BPSI 405
1/146
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
147 Terms
T/F? 3 O2 molecules bound to Hgb is 75% saturation.
True
T/F? Each Hgb protein can bind 4 O2 molecules.
True
T/F? Hgb is a protein that O2 can bind to.
True (Hgb)
T/F? O2 is transported by RBCs.
True
T/F? Each Hgb protein can bind to 1 O2 molecule.
False (O2)
What is the systolic BP for category 2 hypertension?
>140 mmHg
Fumaryl diketopiperazine (FDKP) is a proprietary _____ that is the primary component of Technosphere Microparticles.
excipient;
this is used to deliver insulin to the alveolus of the human lung
Technosphere Microparticles (2.25 micrometer diameter) self-assemble from FDKP. This is a key respirable range for a lung.
Particles must dissolve in lung fluid upon reaching it to release drug
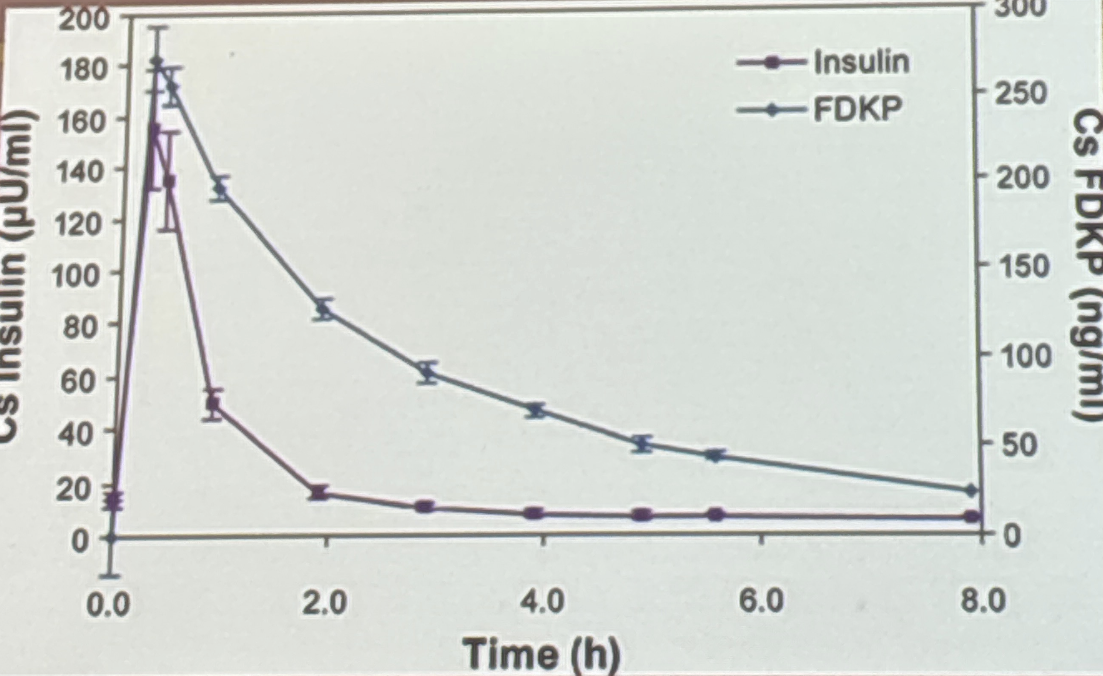
Average serum insulin and FDKP concentrations versus time in healthy volunteers indicate that the lung surface allows
for excipient and drug to be absorbed into bloodstream, more and less respectively
Based on characteristics of lung physiology, the more rapid absorption of insulin from AFREZA to blood vs subcutaneous injections is due to
the largest surface area and vascular bed area of the lung
Due to the growth factor signaling PDFG/VEGF/FGF pulmonary fibrosis, nintedanib is administered to IPF patients
using oral dosage forms
Idopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) has a strong link to
drugs, chronic inflammation, environment, lifestyle
Mode of action of nitedanib in the treatment of IPF is thought to occur via the _____ of _____
inhibition; receptors for profibrotic mediators
Where is the gut microbiome located in the body?
The large/small intestines and colon
How many microorganisms comprise the human microbiota?
100 trillion
What is dysbiosis?
an imbalance of microorganisms in the GI tract
T/F? The terms microbiota and microbiome can be used interchangeably as they define the same concept
False
What are some causes of dysbiosis?
Medication use, changes in diet, infections (for exam it will be all of the above)
What is the gut-brain connection?
nerve and neuron network, e.g. vagus nerve connecting CNS and digestive system
What are some scientifically proven ways to improve gut health?
Exercise, reduce stress, drugs (will be all of the above on exam)
Prevention of recurrence of C. difficile infection (CDI) in individuals >18 years of age
following antibacterial treatment for recurrent CDI has 2 approved drugs
T/F? Probiotic supplements can generally help improve the makeup of microbes in the gut microbiome
False
The orally administered microbiome related product (approved to treat certain types of CDI) contains
gut microbiome spores in a capsulated vehicle with glycerol and saline
Which foods in diet are supportive of the gut microbiome?
Probiotic rich foods
T/F? Rebyota is an oral microbiome-spore gel-capsule & Vowst is a 150mL volume rectal microbiome-live enema PEG3350 in saline
False
NEJM 2018 article describes 2 pts. that got ill, one died, following experimental FMT, from same donor, triggered a
safety alert & screening of donors for infectious E. coli with beta-lactamase
In Ocusert ®, what precorneal nonproductive processes are most negated for pilocarpine?
Tear turnover (production and drainage)
T/F? VOWST and REBYOTA both have an established MOA and defined nonclinical toxicology data/info
False
A 1% ocular suspension of brinzolamide improves ocular PK by (select all)
adding a dissolution step prior to corneal absorption
inc. precorneal residence time via particle dissolution step
Timolol XE ® brand is a topical ______ gel forming solution (rxn with Na in tears)
in situ
For acyclovir, corneal herpes virus, an ocular ointment (select all)
rapid release is expected due to solubility differences
rapid precorneal clearance is also possible after release
To estimate the contribution of the nasal vs conjunctival route to systemic exposure
punctal plug & intranasal dose can be compared to topical
What does a LEFT shift of Hgb O2 dissociation curve indicate?
Dec. temperature
Dec. PCO2
Inc. pH
Dec. 2,3-DPG
Is the Hgb/O2 curve sigmoidal?
Yes
What does the x-axis on the Hgb/O2 curve show?
PO2
What does the y-axis on the Hgb/O2 curve show?
Hgb saturation
What is the one difference in symptoms of a myocardial infarction between men and women?
Shoulder pain in women
What treats hypertension?
Diuretics, beta blockers, ARBs
T/F? MI and cardiac arrest are both medical emergencies and are the same thing.
False
Cardiac arrest and MI are because of an issue with what?
MI —> circulation issue
CA —> electrical issue
What is Phase 0 in action potentials?
Rapid depolarization
What is Phase II in action potentials?
Plateau phase
What is Phase III?
Repolarization
What is Phase IV?
Resting membrane potential (not in pacemaker cells though)
What cells are FUNNY channels found in?
Pacemaker cells
Pacemaker cells have which Phases?
IV, 0, III
Gas exchange happens in alveoli and blood of…
Pulmonary capillaries
Do PCs have a refractory period?
No, only contractile cells do
What is the threshold for PCs?
-40mV
What is the threshold for CCs?
-70mV
How much time does it take for the CC to contract?
~200 milliseconds
What is the rising phase of action potentials called?
Depolarization
Do PCs have a resting potential?
No, the FUNNY channel makes it so that there is a continuous influx of charge; i.e. it is always moving towards threshold
Electrical signals in the heart go from ___ to the ___.
SA node → AV node
What ions are responsible for action potentials?
Na+, Ca++, K+
When are cardiac muscles at work?
All the time
Types of cell-cell junctions?
Desmosomes, fasciae adherent, and gap junctions
Where are B and T cells kept?
Bone marrow and thymus; they end up in lymphatic nodes
Where are B cells found?
Cortex of lymph nodes
Where are T cells found?
Medulla of lymph nodes
How many efferent lymphatic vessels are there?
One (lymphatic)
Where are MALT membranes found?
Tonsils, adenoids, bronchus, gut-associated
What is the function of the lymphatic system?
Immune, filtration, and water balance
What causes edema?
Lymphatic system is not absorbing water and it stays in interstitial area
What collects interstitial fluid?
Lymphatic capillaries
Name the 2 ducts.
thoracic and right lymphatic ducts
What way do lymphatic vessels travel?
One direction (no backwards travel)
What moves lymph?
Muscle contraction
What is lymphoma?
Cancer of the lymphatic system
Can the CYP3A4 enzyme be affected by genetic polymorphism?
No (polymorphism)
Gluconeogenesis
Glucose from non-carbohydrate sources
Glucogenolysis
Glycogen → glucose
How many lobules in the liver?
100,000 lobules
How many hepatocytes are there?
1,000,000 hepatocytes
What does biotransformation do for excretion of stuff?
Makes stuff go from nonpolar → polar to increase excretion
What % of glucose is reabsorbed by the proximal convoluted tubule?
100% glucose
After how much loss of kidney function is dialysis required?
Once 85-95% function is lost
Does the left or right kidney sit lower in the body?
The right sits lower
Are the efferent or afferent arterioles wider?
Afferent arterioles
What is the name of the capillary that runs length of nephrons?
Peritubular capillary
How many nephrons are there?
100M nephrons
What % of filtrate is reabsorbed at proximal convoluted tubule?
65% filtrate
What is the rest of this equation? excreted =
filtered - reabsorbed + secreted
What is ACE produced in?
It is produced in the lungs
Where is the hormone ADH held in?
Posterior pituitary gland
Is the contraction of skeletal muscles voluntary?
Yes, all movement of the skeletal muscles is voluntary
Which muscles are striated?
All but smooth muscles
Of actin and myosin, which is thick and which is thin?
Actin is thin and myosin is thick
For ATP produced, which filament does it bind to?
It binds to myosin
Is the action potential of the skeletal muscles the same as in the rest of the body?
No, it is not the same
How are signals passed in skeletal muscles?
Electrical → chemical → electrical
What chemical messenger is released from synapse to terminal?
ACh is released
Which band in filaments is dark?
The A band
Tropomyosin is considered the…
the bike chain
Toponin is considered the…
the lock
What releases the lock (troponin)?
Ca++ ions from sarcoplasmic reticulum
What is another name for the CNS?
Neuroaxis
Where do the peripheral nerves of the autonomic nervous system end?
Target organs, not muscle
Is the autonomic nervous sympathetic or parasympathetic?
They are both sympathetic and parasympathetic
Where are first order neurons?
Brainstem and spinal cord