Pharmacotherapy: Intro to Pain Classification & Assessment + Non-Opioid Treatments
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Duration of Pain
- Acute: <30 days
- Chronic: some say sub-acute 1-3 months
Intensity of pain
- mild
- moderate
- severe
Origin of pain
- joint
- musculoskeletal
- nerve
- bone
Type/cause of pain
- nociceptive
- neuropathic
- inflammatory
- malignant
Acute vs. chronic pain
- Acute: a sudden sensation that alerts us to possible injury
- Chronic: pain that persists- often for months or even longer
Acute Pain
- Duration:
- Purpose:
- Cause:
- Characteristics:
- Duration: typically short (<30 days)
- Purpose: body's communication to warn of potential harm or injury
- Cause: *due to identifiable cause/noxious stimulus: surgery, illness, trauma/injury
- Characteristics: HTN, tachycardia, diaphoresis, mydriasis, pallor
Chronic pain
- Duration:
- Purpose:
- Cause:
- Duration: long (>3 months-yrs)
- Purpose: none, maladaptive
- Cause: Continued pain sensations w/o time relationship to noxious stimulus, and sometimes without an identifiable cause
Characteristics of chronic pain
• Often has association with psychological components such as anxiety and depression
• Presentation may change (eg, sharp to dull, specific/obvious to diffuse/vague)
T/F: Chronic pain is NOT associated with signs of acute pain such as increased BP, HR, etc
TRUE
Acute Pain:
- Dependence and tolerance to medication:
- Psychological component:
- Organic cause:
- Environmental/family issues:
- Insomnia:
- Treatment goal:
- Depression:
- Dependence and tolerance to medication: unusual
- Psychological component: usually not present
- Organic cause: common
- Environmental/family issues: usually minor
- Insomnia: unusual
- Treatment goal: cure
- Depression: uncommon
Chronic Pain:
- Dependence and tolerance to medication:
- Psychological component:
- Organic cause:
- Environmental/family issues:
- Insomnia:
- Treatment goal:
- Depression:
- Dependence and tolerance to medication: Common
- Psychological component: Often a significant factor
- Organic cause: may not be present
- Environmental/family issues: Can be significant
- Insomnia: Common
- Treatment goal: Functionality
- Depression: Common
Regardless of acute vs chronic, relieving pain as much as possible is...
ALWAYS a primary focus
Goals of therapy for acute pain*****
• Pain control
• assist in the body HEALING itself
• Reduce pain to allow for movement and training to rebuild/strengthen body tissue
• Emphasis on healing or restoration of the previous state (pre-pain/injury)
Goals of therapy for chronic pain*****
• Pain Control
• assist pt in MANAGING pain
• May include decreasing pain even reducing medication use
• Emphasis on improving/maintaining level of function and quality of life (not likely pain-free or restore pre-pain function)
What is the diagnosis of pain based on?
- pain is subjective
- Pt description
- Hx
- Physical exam
T/F: Behavior, cognitive, social & cultural factors may affect pain
TRUE
Mental factors which may lower pain threshold (increasing perception of pain)
• Anxiety
• Depression
• Fatigue
• Anger
• Fear
T/F: There are diagnostic lab tests for pain
FALSE, though lab tests may be conducted to identify potential underlying causes
Imaging for pain
May be conducted to identify underlying causes
Pain assessment scales
Best to use multidimensional options to measure intensity, quality, and location as well as the impact pain is having on mood or activity
Assess and Reassess Treatment
1. Is pain relief adequate?
2. Monitor (side effects, efficacy, changes)
3. Titrate, adjust, change any & all pain meds as necessary**
4. REPEAT***

Assessing and Reassessing Treatment
- essential for both acute & chronic pain monitoring
- also essential to titrate medications down as pain subsides or is better managed
- need to monitor for relief as well as potential hazards of all medications used
First-line options for pain
- NON-Pharm
- absolutely essential for healing and proper treatment
- Medications are helpful too, but they cannot fix everything
Non-pharm treatment options****
• Exercise
• Physical therapy
• Thermal therapy (heat/ice)
• Diet
• Weight loss
• Electroanalgesia
• Psychological techniques
• "Alternative" Options
Electroanalgesia
• Noninvasive: transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS)
• Also more invasive options involving implantable devices
Psychological techniques
• Cognitive-behavioral therapy
• Relaxation training
• Mindfulness-based stress reduction/meditation
• Biofeedback
"Alternative" Options****
• Tai Chi
• Yoga
• Acupuncture, acupressure
• Massage
• Manipulation (chiropractic, osteopathic muscle)
Second Line: Medication Options
choice of class/agent depends on type of pain & other pt factors
What are first line for initial treatment of mild to moderate pain?
- non-opioid analgesics
- also are additive options for moderate-severe pain
Non-Opioid Analgesics: APAP*****
- acetaminophen
- MOA: uncertain. centrally activates the descending serotonergic pathways
- also a different method of prostaglandin inhibition than NSAIDs
Side effects of APAP (4)*****
• GI (N/V)
• Headache
• Hepatotoxicity
• Skin rash
Concerns with use of APAP****
• Not recommended in liver disease or excessive alcohol consumption (toxicity)
• Potential for overdose with multiple combination products*
Non-Opioid Analgesics: NSAIDs****
- NSAID = Non-Steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
- MOA: inhibits COX 1 and 2, decreasing prostaglandin production
• Superior for pain resulting from inflammation
Side effects of NSAIDs****
• GI upset/ulcer/GI bleed
• Increased risk of CV events
• Nephrotoxicity, water retention
• Increase bleed risk
• Elevated hepatic enzymes
• Skin rash
• Tinnitus
Concerns with use of NSAIDs****
- CV, GI, renal concerns
- use at lowest effective dose for shortest amount of time (<7-10days when possible)
What are effects that distinguish NSAIDs from narcotic anaglesics?
• antipyretic
• anti-inflammatory (at higher doses)
• have a ceiling effect to the analgesic benefit
• do not cause tolerance
• do not cause physical or psychological dependence
NSAIDs can be used for most types of pain, including....
• Acute pain of skeletal muscle or dental origin
• Inflammation of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis
• Pain due to bone metastases
• Can have additive effect with narcotic analgesics
NSAID Complications: CV (stroke, MI) ***
- What is it associated with?
- Risk factors?
- associated with prolonged use
- age 65+
- male
- pre-existing CV disease
- multiple CV risk factors
NSAID Complications: Renal impairment ***
- What the risk of renal impairment double with?
- associated with prolonged use
- risk of renal impairment doubles after one year of use
NSAID complications: GI bleeding ***
- risks
- may occur even w/ short term use (and w/o warning)
- risk doubles with concomitant use of aspirin
- female
- age 75+
- Hx of GI bleeding episodes or CV complications
NSAIDs interaction w/ anticoagulants & antiplatelet drugs***
increases bleeding
T/F: Efficacy is similar across NSAID agents. Reasonable to switch from one to another as pt-specific efficacy may vary
TRUE
What factors do the selection of NSAIDs depend on?
- Availability: OTC vs. prescription
- Pharmacokinetics: onset of relief, duration of action
- Pharmacologic characteristics
- Side effect profile
- Cost
- Available dosage forms: oral, topical (similar efficacy to oral w/o systemic issues), injectable (ibuprofen IV, ketorolac IM), nasal spray (ketorolac)
Acetaminophen (APAP)*****
- Usual Dosage range:
- Max Dose:
- Other unique details:
- Usual Dosage range: 325-1,000 mg q4-6h
- Max Dose: 4000 mg/4g daily
- Other unique details: Max dose reduced in elderly, renal, and hepatic insufficiency
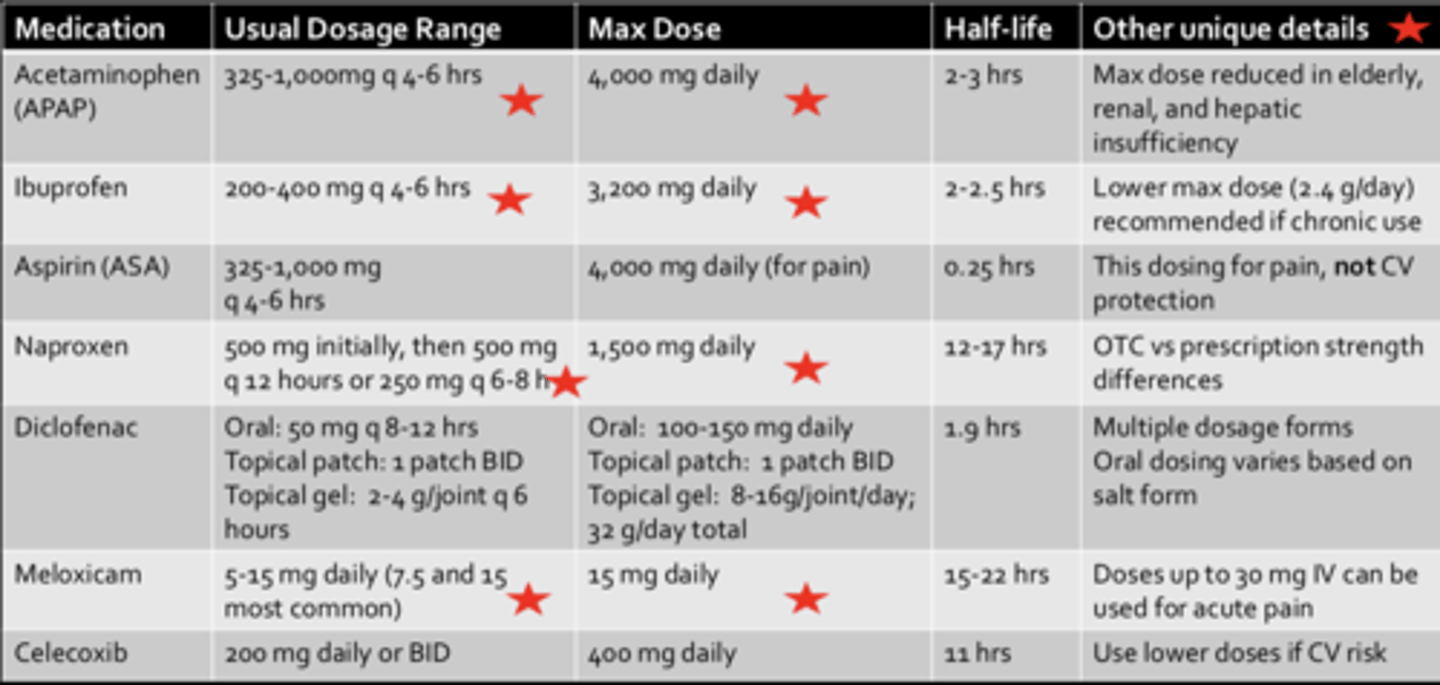
Ibuprofen***
- Usual Dosage range:
- Max Dose:
- Other unique details:
- Usual Dosage range: 200-400 mg q4-6h
- Max Dose: 3200 mg daily
- Other unique details: Lower max dose (2.4 g/day) recommended if chronic use
Naproxen****
- Usual Dosage range:
- Max Dose:
- Other unique details:
- Usual Dosage range: 500 mg initially, then 500 mg q12h or 250 mg q6-8h
- Max Dose: 1500 mg daily
- Other unique details: OTC vs prescription strength differences
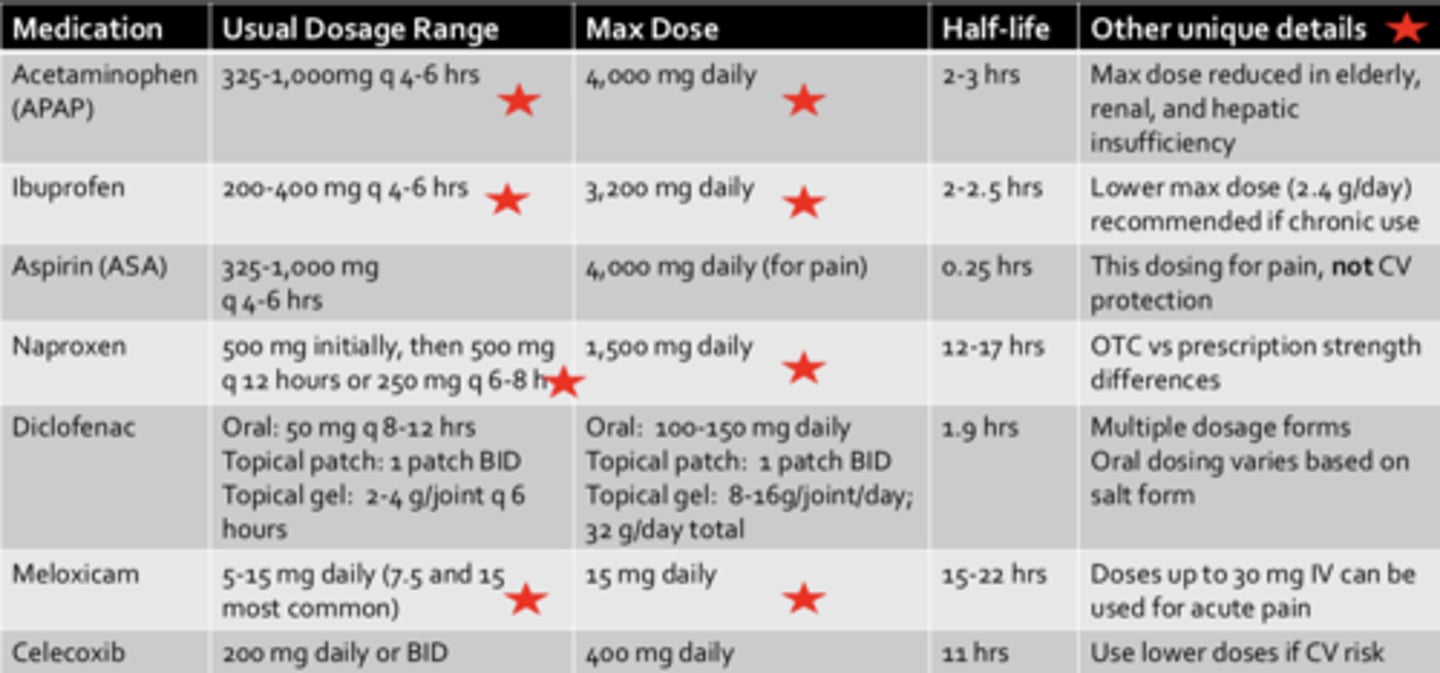
Meloxicam ***
- Usual Dosage range:
- Max Dose:
- Other unique details:
- Usual Dosage range: 5-15 mg daily (7.5 and 15 most common)
- Max Dose: 15 mg daily
- Other unique details: Doses up to 30 mg IV can be used for acute pain
ASA (aspirin) in combo. with NSAIDs
- ibuprofen can hinder the CV prevention effect of aspirin by inhibiting the antiplatelet effect when taken 2-12 hours before aspirin
- preferential binding to platelets instead of ASA
T/F: Ibuprofen affects the antiplatelet effect if taken ≥2 hours after aspirin
FALSE, does not affect if taken ≥2 hours after aspirin. Aspirin binds to platelets first (irreversible) so ibuprofen can't
When using both aspirin and NSAIDs, which should be taken first?
aspirin
Pros of topical NSAIDs
- lower serum conc. than oral admin. (minimal systemic absorption)
- limits the potential of adverse effects
- promising options for inflammatory pain when systemic effects would be detrimental
Cons of topical NSAIDs
- can be expensive
- multiple daily topical administration can be burdensome
- diclofenac (patch, gel, solution)
Other non-opioid topical options
• Capsaicin: Cream or patch. Must be used consistently for best results
• Lidocaine: Solution, patch, cream
• Rubefacients (menthol, camphor, methyl salicylate
Non-Opioid Co-analgesic options
- anticonvulsants
- antidepressants
- muscle relaxants
- anti-spasticity agents
- corticosteroids
- "emerging" options: cannabis, ketamine
What is the first line treatment for pain management?
non-pharm
What is the main difference in goals between acute and chronic pain management?
Healing Vs. Function/Management
What concerns/precautions are there for NSAID use? (Top 3)
- CV
- GI
- renal
What's the max daily dose of ibuprofen?
3200 mg, unless chronic then 2400 mg
Name 3 different classes of non-opioid pain medications
- NSAIDs
- APAP
- any other (capsaicin, rubefacient)