UWORLD Psychiatry Step 2 CK
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
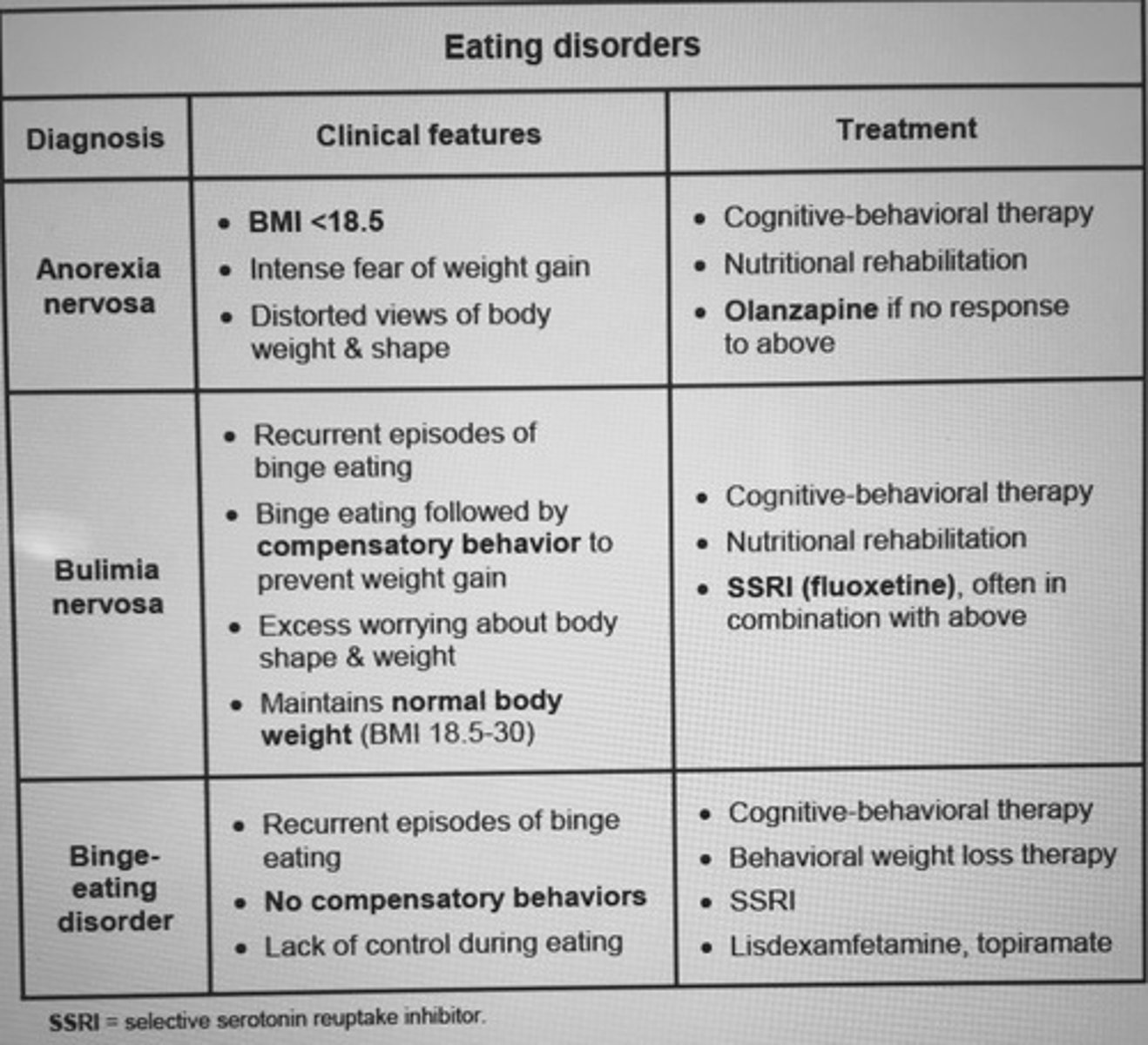
Eating disorders clinical features of anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge-eating disorder.
Key features of somatic symptom & related disorders.
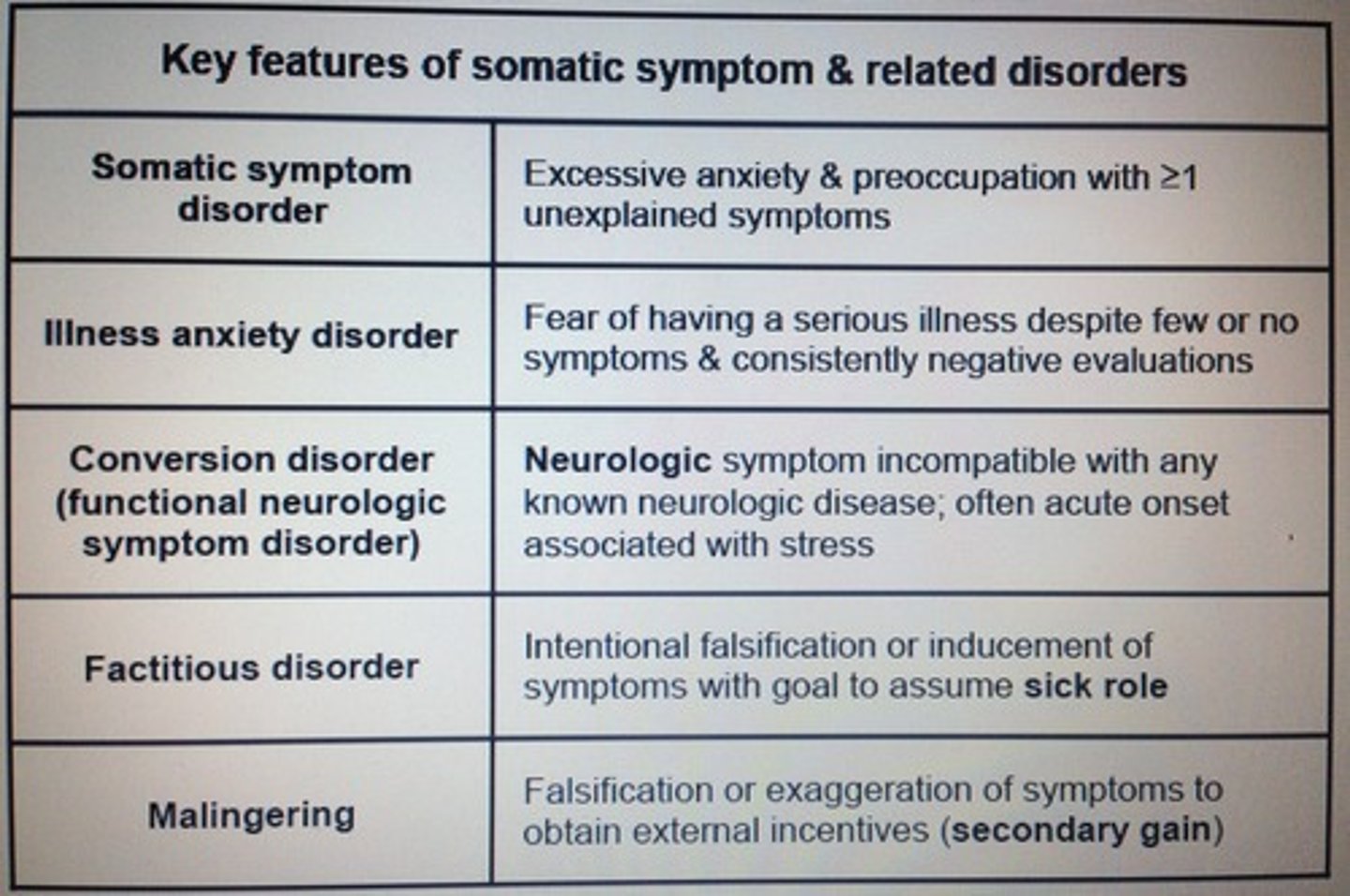
Somatic symptoms disorder according to DSM-5.
1. One or more physical symptoms that are distressing or result in sig. disruption of daily life
2. Excessive thought, feelings, or behaviors related to these symptoms
3. Persistent symptoms > 6 mo.
Antipsychotic medication effects (dopamine antagonism) in dopamine pathways.
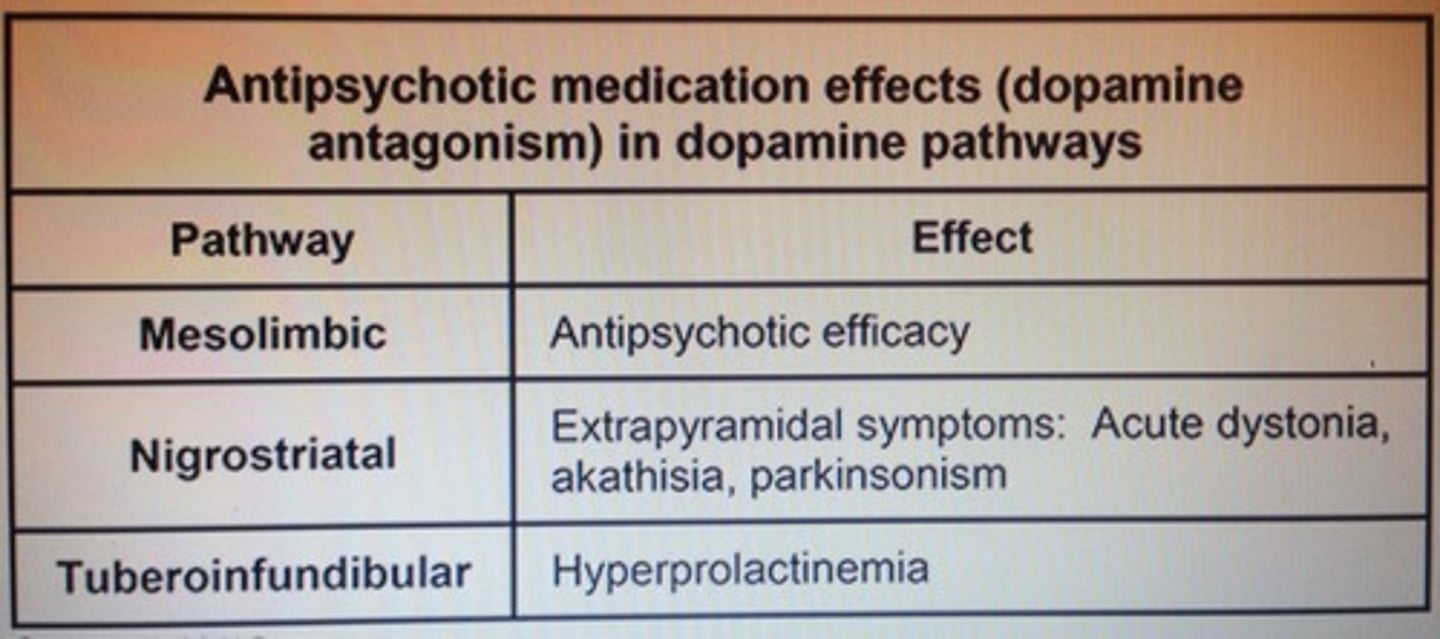
If pt has been on risperidone and is presenting with EPS such as dystonia, parkisonism, terdive dyskinesia, akathisia the best management is?
Replace it w/ clozapine
- check CBC, monitor for agranulocytosis
Pts w/ short life expectancy that have symptoms of depression should be treated with?
Methylphenidate, modafinil since SSRI usually take longer to reach therapeutic effect
SSRIs best option in pts w/ longer life expectancy
Pts taking MOAi like phenelzine should avoid foods high in tyramine, as the combo can result in ____.
HTN crisis, monitor BP
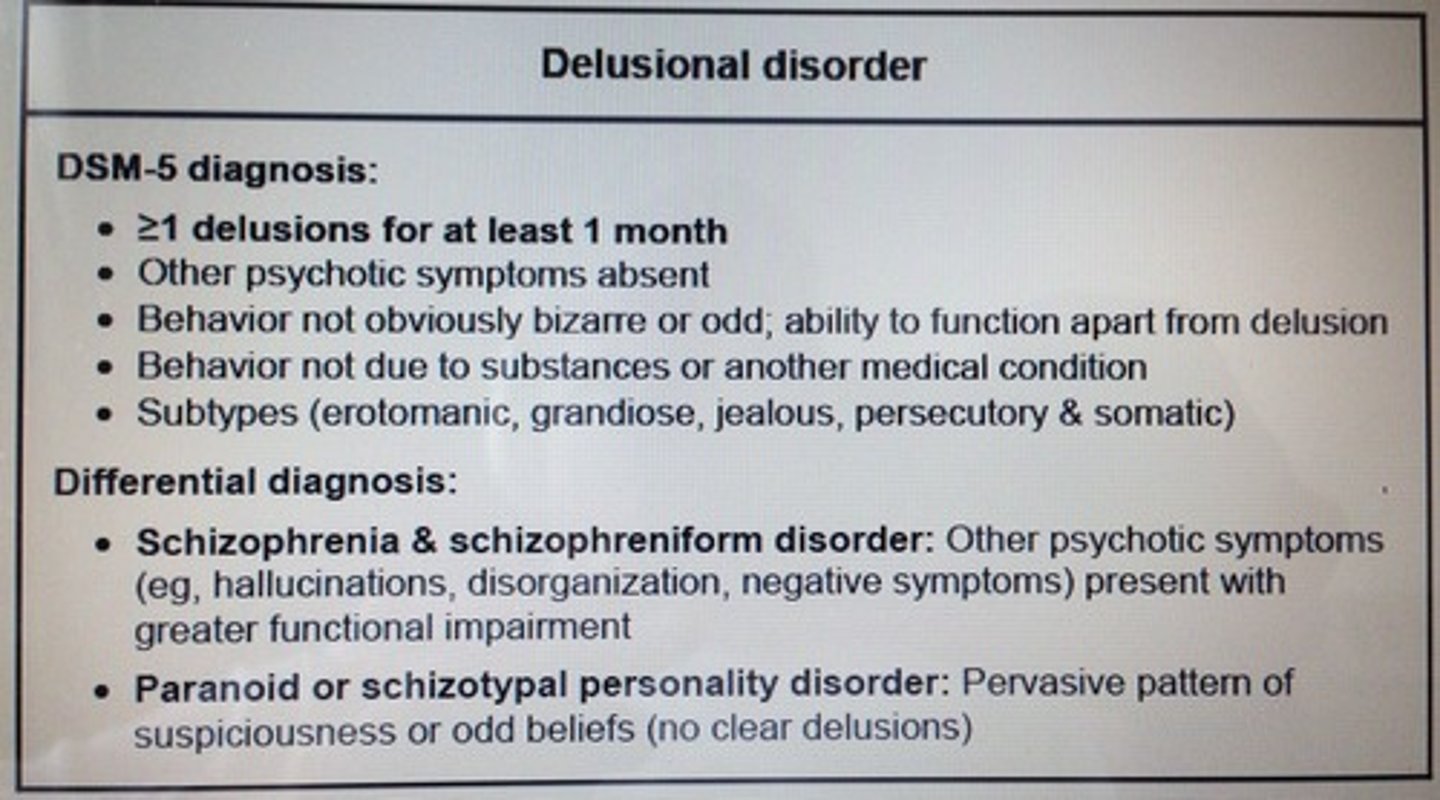
Delusional disorder DSM-5 diagnosis criteria?
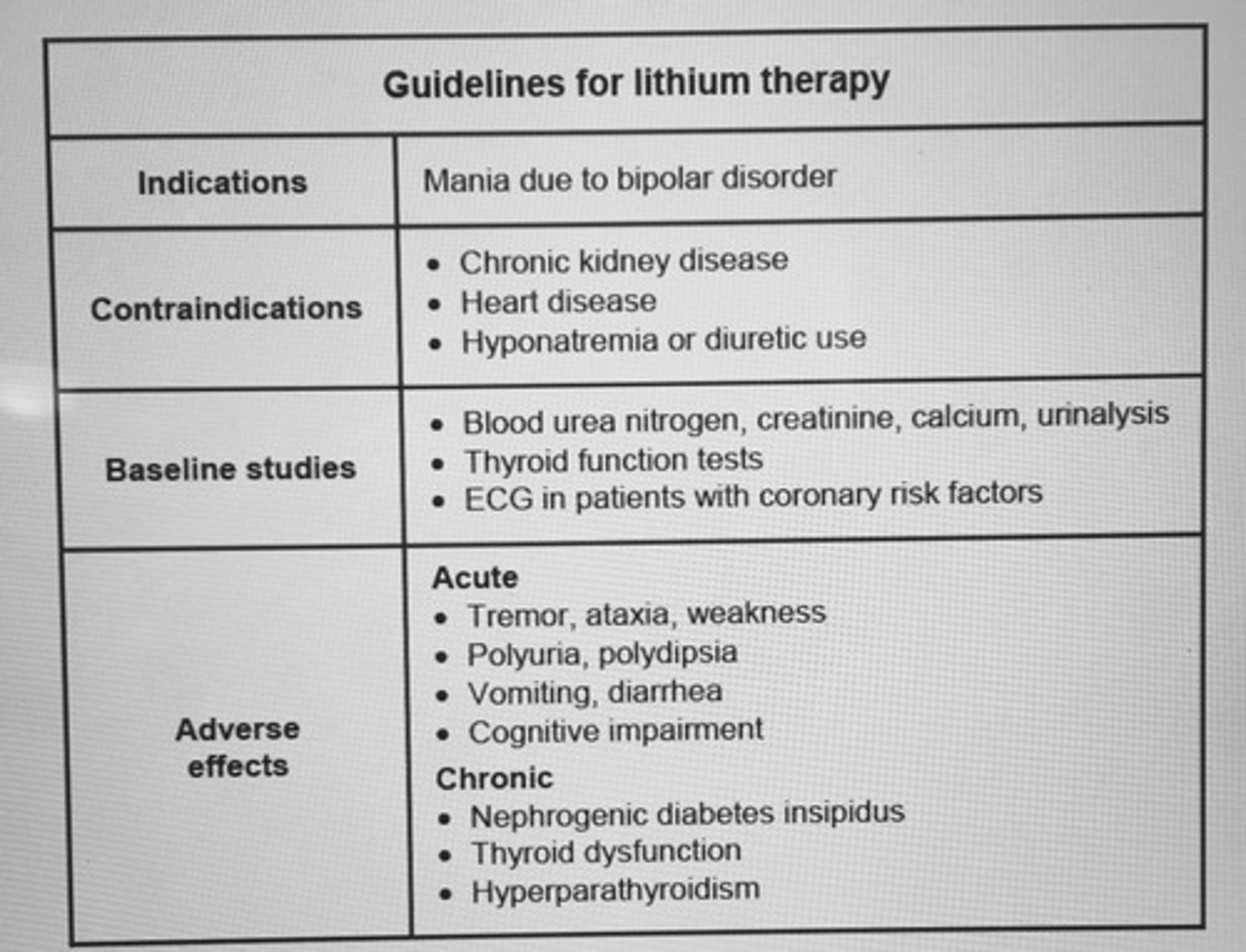
Guidelines for lithium therapy
Common drugs affecting lithium levels
Diuretics
NSAIDs, except aspirin
SSRI
ACEi, ARBs
Anti epileptics (Carbamazepine, phenytoin)
- monitor Lithium levels every 6-12 mo. and 5-7 days after dose changes or stating other meds
Common defense mechanisms

SE Clozapine
Agranulocytosis - check CBC
Lowers seizure threshold
Most antidepressants must be taken for ___ before they provide symptomatic relief.
4-6 weeks
Electroconvulsive therapy for depression indications?
- Tx resistance
- Psychotic features present
- Emergency conditions such as pregnancy, refusal to eat or drink, imminent risk of suicide
What tx is indicated to achieve rapid response in depressed geriatric pts who are unable to eat or drink, psychotic, or actively suicidal?
ECT
- induces a 30-60 sec. generalized tonic-clonic seizure
First-line pharm tx for bipolar disorder includes?
1. Atypical antipsychotics (risperidone, aripirazole, olanzapine)
2. Lithium
3. Valproic acid
Lithium should not be administered to pts with ___.
Renal dysfunction
Mild/moderate ill pts bipolar disorder tx?
Mono therapy atypical antipsychotics
OR
Mono therapy w/ Lithium OR Valproic acid
For severe episodes of bipolar disorder tx?
Combo Lithium OR Valproate
PLUS
Atypical antipsychotic
Persistent depressive disorder (dysthymia) DSM-5 criteria.

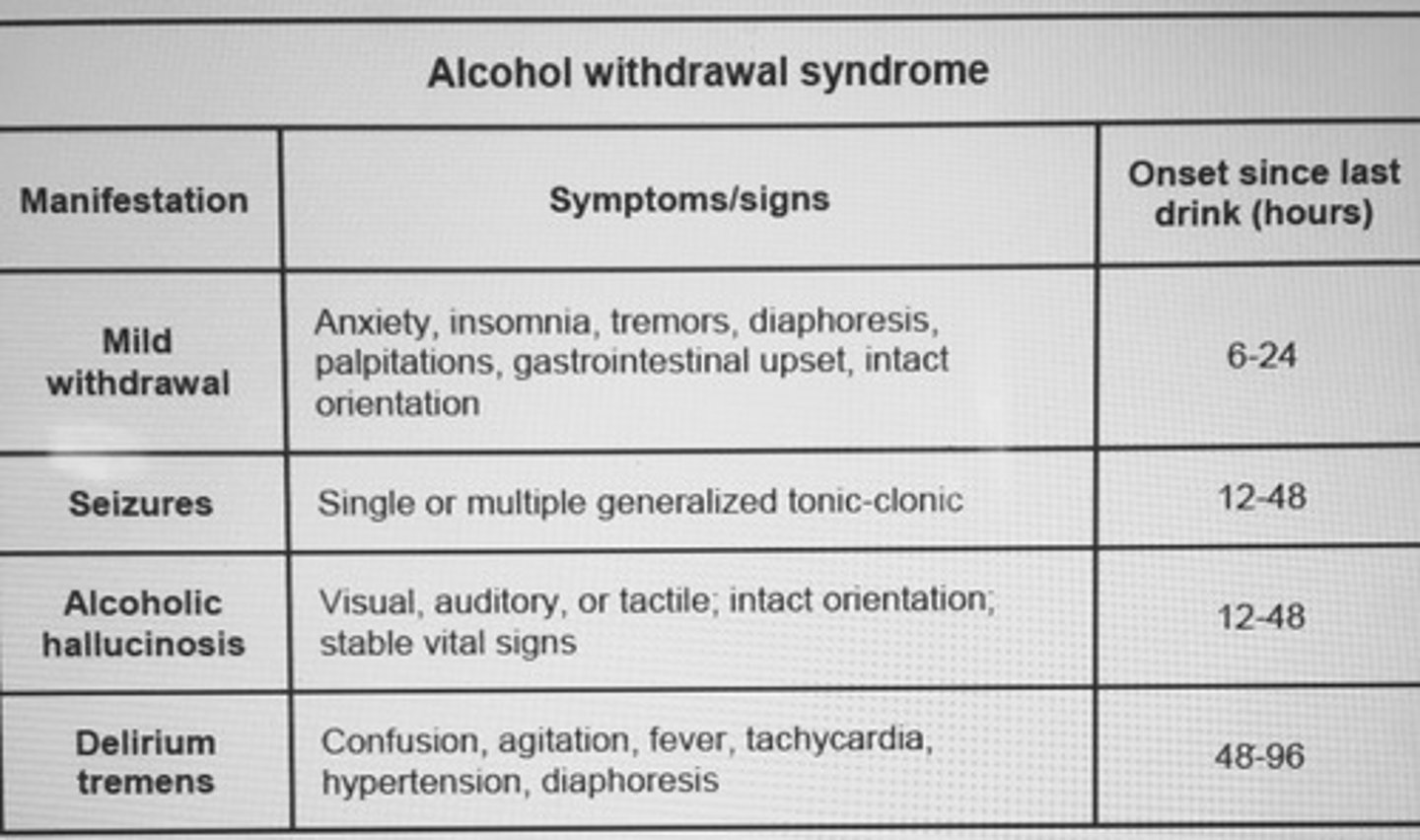
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome time-line.
give Lorazepam IV form preferred inpatient setting, pts comorbid liver dz
Intoxication MDMA causes?
HTN
Tachy
Hyperthermia
Serotonin syndrome (high fever, altered mental status, seizures)
Hyponatremia
Death
Long-term use can lead to Neurotoxicity
* MDMA w/ other serotonergic drugs such as serotonergic antidepressants can INC risk serotonin syndrome
MDMA (synthetic amphetamine) NOT detected routine tox screens
Meds approved as first-line tx for OCD?
Clomipramine (Anafranil) - if pt fails to respond initial tx SSRI
Fluoxetine (Prozac)
Fluvoxamine (Luvox)
Paroxetine (Paxil)
Sertraline (Zoloft)
Which pts are candidate for long-term/lifetime maintenance with lithium?
Following first episode, maintenance therapy at least 1 year
Pt experience 2 episodes of acute mania
Pt experience 3 or more relapses are recommended to have lifetime maintenance
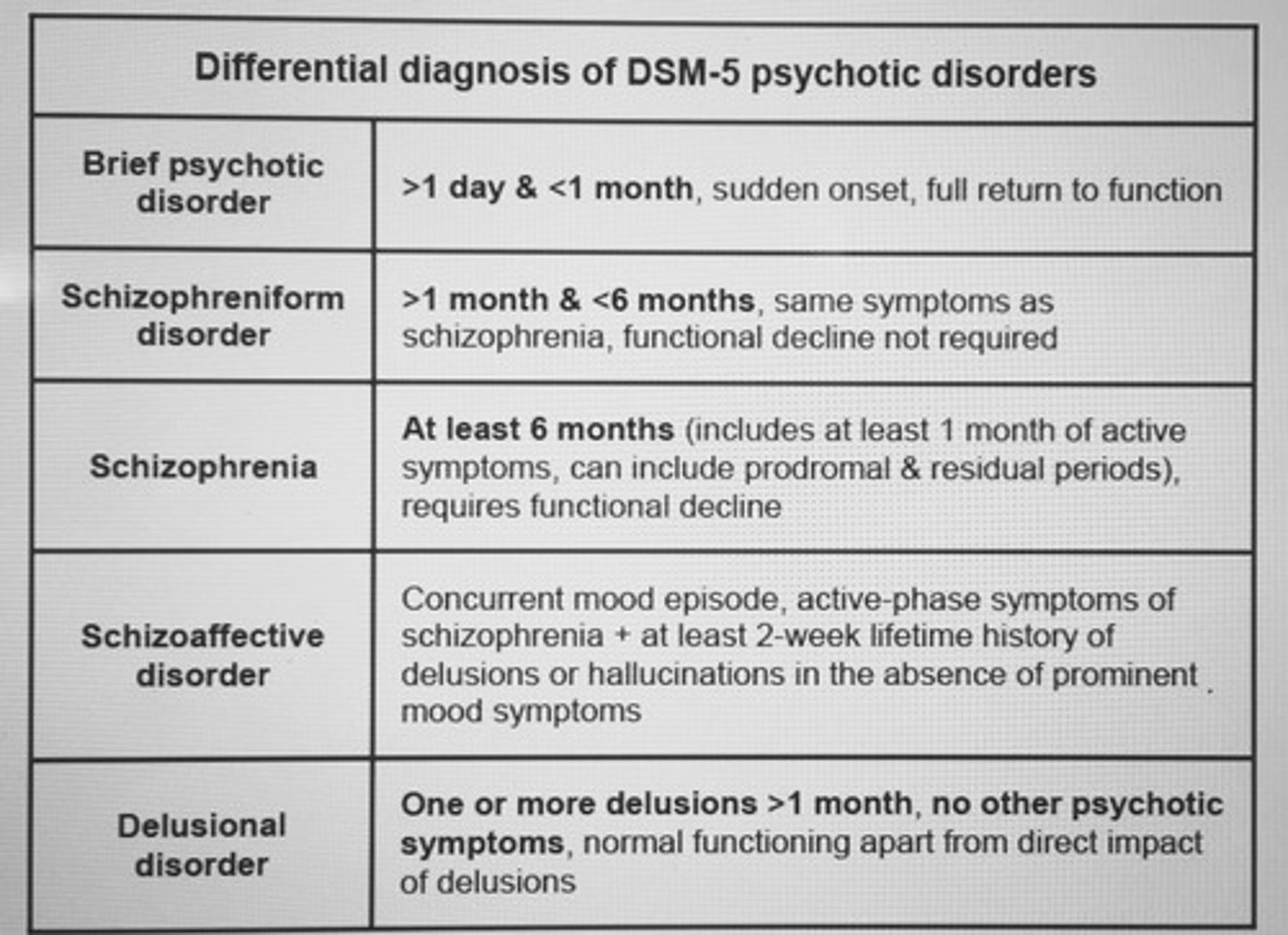
Differential diagnosis of DSM-5 psychotic disorders
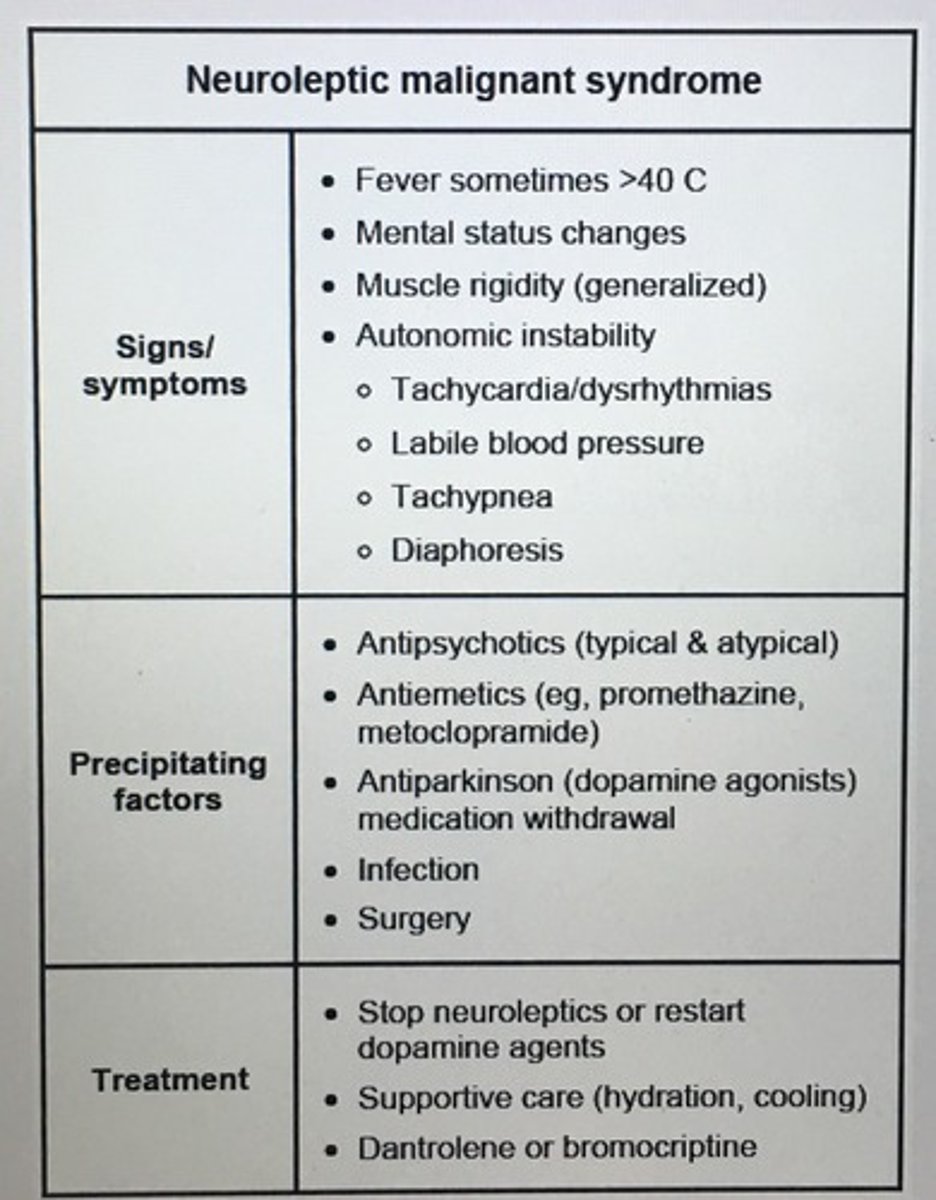
Clinical features of neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS)?
Hyperthermia
Autonomic instability
Muscle rigidity
Altered sensorium
Labs: elevated CPK, rhabdomyolysis -> myoglobinuria can lead to acute renal failure
Tx: D/c med antipsychotic (haloperidol), aggressive cooling, antipyretics, fluid/electrlyte repletion, alkaline diuresis in case rhabdo) give dantrolene sodium, amantadine, bromocroptine
Prolactinomas vs antipsychotic medications (risperidone) prolactin level difference?
Prolactinomas tend to product high levels of prolactin > 200 ng/mL
Antipsychotic meds cause hyperprolactinoma secondary to their dopamine blockage effect
Specific phobia clinical features and tx?

Treatment of acute mania
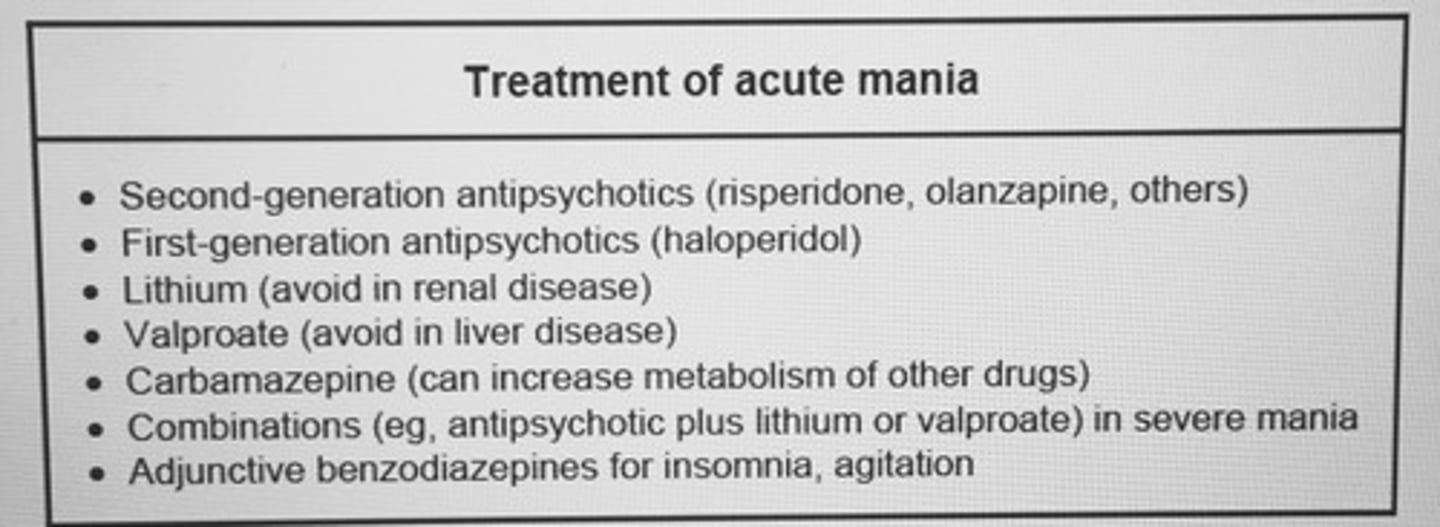
Bupropion should be avoided which pts?
DEC seizure threshold
- avoid pts w/ seizure disorders or conditions that predispose to seizures (concurrent alcohol or BZD use, eating disorders)
- hx of anorexia nervosa/bulimia is contraindicated to bupropion use
Acute psychotic pts should be assessed for?
- Suicidal/homicidal ideation
- Command hallucinations to hurt others or self
- Ability to care for self
* Indications for involuntary psychiatric hospitalization include being a danger to self or others and/or grave disability
Extrapyramidal SE of antipsychotics (rigidity, bradykinesia, tremor, and akathisia) can be tx with?
Anticholinergic meds like benztropine
Abrupt cessation of alprazolam, short acting BZD is associated with significant withdrawal symptoms such as ___.
Generalized seizures
Confusion
Antipsychotic extrapyramidal effect.
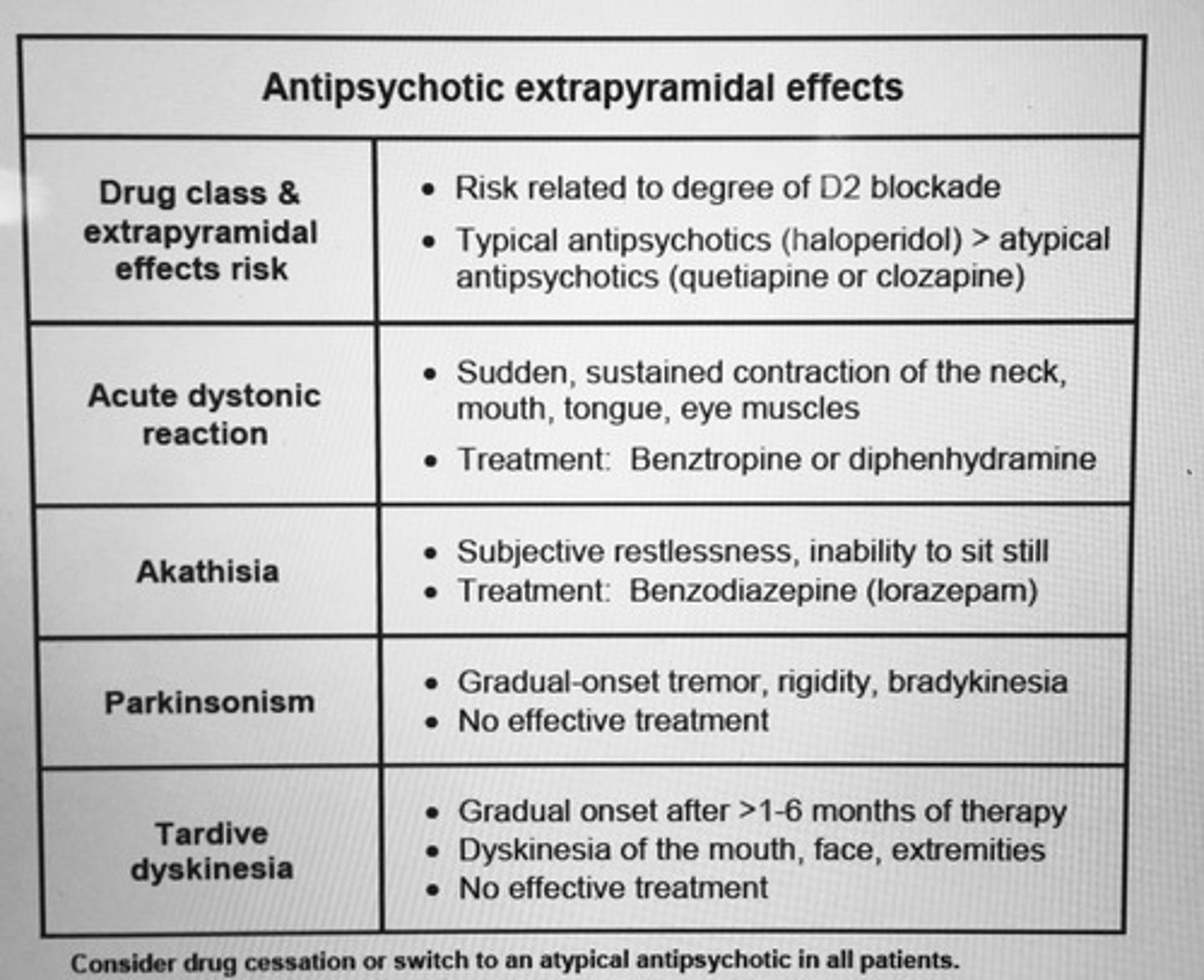
DSM-5 criteria Schizoaffective disorder.
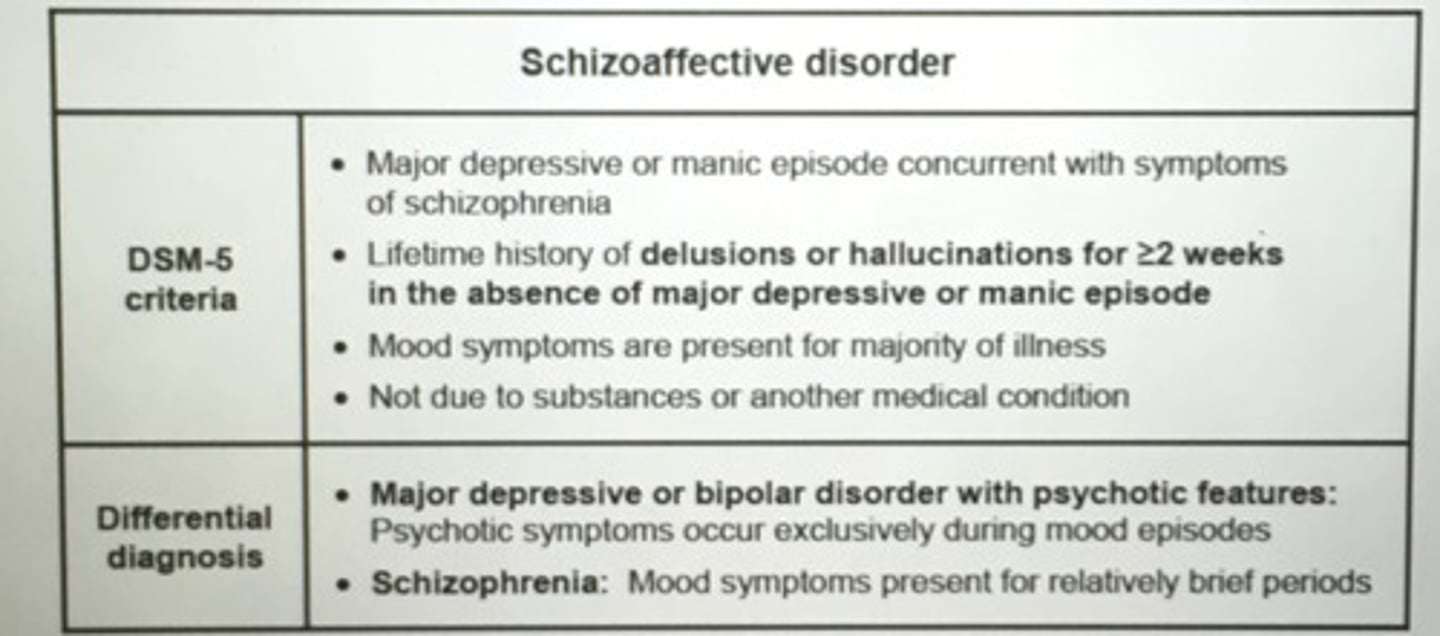
Conversion disorder common presenting symptoms.
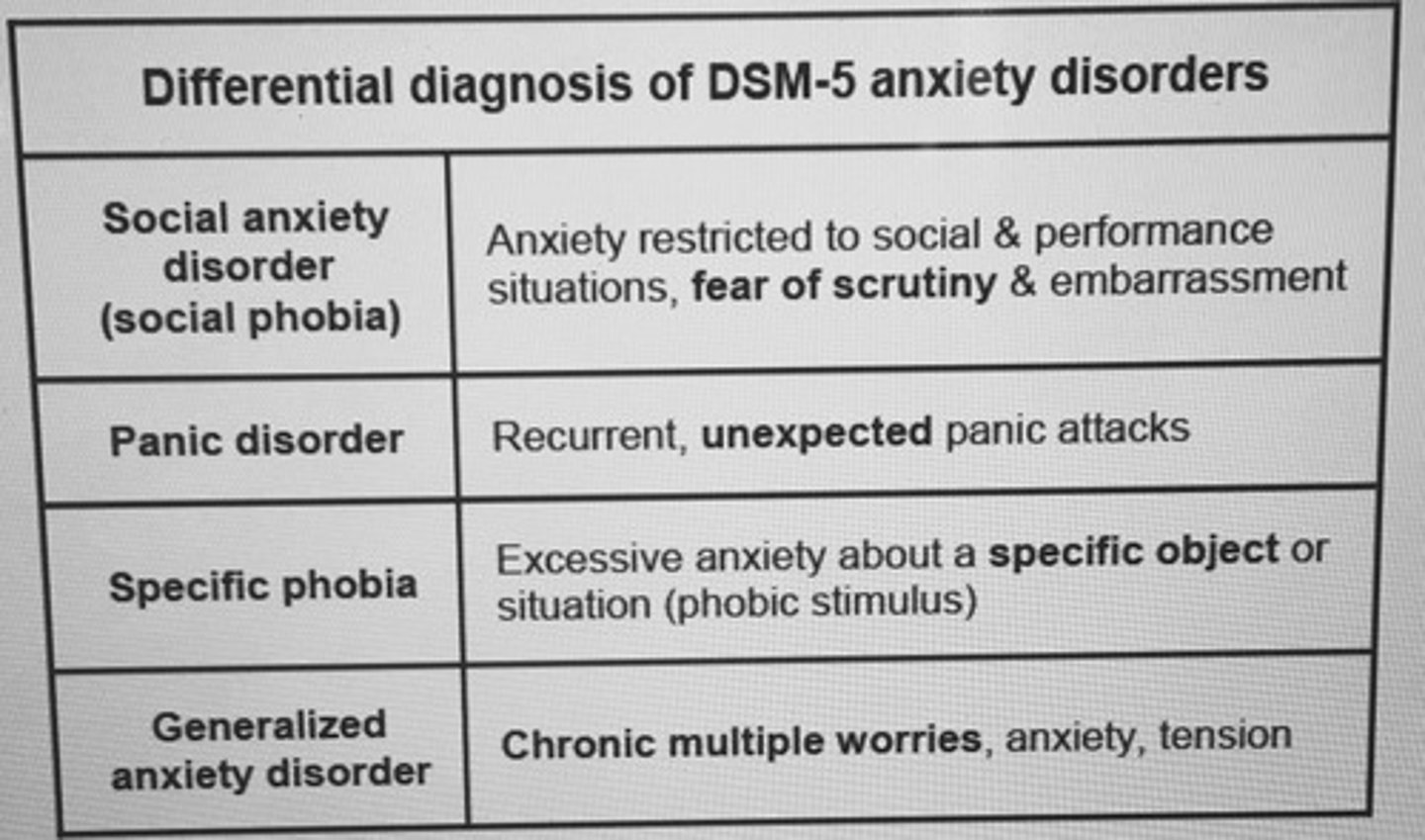
Differential diagnosis of DSM-5 anxiety disorders
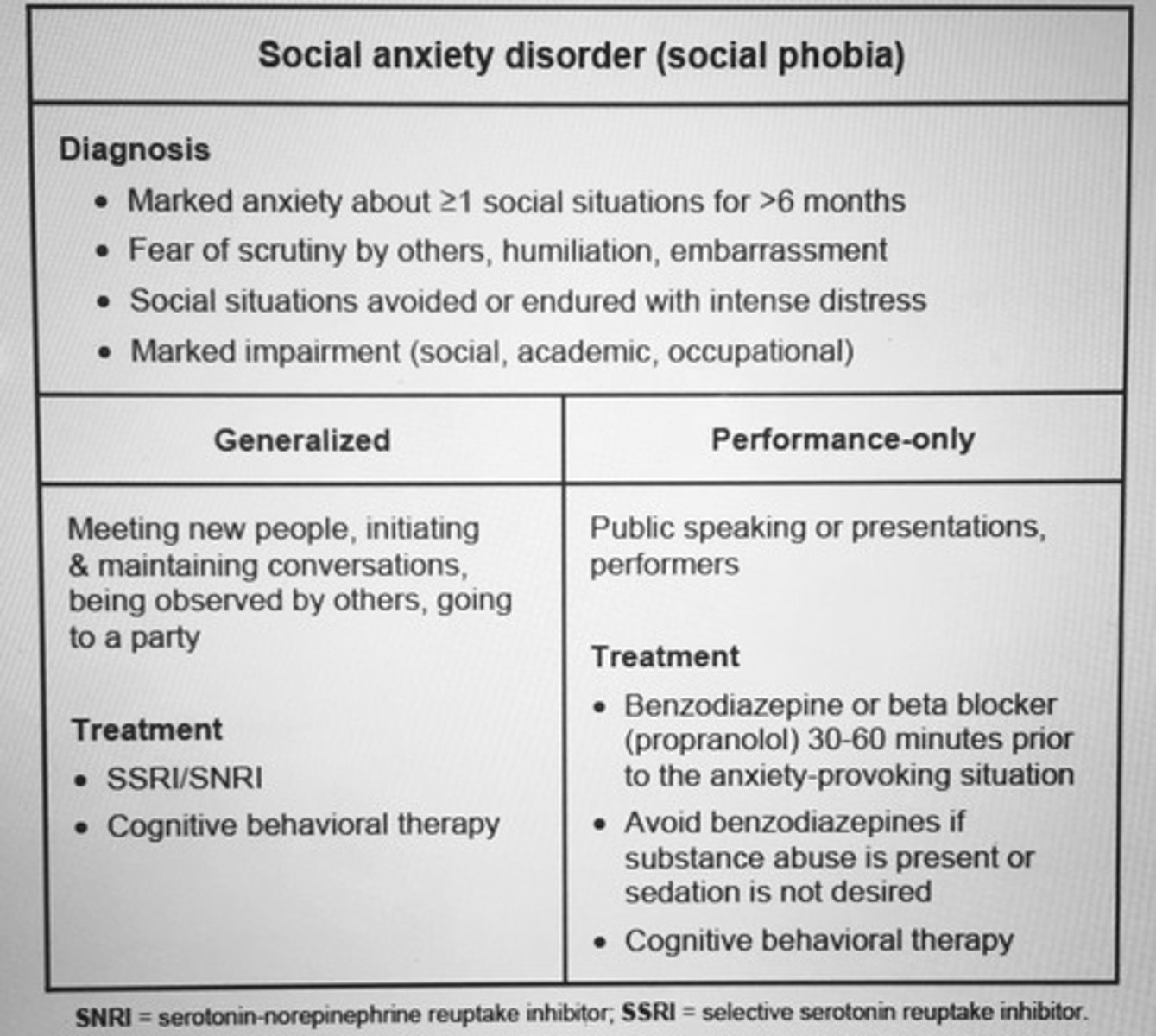
Social anxiety disorder generalized vs performance treatment.
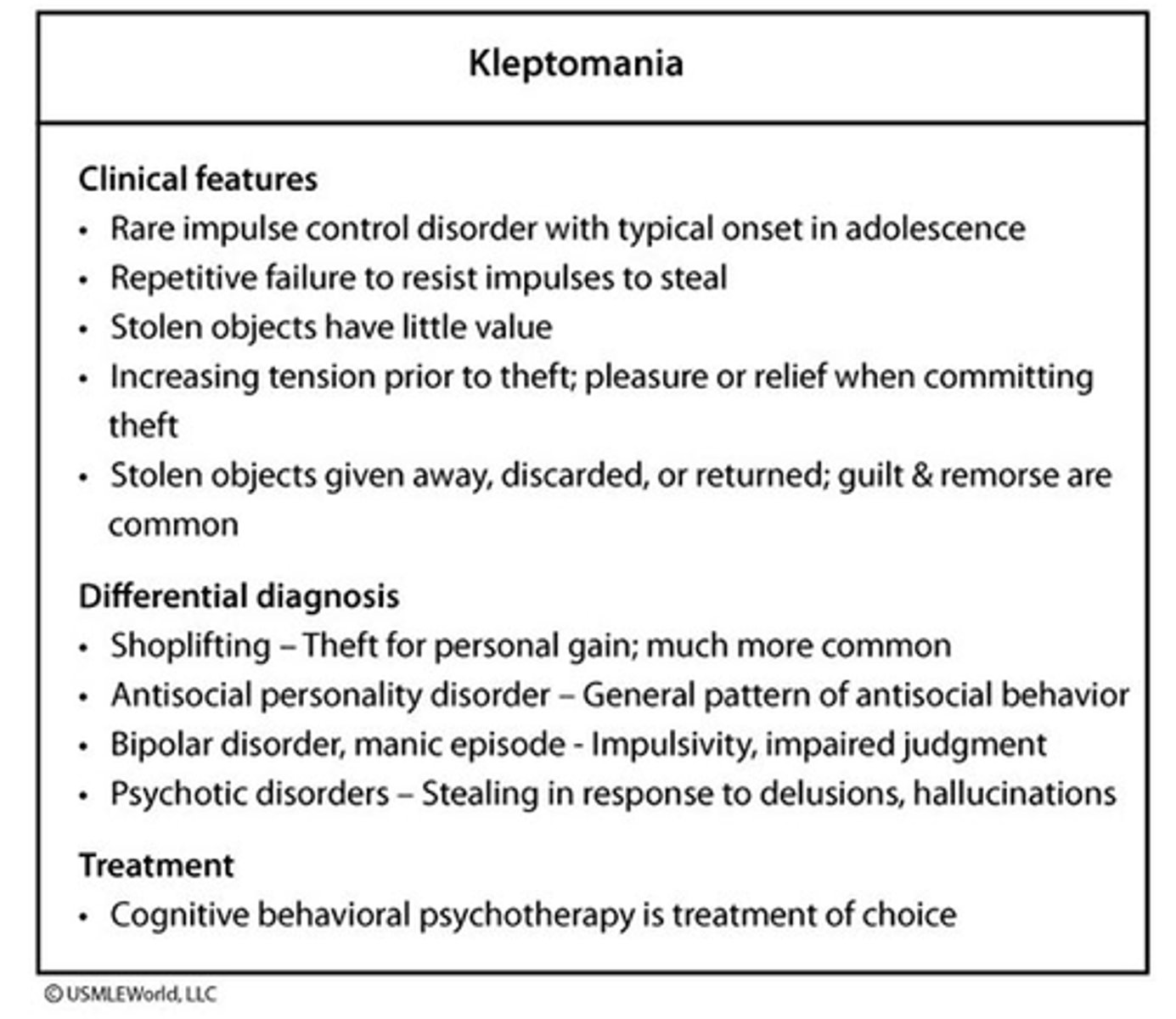
Kleptomania clinical features and treatment.
Hoarding disorder is responsive to tx with?
SSRI and CBT
Acute vs continuation vs maintenance phase of illness.
Acute phase:
- aim to achieve remission of the active sxs (absence or minimal symptoms, pt no longer meets dx criteria for the syndrome)
- Tx response: when pt demonstrates significant improve, 50% reduction in the baseline level of severity
Continuation phase:
- stabilize the pts revision (sustained remissions) prevent relapse, pharm that led to remission usually maintained during continuation phase
Maintenance phase:
- recovery signified that the episode is over and presents the option of the pt either D/C tx or continue maintenance therapy, following recovery subsequent episode is recurrence
High dose glucocorticoids often given for allergic, inflammatory, or autoimmune condition can cause which psych SE?
Glucocorticoid-induced psychosis
- substance/medication induced psychotic disorder
- can also cause manic or depressive symptoms
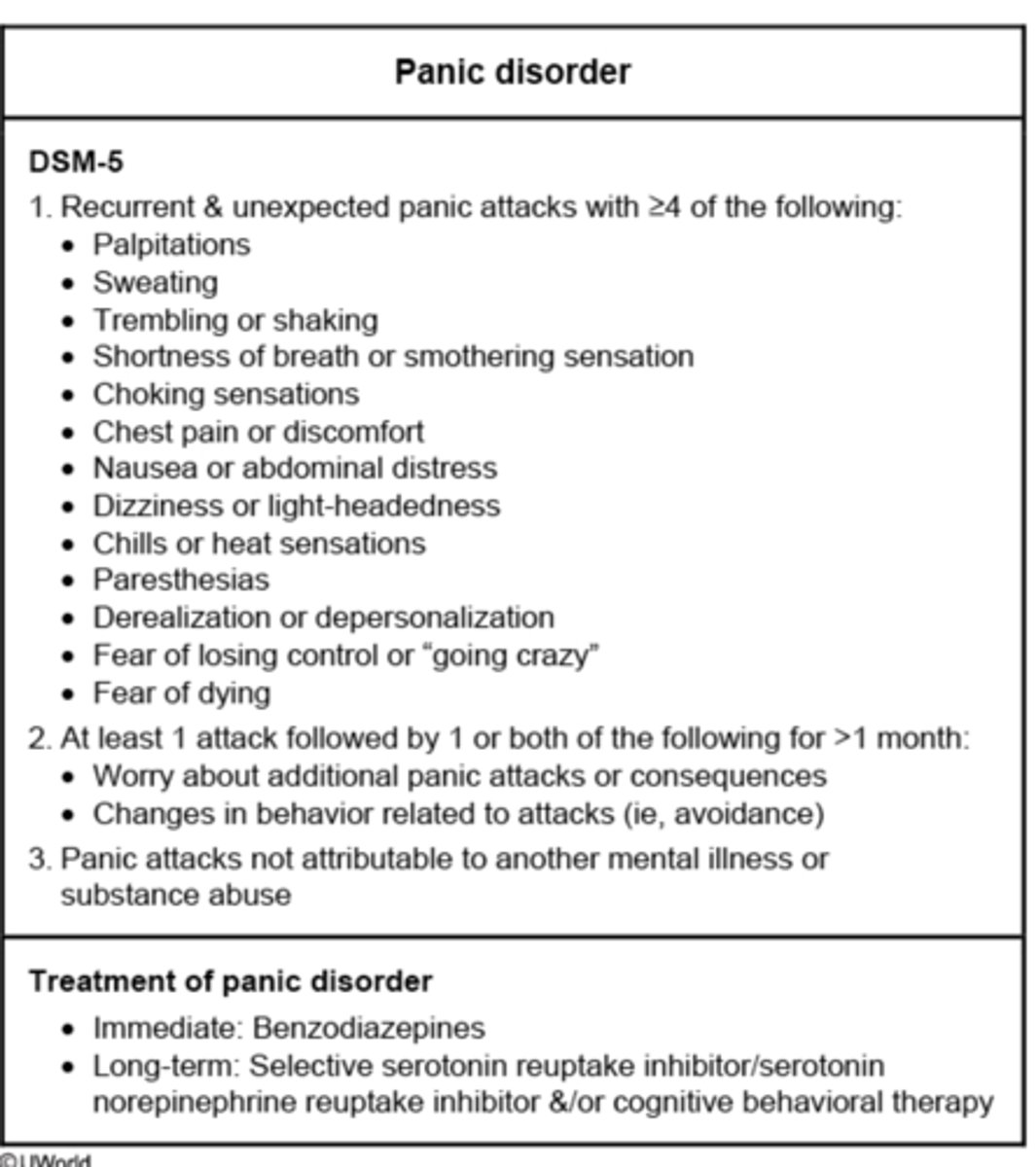
Panic disorder DSM-5 criteria and treatment.
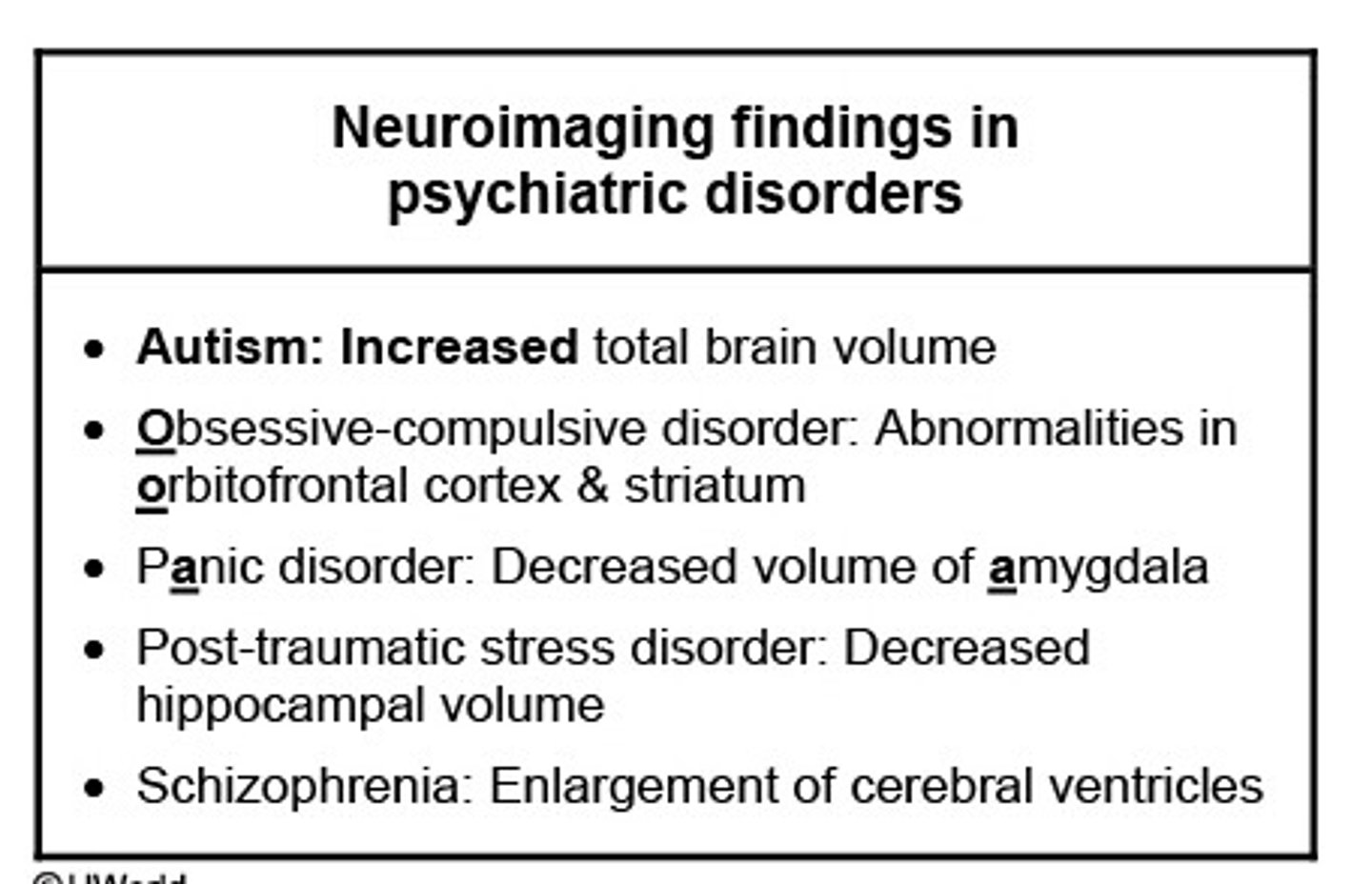
Neuroimaging findings in psychiatric disorders:
- Autism
- OCD
- Panic disorder
- PTSD
- Schizophrenia
Generalized anxiety disorder characterized by?
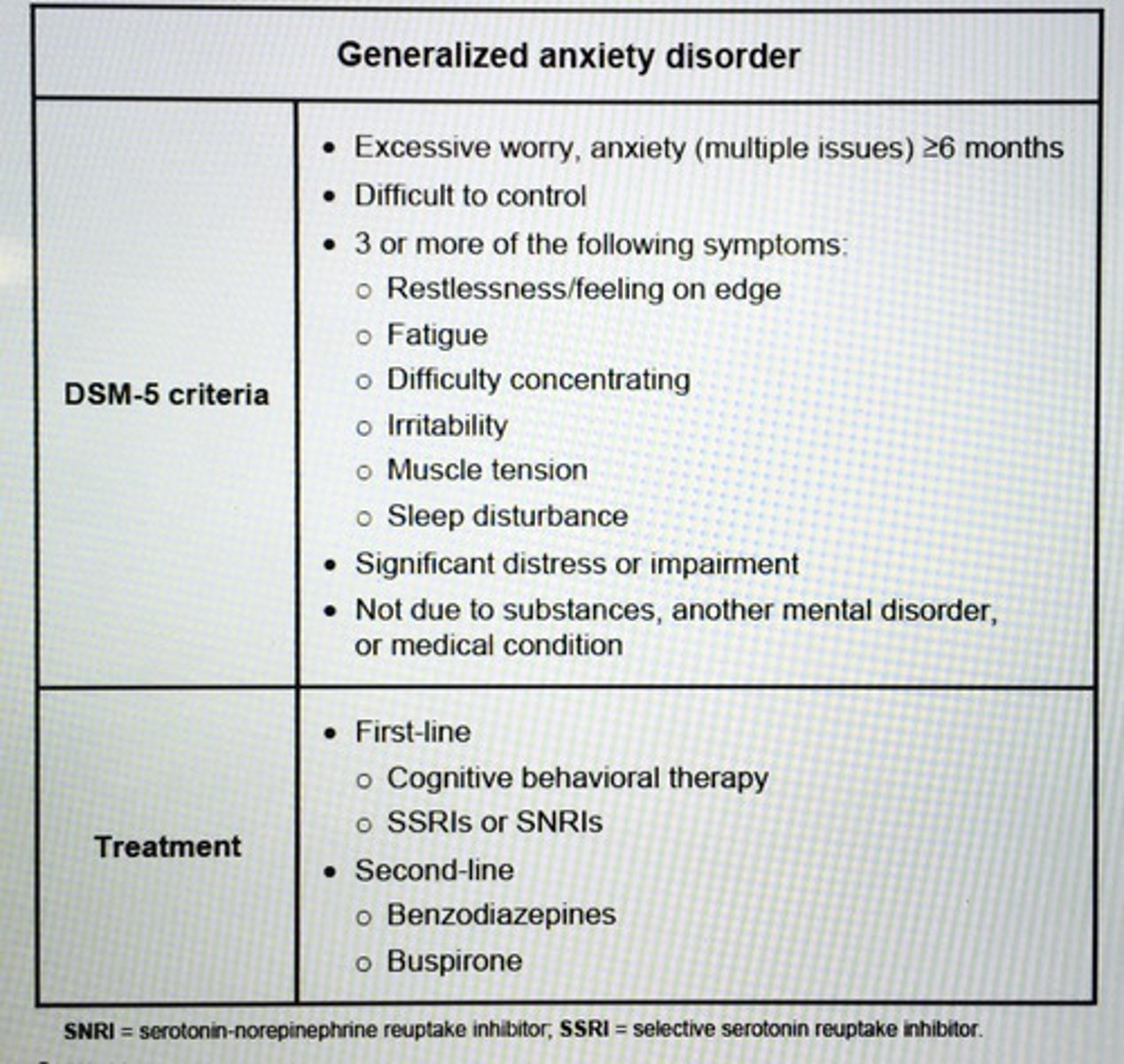
- Excessive anxiety about multiple events w/ 3 or more of the following:
- Impaired sleep
- Poor concentration
- Irritability
- Muscle tension
- Restlessness
- Easy fatigue
* for at least 6 mo.
Pt presents with inability to remember past, confusion about personal identity, and sudden unexpected travel. May assume new identities.
Dissociative fugue
Most common SE Olanzapine?
Sedation - antagonism H1
Wt gain - antagonism H1 and 5-HT2c receptors
Generalized anxiety disorder DSM-5 criteria and tx?
Monitoring guidelines when giving pts clozapine or olanzapine.
Baseline & regular follow-up:
- BMI
- Fasting glucose & lipid panel
- Blood pressure
- Waist circumference
Metabolic syndromes caused by these drugs
- Wt gain, dyslipidemia, hyperglycemia
A child with first-degree relative that has bipolar disorder then they have ___ % risk of developing the condition in their lifetime.
5-10%
* a child whose parents both suffer from bipolar disorder has 60% risk developing the condition
* Monozygotic twins ind. who from from bipolar disorder 70% chance
Borderline personality disorder, self injury which type of therapy?
Dialectical behavioral therapy
Substance use disorder which type of therapy?
Motivational interviewing
- address ambivalence to change
Comorbidities associated with panic disorder?
Major depression
Bipolar disorder
Agoraphobia (fear of public places)
Substance abuse
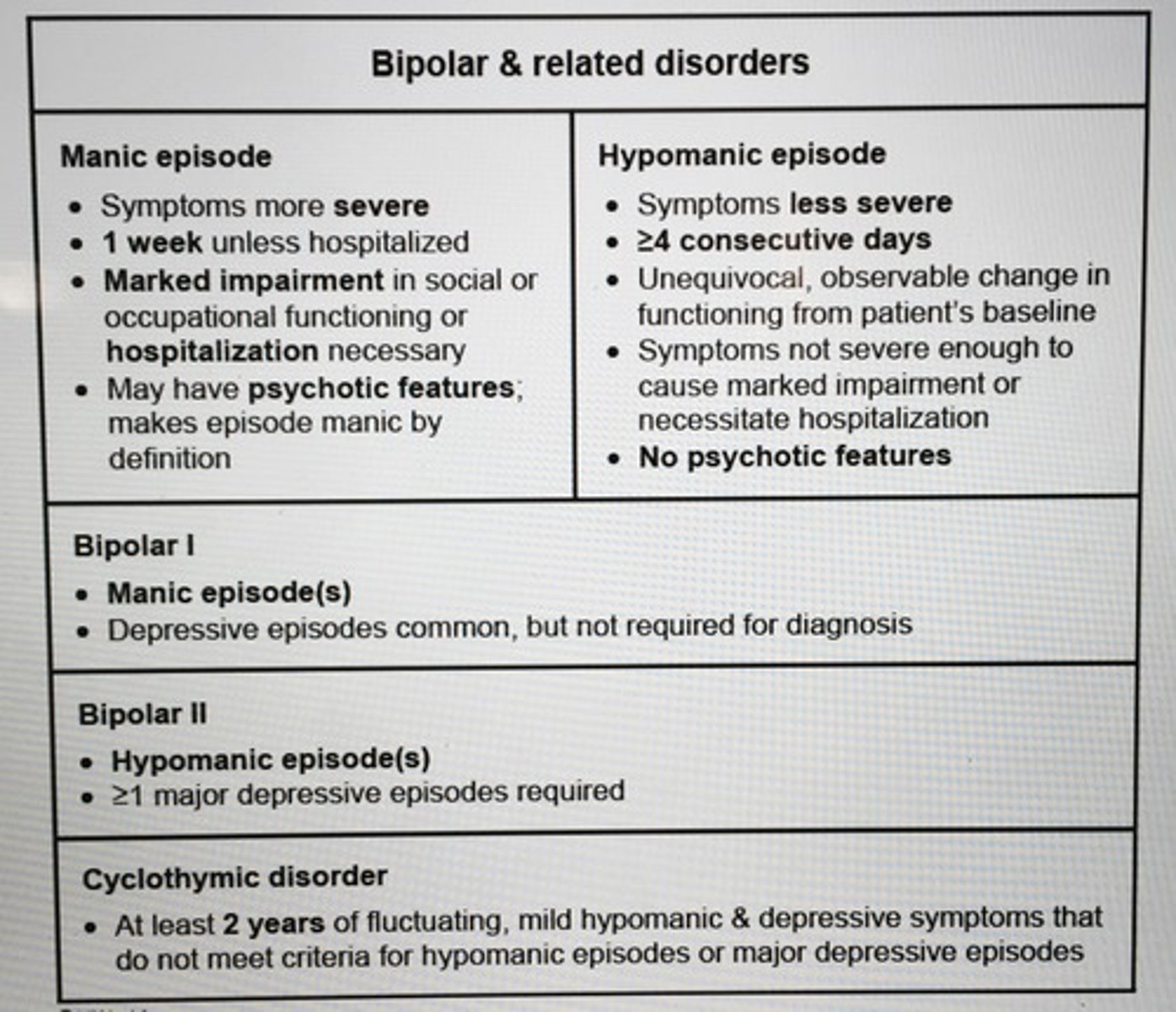
Bipolar I vs II vs Cyclothymic disorder
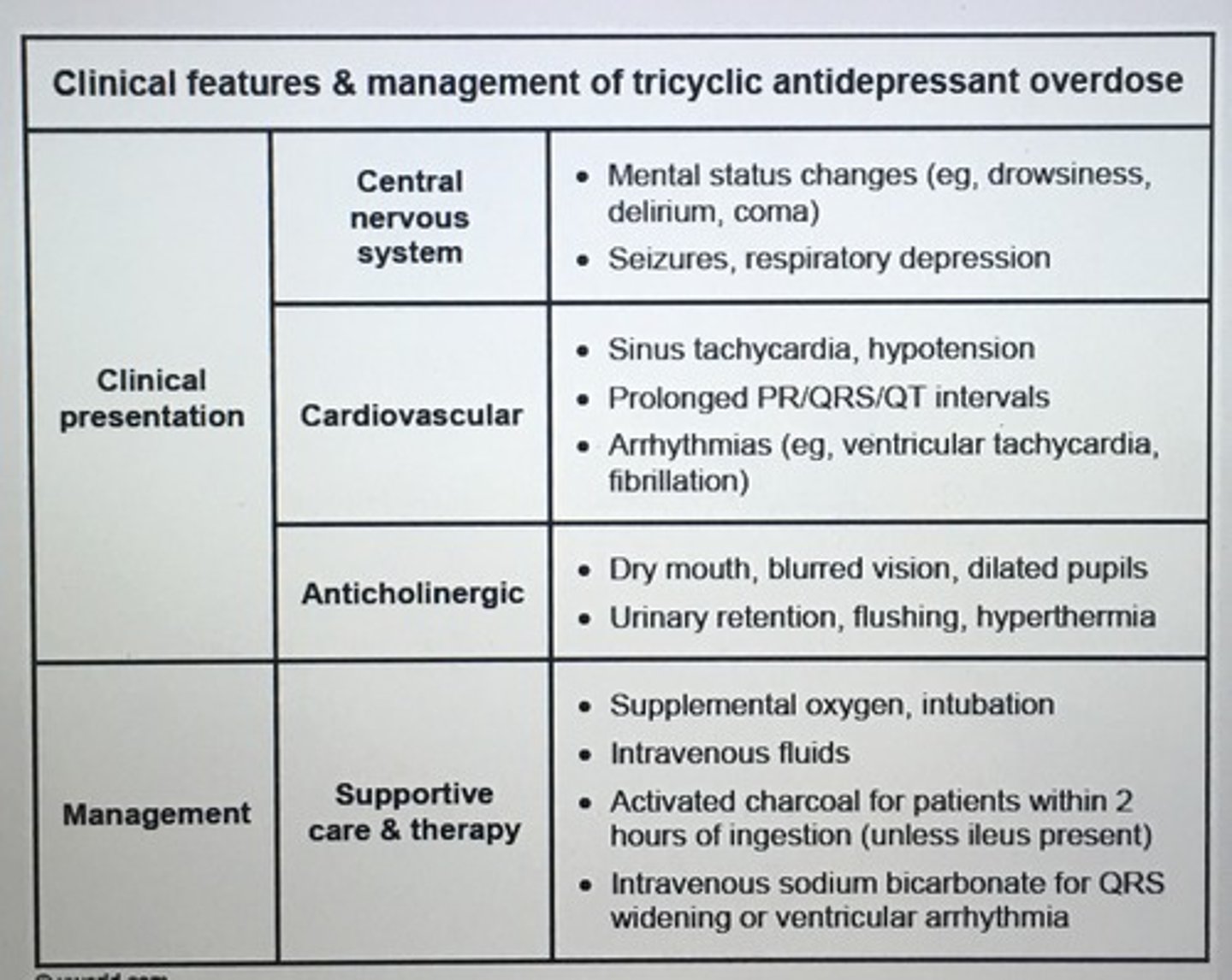
TCA overdose is characterized by CNS depression, hypotension, and anticholinergic effects including ____.
Dilated pupils
Hyperthermia
Intestinal ileus
QRS prolongation on EKG -> vent arrhythmias
Tx TCA overdose
Sodium bicarbonate and ABC's
- improve BP
- shorten QRS interval > 100 msec
- prevent arrhythmia
Sodium bicarb INC serum pH and extracellular Na, alleviating cardio-depressant action on sodium channels
Which antipsychotic can lead to extreme hypothermia?
Fluphenazine
- typical antipsychotic
- inhibits body's shivering mechanism and/or inhibiting autonomic thermoregulation
Recent onset confusion
Muscle rigidity
Diaphoresis
CK of 50,000
Dx.
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome
- tx with dantrolene, muscle relaxant or bromocriptine (dopamine agonist) and amantadine
Pts with ___ overdose present with slurred speech, unsteady gait, and drowsiness.
BZD overdose
Clinical features & management of TCA overdose
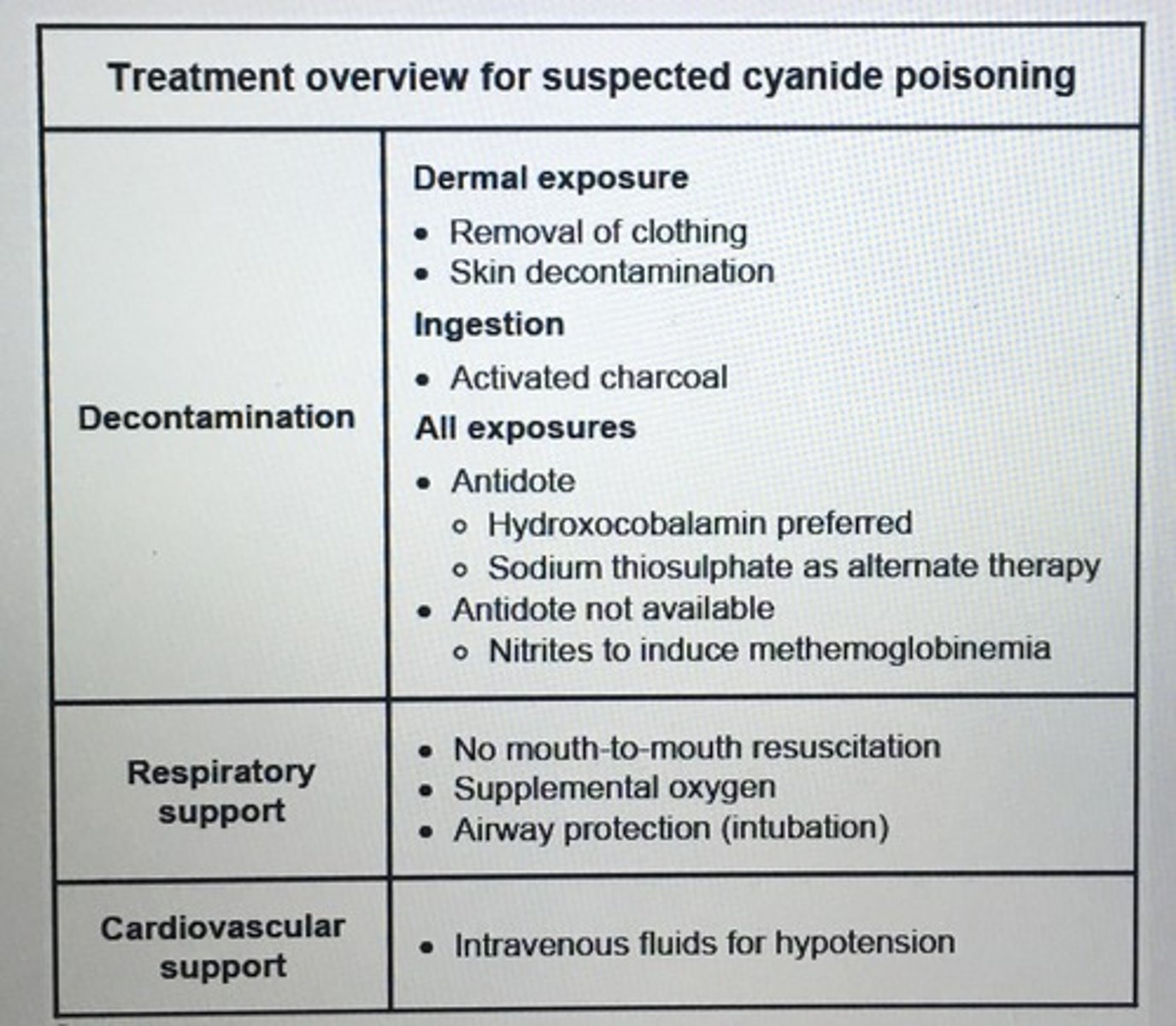
Treatment overview of suspected cyanide poisoning.
cyanide inhibits cytochrome oxidase a3 in mitochondrial ETC, blocks oxidative phosphorylation, promotes anaerobic metabolism, lactic acidosis
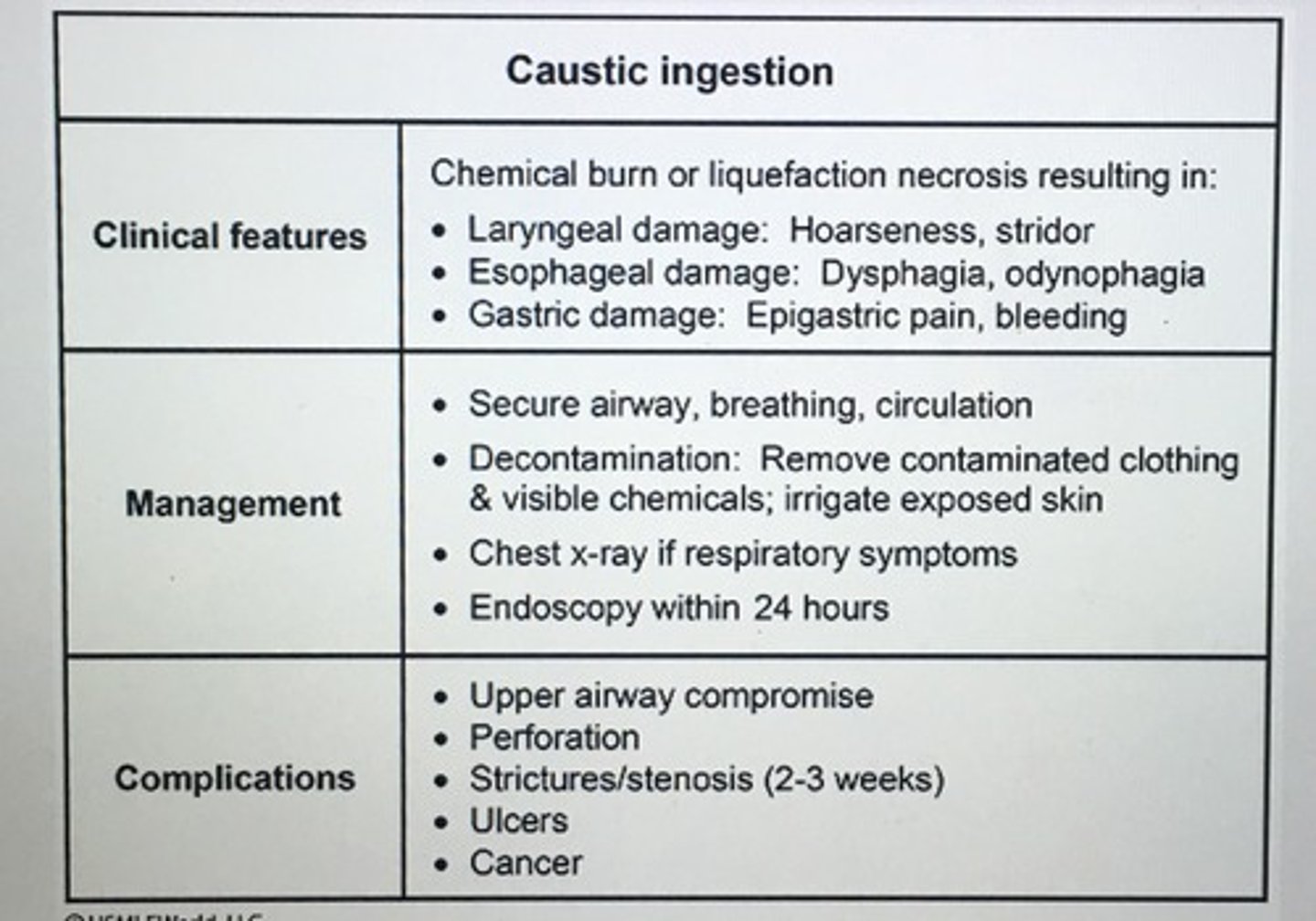
Caustic ingestion management.
Remove contaminated clothing
Endoscopy w/in 24 hours
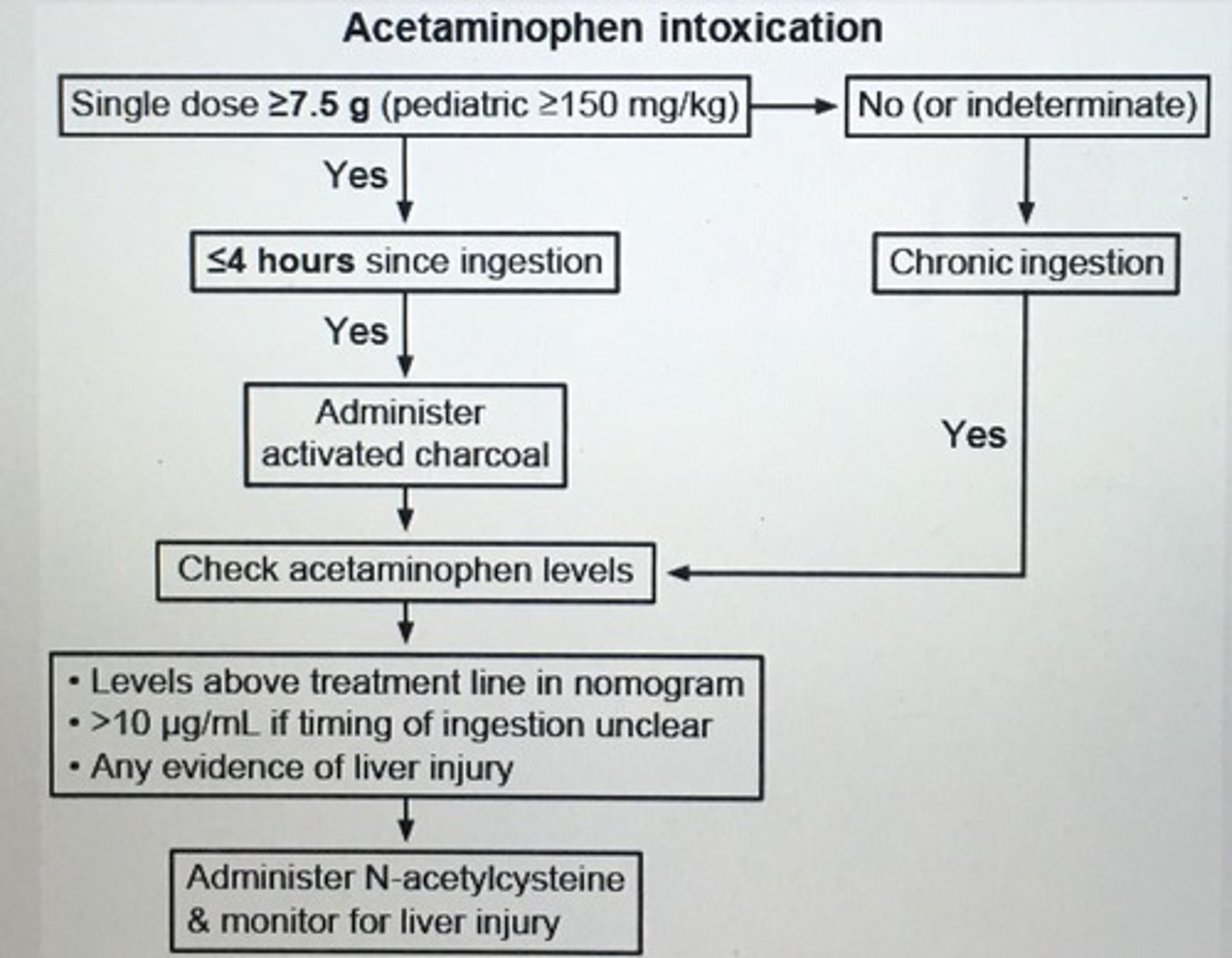
Acetaminophen intoxication
___ is associated with hypocalcemia and calcium oxalate deposition in kidneys. Leads to flank pain, hematuria, oliguria, AKI, and AGMA. Tx is with ___.
Ethylene glycol
- Fomepizole or ethanol to inhibit alcohol dehydrogenase
- sodium bicarbonate to alleviate the acidosis
- hemodialysis in case severe acidosis or end organ damage
Signs and symptoms of neuroleptic malignant syndrome
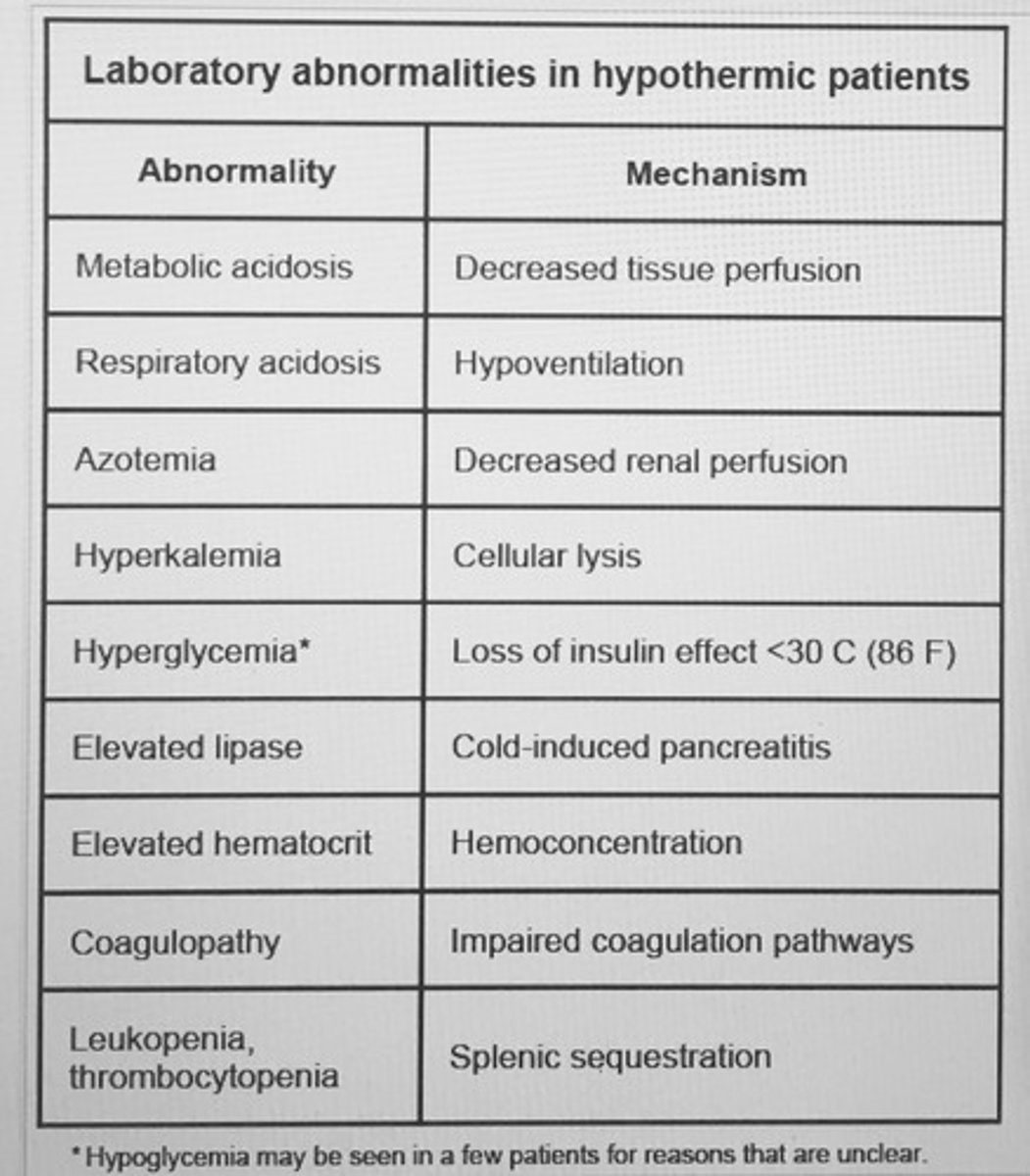
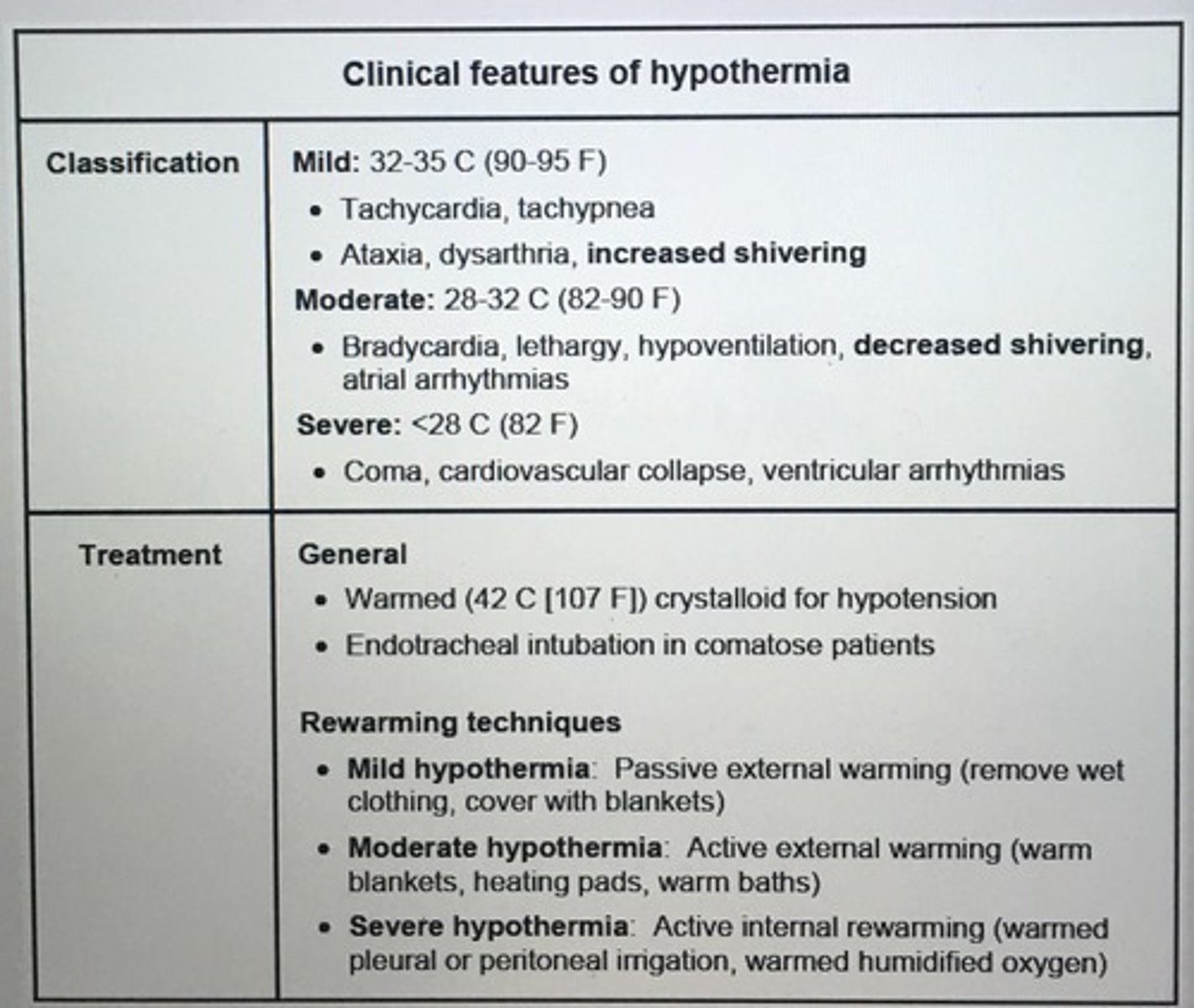
Clinical features of hypothermia
tx warm 1-2 C/hr
Laboratory abnormalities in hypothermic patients.