ELISA Steps
1/5
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
Step 1
Multiple patient samples added to wells
Step 2
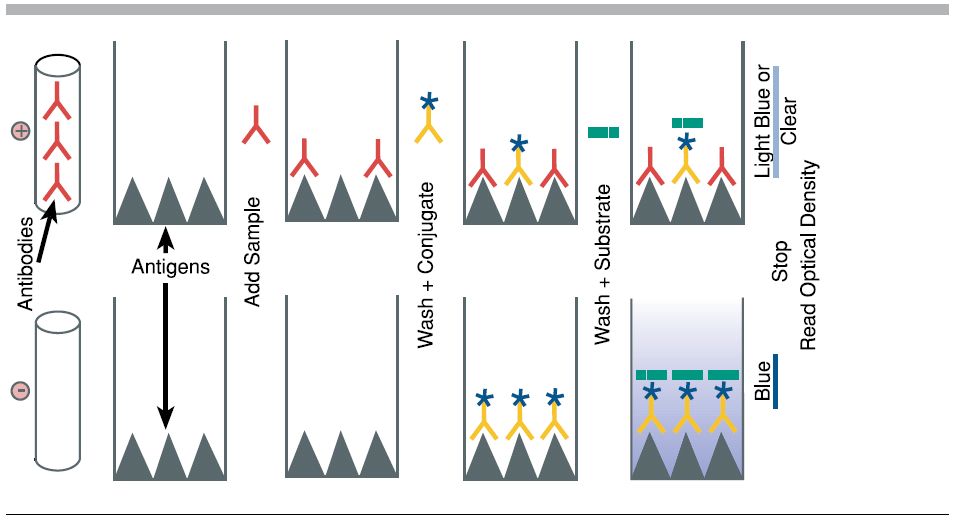
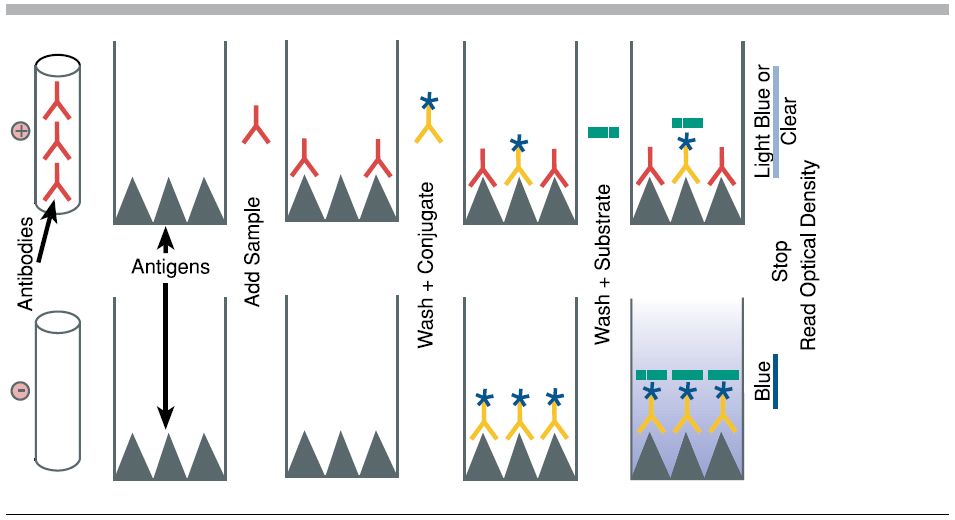
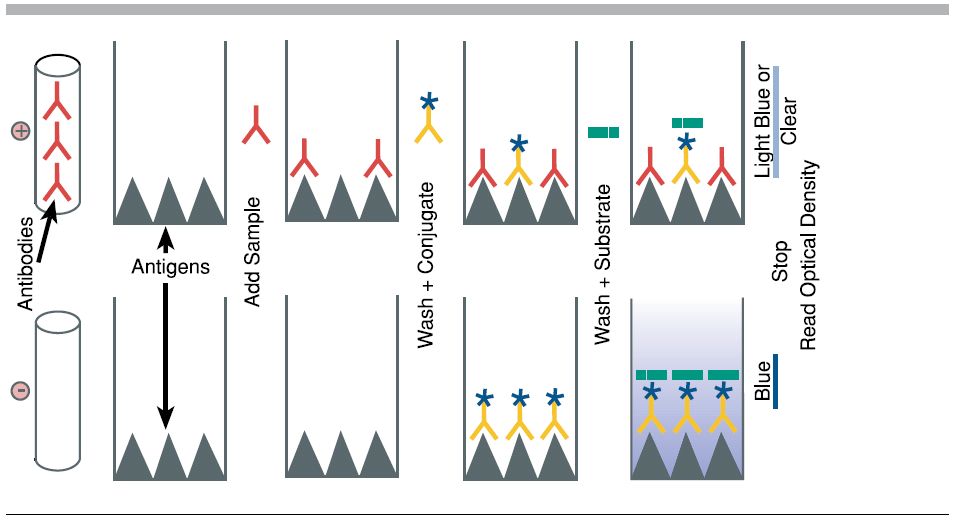
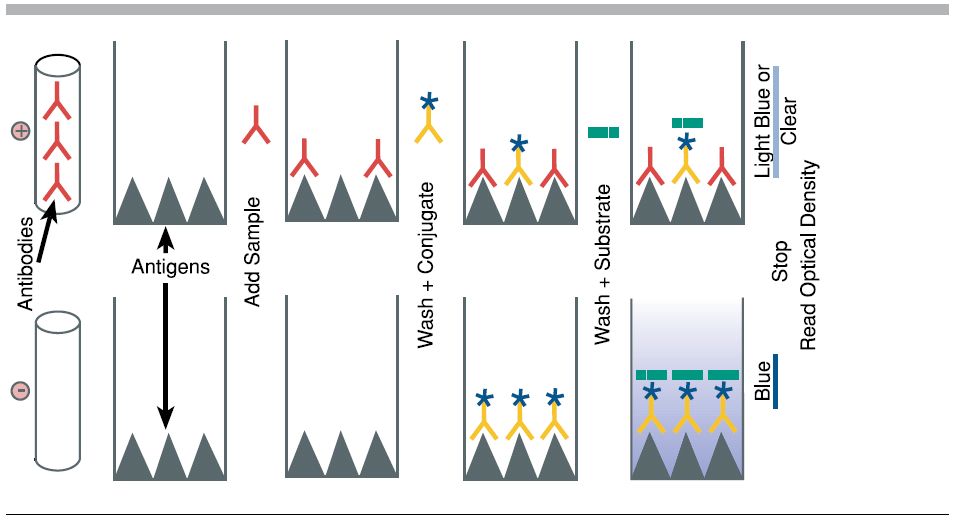
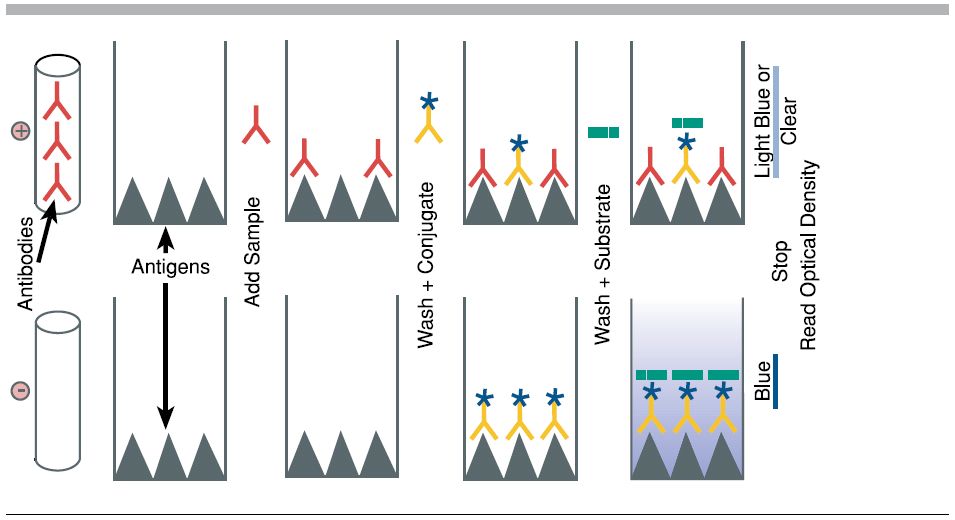
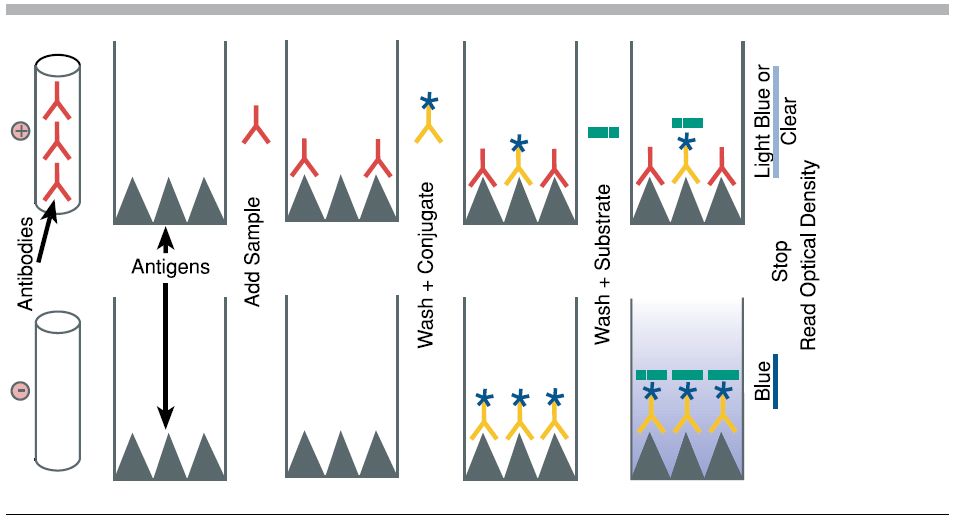
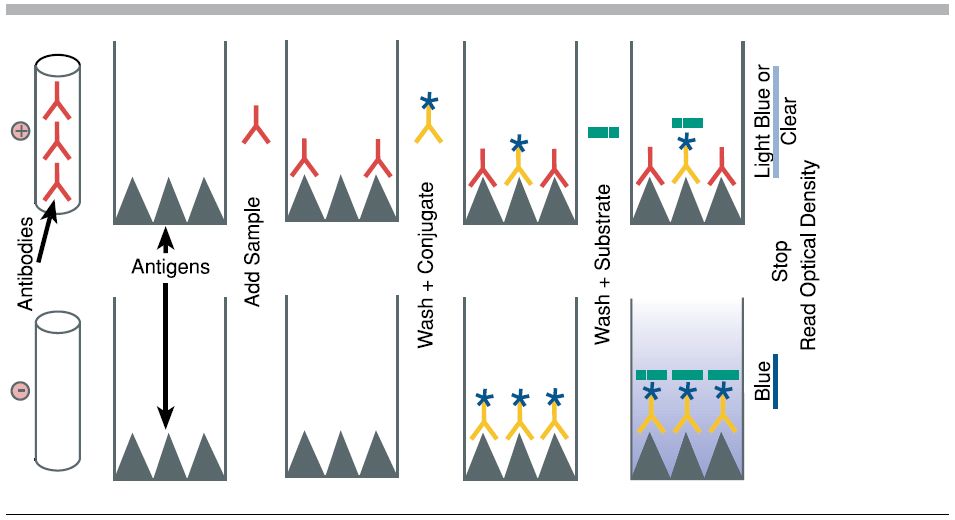
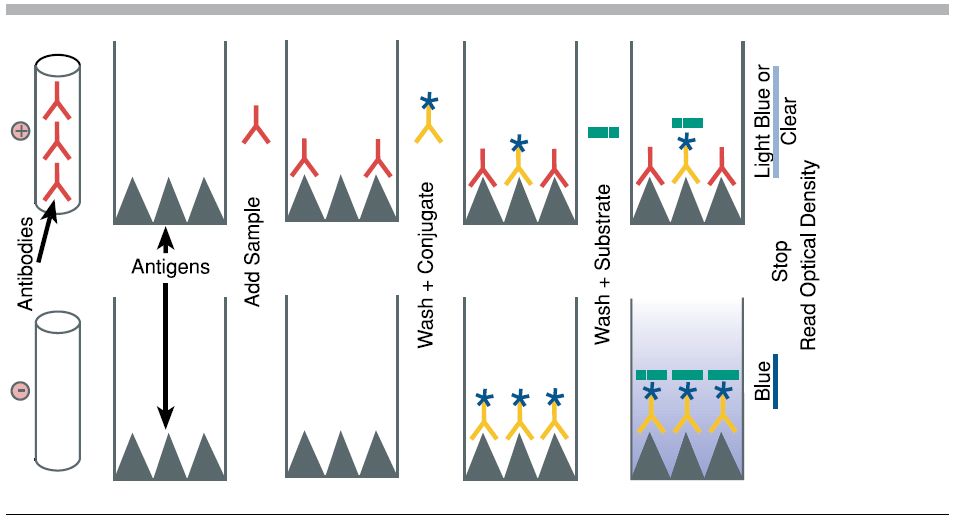
Purpose: To attach the target antigen (from patient samples) to the wells of a microplate.
Process: Patient samples are pipetted into the wells. If the patient is infected, their sample contains antigens that will adhere to the plastic surface of the well.
Key Concept: The plastic wells are designed to bind proteins, allowing antigens to stick.
Step 3
Purpose: To detect the presence of the antigen.
Process: A solution containing primary antibodies is added. These antibodies are specific to the antigen being tested (e.g., a bacterial protein).
Key Concept: If antigen is present, the primary antibody will bind to it. If not, it will be washed away in the next step
Step 4
Purpose: To enable detection of the antigen-antibody complex.
Process: Secondary antibodies, which are linked to an enzyme, are added. These bind to the primary antibodies.
Key Concept: The enzyme attached to the secondary antibody is what will produce a visible signal in the final step.
Step 5
Purpose: To produce a color change indicating the presence of antigen.
Process: A substrate for the enzyme is added. If the enzyme is present (meaning antigen was detected), it will catalyze a reaction that changes the color of the solution.
Key Concept: The intensity of the color correlates with the amount of antigen present.
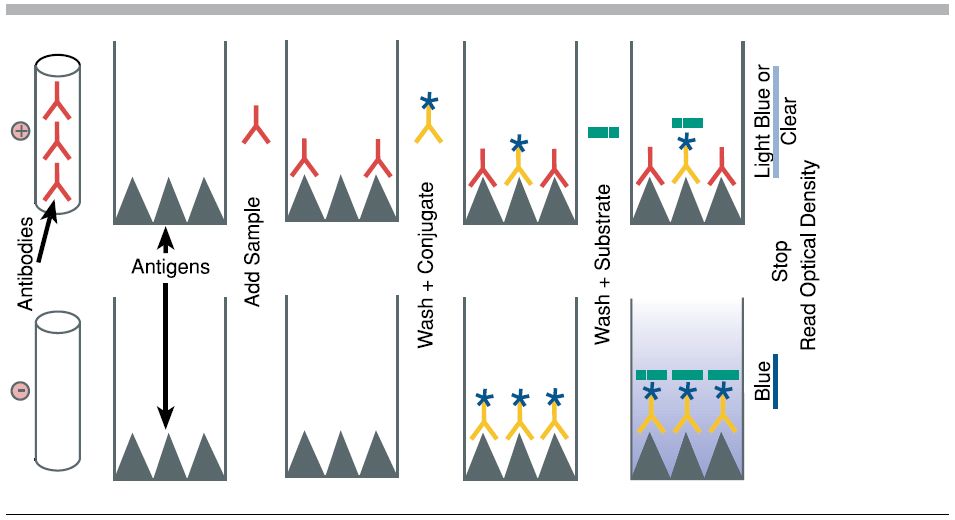
Step 6
Purpose: To analyze results and determine which patients are infected.
Process: Wells that turn yellow indicate a positive result. The deeper the color, the higher the concentration of antigen.
Key Concept: This step mimics how diagnostic labs quantify infection levels using spectrophotometers or visual comparison