BMS 302 10
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
When taking a blood pressure, the first sound that you hear represents the _____, and is the pressure that is generated during _____.
systolic reading; contraction of the ventricles
Mean arterial pressure must be homeostatically maintained..
to insure adequate perfusion of all vascular beds.
to insure sufficient pressure so that the forces of gravity can be overcome.
to prevent one from passing out if the brain is insufficiently perfused.
to allow one to change positions such as going from reclining to standing without feeling faint.
through the baroreceptor reflex.
As the heart to brain distance becomes greater, the MAP at the level of the heart _____ , while the MAP at brain level _____ when compared with different species.
increases; remains about the same
Systolic blood pressure is reflected or influenced by _____, whereas diastolic pressure is reflected by _____.
cardiac output; peripheral resistance
You are measuring the blood pressure in a patient using a sphygmomanometer. You could detect an increase in venoconstriction by observing _____________, and you could detect an increase in vasoconstriction of the arterioles by observing ______________.
an increase in systolic pressure; an increase in diastolic pressure
If heart rate doubles and stroke volume doubles, cardiac output will:
4X
Which of the following factors can affect stroke volume?
End diastolic volume
venous return
heart rate
ejection fraction
ventilation
exercise
SAN simulation
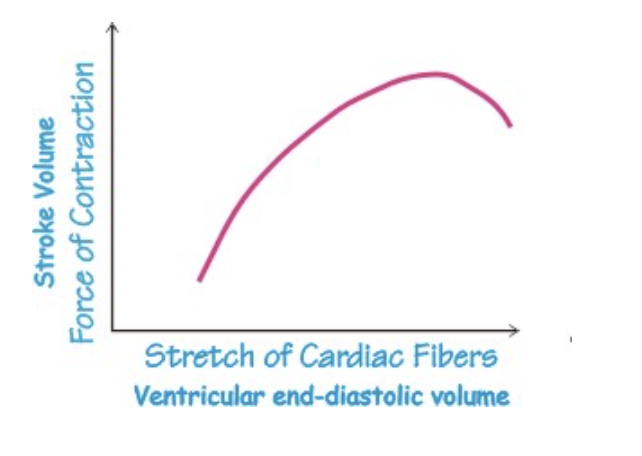
what principle does this graph represent
Starling's Law, which is an intrinsic autoregulation mechanism that matches cardiac output to venous return.
what is responsible for adjusting mean arterial pressure on a moment to moment basis
the baroreceptor reflex
venous valves functions
prevents blood from pooling in extemities
assist in reducing the effect of hydrostatic pressure on blood returning to the heart
when impaired, are the cause of varicose veins
List three mechanisms the body has developed to maintain the return of blood (venous return) to the heart from the extremities.
skeletal muscle pump
thoracic pump
venoconstriction
Which of the following facilitates venous return?
increase in venous tone
skeletal muscle pump
thoracic pump
fainting
postural changes like lying down w/ feet up
skeletal muscle pump
muscle contraction squeeze veins forcing blood back toward the heart past one way valves
thoracic pump
negative pressure in chest '“pull” blood into the thorax and heart w/ each inhalation
venoconstriction
smooth muscle in the elastic venous vessels contracts forcing blood from the venous system back toward the heart
What branch of the Autonomic Nervous System innervates the veins?
SANS
What autonomic output leads to venoconstriction?
increased SANS
What is the effect of venoconstriction on venous return?
increases
What autonomic output leads to venodilation?
decreased SANS
What is the effect of venodilation on venous return?
decreases
Increased sympathetic activity stimulates the smooth muscle (effector) in the wall of the veins to ________ and therefore ______ the diameter of the vessel.
contract; decrease
List three factors that can alter peripheral resistance.
viscosity
length
diameter
Which of the following vessels play the most important role in altering peripheral resistance?
arterioles
Decreased sympathetic activity stimulates the smooth muscle (effector) in the wall of the veins to ________ and therefore ______ the diameter of the vessel.
relax; increase
With a generalized vasoconstriction of arterioles..
mean arterial blood pressure increases.
peripheral resistance increases
blood vessels decrease in diameter
blood flow "downstream" from the vasoconstriction decreases
diastolic pressure increases
What branch of the Autonomic Nervous System innervates the arterioles?
SANS
What is the effect of arteriolar vasoconstriction on peripheral resistance?
increases
What autonomic output leads to arteriolar vasoconstriction?
increased SANS
What autonomic output leads to arteriolar vasodilation?
decreased SANS
What is the effect of arteriolar vasodilation on peripheral resistance?
decreases
Increased sympathetic activity stimulates the smooth muscle (effector) in the wall of the arterioles to ________ and therefore ______ the diameter of the vessel.
contract; decrease
Decreased sympathetic activity stimulates the smooth muscle (effector) in the wall of the arterioles to ________ and therefore ______ the diameter of the vessel.
relax; increase
Veins and arterioles are in a partially contracted state under rest and repose conditions.
called sympathetic tone
The partially contracted state is the result of a tonic sympathetic stimulation of the smooth muscle in the walls of the vessels.
Under Fight or Flight conditions:
Increased Sympathetic Nervous System stimulation causes arterioles controlling blood flow to visceral organs to constrict.
Blood flow to visceral organs decreases.
Metabolic by-products from contracting skeletal muscle causes a local vasodilation of arterioles in skeletal muscle.
Blood flow to active skeletal muscle increases.
Match the component of the baroreflex arc induced when one goes from a reclining to a standing position listed in the left column with the best description in the right column.
stimulus- decreased MAP
receptor- baroreceptors located in carotid artery and aortic arch
afferent pathway- decreased frequency of impulses along sensory neurons
integrator- cardiac and vasomotor centers of medulla
efferent pathways- sympathetic neurons to heart & vessels and parasympathetic neurons to heart
effectors- cardiac muscle and smooth muscle of vessels
response- increased MAP
During moderate exercise, systolic pressure increases because cardiac output _____ and diastolic pressure is maintained close to resting levels or decreases as blood flow to exercising skeletal muscle _____, and blood flow to the digestive tract _____.
increases; increases; decreases
hypertension
is diagnosed when blood pressure readings exceed 140/90