ASC 310 - Equine Respiratory System
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:32 PM on 4/26/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
1
New cards
Functions Of the Respiratory System
1. Draw Air Into Lungs
2. Transfer Oxygen
3. Acid/Base Regulation
4. Humidification
5. Thermoregulation
6. Defense Against Contaminants
7. Smell
8. Communication
9. Increase Abdominal Pressure
2
New cards
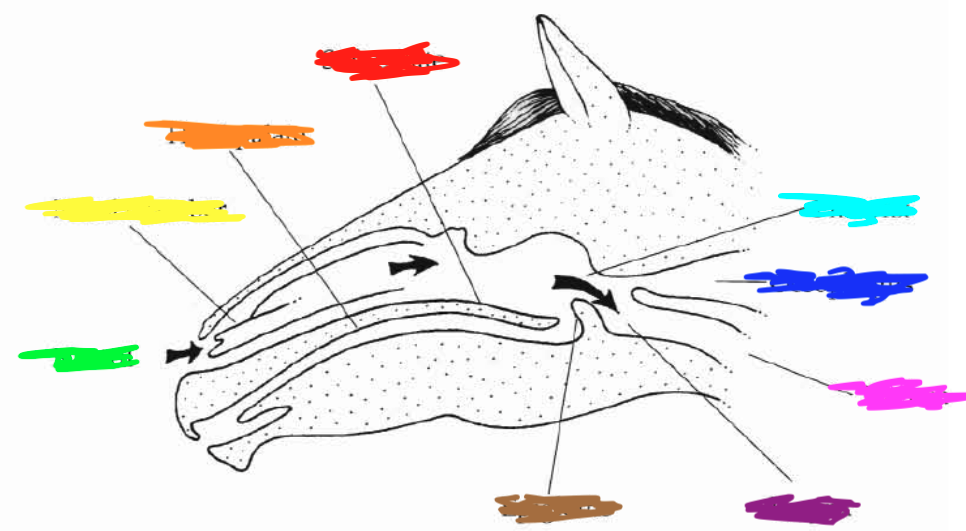
Which color is pointing to the **soft palate**?
Red
3
New cards
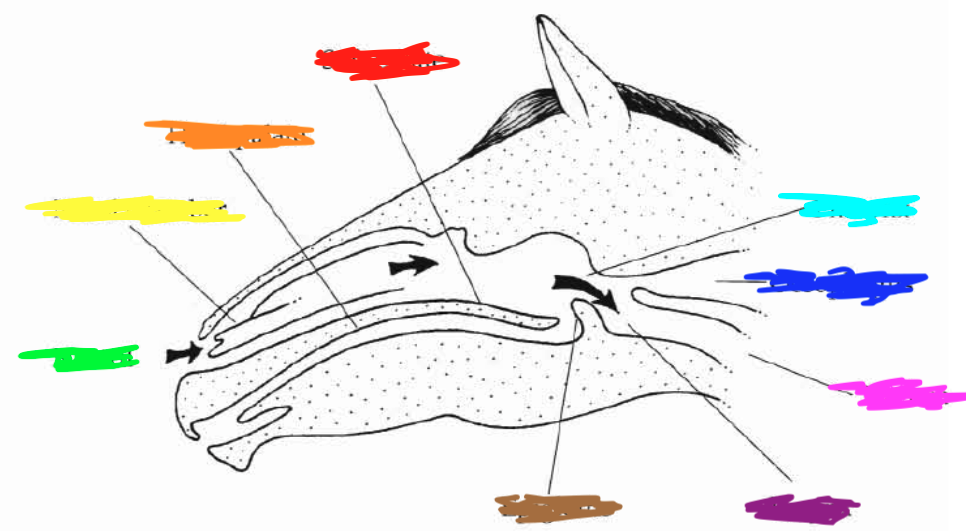
Which color is pointing to the **hard palate**?
Orange
4
New cards
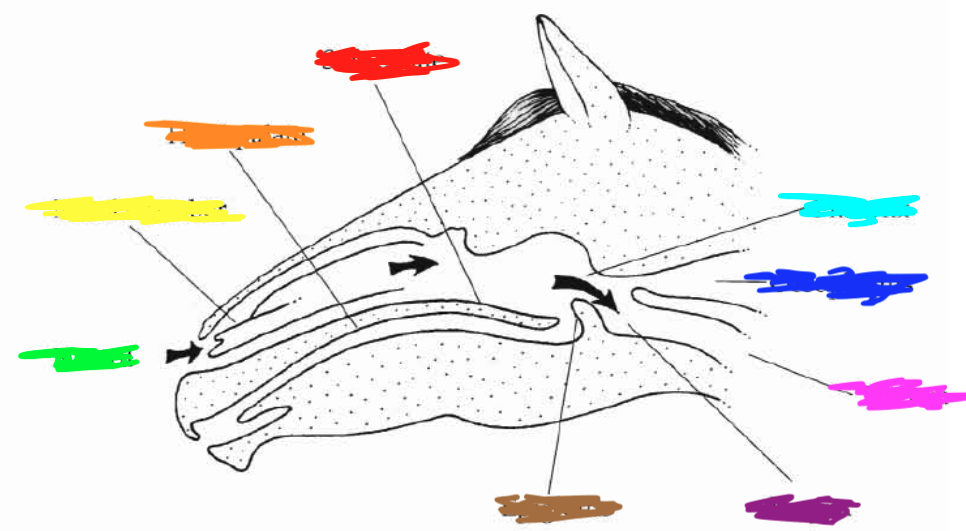
Which color is pointing to the **nasal chamber**?
Yellow
5
New cards
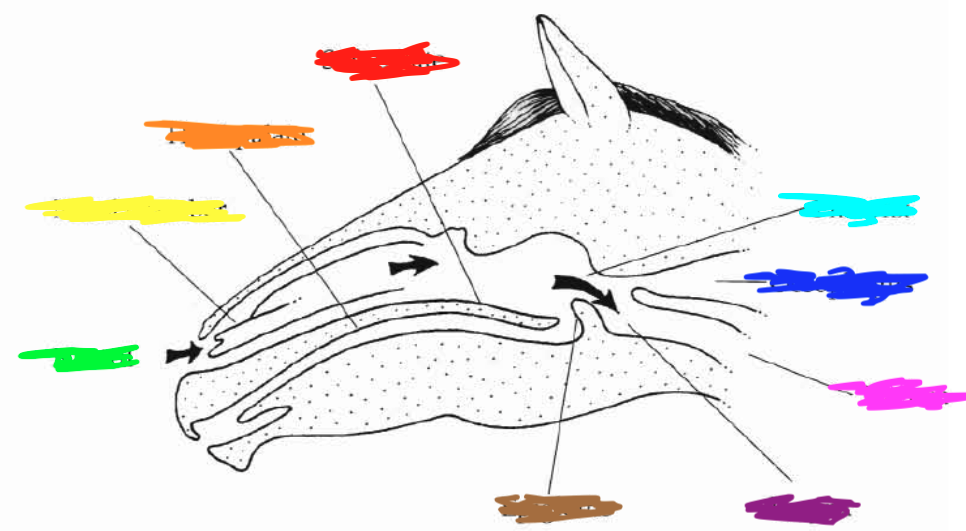
Which color is pointing to the **nostril**?
Green
6
New cards
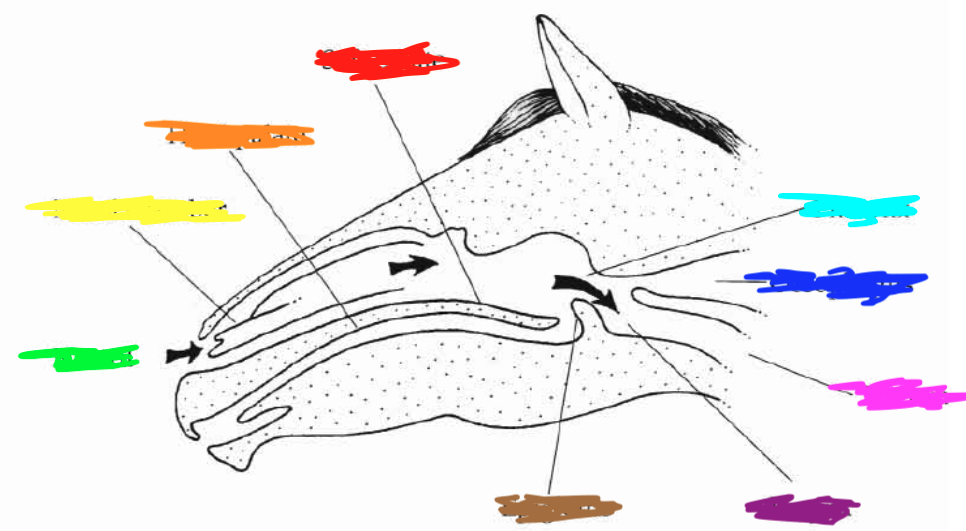
Which color is pointing to the **pharynx**?
Light Blue
7
New cards
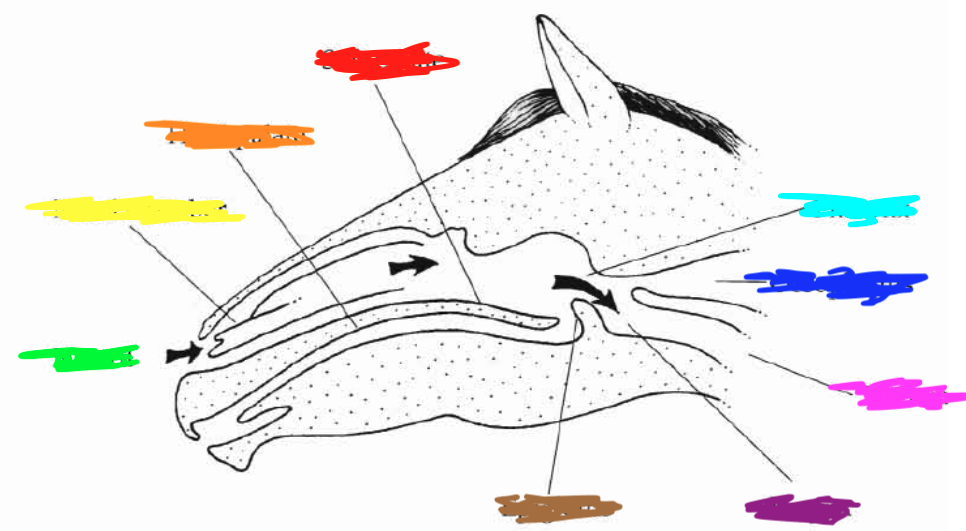
Which color is pointing to the **esophagus**?
Dark Blue
8
New cards
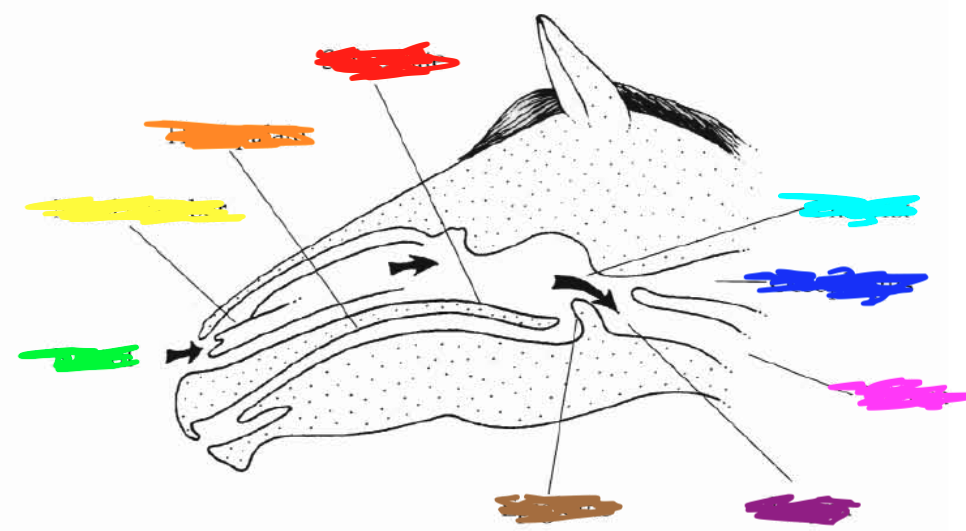
Which color is point to the **trachea**?
Pink
9
New cards
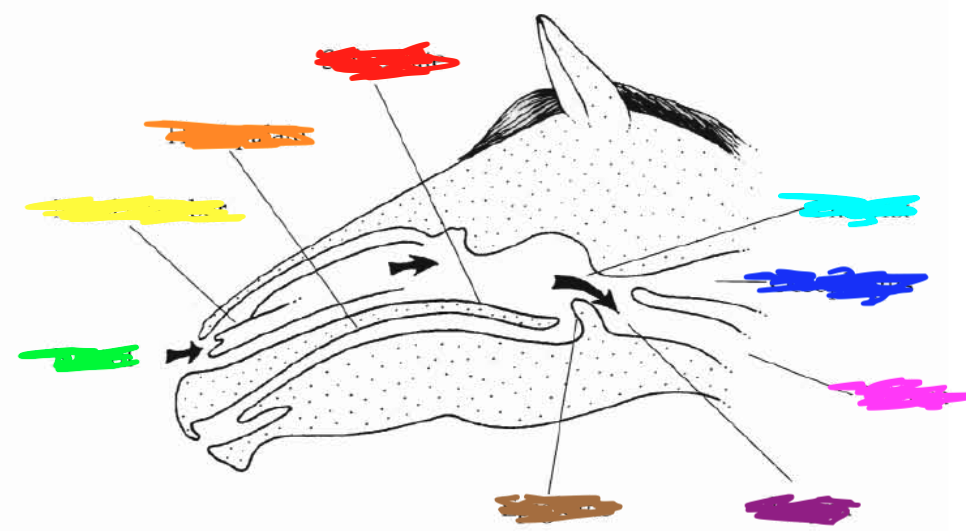
Which color is pointing to the **larynx**?
Purple
10
New cards
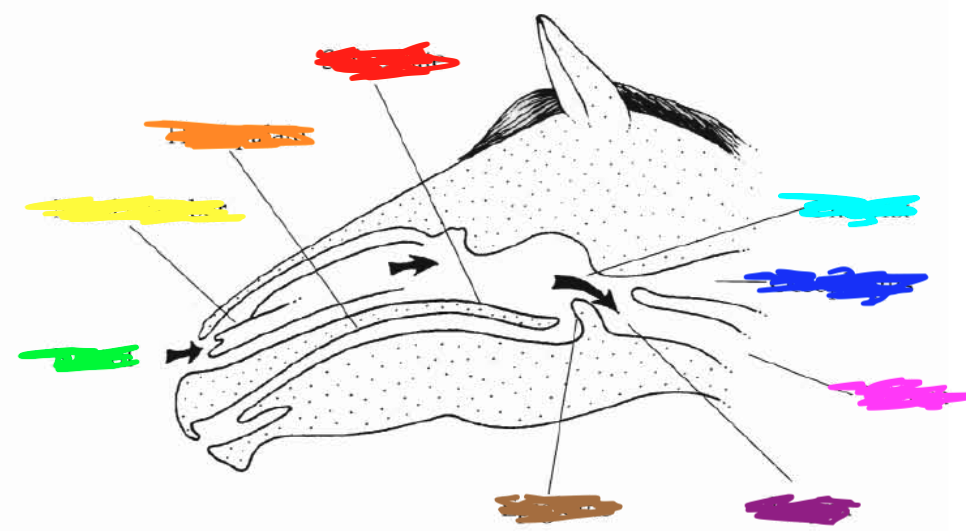
Which color is pointing to the **epiglottis**?
Brown
11
New cards
How do the nasal cavity and the sinuses interact?
They help to humidify and warm air as well as filter out particulates.
12
New cards
Paper-like structures in the nose that have a lot of capillaries (very vascular) and help with transfer of water.
Nasal Tubinates
13
New cards
These cells are found in the horse’s nasal cavity containing olfactory receptors.
Epithelial Cells
14
New cards
Means Smell
Olfactory
15
New cards
Do olfactory messages cross diagonally into hemispheres of the brain?
No, if it goes in through the left nostril it will go to the left hemisphere of the brain. Sam with the right nostril will go to the right hemisphere.
16
New cards
Concentrating the air so that the horse can smell and detect pheromones.
Flehmen Response
17
New cards
Condition where the soft palate obstructs the airway during exercise. Common in horses, symptoms include coughing, gurgling, and poor performance. Treatment can include surgery or training modifications.
Dorsal Displacement of the Soft Palate
18
New cards
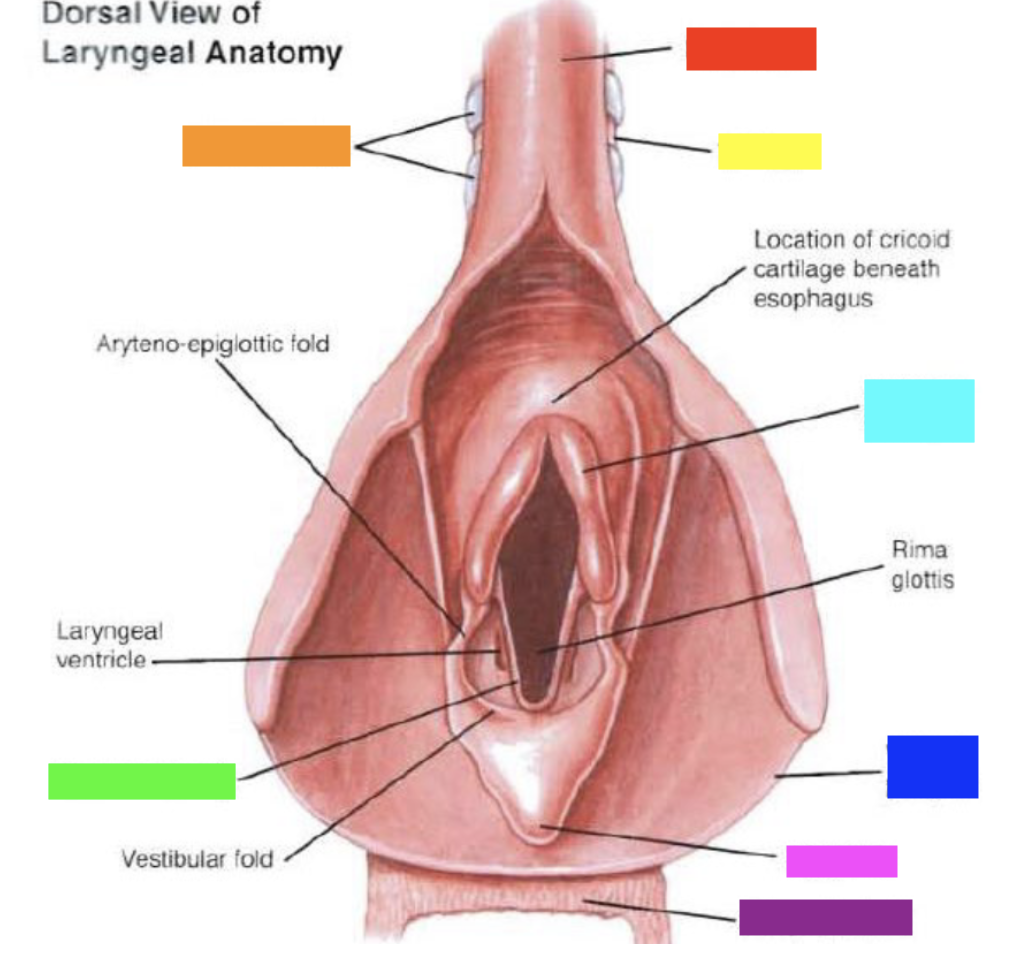
Which color is pointing to the **esophagus**?
Red
19
New cards
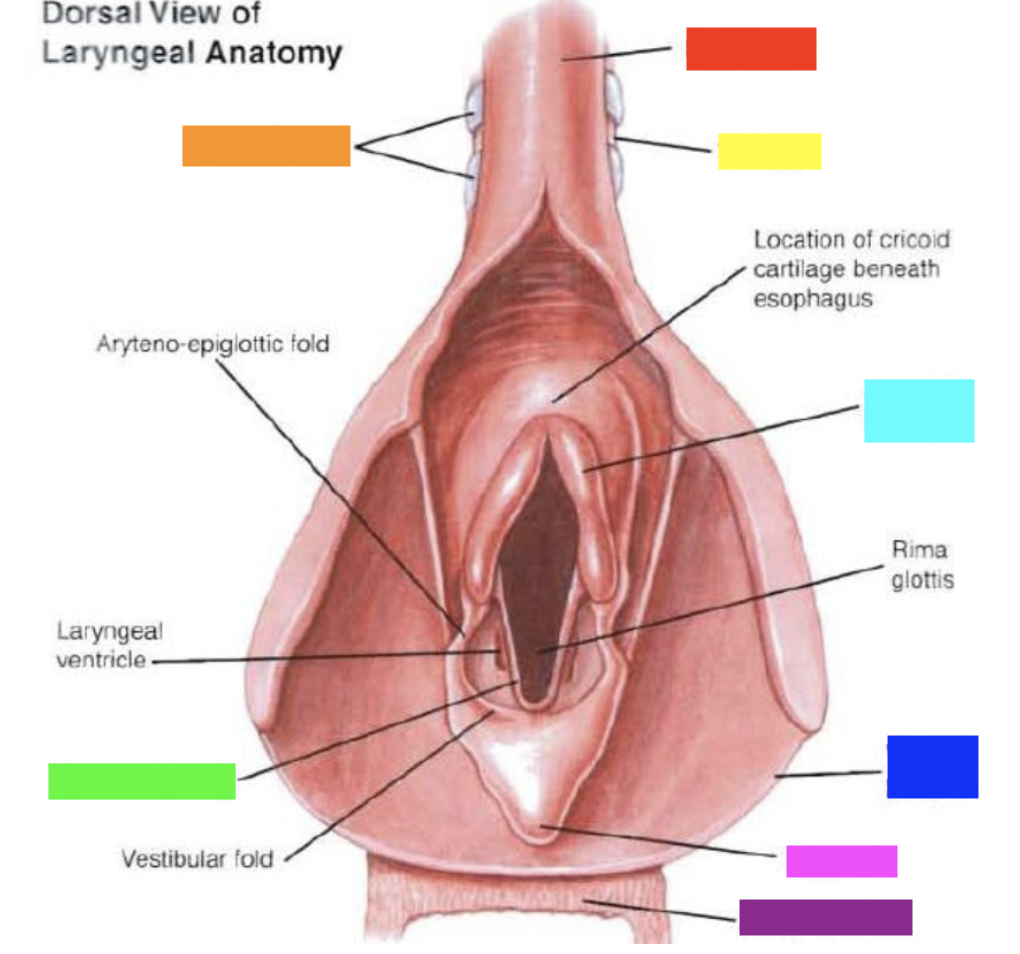
Which color is pointing to the **tracheal rings**?
Orange
20
New cards
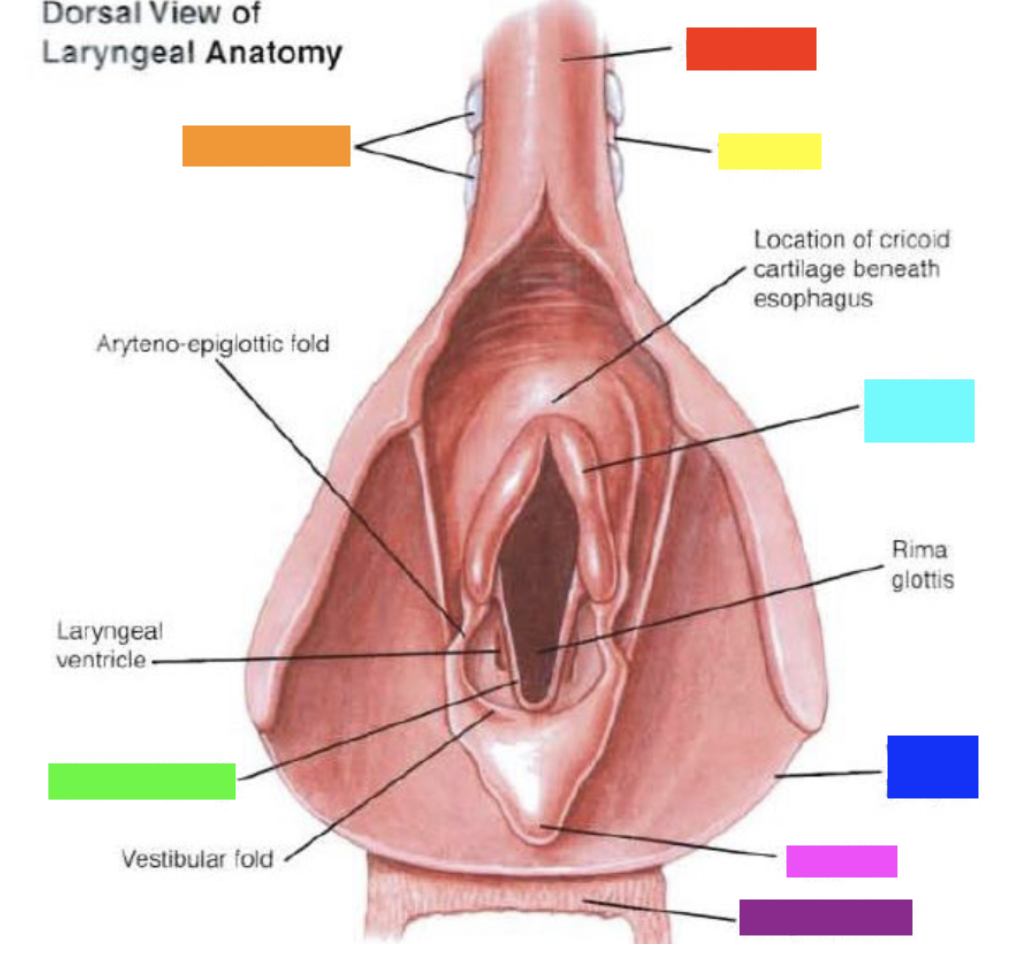
Which color is pointing to the **trachea**?
Yellow
21
New cards
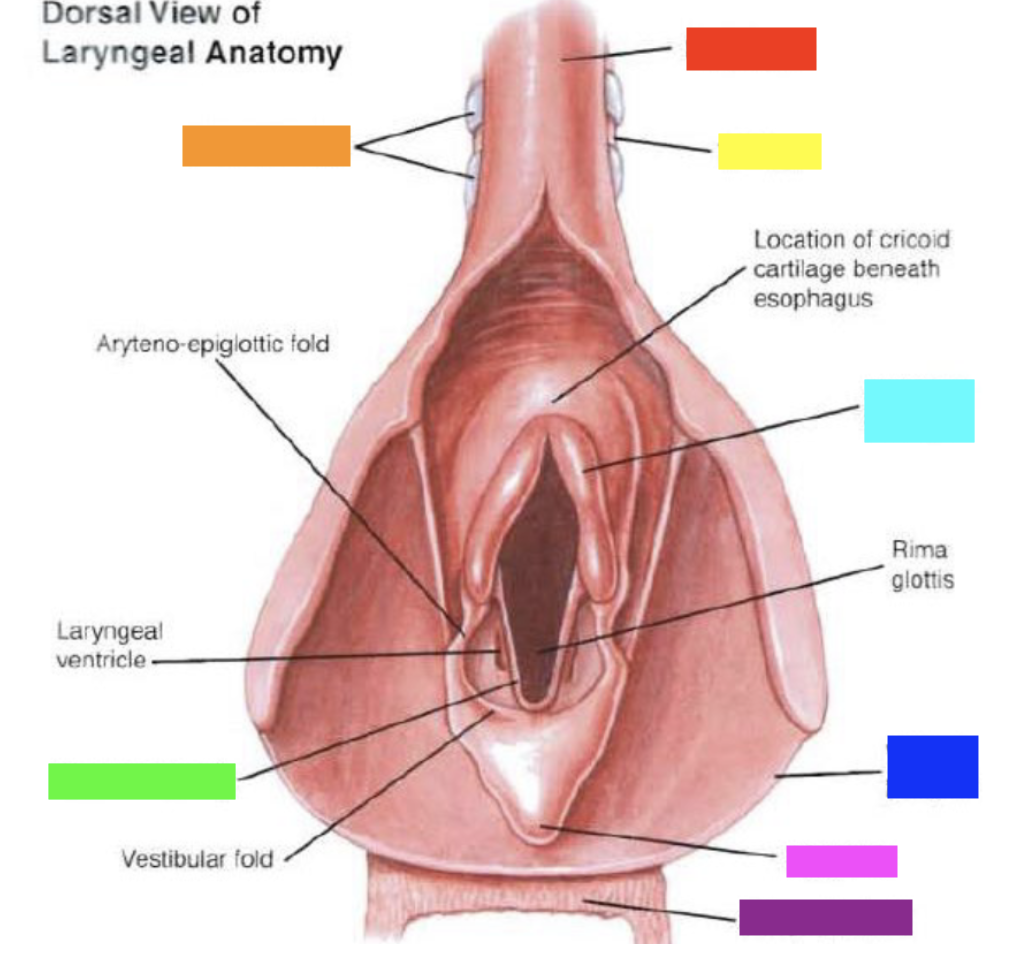
Which color is pointing to the **vocal fold (cord)**?
Green
22
New cards
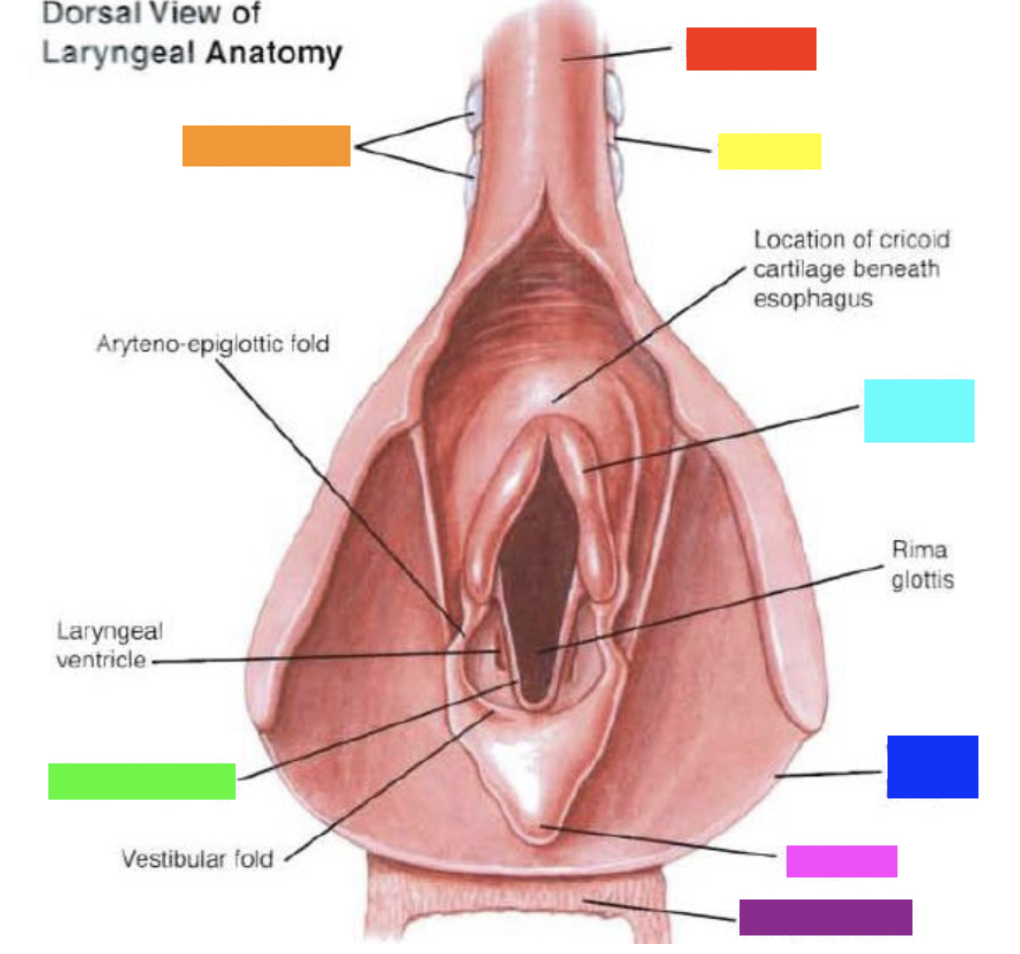
Which color is pointing to the **arytenoid cartilage**?
Light Blue
23
New cards
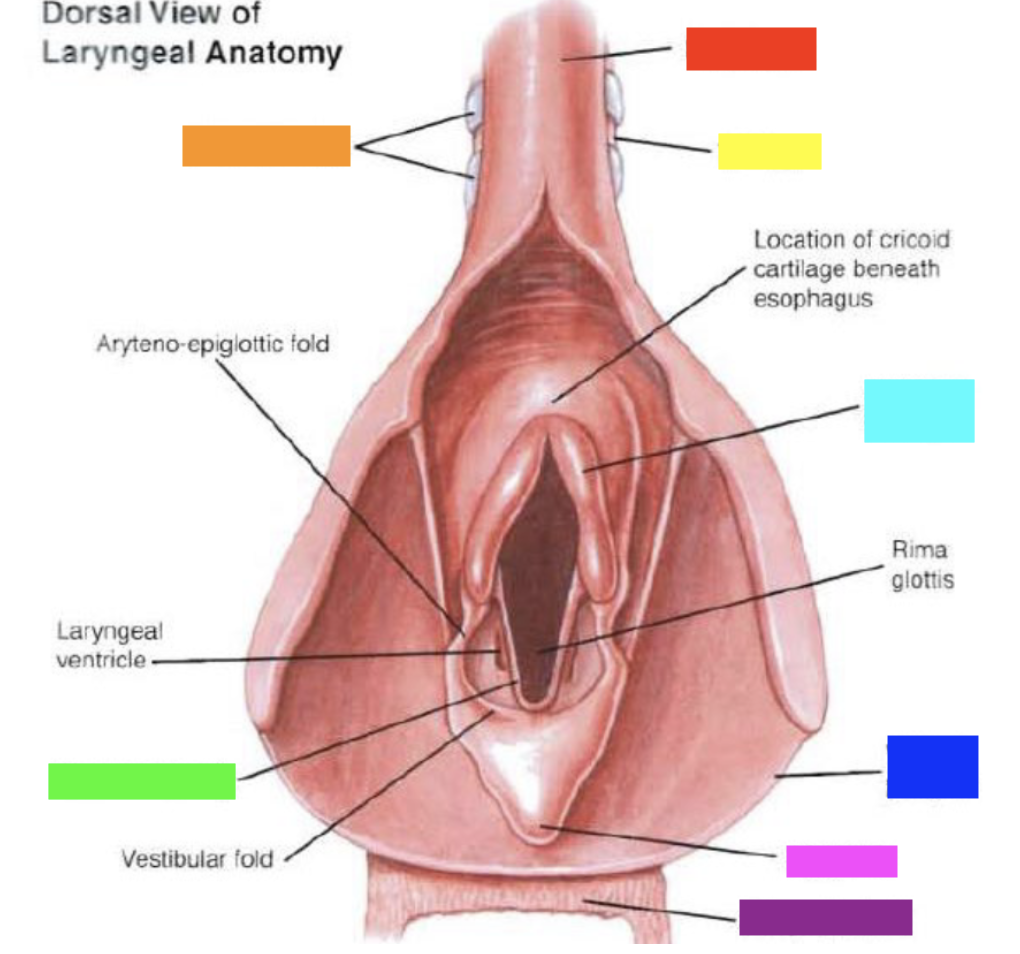
Which color is pointing to the **wall of pharynx**?
Dark Blue
24
New cards
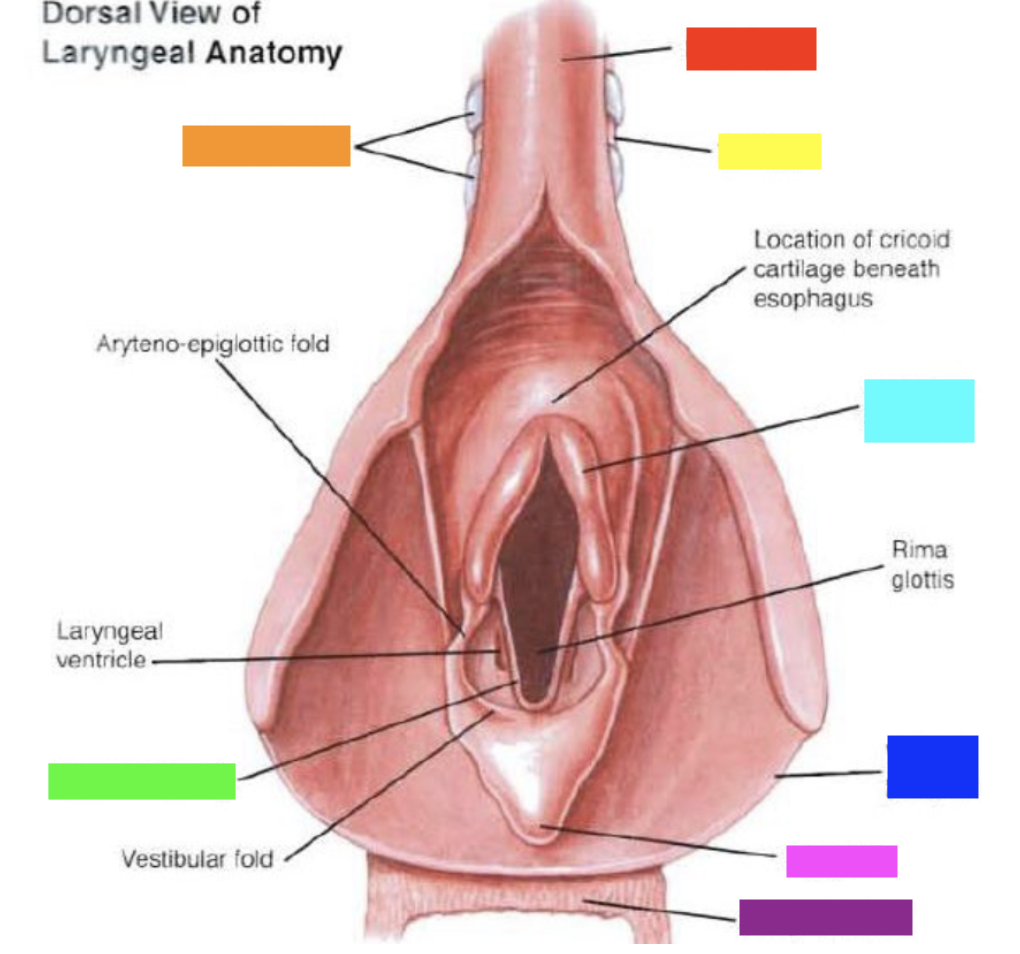
Which color is pointing to the **epiglottis**?
Pink
25
New cards
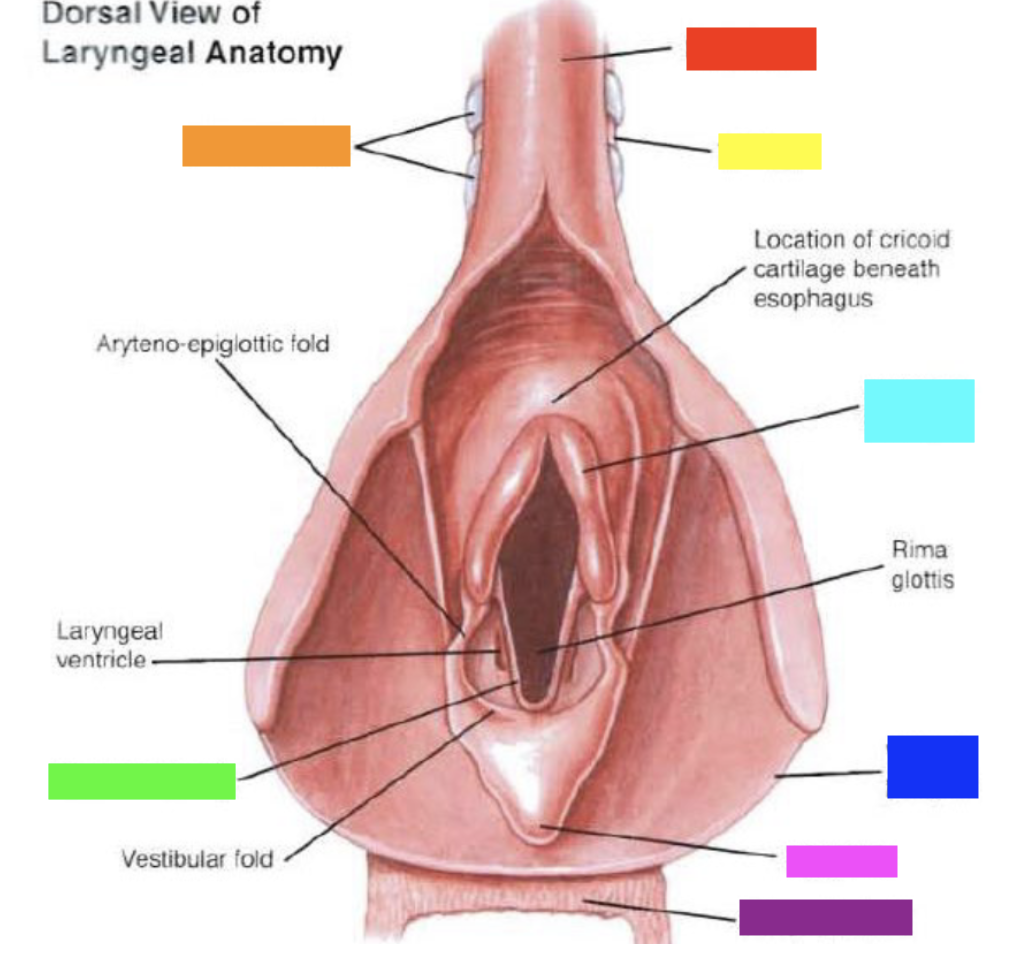
Which color is pointing to the **soft palate (cut)**?
Purple
26
New cards
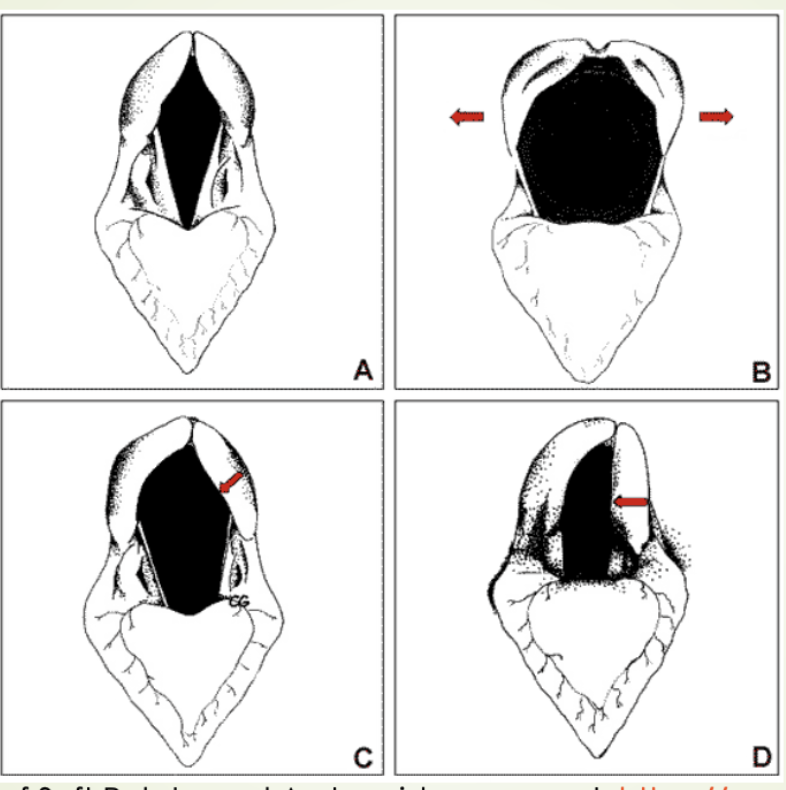
What is image A picturing?
Resting
27
New cards
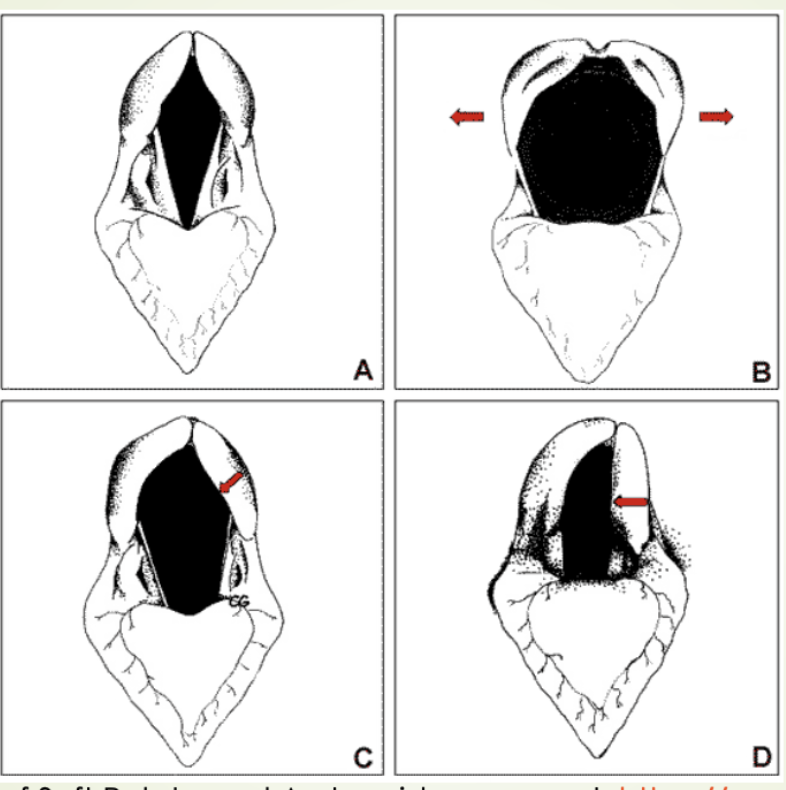
What is image B picturing?
Full Abduction During Exercise
28
New cards
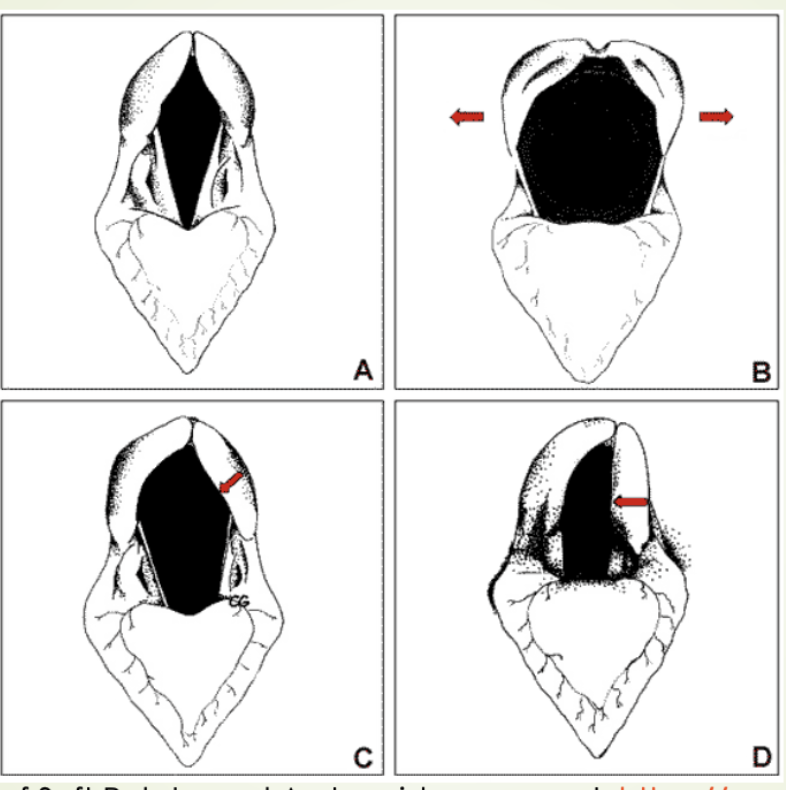
What is image C picturing?
Asynchronism
29
New cards
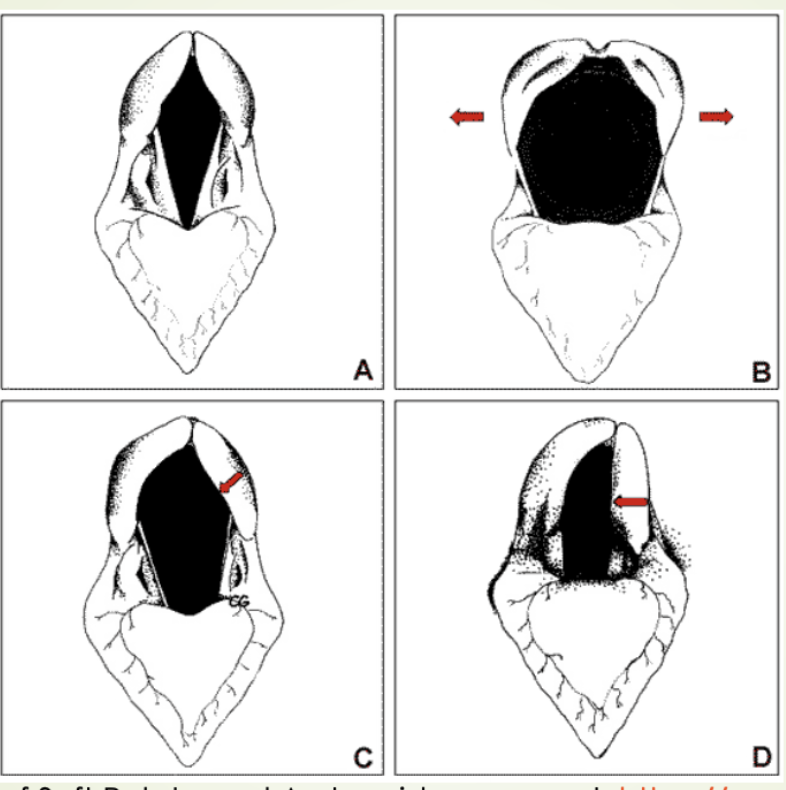
What is image D picturing?
Laryngeal Hamiplegia (can not fully adduct)
30
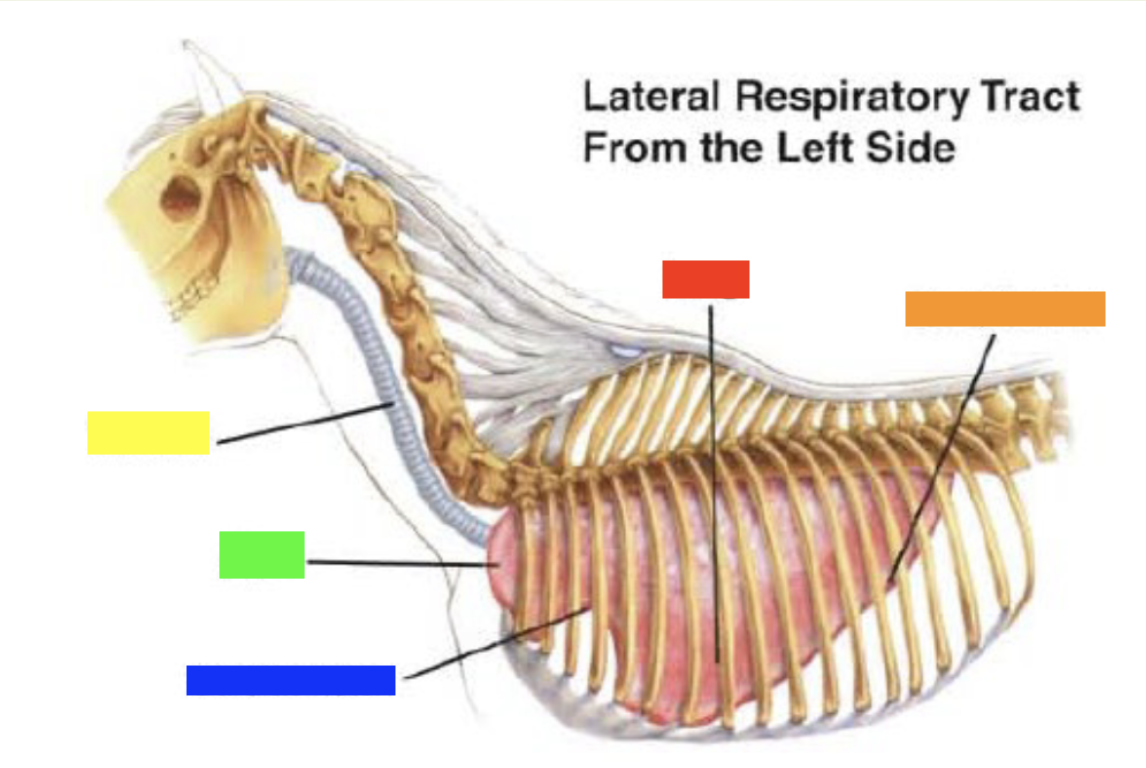
New cards
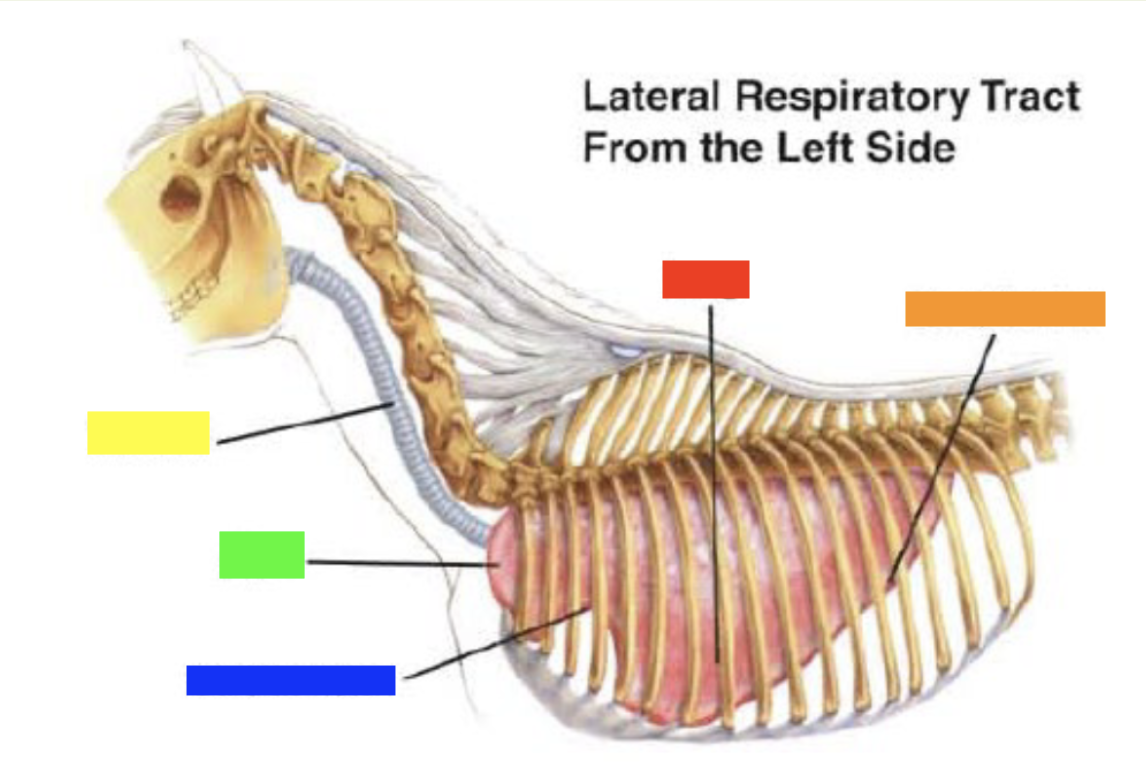
Which color is pointing to the **lung**?
Red
31
New cards
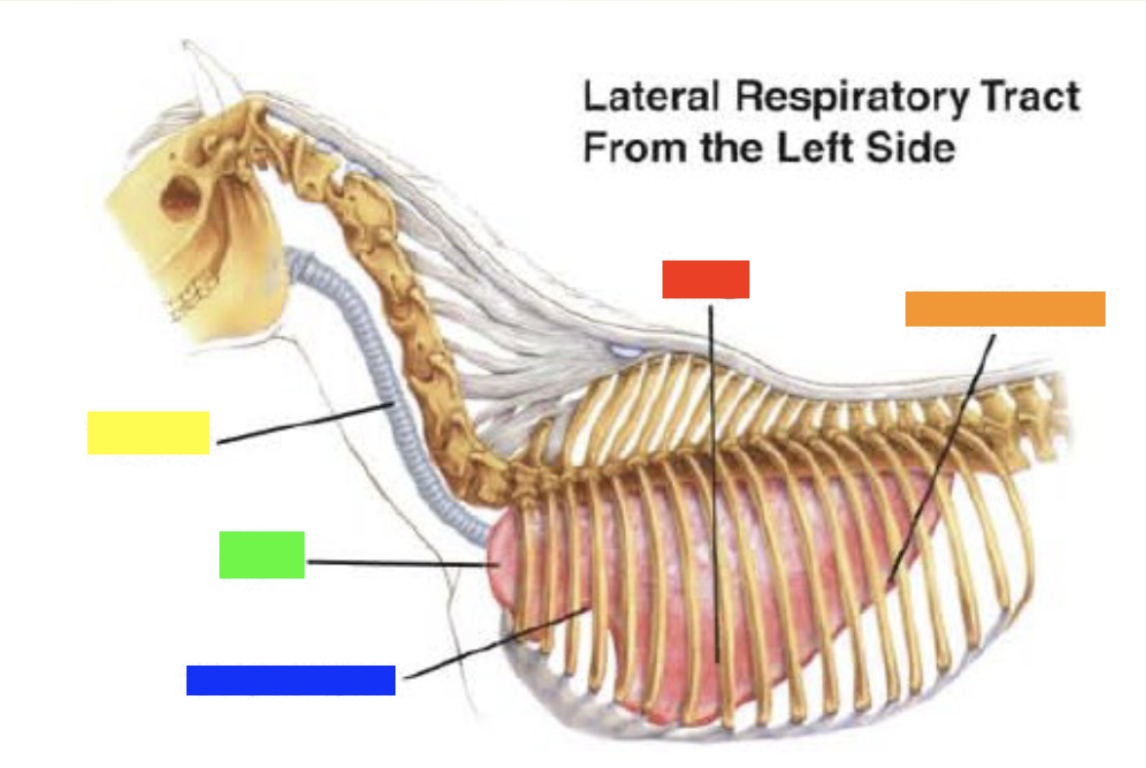
Which color is pointing to the **basal border**?
Orange
32
New cards
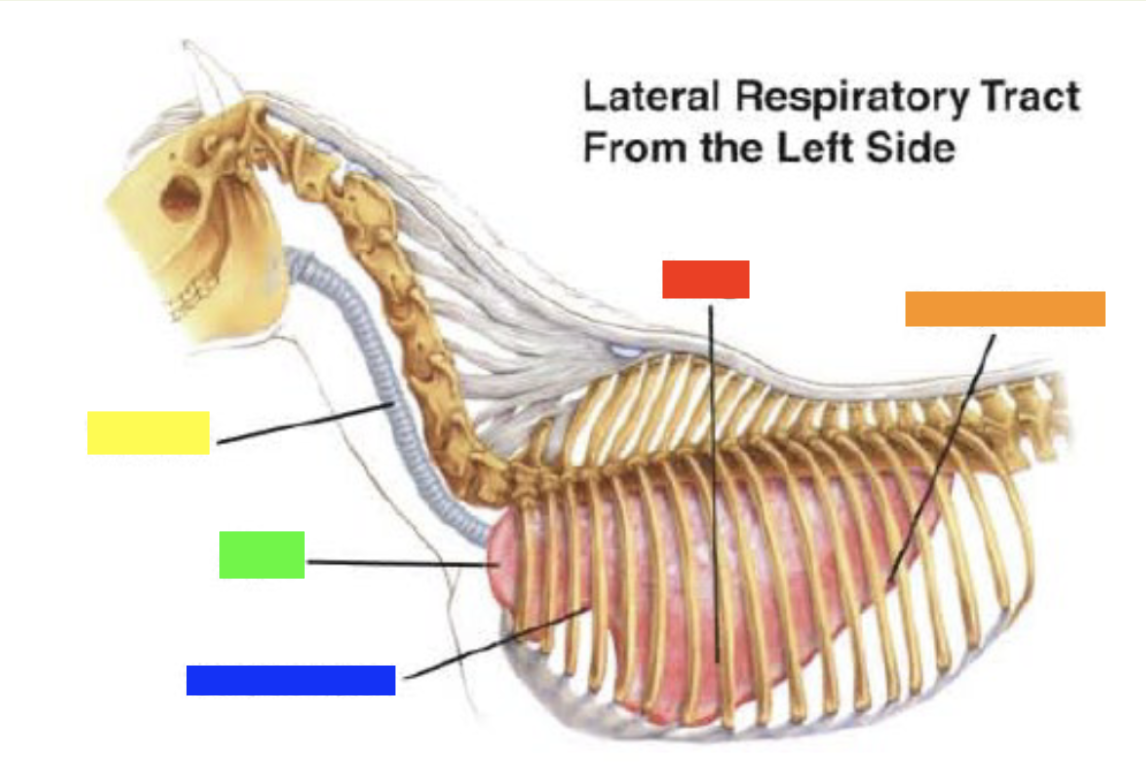
Which color is pointing to the **trachea**?
Yellow
33
New cards
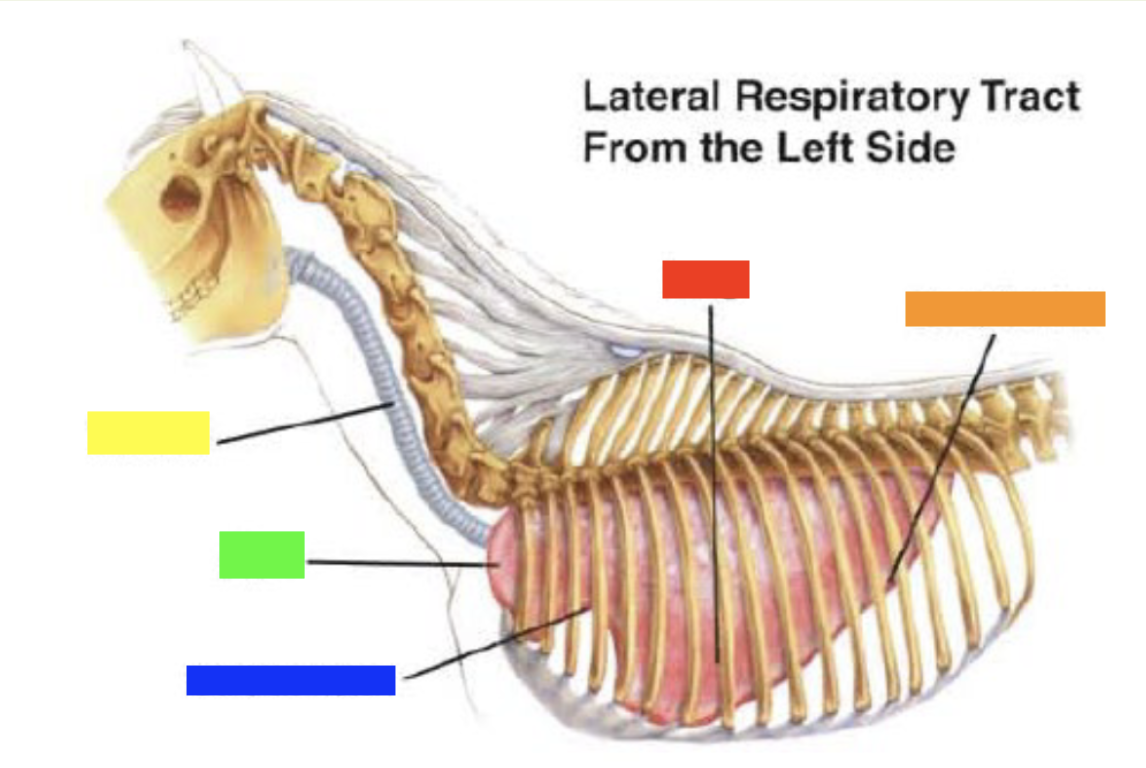
Which color is pointing to the **apex**?
Green
34
New cards
Which color is pointing to the **cardiac notch**?
Blue
35
New cards
Separates the thoracic cavity and the abdominal cavity. When it contracts, negative pressure is created inside the thorax, enabling air to come in.
Diaphragm
36
New cards
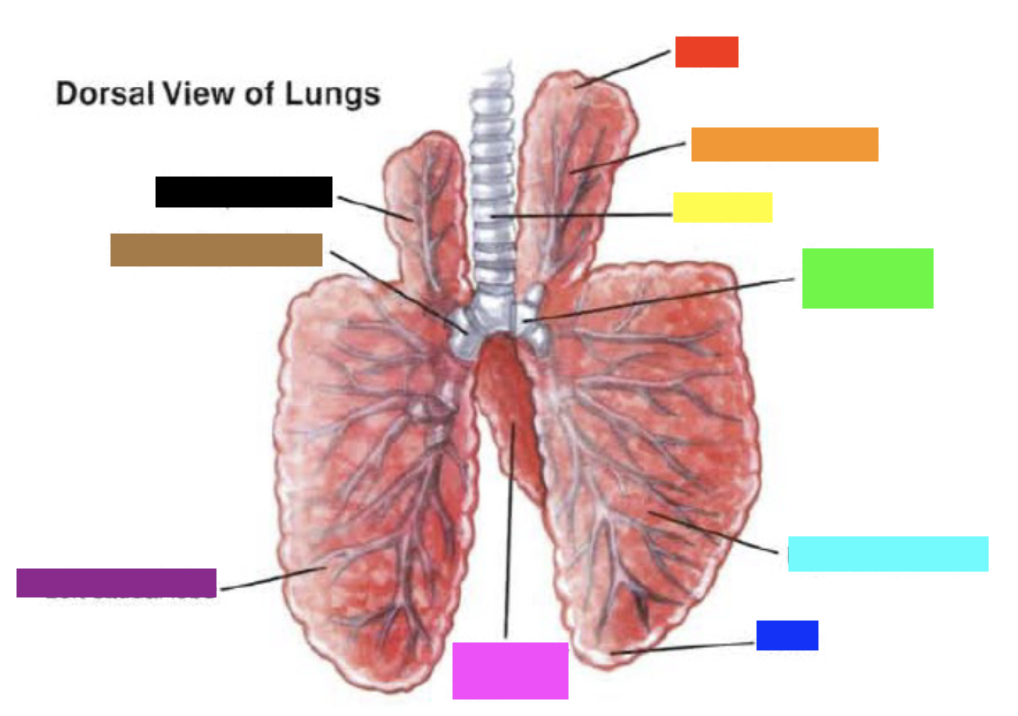
Which color is pointing to the **apex**?
Red
37
New cards
Which color is pointing to the **right apical lobe**?
Orange
38
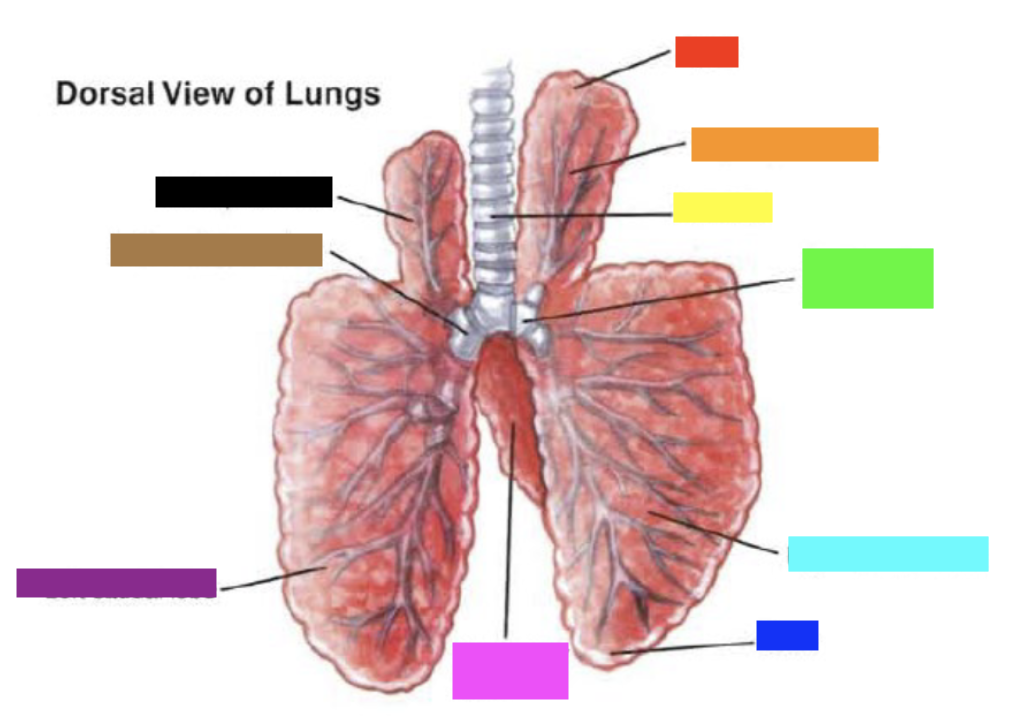
New cards
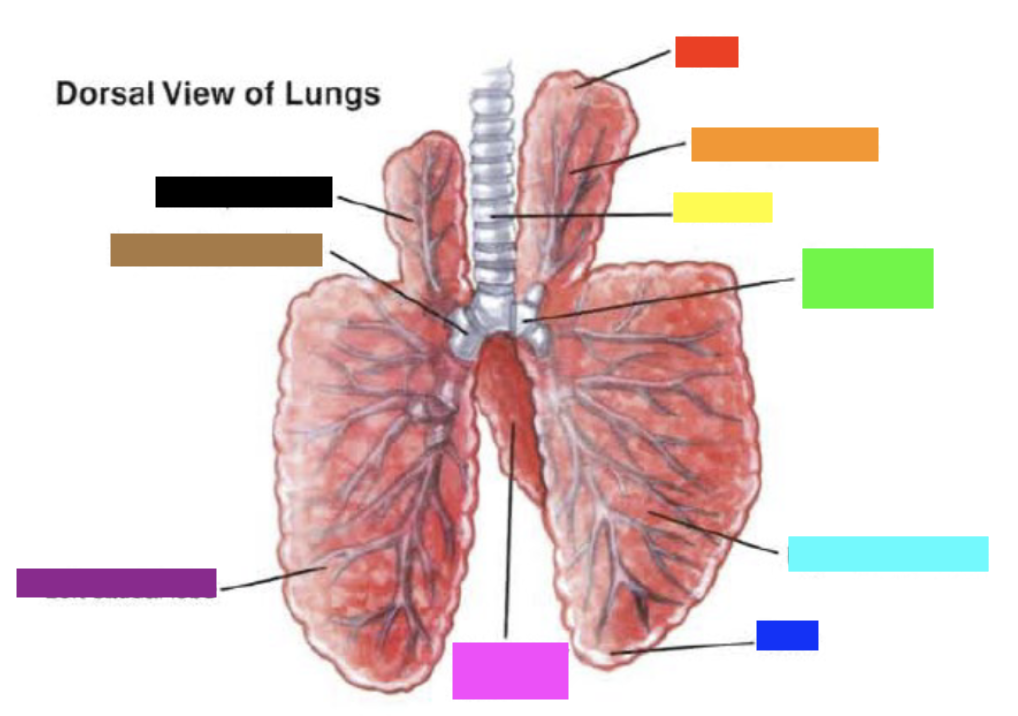
Which color is pointing to the **trachea**?
Yellow
39
New cards
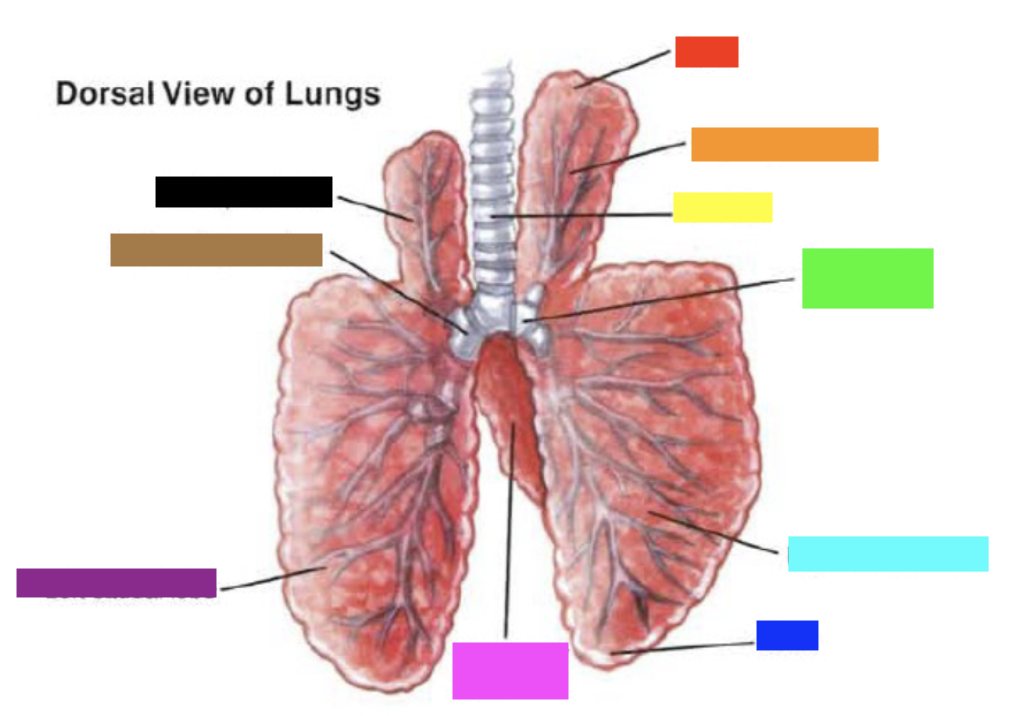
Which color is pointing to the **right main bronchus**?
Green
40
New cards
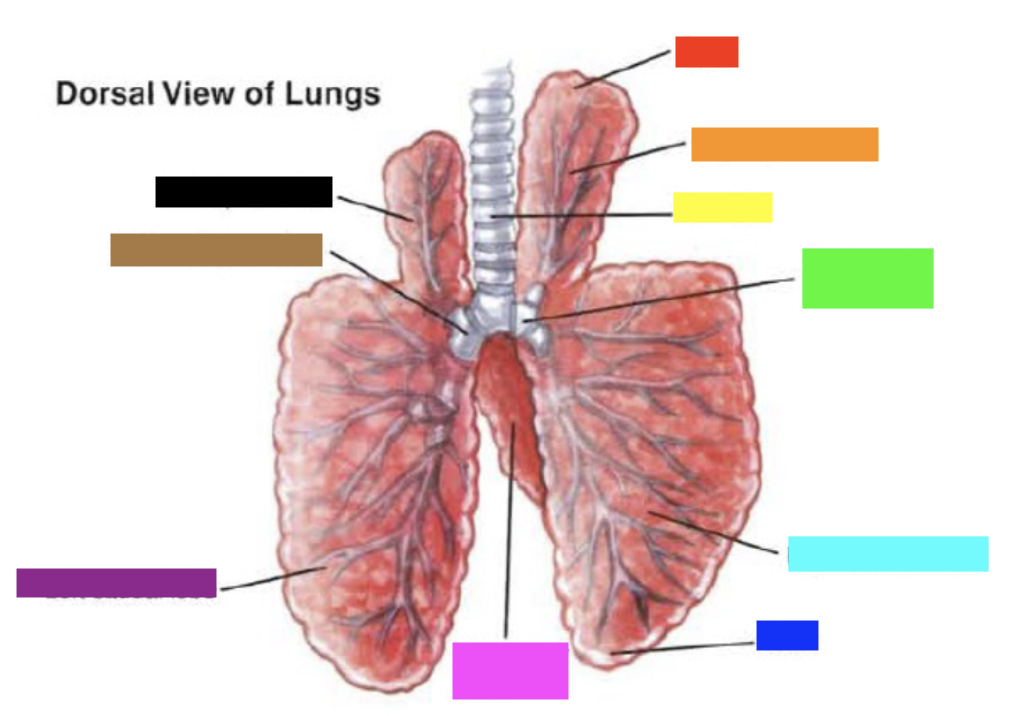
Which color is pointing to the **right caudal lobe**?
Light Blue
41
New cards
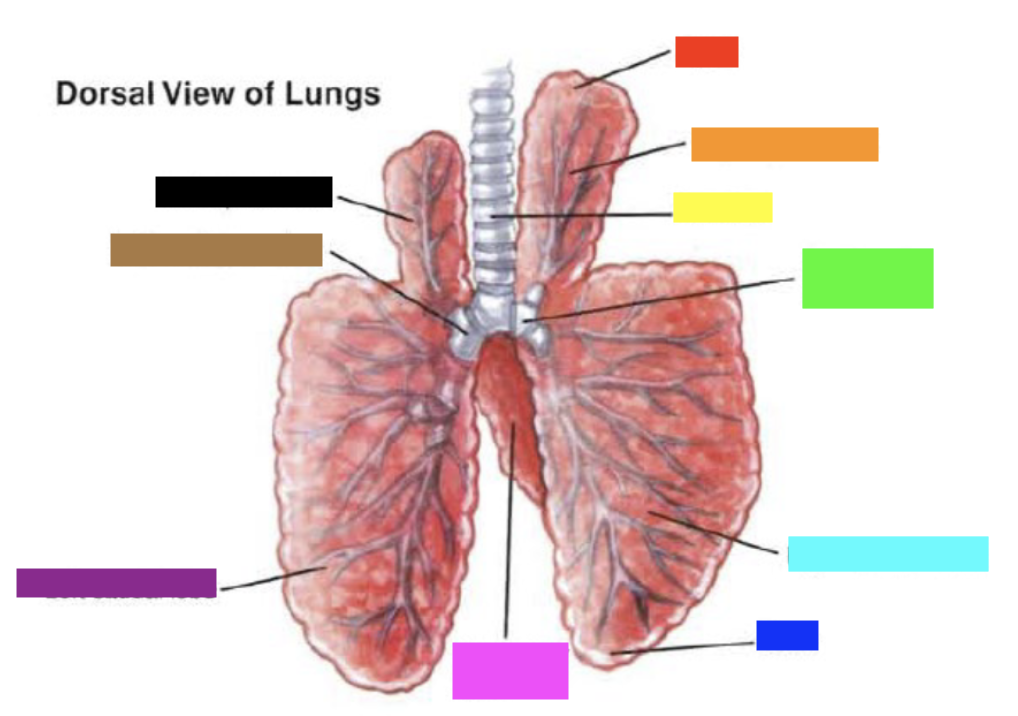
Which color is pointing to the **base**?
Blue
42
New cards
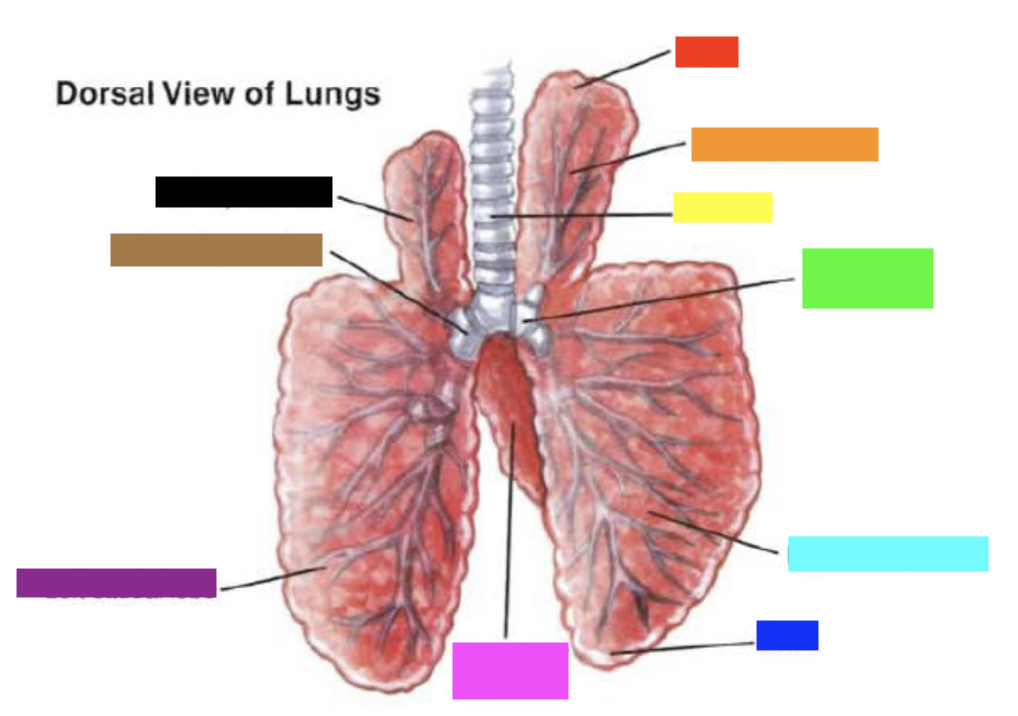
Which color is pointing to the **accessory lobe**?
Pink
43
New cards
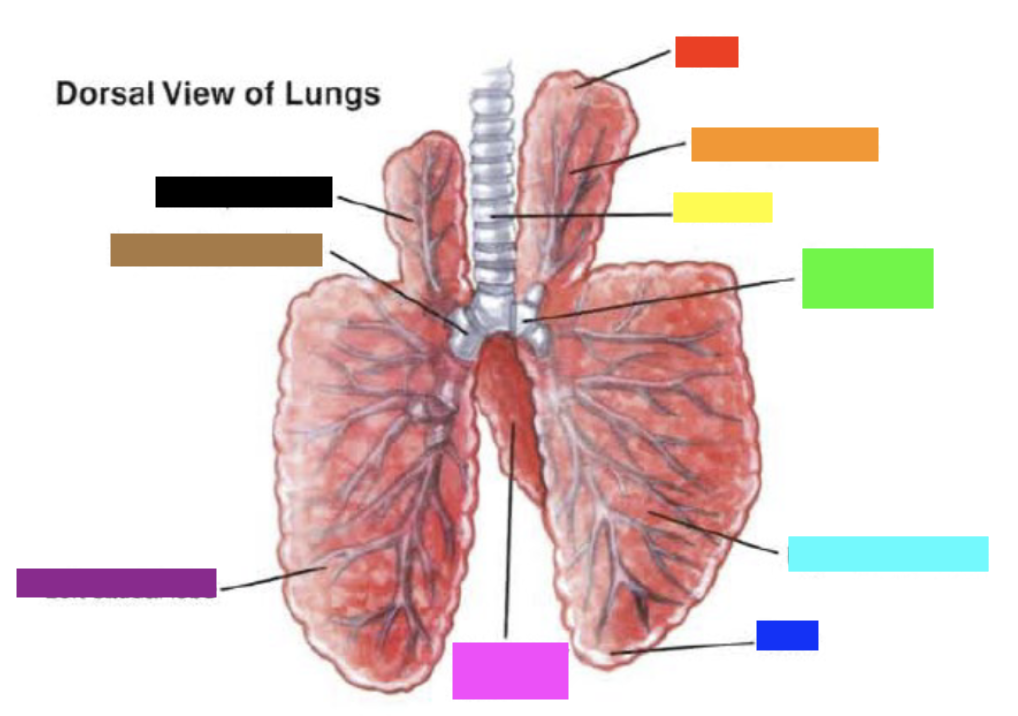
Which color is pointing to the **left caudal lobe**?
Purple
44
New cards
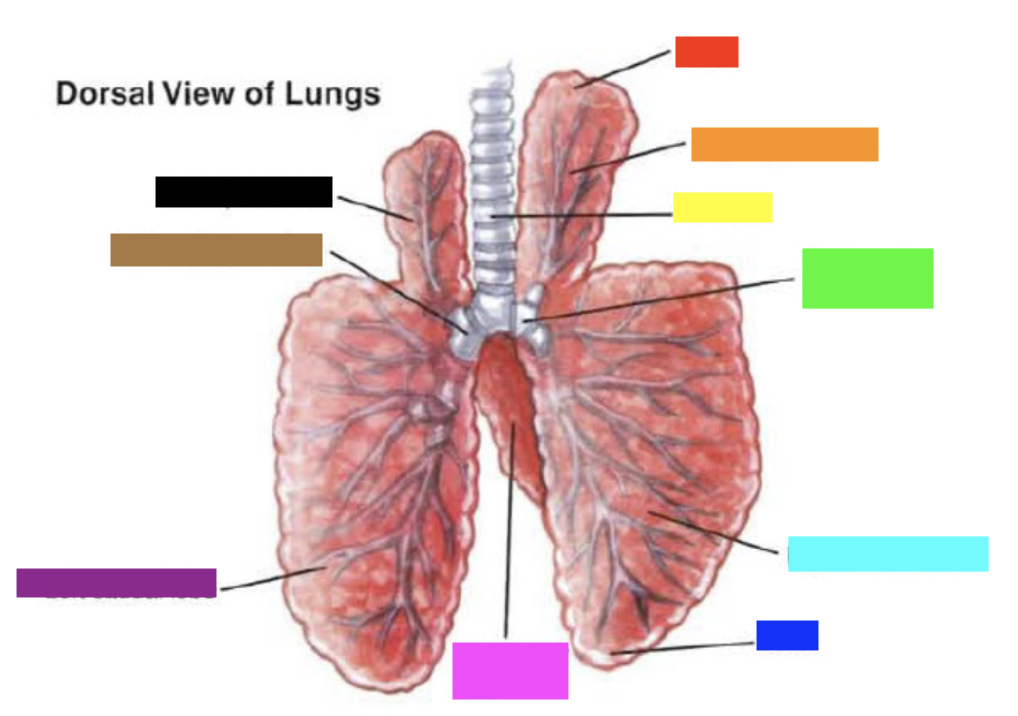
Which color is pointing to the **left main bronchus**?
Brown
45
New cards
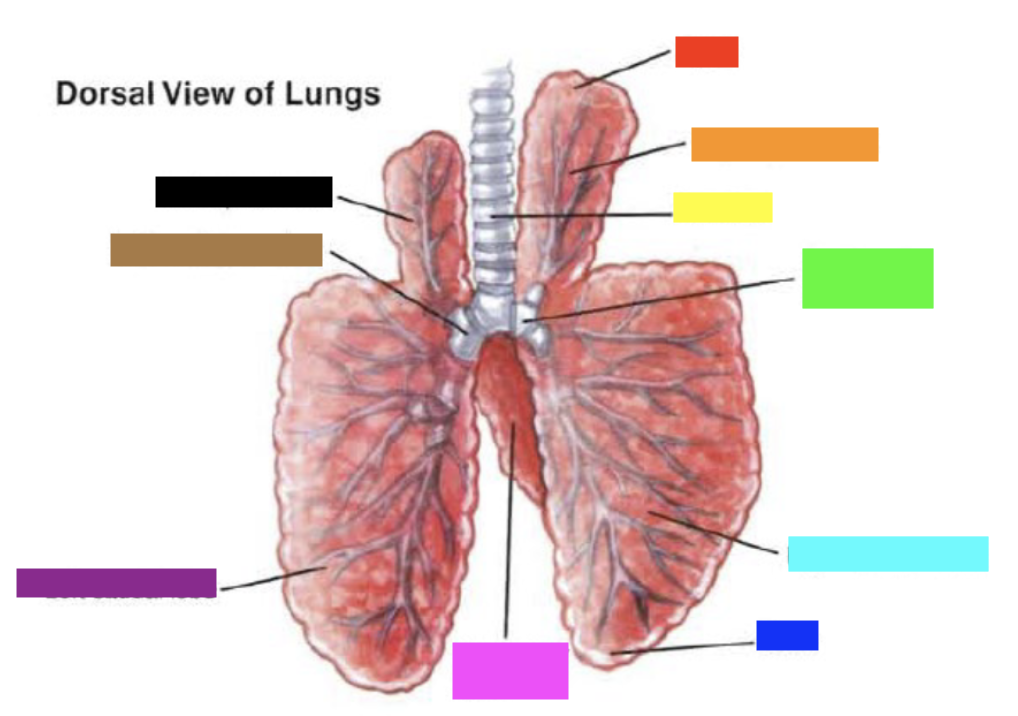
Which color is pointing to the **left apical lobe**?
Black
46
New cards
Where does gas-exchange occur in the airways?
Lower Airway ONLY - Alveoli
47
New cards
* Found in the lower airways of the horse
* Produce mucus
* Sweep particles and mucus back up the airways
* Found in trachea
* Push dust/particles back up the airway
* Produce mucus
* Sweep particles and mucus back up the airways
* Found in trachea
* Push dust/particles back up the airway
Secretory Ciliated Epithelium
48
New cards
Are horses obligate nasal breathers…if so what does that mean?
Yes, horses can not breath through their mouth.
49
New cards
The amount of air inhaled and exhaled during normal breathing is called __________.
Tidal Volume
50
New cards
What can increase a horses tidal volume?
* Stretching Neck Out
* Nostrils Fully Dilated
* Larynx Fully Dilated
* Reduced Resistance to Airflow
* Can Dilate Trachea & Brachea
* Nostrils Fully Dilated
* Larynx Fully Dilated
* Reduced Resistance to Airflow
* Can Dilate Trachea & Brachea
51
New cards
A respiratory disease in horses that causes narrowing of the airways, leading to difficulty breathing, coughing, and wheezing. It is commonly triggered by allergens like dust, mold, and pollen.
RAO - Recurrent Airway Obstruction
52
New cards