+ in the intermembrane space reenter the mitochondrial matrix by moving down the electrochemical gradient (travel through ATP synthase)
-catalyzes the joining of phosphate to ADP to form ATP
ATP synthase
Large protein that uses energy from H+ ions to bind ADP and a phosphate group together to produce ATP
How many H+ ions move through ATP synthase to synthesize 1 ATP?
4 H+
How much ATP does cellular respiration generate?
36 molecules of ATP per molecule of glucose
How much ATP does each NADH produce? (10 H+)
2.5 ATP
How much ATP does each FADH2 produce? (6 H+)
1.5 ATP
How many molecules of water are produced in cellular respiration? how many CO2?
6 H2O, 6 CO2
How much ATP is produced in oxidative phosphorylation?
28 (10 NADH= 25 ATP, 2 FADH2= 3 ATP)
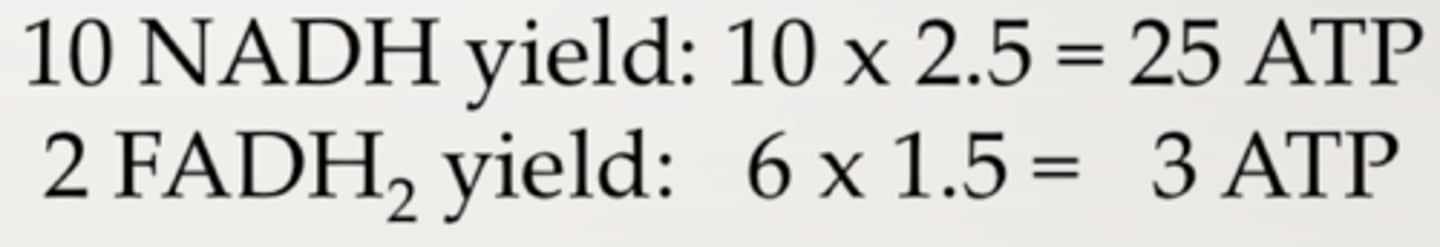
What does fermentation produce?
2 pyruvate, 2 NADH, and 2 ATP net
What happens to fermentation is oxygen is not present?
pyruvate is fermented and does not enter the krebs cycle (accepts e- from NADH forming lactate and NAD+)
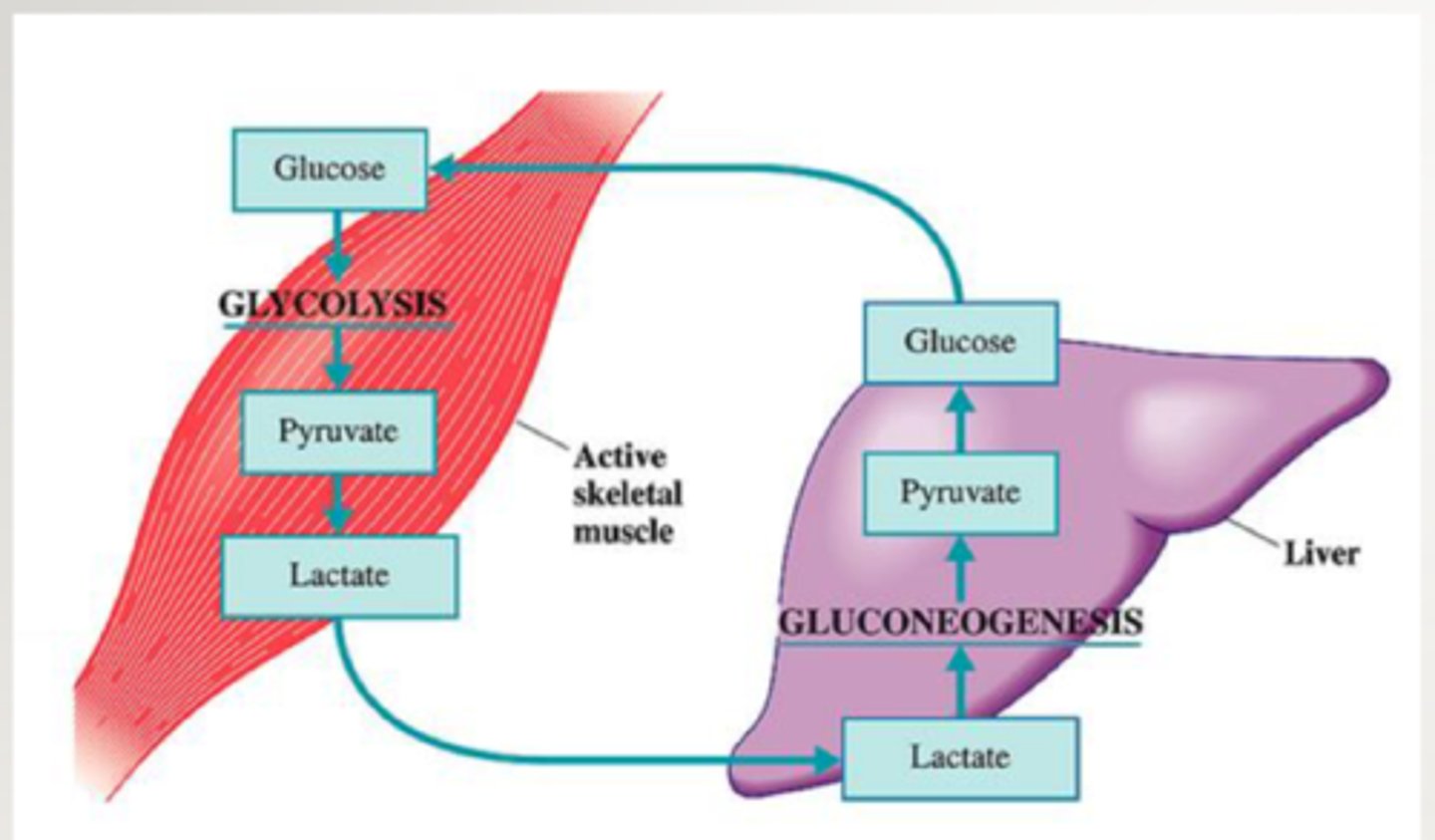
what happens to lactate after fermentation?
Lactate is transported to liver for conversion back to pyruvate, providing a steady supply of NAD+ that can enter glycolysis)