BIOL 3200 - CH. 12 READING QUIZ
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
How does an action potential spread along the cell membrane?
a) Potassium leak channels quickly reverse the action potential to move the membrane depolarization away from the original site.
b) A change in membrane potential triggers the opening of nearby voltage-gated sodium channels in a one-way direction.
c) Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels are activated by the action potential and the calcium diffuses along the membrane.
d) The ions entering the cell upon triggering an action potential travel laterally along the membrane to carry the charge.
b) A change in membrane potential triggers the opening of nearby voltage-gated sodium channels in a one-way direction.
Which factors determine the force driving the passive transport of charged solutes across the membrane?
a) concentration gradient only
b) membrane potential only
c) electrochemical gradient
d) ATP gradient
c) electrochemical gradient
Which of the following is a cell type in humans that uses voltage-gated ion channels?
a) muscle cells
b) skin cells
c) liver cells
d) gut epithelial cells
a) muscle cells
Which of the following is a difference between transporters and channels?
a) Transporters move solutes against their concentration gradient, whereas channels can move solutes with or against their concentration gradient.
b) Channels do not discriminate between ions, whereas transporters bind their solute with extreme specificity.
c) Transporters can facilitate both active or passive transport of solutes; channels facilitate only passive transport.
d) Channels are single-pass transmembrane proteins, whereas transporters are multipass transmembrane proteins.
c) transporters can facilitate both active or passive transport of solutes; channels facilitate only passive transport.
A sodium-potassium antiport maintains the extracellular concentration of sodium at levels that are about 20-30 times higher than inside the cells. What directly supplies the energy for maintaining this gradient?
a) Potassium supplies the energy, as it is moving along its concentration gradient.
b) Sodium supplies the energy, as it is moving along its concentration gradient.
c) ATP hydrolysis drives the function of the pump.
d) A proton gradient in the mitochondria drives the antiport.
c) ATP hydrolysis drives the function of the pump.
What is the conformation of the voltage-gated Na+ channel that keeps the action potential from traveling backward along the axonal membrane?
a) inactivated
b) open
c) closed
d) triggered
a) inactivated
Which ion is generally maintained at a high concentration inside the cell and a low concentration outside the cell?
a) Na+
b) K+
c) Cl-
d) H+
b) K+
What is the molecular target of the antidepressant Prozac?
a) the symport that drives reuptake of serotonin
b) the Na+ channels that activate the neuron
c) the K+ channels that deactivate action potentials
d) the serotonin receptor, a transmitter-gated ion channel
d) the serotonin receptor, a transmitter-gated ion channel
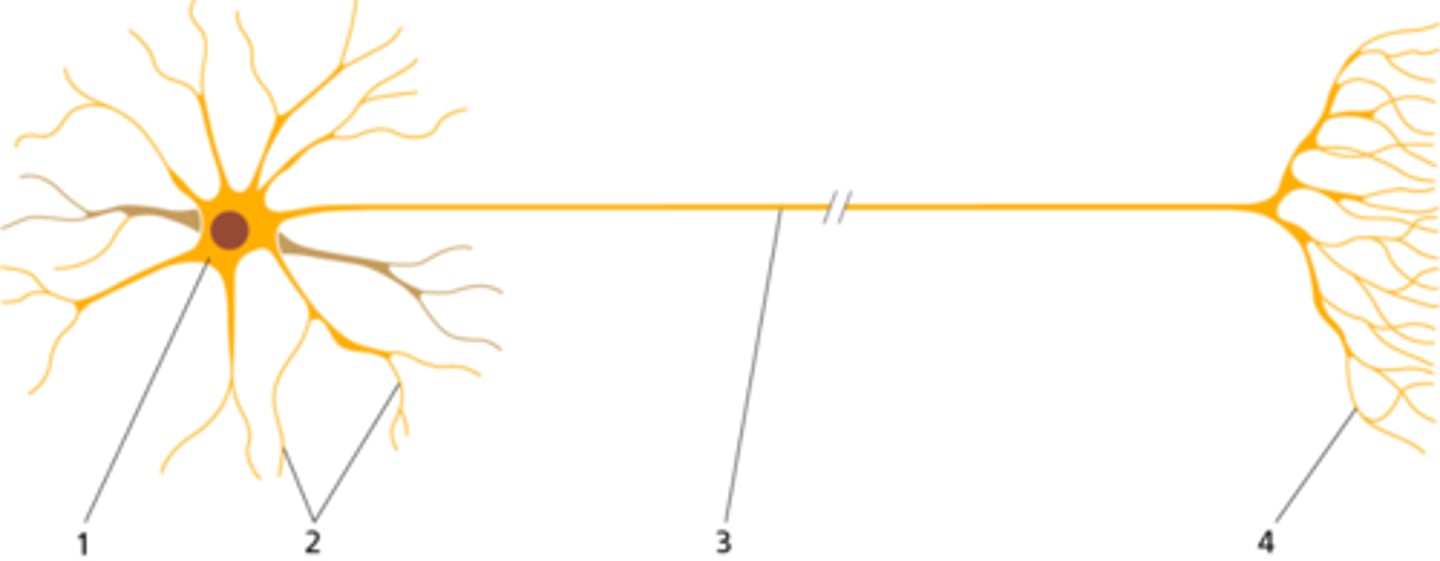
Shown is a diagram of a nerve cell. Which line indicates the location of the dendrites?
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
b) 2
What is responsible for moving glucose from the gut lumen into intestinal epithelial cells?
a) uniport glucose transporter
b) glucose-sodium symport
c) glucose-sodium antiport
d) passive diffusion
b) glucose-sodium symport
Which of the following is NOT used as a source of energy by a transmembrane pump to actively transport a solute?
a) ATP
b) Na+
c) H+
d) K+
d) K+
Which of the following ions has a low cytosolic concentration so that a flood of this ion into the cell can be used as a signal for cell processes like fertilization?
a) Ca2+
b) H+
c) K+
d) phosphate
a) Ca2+
What is the role of K+-gated ion channels in an action potential?
a) They lead to the action potential reaching its highest state of cell depolarization.
b) They help reverse the action potential by repolarizing the cell.
c) They do not have a role in action potentials.
d) They provide the energy for the sodium-potassium pump to reestablish resting potential.
b) They help reverse the action potential by repolarizing the cell.
Which of the following would be able to cross a protein-free lipid bilayer most rapidly?
a) a chloride ion (charged, small)
b) glucose (uncharged polar, large)
c) ethanol (uncharged polar, small)
d) a steroid hormone (nonpolar, large)
d) a steroid hormone (nonpolar, large)
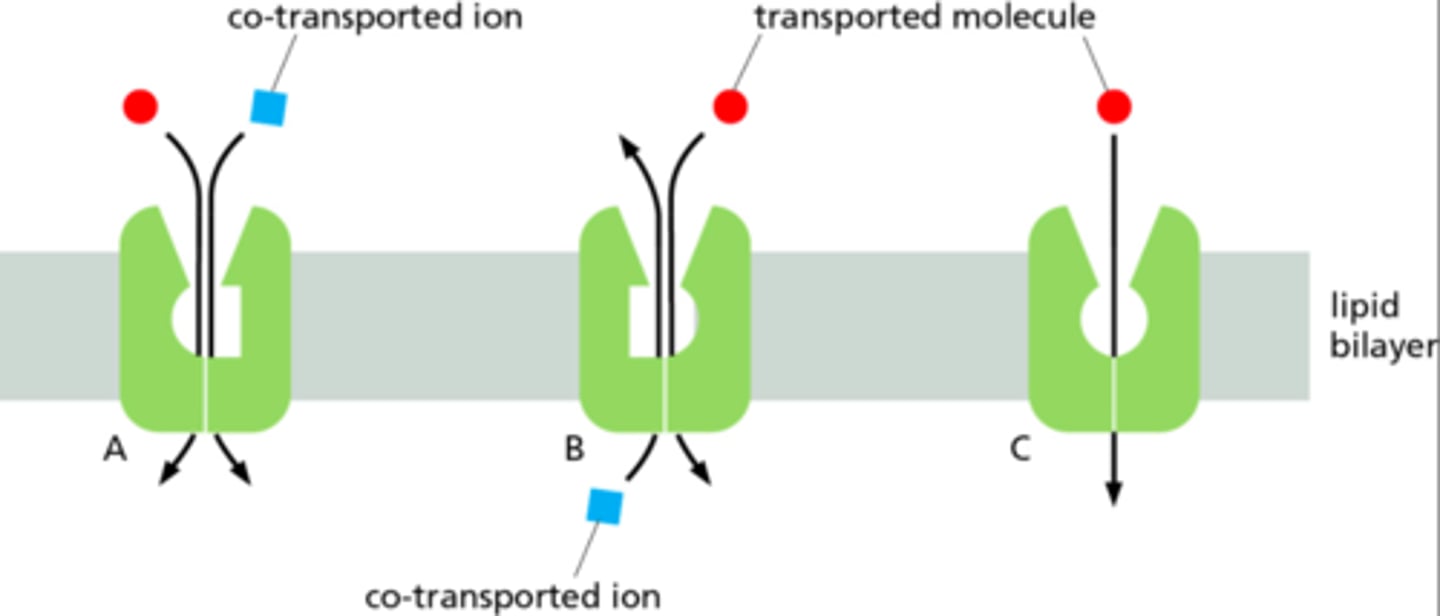
Which of the following represents a symport transporter protein?
a) A
b) B
c) C
d) none of these are a symport.
a) A
How is an electrical signal converted to a chemical signal at a nerve terminal?
a) Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels are activated and the influx of Ca2+ triggers the release of neurotransmitters.
b) Ligand-gated channels are bound by ions and open to allow the flow of neurotransmitters out of the cell.
c) Mechanically gated channels change conformation due to the electrical signal and create a mechanical signal.
d) The influx of ions leads to a pH change, chemical transformation, and signaling.
a) Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels are activated and the influx of Ca2+ triggers the release of neurotransmitters.
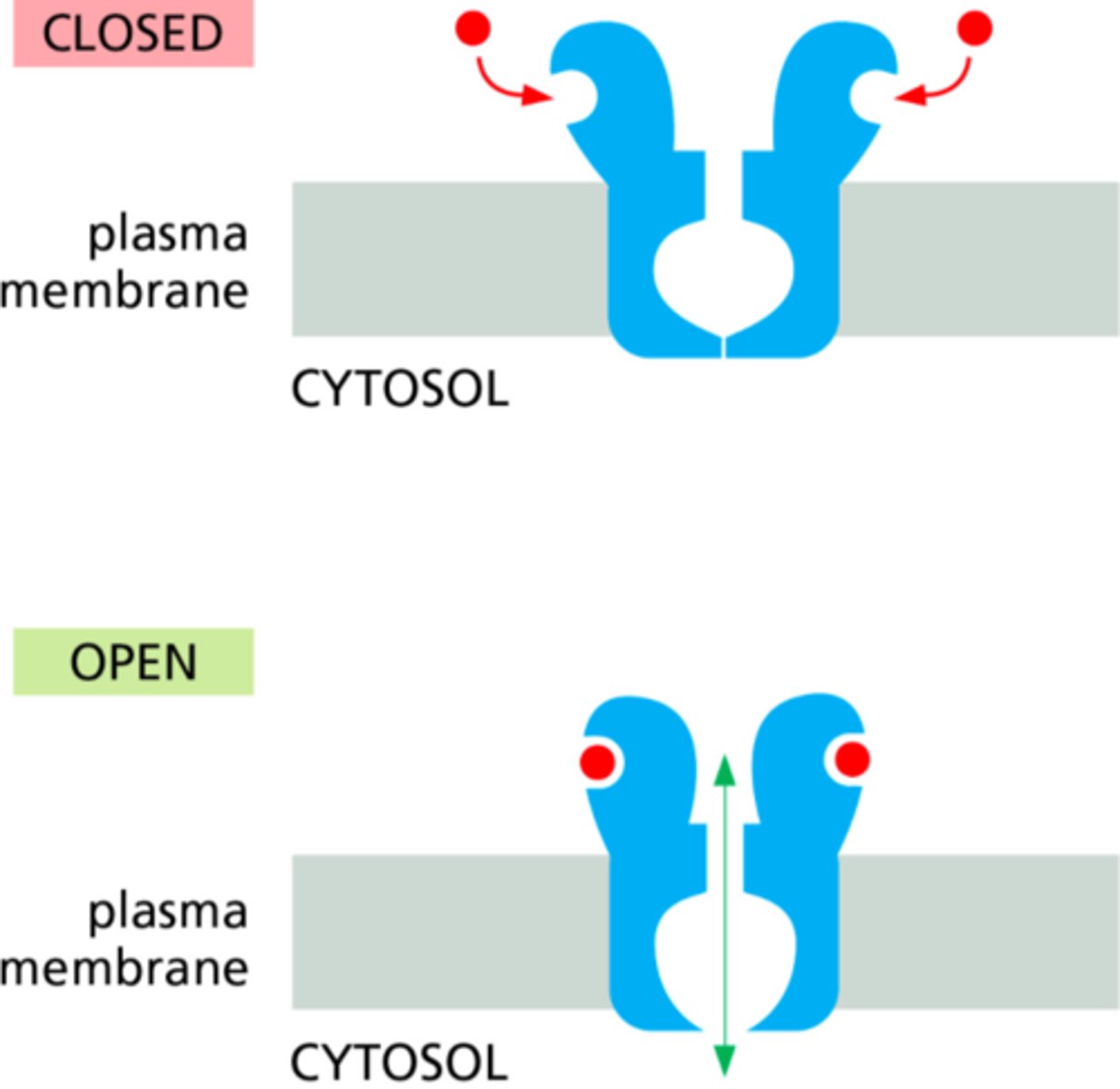
An extracellular molecule binds to a channel and triggers it to move more often to the open conformation than the closed conformation, as shown in the figure. This is referred to as a ___________ channel.
a) voltage-gated
b) ligand-gated
c) mechanically gated
d) light-gated
b) ligand-gated
How are voltage-gated ion channels opened by voltage sensors?
a) Voltage sensors on the channel change their amino acid side chains from positively to negatively charged.
b) When membrane potential changes sufficiently, the electrical force causes voltage sensor domains to change conformation.
c) Ion binding to voltage sensors causes the channel pore to widen and open.
d) Changes in membrane potential lead to increased gene expression of voltage-gated ion channel proteins.
b) When membrane potential changes sufficiently, the electrical force causes voltage sensor domains to change conformation.
Cells, compared with the extracellular fluid are
a) electrically neutral.
b) slightly positively charged.
c) extremely positively charged.
d) slightly negatively charged.
d) slightly negatively charged.
Ion channels contain a selectivity filter that
a) binds with extreme sensitivity to their specific ion, akin to an enzyme forming a specific binding site for a substrate.
b) selects for ions based on size and charge due to the width of the channel and charge of amino acids lining the channel.
c) selects for size of ions based on interactions with the ion transport protein.
d) selects for positively charged ions by virtue of the negatively charged amino acids lining the pore, but allows similar ions through, like Na+ and K+.
b) selects for ions based on size and charge due to the width of the channel and charge of amino acids lining the channel.