Epithelial & Connective Tissues
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
cellularity
the characteristic of epithelia that refers to the number of cells tightly packed together.
polarity
refers to the presence of distinct apical and basal surfaces in epithelial tissue.
avascularity
refers to the absence of blood vessels in epithelial tissue.
regeneration
the ability of epithelial tissue to renew and repair itself.
basal lamina
a thin layer of extracellular matrix that epithelial cells attach to.
CAMs (cell adhesion molecules)
transmembrane proteins on the cell surface that help cells stick to each other and to their surroundings like the extracellular matrix.
they act as “molecular glue” to maintain tissue structure and are crucial for cell communication, development, and immune responses.
occluding (tight) junctions
specialized cell-cell junctions that form a seal, or “tight” barrier, between two plasma membranes.
they prevent the uncontrolled passage of fluids, solutes, toxins, and microbes between cells.
isolates wastes in the lumen.
gap junctions
specialized channels formed by connexin proteins that allow small molecules, ions, and metabolites to directly pass between adjacent cells.
allow rapid communication between adjacent cells by enabling ions to pass.
coordinate contractions in heart muscle.
desmosomes
cell junctions that provide structural support and adhesion between cells.
tie cells together, allowing bending and twisting.
hemidesmosomes attach cells to the basal lamina.
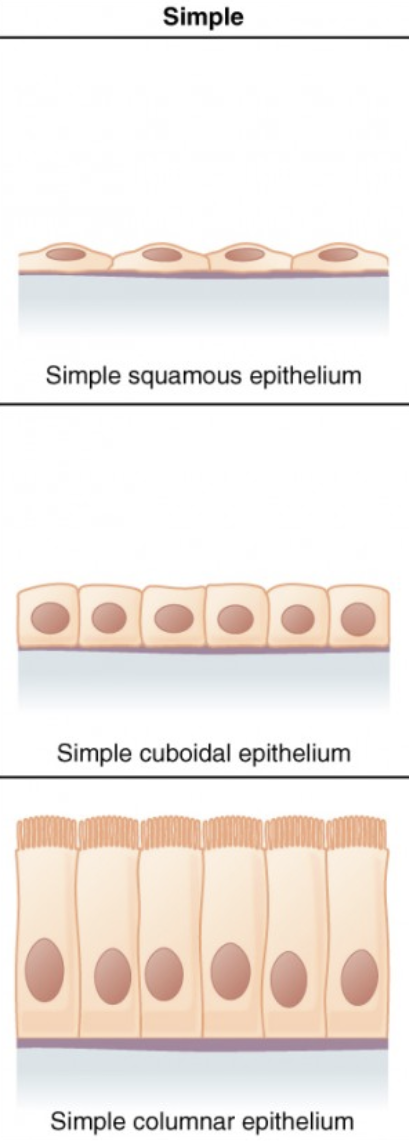
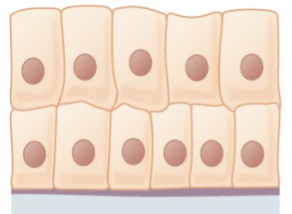
simple epithelium
a single layer of cells.
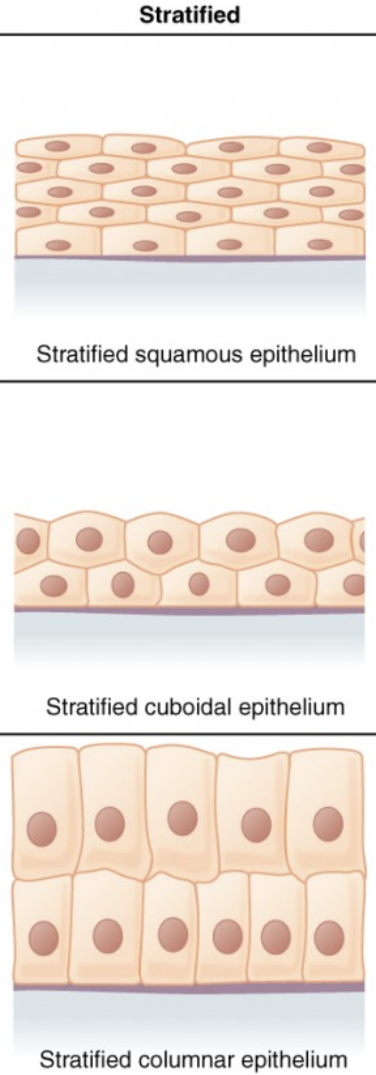
stratified epithelium
multiple layers of cells.
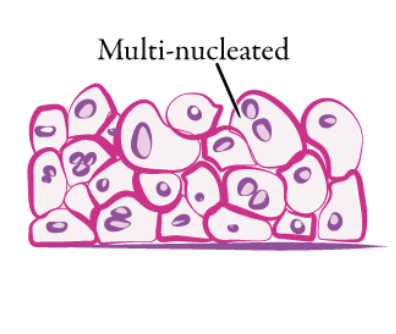
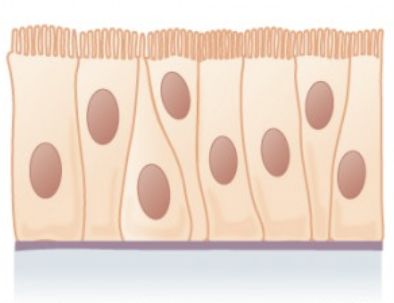
pseudostratified epithelium
found in lining of nasal activity, trachea, bronchi, and portions of male reproductive tract.
protection, secretion.
transitional epithelium
stratified, multi-layered tissue with cuboidal to squamous cells.
merocrine
secretion is produced in the Golgi apparatus and released by exocytosis without damaging the cell.
this process is used by sweat glands, salivary glands, and pancreatic glands to secrete substances such as watery sweat, saliva, and digestive enzymes.
apocrine
secretion produced by shedding of cytoplasm.
where a portion of the cell pinches off to release its contents.
in mammals, apocrine glands are found in areas like the armpits and groin where they secrete a fluid into hair follicles. this secretion is initially odorless but can develop a smell when broken down by bacteria.
holocrine
secretion where a cell ruptures and disintegrates completely to release its contents.
this process is characteristic of sebaceous glands, which release the oily substance sebum to lubricate and protect the skin.
found on the face, chest, and back, as well as other areas of the body.
epithelial tissues
covers exposed surfaces, supports other tissues, transports materials, provides sensation, produces specialized secretions, and stores energy.
cellularity, polarity, attachment, avascularity, and regenerations.
apical surface
faces the external environment or a tissue lumen and is involved in secretions or absorption.
projections like microvilli (increase surface for absorption) and cilia (movement).
intercellular cement
a substance between epithelial cells that holds them together, providing structural integrity and acting as a barrier against the passage of substances.
composed of proteoglycans and lipids like ceramides.
hyaluronan
vital component that supports tissue structure, hydration, and protection.
plays a crucial role in epithelial cell migration, wound healing, and the strength of the epithelial barrier, which protects against injury and infection.
lamina lucida
clear, thin layer secreted by epithelia, barrier to proteins.
lamina densa
dense layer, thick fibers, produced by connective tissue, strength and filtration.
simple squamous
found in air sacs of the lungs and the lining of the heart, blood and lymph vessels.
reduces friction, controls vessel permeability, and performs absorption and secretion.
simple cuboidal
found in glands, ducts, portions of kidney tubules, and thyroid gland.
limited protection, secretion, absorption.
simple columnar
lining of stomach, intestine gallbladder, uterine tubes, and collecting ducts of kidneys.
protection, secretion, absorption.
stratified squamous
found in surface of skin. lining of mouth, throat, esophagus, rectum, anus, and vagina.
provides physical protection against abrasion, pathogens, and chemical attack.
stratified cuboidal
lining of some ducts (rare).
protection, secretion, absorption.
stratified columnar
found in small areas of the pharynx, epiglottis, anus, mammary gland, salivary gland ducts, and urethra.
protection.
endocrine glands
composed of glandular epithelial tissue that secretes hormones and other signaling molecules directly into the bloodstream, rather than through ducts.
organized into structures like the thyroid, pituitary, and adrenal glands, which function to regulate various bodily processes by releasing their products into the body’s internal fluid environment.
exocrine glands
secrete substances like sweat, tears, saliva, and digestive juices onto a body surface through a duct or opening.
instead of releasing hormones directly into the bloodstream, they transport their secretions to a specific location such as the skin or the gastrointestinal tract using a duct.
examples include sweat glands, salivary glands, and glands in the stomach and pancreas that secrete digestive enzymes.
serous glands
exocrine glands that secrete a watery, protein-rich fluid containing enzymes. their secretions contribute to functions like digestion and lubrication.
mucous glands
exocrine glands that secret mucus, a thick, sticky fluid that protects and lubricates various surfaces in the body.
connective tissue
specialized cells, solid extracellular protein fibers, fluid extracellular ground substance.
connect epithelium to the rest of the body, provide structure, store fat, transport materials, have no contact with environment, highly vascular, the most abundant tissue type.
embryonic connective
not found in adults
mesenchyme is the first connective tissue in embryos
mucous connective tissue - loose embryonic connective tissue
loose connective tissue
also known as areolar tissue, type of connective tissue that has a high volume of ground substance and a sparse arrangement of fibers.
includes collagen, elastic, and reticular fibers.
this structure allows it to connect, support, and cushion organs and tissues while providing flexibility.
found under the epidermis, surrounding blood vessels, and in organs like the liver, sleep, and kidney.
for example, fat.
dense connective tissue
type of connective tissue made mostly of tough collagen fibers and fibroblasts, which supports and protects body structures.
more fibers, less ground substance.
comes regular, irregular, and elastic.
for example, tendons.
fibroblasts
connective tissue cells that play a crucial role in wound healing, tissue repair, and maintaining the structural integrity of various organs and systems.
contributes to the formation of connective tissue and connects other tissues or organs in the body.
the most abundant, secrete proteins and hyaluronan.
found in all the CT proper.
fibrocytes
rare, circulating bone marrow-derived cells that migrate to sites of injury to play roles in both healing and fibrotic diseases.
2nd most abundant.
macrophages
powerful immune cells that act as the body’s “big eaters”, performing crucial roles in host defense, tissue homeostasis, and repair.
they engulf and digest pathogens and cellular debris through a process called phagocytosis.
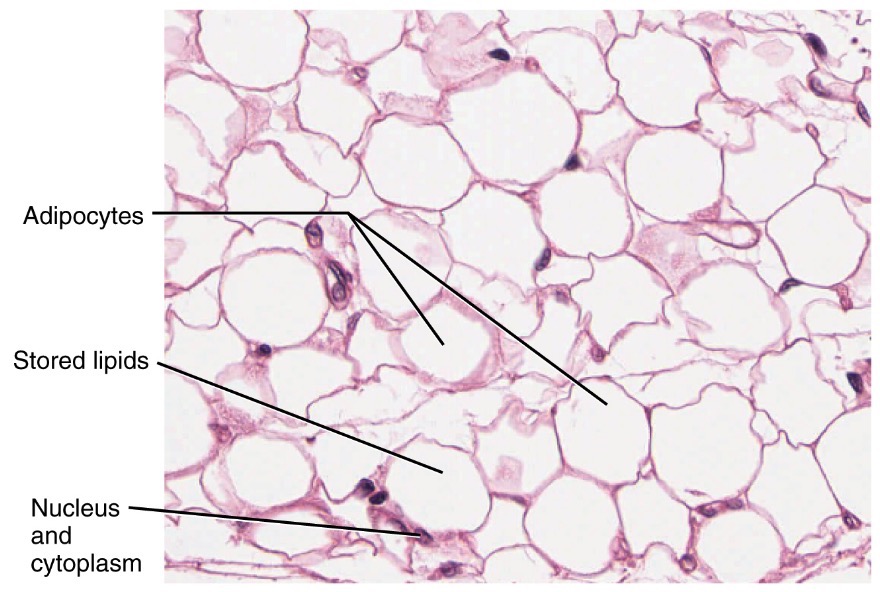
adipocytes
fat cells that store lipids, regulate metabolism, and have important endocrine functions by secreting hormones like leptin and adiponectin.
mesenchymal cells
stem cells that differentiate into fibroblasts, macrophages, etc.
they play a crucial role in tissue repair, regeneration, and immune modulation.
melanocytes
cells that produce and contain the pigment melanin, which determines the color of skin, hair, and eyes.
their primary function is to protect the skin from the sun’s harmful UV rays by absorbing and neutralizing them with melanin.
they also play a role in immunity and the development and function of other tissues like the heart and ear.
mast cells
immune cells that play a crucial role in allergic reactions and inflammation.
they are large, round cells that contain granules filled with various substances such as histamine, heparin, proteases, and cytokines.
they are found in various tissues throughout the body, including the skin, lungs, and gastrointestinal tract.
lymphocytes
a type of white blood cell that are crucial to the immune system, helping to fight infection by recognizing and destroying pathogens like bacteria and viruses.
collagen fibers
type of protein that form the structural framework of many tissues in the body, including skin, bones, tendons, and ligaments.
most common fibers in connective tissue proper
thick, strong, flexible, resist force in one direction.
composed of type 1 collagen.
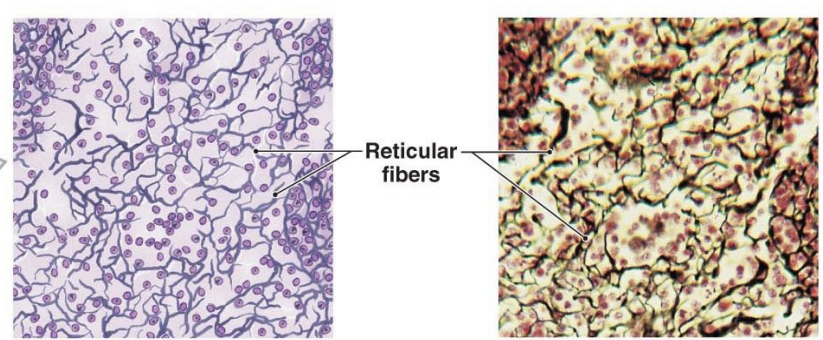
reticular fibers
type of fiber that form a fine, mesh-like network to provide structural support in various organs.
fine, branching, and delicate fibers.
composed of type 3 collagen.
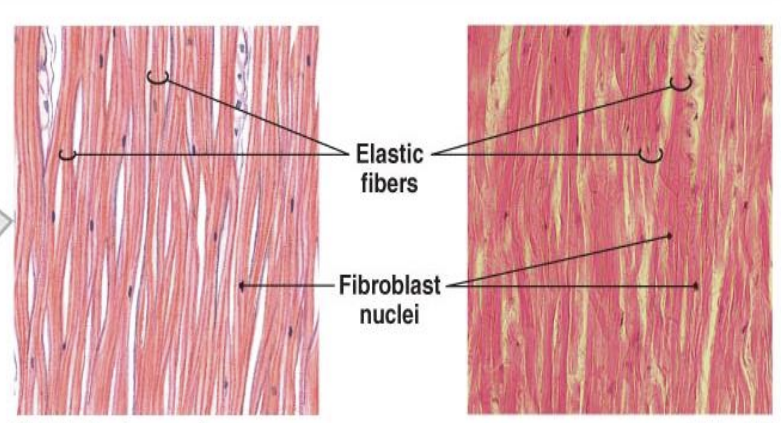
elastic fibers
connective tissue fibers in vertebrate tissues, primarily composed of the protein elastin, which provide tissues like skin, lung, and blood vessels with the ability to stretch and recoil elastically.
areolar tissue
type of loose connective tissue that is highly vascular and flexible, acting as a “universal packing material” to support and bind other tissues.
least specialized, open framework, elastic fibers, holds blood vessels and capillary beds.
it is found throughout the body, beneath the skin, and in spaced between organs where it helps cushion, protect, and hold organs in place.
adipose tissue
type of loose connective tissue that stores energy in the form of triglycerides.
contains adipocytes (fat cells).
provides padding and cushions shocks; insulates and stores energy,
is found throughout the body, particularly under the skin, around organs, and in bone marrow.
reticular tissue
type of connective tissue that forms a delicate, three dimensional network of fibers and cells.
reticular fibers, ground substance, and reticular cells, lymphocytes, macrophages, and other immune cells.
found in various organs and tissues throughout the body, providing structural support and a framework for other cell types.
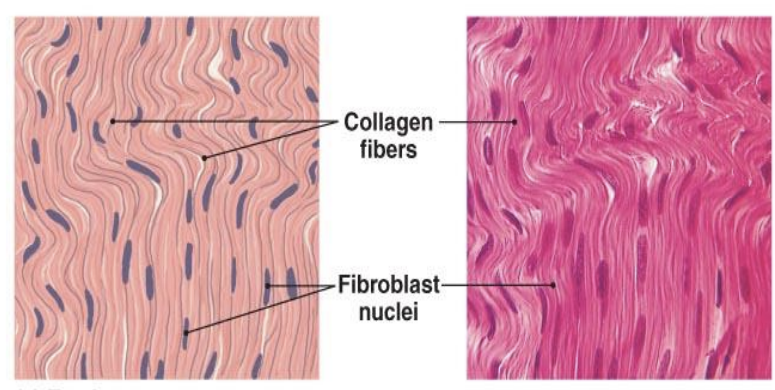
dense regular connective tissue
type of tissue characterized by densely packed, parallel collagen fibers that provide high tensile strength in one direction.
found in structures such as tendons and ligaments where it connects muscles to bones or bones to bones.
has fibroblasts aligned in rows between the collagen bundles, which appear as flattened nuclei in adults.
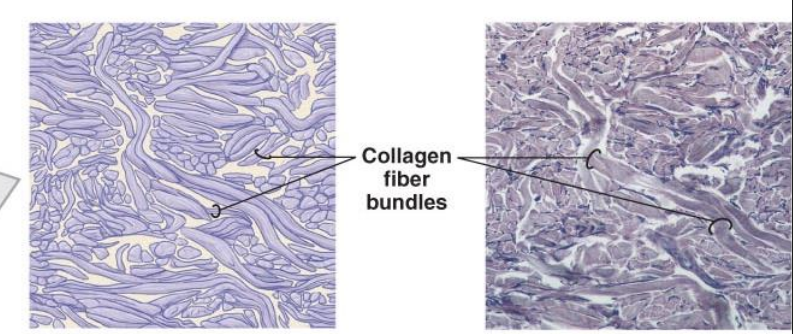
dense irregular connective tissue
type of tissue characterized by a dense network of collagen fibers that are arranged in an irregular, multidirectional pattern, providing strength and resistance to tension from all angles.
found in the dermis of the skin, fibrous capsules of organs like the kidneys and spleen, and joint capsules.
elastic tissue
provide stretch and recoil thanks to abundant elastic fibers, allowing organs and tissues to return to their original shape after deformation.
found in large blood vessels, ligaments, the skin, lungs, and the epiglottis, where their ability to stretch and bend is crucial for proper function.
fluid connective tissue
type of connective tissue that consists of a liquid matrix called ground substance and various cells.
plays crucial roles in transport, support, and defense in the body.
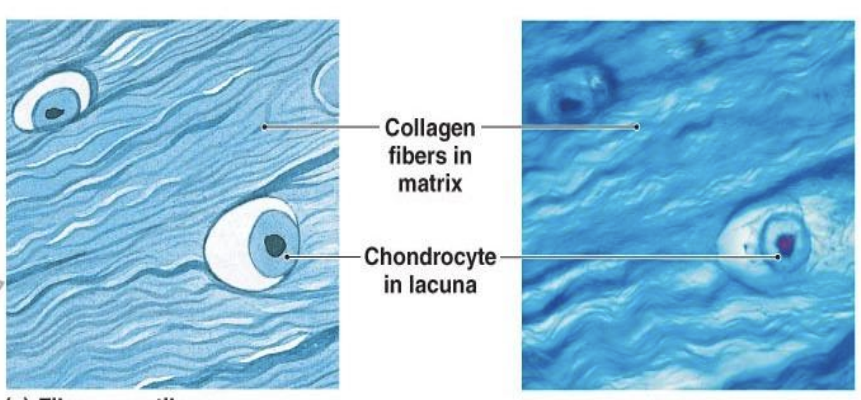
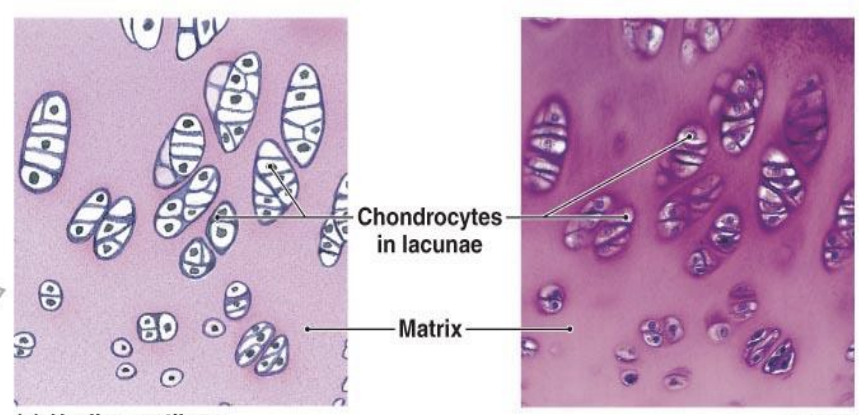
hyaline cartilage
most common and weak type of cartilage in the body, recognized by its smooth, glassy, bluish-white appearance and stiff, flexible properties.
functions are to provide smooth, low friction surfaces for joints to allow effortless movement, to act as a shock absorber, to provide support to structures like the nose, larynx, and trachea, and to serve as a bone precursor during fetal development and growth.
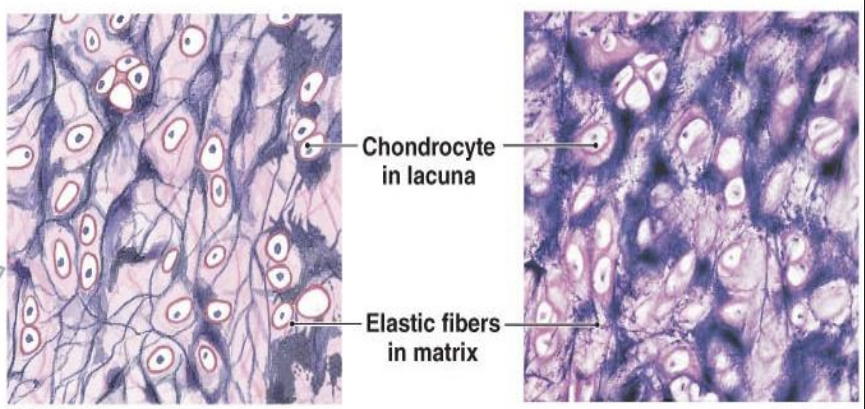
elastic cartilage
most flexible type of cartilage found in the external ear, epiglottis, and larynx, which allows structures to bend and spring back to their original shape.
dense network of elastic fibers in addition to collagen fibers.
fibrocartilage
strongest, most flexible, and shock-absorbing type of cartilage found in locations like intervertebral discs and menisci.
contains fibrous bundles of collagen.
simple squamous
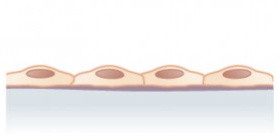
simple cuboidal
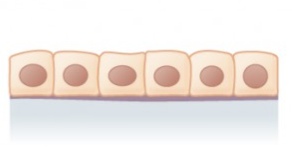
simple columnar
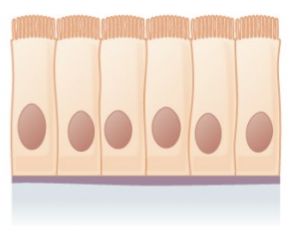
stratified squamous
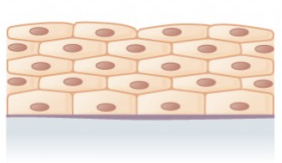
stratified cuboidal
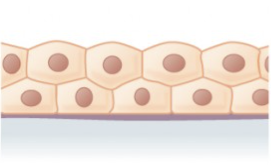
stratified columnar
pseudostratified
areolar tissue
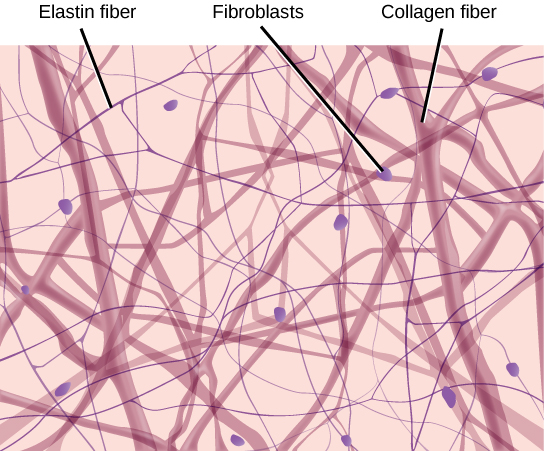

adipose tissue
reticular tissue
dense regular connective tissue
dense irregular connective tissue
elastic tissue
hyaline cartilage
elastic cartilage
fibrocartilage