Adrenal Gland & Pineal Gland & Pancreas & Ovaries/Testes & Thymus & Other Organs - Chapter 17
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
gl twin 😭

Adrenal Gland Location
Sits atop the kidneys and is a retroperitoneal organ.
Btw is glandular tissue
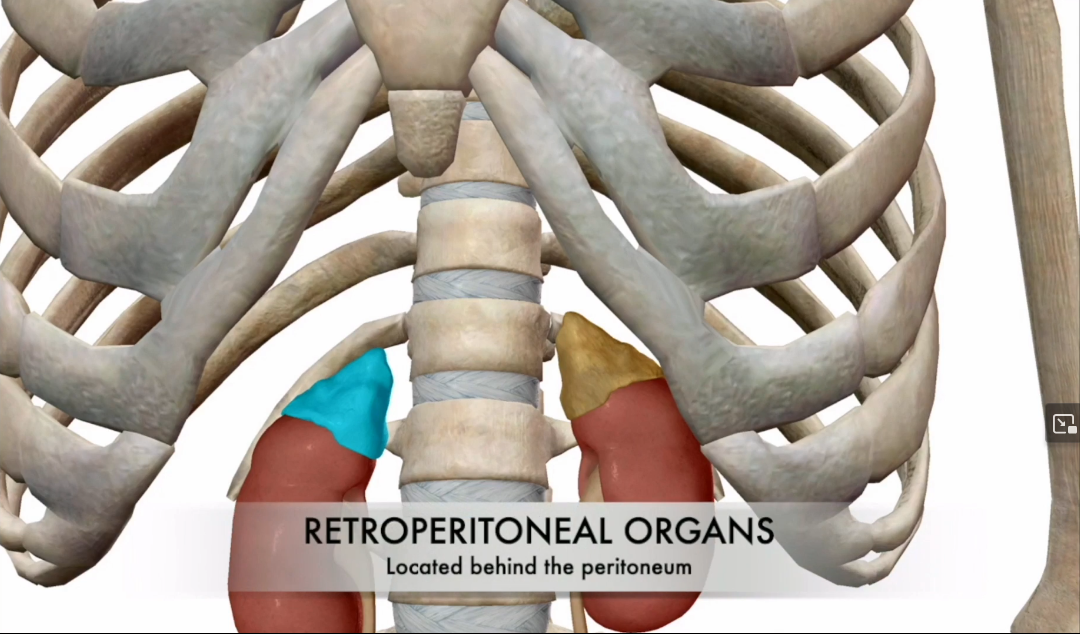
What are the two parts of the Adrenal Gland?
Cortex
Medulla
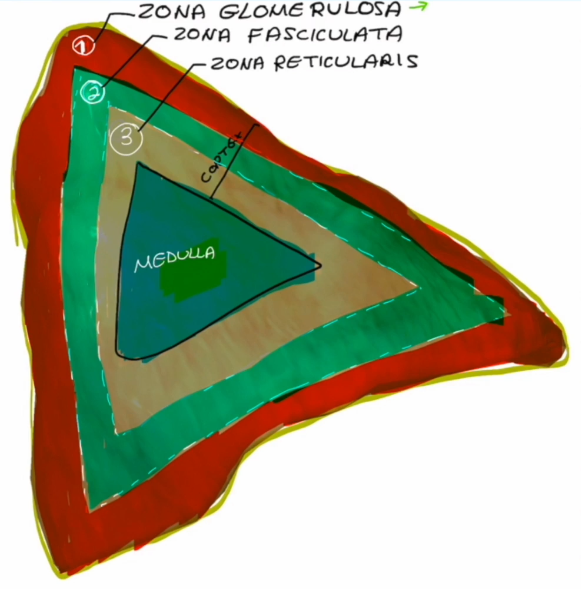
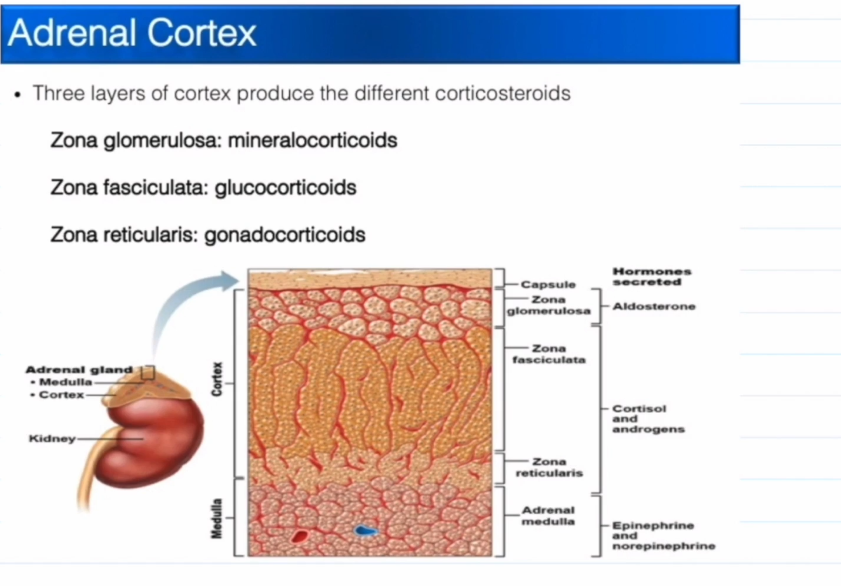
Cortex layers, superficial to deep:
Zona Glomerulosa
Zona Fasciculata
Zona Reticularis

Zona Glomerulosa Hormone:
Mineralocorticoids (Aldosterone)
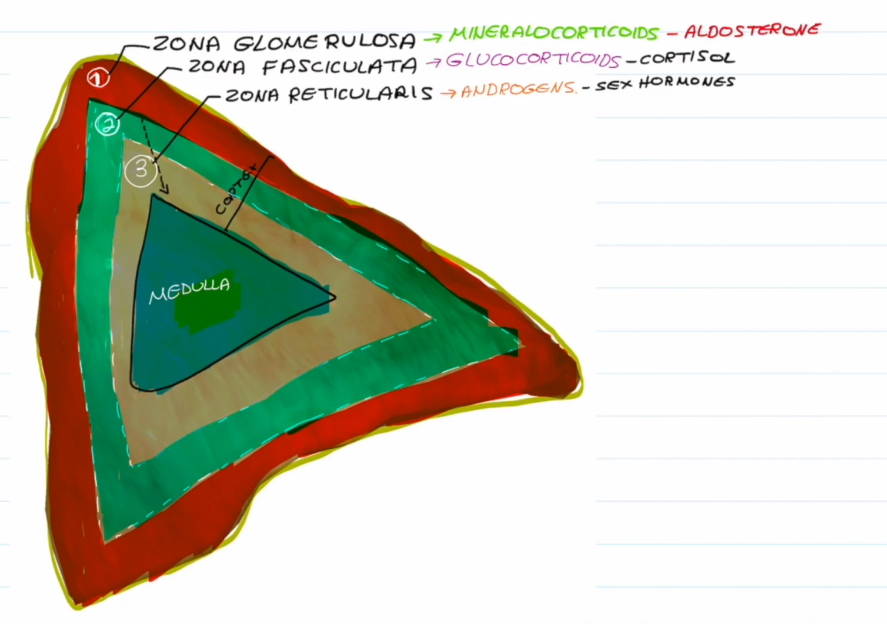
Zona Fasciculata Hormone:
Glucocorticoids (Cortisols)
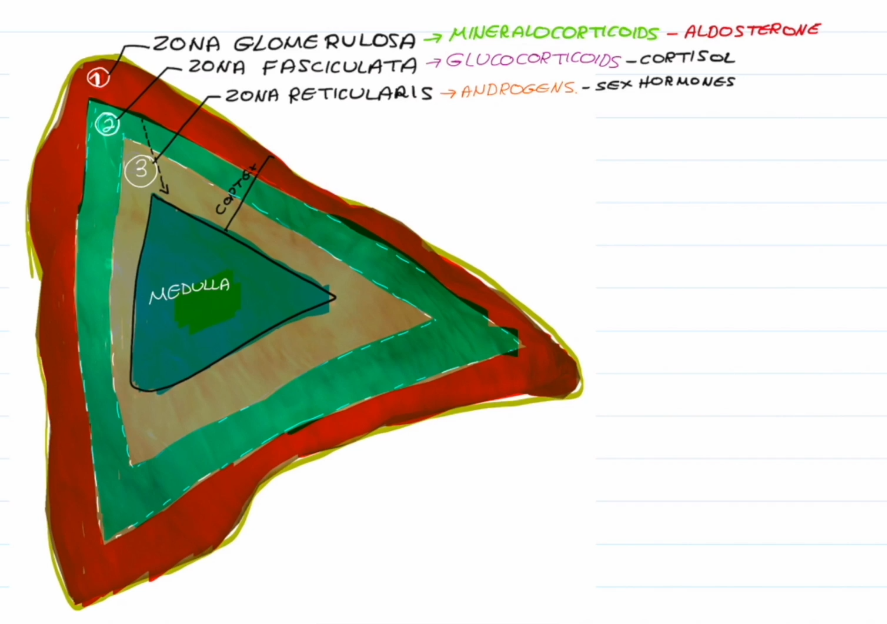
Zona Reticularis
Androgen (Sex Hormones)

What kind of tissue is the medula and what does it release?
Medula is neural tissue and releases epinephrine and norepinephrine
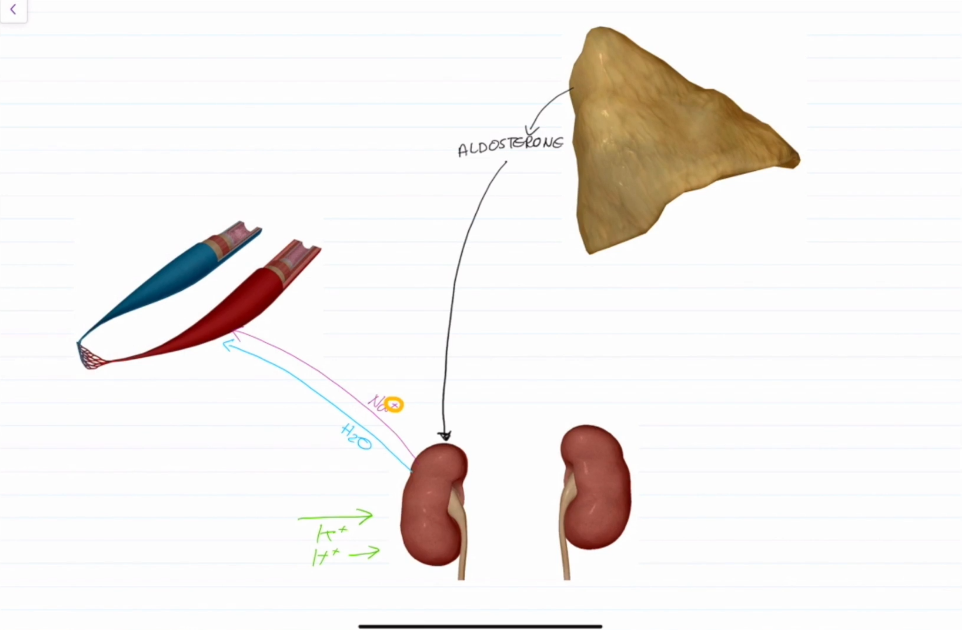
What do Mineralocorticoids do?
Mineral = ions Na+ and K+
Na+ effects Extracellular Fluid (ECF) Volume, blood volume, and therefore blood pressure
K+ sets resting membrane potential of cells.

Aldosterone Function
Most potent of the mineralocorticoids.
Stimulates Na+, and therefore water reabsorption into the blood via the kidneys.
Eliminates K+ and H+ from the blood back into the kidneys
Glucocorticoids Function
Keep blood glucose levels relatively constant
Maintain blood pressure by initiating vasoconstriction.
Ts the stuff that make u stress out
Hypothalamus releases CRH (Corticotropin releasing hormone → Anterior Pituitary Gland releases ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic Hormone) → Adrenal gland (Zona Fasciulata) releases cortisol)
Preforms Glucogenesis uses fat to turn protein into carbohydrates for immediate energy when stressed.

Gonadocorticoids (Sex Hormones) Function
Weak androgens are converted to testosterone in males and estrogen in females.
They contribute to the onset of puberty, secondary sex characteristics, sex drive in females, and estrogens in postmenopausal women
Medullary Chromaffin Cells Function
Produce 80% epinephrine and 20% norepinephrine
Causes vasoconstriction, increased heart rate, increaes blood glucose levels, shunts blood to yo muscles

Hypersecretion of Glucocorticoids
Called Cushing’s Syndrome (Disease if tumor is present)
Depresses the cartilage and the bone
Inhibits inflamation
Depresses the immune system

Hyposecretion of Glucocorticoids
Decrease in glucose and sodium in the blood
Causes weight loss, dehydration, and hypotension

Pheochromocytoma
Tumor located in the chromaffin cells of the medulla
Lots of Epinephrine and Norepinephrine get released
Increased HR, BV, and therefore blood pressure

Pineal Gland Location
Near the posterior aspect of the third ventricle
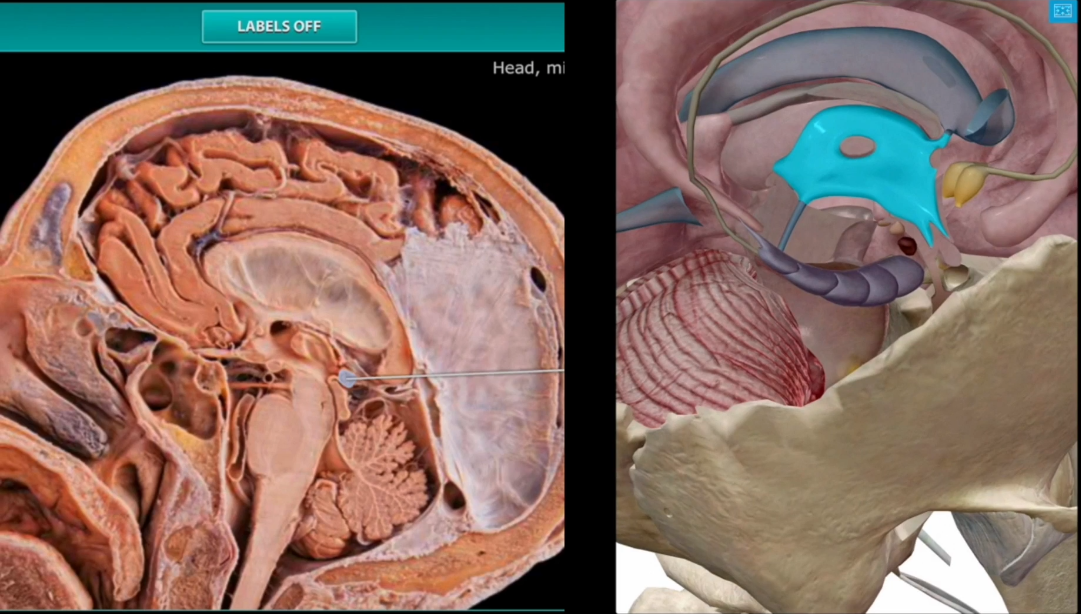
Pineal Gland Function
Secrets melaonin (which is derived from seratonin0: Leads to
Sexual maturation
Day/night cycle (And anything involving rythym: body temperatuire/ sleep/appitite
Production of antioxidants
Is located very close to the Superior Colliculi, which processes light from the optic nerves. Ergo, if someone turns on a light you wake up

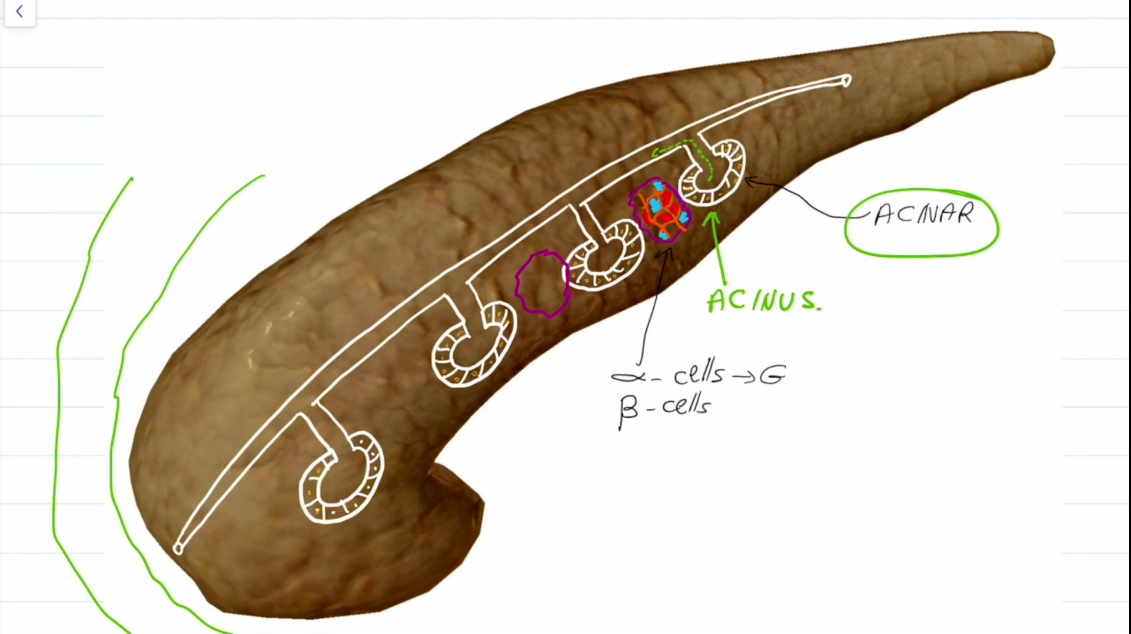
Where is the Pancreas Located?
Behind the stomach.
It has exocrine and endocrine functions, however we will focus on the endocrine functions
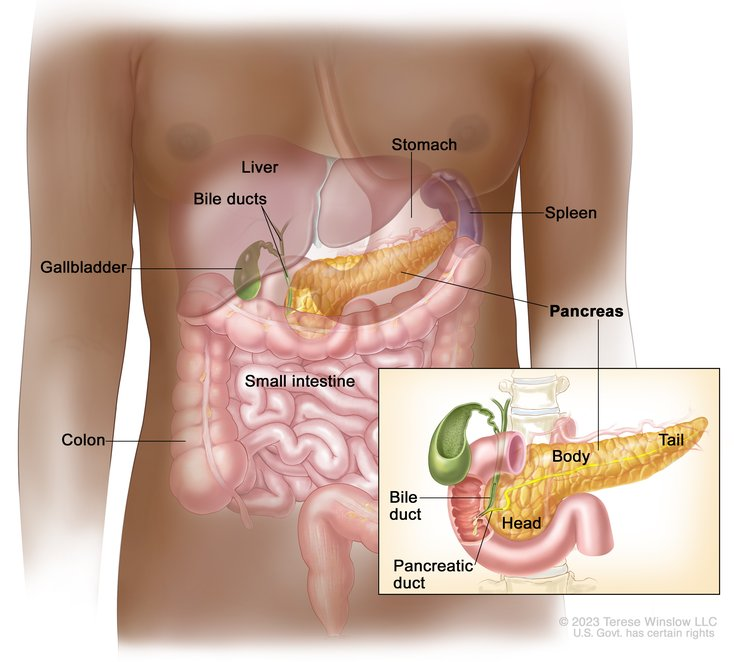
What kinds of cells does the Pancreas have?
Acinar cells create digestive enzymes (exocrine)
In between them are Islet of Langerhan Cells, which contain Alpha and Beta Receptors
Alpha receptors produce glucagon
Beta receptors produce insulin
How does Insulin work?
Too much glucose in the blood.
Insulin is released by the pancreas
Insulin instructs cells to take and store glucose, and tells the liver to store glucose as glycogen
Glucose levels drop in the blood
Inhibits Glycogenolysis: Breakdown of glycogen into sugar
Inhibits Gluconeogenesis: Synthesis of glucose from lactic acid and noncarbohydrates
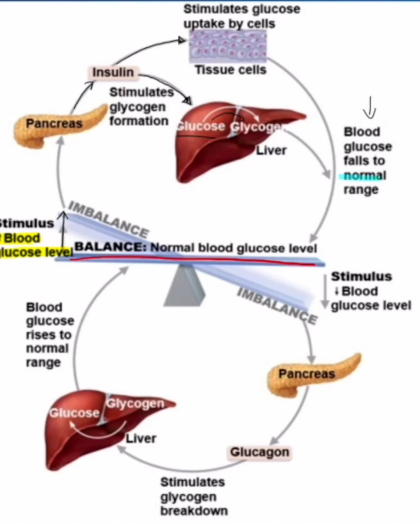
How does Glucagon Work?
Not enough glucose in the blood
GLucagon is released by the pancreas
Glucagon instructs the liver to process glycogen stores into glucose, and then to release glucose into the blood
Glucose levels rise in the blood
Encourages Glycogenolysis: Breakdown of glycogen into sugar
Encourages Gluconeogenesis: Synthesis of glucose from lactic acid and noncarbohydrates

How does insulin work at the cell level?
Insulin interacts with a receptor
IGF-1 (Insulin-like growth factor 1) if formed within the cell
A channel known as Glut-4 fuses with the cell membrane
Glucose is now able to enter the cell freely.
Note, the liver, kidneys, and brain have no need for insulin to take in sugar. They all need a large amount to survive.

Diabetes mellitus (DM)
Two types: Type 1 and Type 2
Type 1 (Hyposecretion) usually results from an autoimmune disease and is caused by a lack of insulin
Type 2 (Hypoactivity) is caused by excessive sugar in the blood, leading to insulin receptors being dulled and becoming inactive (Can be reversed)

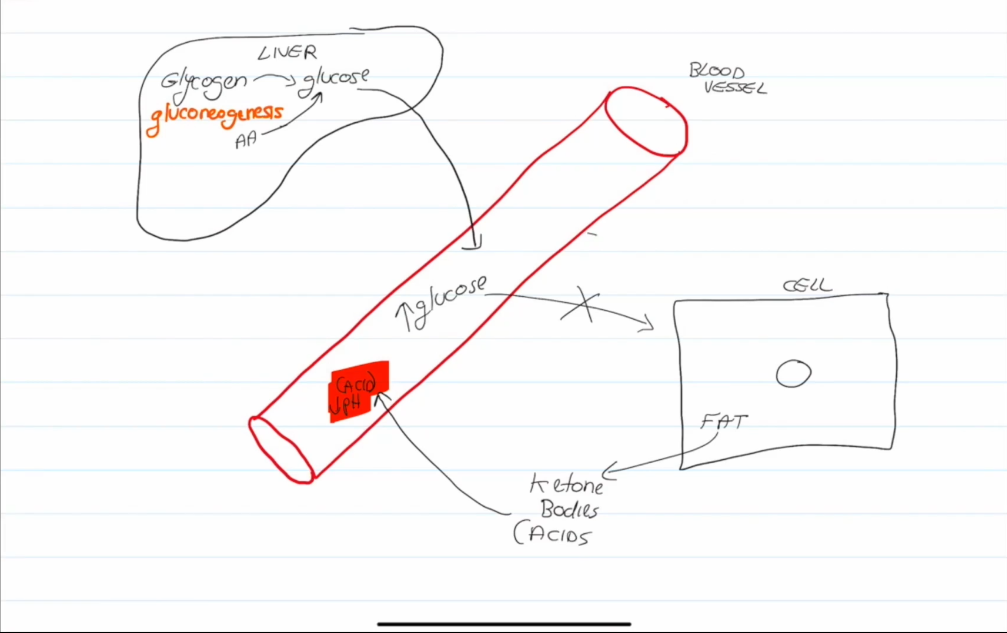
Diabetes mellitus (DM) Dangers
Excessive sugar in the blood causes the blood to thicken.
Fats use lipids for energy, which leads to the formation of ketones, ketones can leak into the blood and alter blood pH.
Untreated ketoacidosis can lead to coma and death
Diabetes mellitus (DM) Cardinal Signs:
Polyuria, pissin
Polydipsia, drinkin
Polyphagia, eatingn

Ovaries and Placenta
Ovaries produce estrogen and progesterone. Are stimulated by FSH and LH.
Estrogen Matures reproductive organs, spurs on the appearance of secondary sex charecteristics, with progesterone cause breast development and menustral cycle
Placenta does the same but also releases hCG (tells u ur gregnant)
Testes
U know where they are bro 💀
Produce testosterone, which matures reproductive organs, spurs on the appearance of secondary sex characteristic, lead to sperm production, maintain reproductive drive
Thymus
Only kids should have it, but it sits on teh heart and makes white blood cells

Other organs:
Kidneys mak eErythropoietin EPO, makes Red blood cells
Stomach makes grehlin make u hungry
Liver makes angiotensinogen idfk
Heart make Atrial Natriuretic Peptide ANP causes vasodilation