ANAT 3001 pathways and autonomics
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
sensory vs motor pathways
how information gets from body to brain and commands from brain to body
each pathway relayed by several neurons
ascending pathway
carry sensory information to brain
travel through ascending tracts in spinal cord
descending pathway
carry motor information from brain to targets
travel through descending tracts in spinal cord
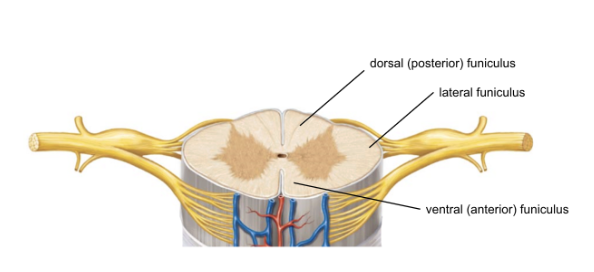
white matter
funiculi - functionally distinct regions of white matter in spinal cord
each contain multiple tracts
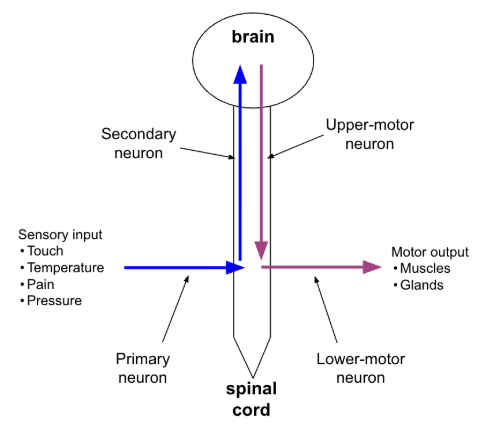
sensory pathways
utilize 2-3 neurons in a series to transmit information to brain
primary, secondary, & tertiary neurons
pathways
posterior funiculus
posterior funiculus
carries information on fine touch, pressure, conscious proprioception
medial lemniscal pathway (3 neurons)
primary neuron
secondary neuron
tertiary neuron
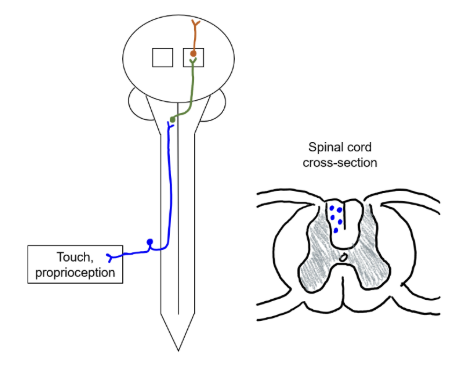
primary neuron
cell body in dorsal root ganglia
axon ascend in posterior funiculus to medulla oblongata
secondary neuron
cell body in medulla oblongata
axon cross over (decussate) in medulla oblongata (medial lemniscus tract), travel to thalamus
tertiary neuron
cell body in thalamus
axon travels to postcentral gyrus (primary somatosensory cortex)
motor pathways
originate in cerebral cortex (or cerebral nuclie), descend from brian
at least 2 neuron in pathway
upper motor neuron (UMN)
lower motor neuron (LMN)
UMN synapses with LMN directly or with interneurons
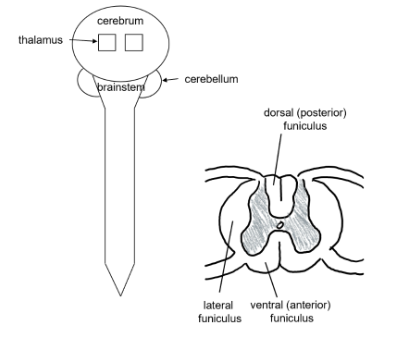
corticospinal tract
control precise, skilled voluntary movement (skeletal muscle)
corticospinal tract - UMN
cell body in pre central gyrus (primary motor cortex)
decussate at
medulla oblongata - lateral funiculus
spinal cord - ventral funiculus
corticospinal tract LMN
cell body in ventral horn of spinal cord
axon travels to target in body
functional organization of the nervous system
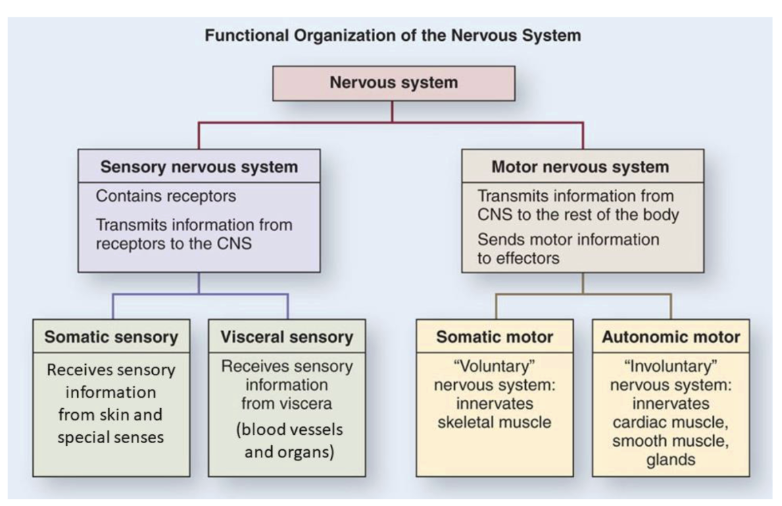
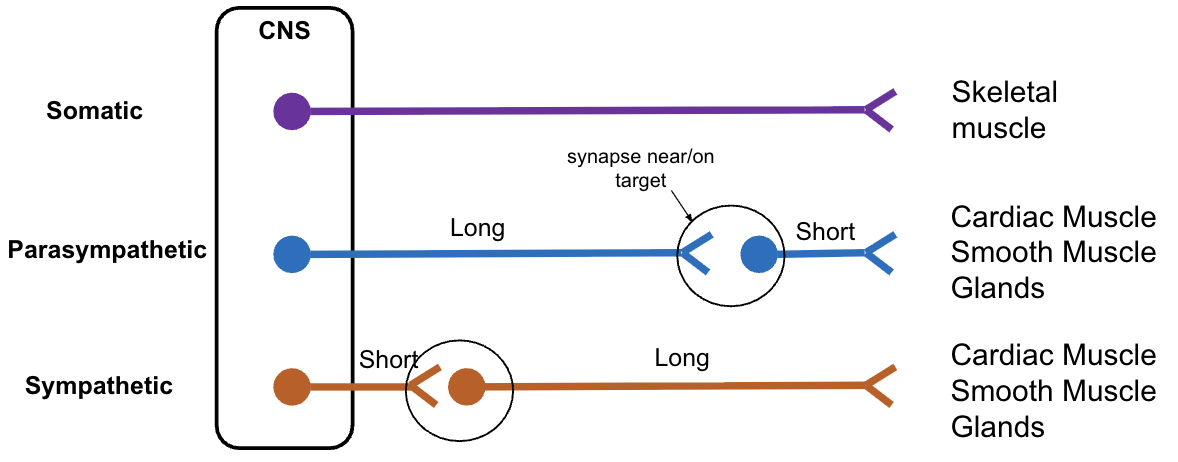
somatic vs visceral: sensory neurons
visceral sensory is very similar to somatic sensory neurons
both have a single neuron pathway in PNS
both have cell bodies in dorsal root ganglia & synapse in dorsal horn
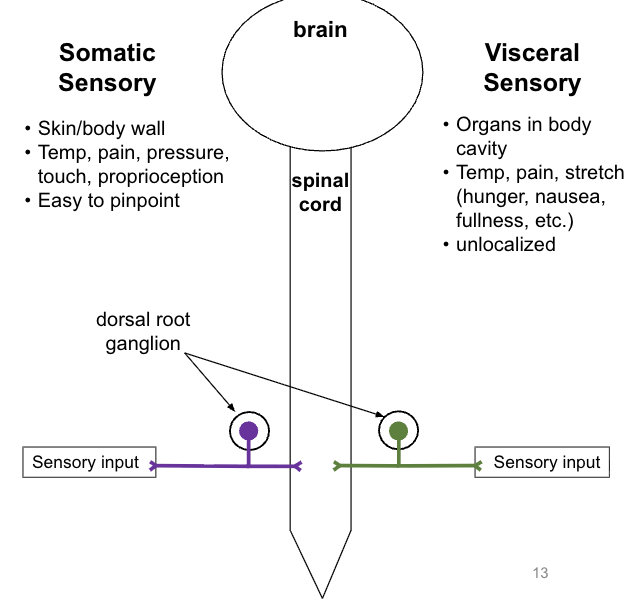
somatic vs visceral: motor neurons
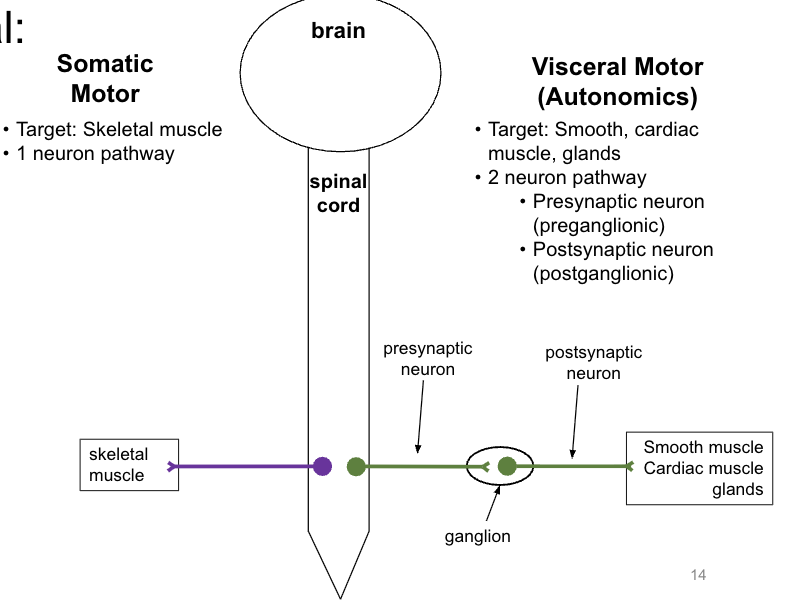
visceral motor innervation (autonomics)
generally to structures in body cavities (not always)
cardiac muscle (myocardium of heart)
smooth muscle (digestive tract, bronchi, blood vessels, eye muscles)
glands (salivary, digestive, lacrimal, reproductive, sweat glands)
unlike somatic motor, can excite or inhibit the target
regulates below conscious level (deep to cortex): heart function, blood pressure, body temp, respiration, sweating, digestion
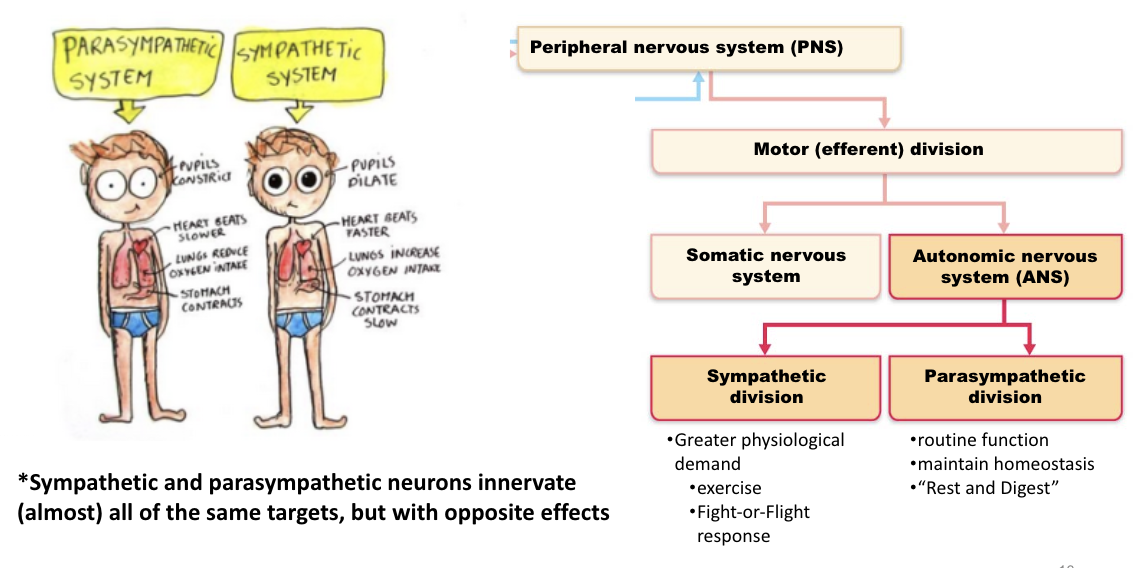
sympathetic vs, parasympathetic
motor neuron comparison
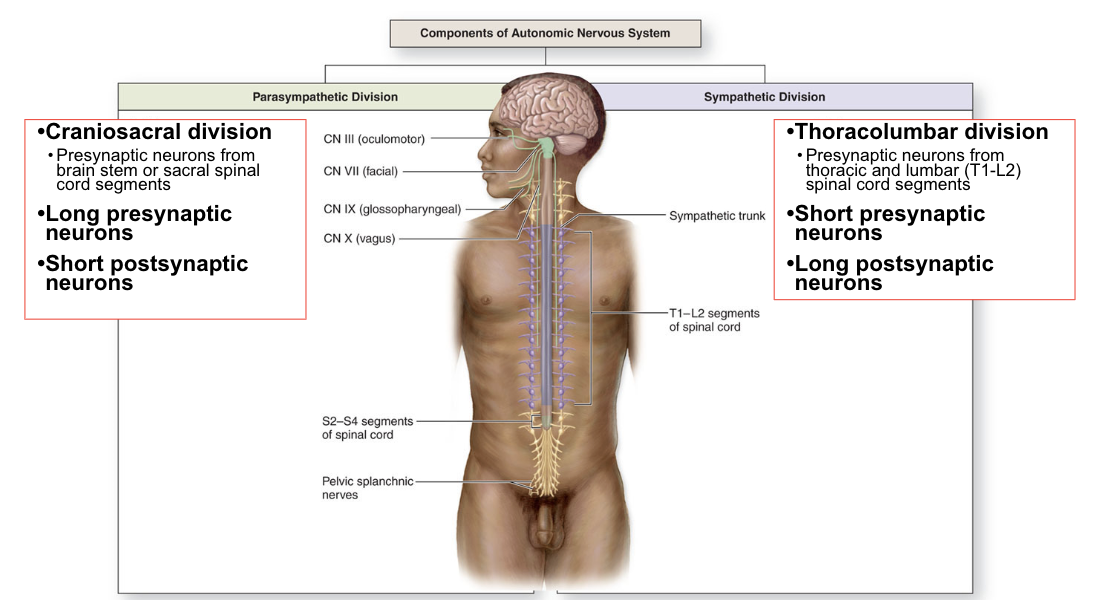
components of autonomic nervous system
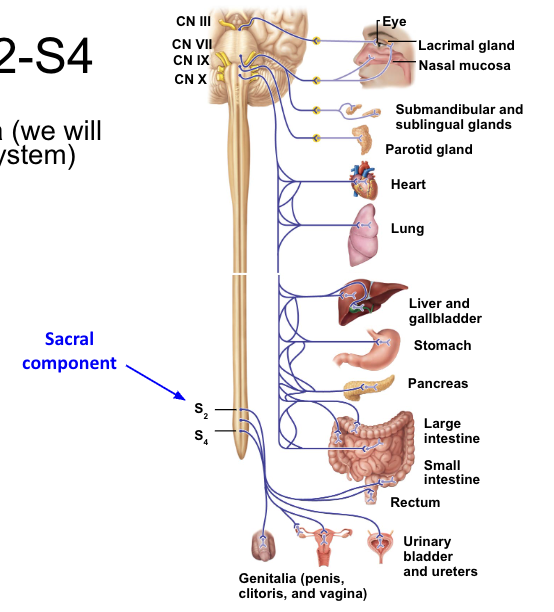
parasympathetics - cranial nerves
oculomotor nerve (CN III)
facial nerve (CN VII)
glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
vagus nerve (CN X)
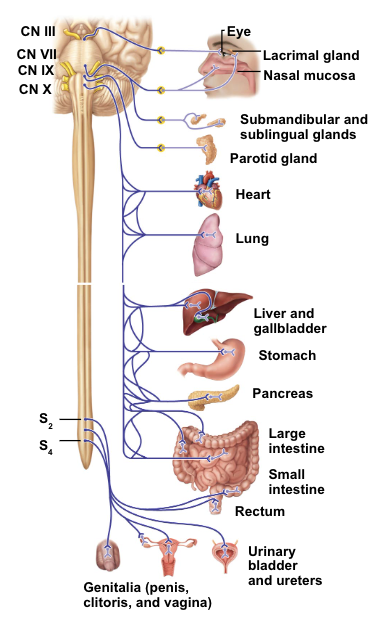
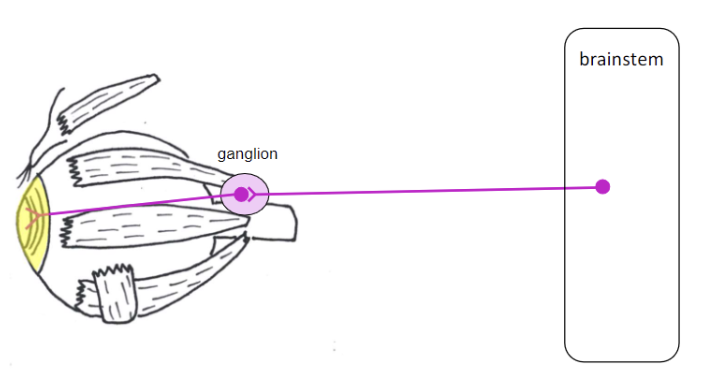
oculomotor nerve (CN III) - targets
pupil - constrict pupil
contract sphincter pupillae muscle
lens - thicken lens
ciliary muscle
lens
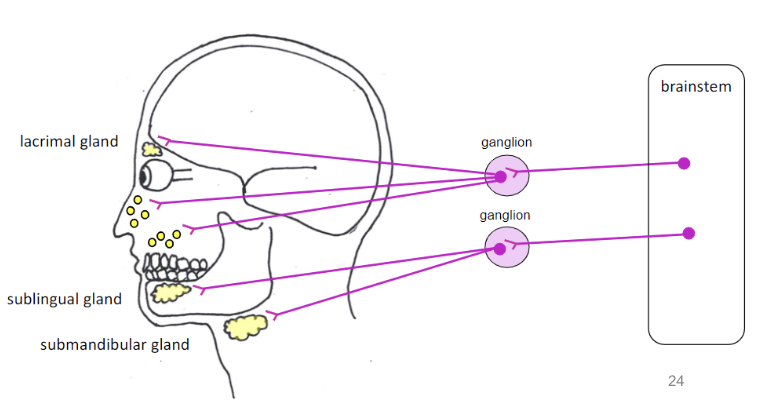
facial nerve (CN VII) - targets
lacrimal gland - produce tears (lacrimation)
submandibular and sublingual salivary glands - produce saliva (salivation)
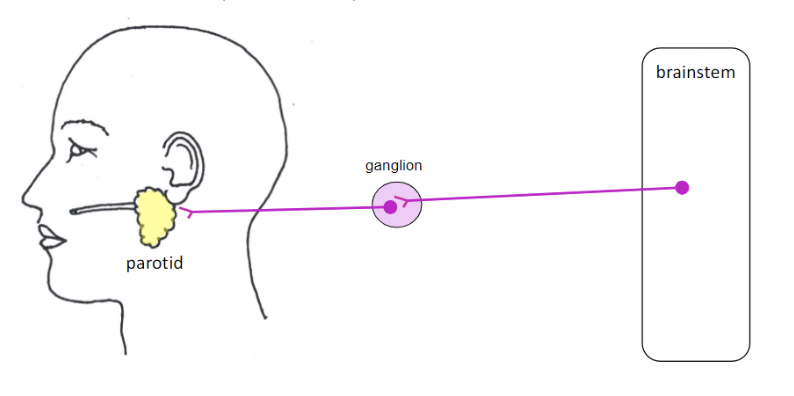
glossopharyngeal nerve CN IX - targets
parotid salivary gland - produce saliva (salivation)
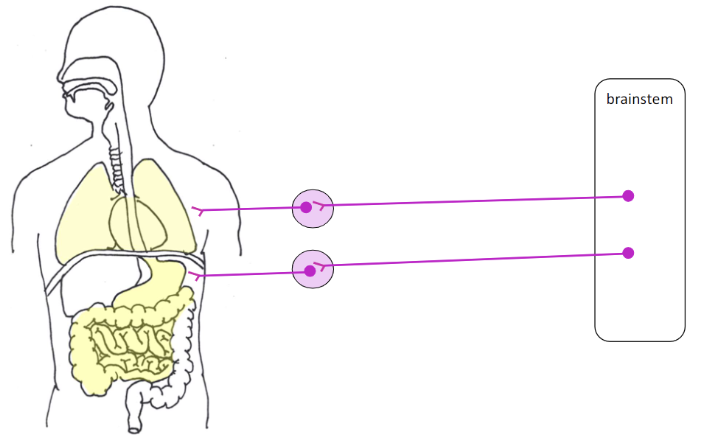
vagus nerve CN X - targets
lungs - constrict bronchioles
decrease air to lungs
heart - decrease heart rate
GI tract - increase activity of digestive system
parasympathetics: S2-S4
pelvic organs & external genitalia
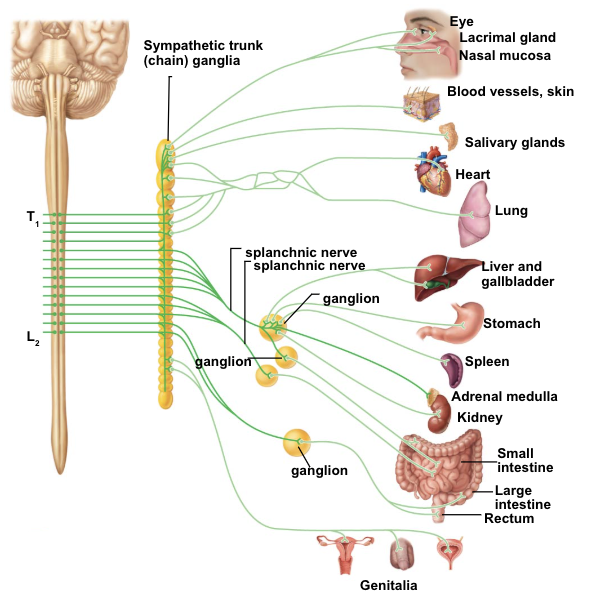
sympathetics - targets & effects
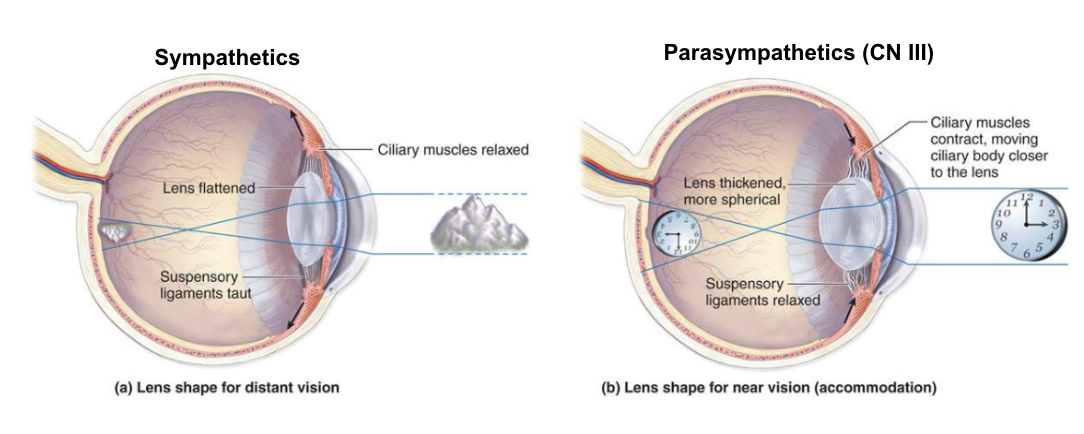
pupil - dilate pupil
lens - thin lens
lacrimal gland - decrease tear production
salivary glands - decrease saliva production
lungs - dilate bronchioles (increase air to lungs)
heart - increase heart rate
GI tract - decrease activity of digestive system
sweat glands - produce sweat
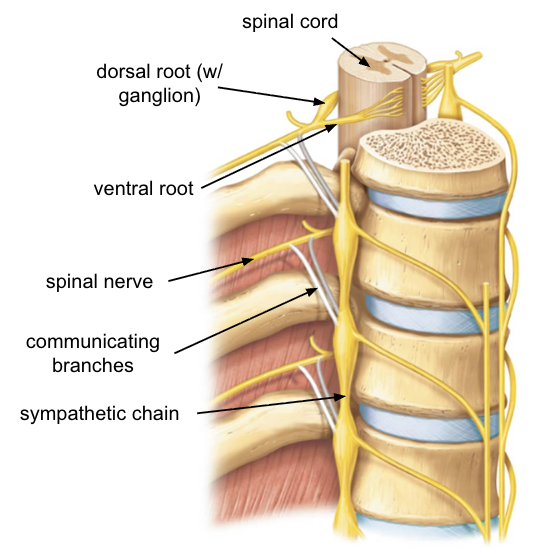
sympathetic chain (trunk)
nerve “chain” with ganglia
pre and postsynaptic sympathetic neurons synapse in ganglia
presynaptic cell bodies in lateral horn os spinal cord between T1-L2
ganglia in sympathetic trunk contain cell bodes of postsynaptic neurons
allows for sympathetic neurons to travel up and down thoracolumbar region
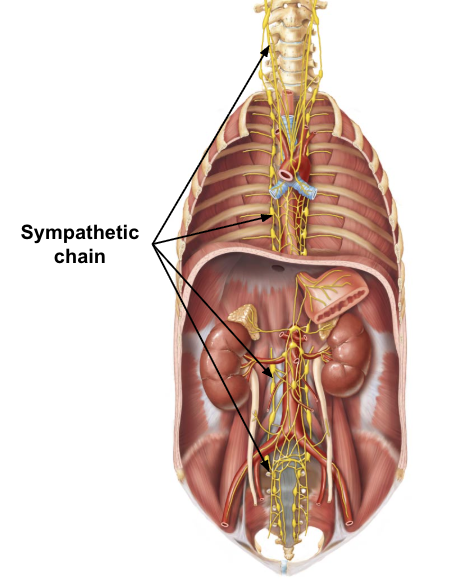
sympathetic chain (trunk) connection
sympathetic chain connects to spinal nerves via short, communicating branches
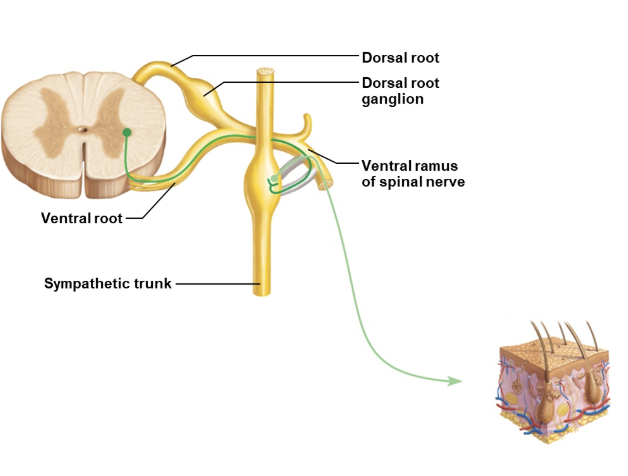
how do sympathetics get to the body wall (pathway 1)
pathway 1
presynaptic neuron enters sympathetic trunk
synapses with postsynaptic neuron in chain ganglion
postsynaptic neuron rejoins spinal nerve to body wall target
targets (no not have parasympathetic innervation)
sweat glands
blood vessels
arrector pilli muscles
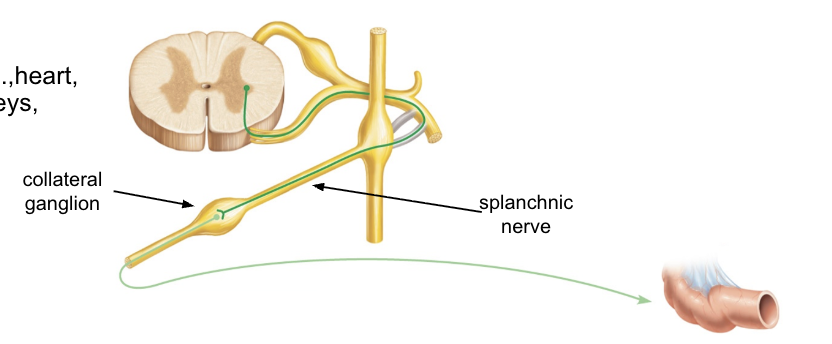
how do sympathetics get to the body cavity (pathway 2)
pathway 2
presynaptic neuron enters sympathetic trunk
joins splanchnic nerve
synapses with postsynaptic neuron at collateral ganglion
postsynaptic neuron travels to target
targets
visceral organs (heart, digestive tract, kidneys, uterus)
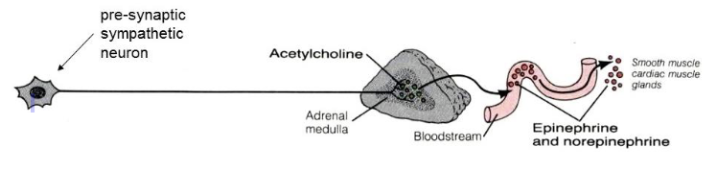
fight or flight response (pathway 3)
pathway 3
presynaptic neuron enters sympathetic trunk and pass through without synapsing
presynaptic neuron travels directly to adrenal gland to synapse with cells in the medulla
cells in adrenal medulla release epinephrine (adrenalin) and norepinephrine directly into bloodstream for rapid, systemic effect
fight or flight
sympathetic division responding to emergency situation