BISC 4120 - Exam 1 Quizzes
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
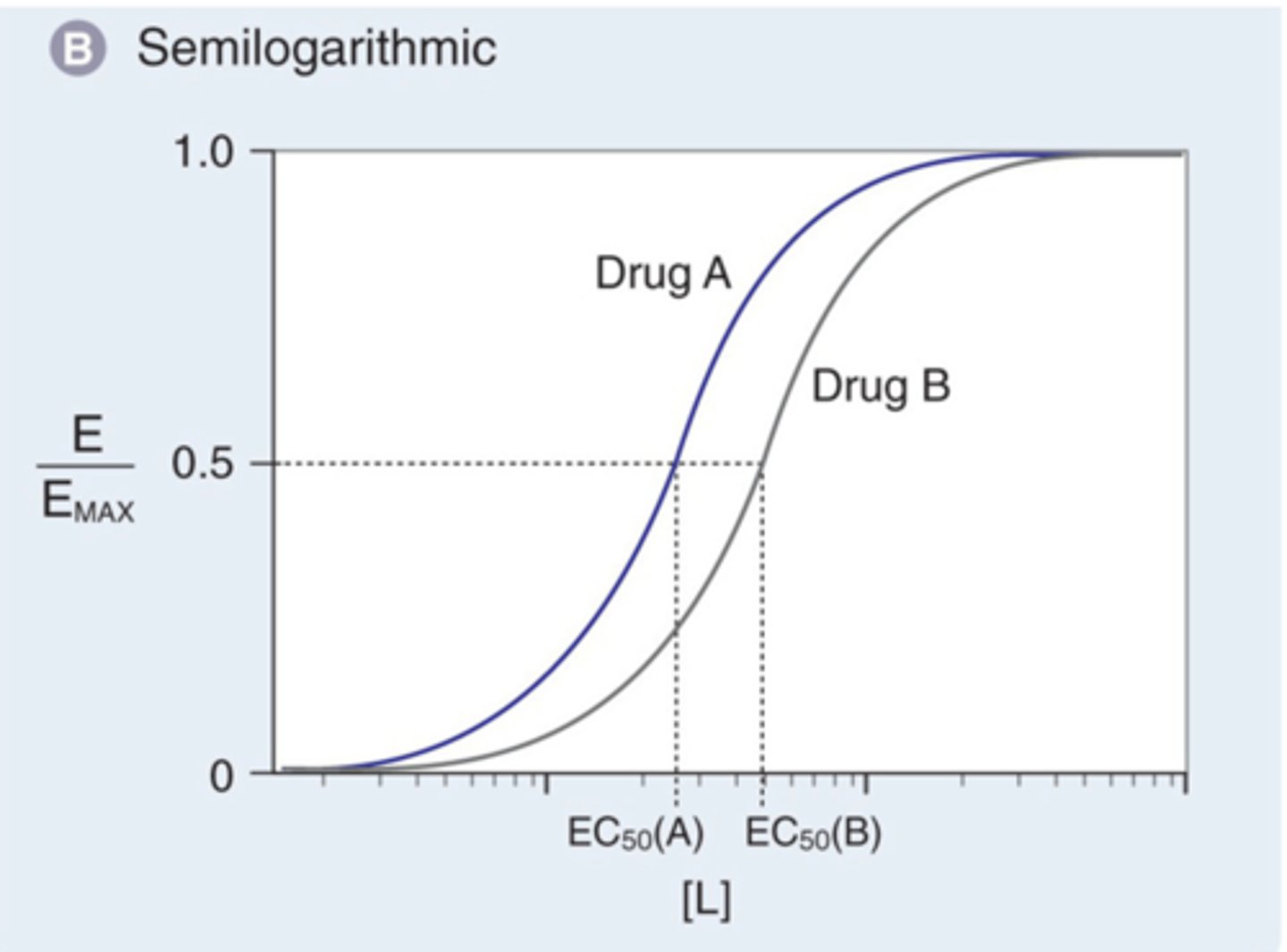
In this example, drug A would be described as:
- less potent
- less efficacious
- more potent
- more efficacious
more potent
Drugs that block the action of an endogenous hormone are known as:
- antagonists
- agonists
- allosteric modulators
antagonist
Which type of receptor activates signal transduction pathways inside the cell by directly phosphorylating target proteins?
- receptor tyrosine kinase
- ligand-gated ion channel
- G protein-coupled receptor
- nuclear receptor
receptor tyrosine kinase
If a drug is dissolved at a concentration of 1x10^-9M, this could also be expressed as:
- 1 nanomolar (nM)
- 1 micromolar (uM)
- 1 millimolar (mM)
1 nanomolar (nM)
One reason that spare receptors occur is because of:
- receptor internalization
- covalent binding of drugs to receptors
- signal amplification by second messenger pathways
signal amplification by second messenger pathways
If a drug has a low Kd, we can also say that it has a:
-low affinity
-high affinity
high affinity
Which of these is associated with receptor antagonism that is surmountable (can be overcome by adding more agonist)?
- competitive antagonist
- negative allosteric modulators
- noncompetitive antagonist
competitive antagonists
If a drug has a narrow therapeutic index, this means that:
- the drug only works for a small percentage of the population
- the drug is specific to a small number of receptor types in the body
- the difference between its therapeutic dose and toxic dose is small
the difference between its therapeutic dose and a toxic dose is small
Constitutive activity describes a phenomenon where:
- some receptors display a low level of activation even in the absence of an agonist
- a partial agonist can block the effects of a full agonist
- a drug increases receptor activity by binding to an allosteric site on the receptor
some receptors display a low level of activation even in the absence of an agonist
On a quantal dose response curve, the ED50 value tells you:
- the minimum dose that causes adverse effects
- the dose that produces half of the maximum effect
- the dose that is effective in half of the population
the dose that is effective in half of the population
A weak acid drug with pKa of 6.2 is taken orally. In the stomach, it will be:
- approximately 50% ionized
- almost 100% non-ionized
- almost 100% ionized
almost 100% non-ionized
Which answer correctly describes the way that a noncompetitive antagonist will shift the dose-response curve?
- the curve will be shifted to the left while maintaining the same shape
- the curve will be shifted to the right and plateau at less than 100%
- the curve will be shifted to the right while maintaining the same shape
the curve will be shifted to the right and plateau at less than 100%
If a drug has a narrow therapeutic index:
- a high concentration of the drug is needed to achieve a therapeutic effect
- there is not much difference between a therapeutic and toxic dose
- the drug binds to many receptors in a nonspecific manner
there is not much difference between a therapeutic and toxic dose
What type of drug would cause an agonist dose-response curve to shift to the left? (become more sensitive)
- positive allosteric modulator
- negative allosteric modulator
- competitive antagonist
- noncompetitive antagonist
positive allosteric modulator
Inverse agonists are drugs that:
- decrease the constitutive signaling of a receptor
- activate the receptor but do not achieve a 100% effect
- bind to a site on a receptor that is distinct from the active site
decrease the constitutive signaling of a receptor
The term for decreased receptor expression after chronic agonist exposure is:
- upregulation
- downregulaiton
- tachyphylaxis
down regulation
A drug molecule is found to be 100% ionized in the small intestine. It is likely that this drug will be:
- poorly absorbed in the small intestine
- extensively absorbed in the small intestine
poorly absorbed in the small intestine
Which of these properties would increase the distribution of a drug into the brain?
- high molecular weight
- high lipid solubility
- high number of charges on the molecule
high lipid solubility
Phase I metabolic reactions:
- are conjugation reactions that add groups such as glucuronic acid to a drug molecule
- typically involve oxidation, reduction, or hydrolysis
- are always required to occur before phase II reactions
typically involve oxidation, reduction, or hydrolysis
Alcohol enhances acetaminophen toxicity because it:
- induces the P450 pathway that produces NAPQI
- acts as a competitive inhibitor of acetaminophen metabolism
- inhibits the metabolism of acetaminophen
induces the P450 pathway that produces NAPQI
A patient experiences an allergic reaction to penicillin. This is an example of _____ toxicity.
- intrinsic
- idealistic
- idiosyncratic
idiosyncratic
A drug undergoes extensive metabolism in the liver via the first pass effect. This means that it will have:
- low bioavailability
- long half-life
- high volume of distribution
low bioavailability
Compared to extensive metabolizers, patients who are CYP2D6 poor metabolizers will experience _____ analgesia when they take codeine.
- more
- less
less
If a drug has a high volume of distribution, this indicates that:
- a large fraction of the drug dose leaves the plasma and binds to tissue sites
- a large fraction of the drug is metabolized by the lover before reaching the systemic circulation
- a large fraction of the drug is excreted unchanged
- a large fraction of the drug dose stays in the plasma
a large fraction of the drug dose leaves the plasma and binds to tissue sites
In a heart that is beating at normal resting rate of 70 beats per minute, what would be the effect of complete blockade of muscarinic receptors by a muscarinic antagonist drug?
- the heart rate would increase approximately 100 beats per minute
- there would be no effect one eating heart rate
- the heart rate would decrease below the normal resting rate
- the heart rate would increase to the maximum (approximately 180-200 beats per minute)
the heart rate would increase approximately 100 beats per minute
Which of these is NOT a location where nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are typically found?
- sympathetic ganglia
- parasympathetic target organs
- parasympathetic ganglia
- the neuromuscular junction
parasympathetic target organs
Many organs receive dual innervation from both divisions of the autonomic nervous system. An important exception is:
- the heart, which only receives parasympathetic innervation
- the bladder, which only receives parasympathetic innervation
- the lungs, which only receive sympathetic innervation
- the blood vessels, which only receive sympathetic innervation
the blood vessels, which only receive sympathetic innervation
What is the mechanism of action and effect for organophosphates?
- inhibition of acetylcholinesterase leading to a cholinomimetic effect
- antagonism of muscarinic receptors leading to a cholinomimetic effect
- inhibition of acetylcholinesterase leading to a cholinolytic effect
- direct activation of nicotinic receptors leading to a cholinomimetic effect
inhibition of acetylcholinesterase leading to a cholinomimetic effect
The drug bethanechol is:
- an anticholinesterase
- an anticholinergic
- an muscarinic antagonist
- a muscarinic agonist
a muscarinic agonist
Which of these symptoms would NOT typically be seen in a patient who overdosed on an anticholinergic medication?
- profuse sweating
- decreased salivation
- altered mental status
- dilated pupils (mydriasis)
profuse sweating
Botulinum toxin works by:
- blocking muscarinic receptors
- inhibiting neurotransmitter release
- inhibiting acetylcholinesterase
- blocking alpha-1 receptors
inhibiting neurotransmitter release
Reflex tachycardia would most likely to occur with which type of drug?
- vasodilator
- beta blocker
- muscarinic agonist
- vasoconstrictor
vasodilator
Norepinephrine is a relatively poor agonist at which receptor type?
- alpha-2
- beta-2
- beta-1
- alpha-1
beta-2
Which of these drugs activates alpha-2 receptors?
- propranolol
- albuterol
- clonidine
- atropine
clonidine
Which drug class can exacerbate asthma?
- alpha-1 agonists
- nonselective beta blocker
- nonselective alpha blockers
- indirect-acting sympathomimetics
nonselective beta blocker
Which drug class has the highest risk of sympathomimetic toxicity?
- nonselective alpha blockers
- indirect-acting sympathomimetics
- alpha-1 agonists
- nonselective beta agonists
indirect-acting sympathomimetics