SAS: Exam 1
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Oral surgery considerations
Intubation: per os, pharyngostomy, tracheostomy
Airway protection (aspiration): pack w/ gauze, Cuffed ET tube
2º airway edema: Gentle tissue handling, Corticosteroids
Incisions: blade/scissors, no electrocautery
Expect extensive bleeding, delicate mucosa
Sut: Interrupted, tension-free closure, Monofilament (PDS 3-0 or 4-0)
Healing: rapid (3w)
Highly vascular, higher temp, phagocytic activity, early epithelial migration, higher metabolic rate, antimicrobial saliva
Dehiscence is common
Can be due to tension
Can be due to infection
Antibiotics: low infection despite lots of bacti present
Ampicillin-sulbactam, Cefoxitin, Clindamycin
Diet: Canned food only 4 wks, feeding tube, liquids
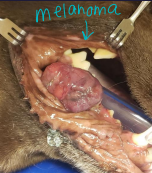
Oral Neoplasms
Et:
Dogs: Acanthomatous epulis, melanoma, SCC, fibrosarcoma, papilloma
Cats: SCC, fibrosarcoma
Dt: CT(extensive), FNA, Biopsy
Tx: Maxillectomy/mandibulectomy (CT first)
Consider eating ability, TMJ function, malocclusion, ulcerations
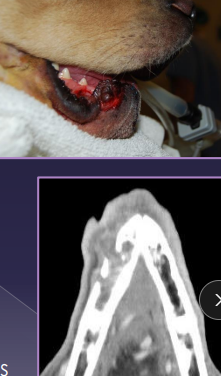
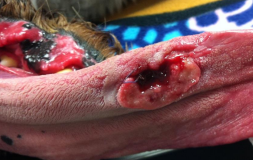
Tongue Disorders
Et: melanoma (rare), SCC (rare), FB, burns, lacerations
Tx: Sut, second intention healing, glossectomy
dogs tolerate 75% removal of tongue, cats do NOT tolerate near-total
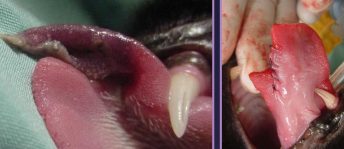
Cleft Palate
Primary (premaxilla/lip) → aesthetic only
Et: congenital, intrauterine insult 25-28d
unilateral, aesthetic, direct access between oral cavity and nasal cavity
Sig: young, brachycephalics
Cs: food caught in rostral nasal cavity
Tx: Sx repair at 5-6m : cosmetic only
Secondary (hard/soft palate)
Et: congenital (#1), intrauterine insult 25-28d, traumatic, midline
Sig: young, brachycephalics
Cs: milk from nose, coughing, gagging, sneezing, nasal discharge, poor growth
Tx: palatoplasty at 12-14w (short fasting time 4-6h)
Too early → friable tissue, poor anesthesia candidate
Too late → defect widens
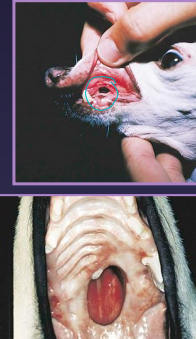
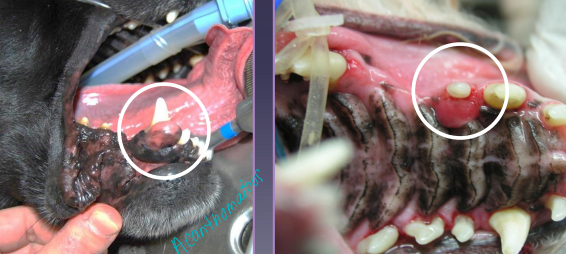
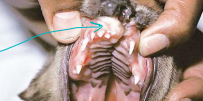
Oronasal Fistula
Acquired secondary cleft
Et: dental dx, malocclusion, trauma, burns, neoplasia, surgery, radiation
Cs: sneezing, unilateral discharge, difficulty eating, halitosis
Dt: dental rads, probing
Tx: debridement + double-layer closure w/ gingival or labial flaps
Sialocele (Salivary Mucocele)
Et: trauma, sialoliths, FB, neoplasia, dental extraction, Sx
Sig: GSD, Silky Terrier, Dachshund, Poodle
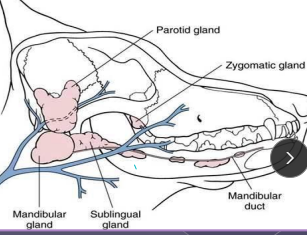
Main: Parotid, Mandibular, Sublingual, Zygomatic
Cs: saliva collects in pseudocapsule, soft tissue swelling
Cervical (#1): soft, fluctuant, non-painful swelling ventral to mandible
Sublingual (ranula): swelling under tongue, halitosis, dysphagia, oral bleeding
Pharyngeal: intraoral swelling into pharynx, cough, dyspnea, stridor
Zygomatic: exophthalmos, 3rd eyelid protrusion, orbital swelling
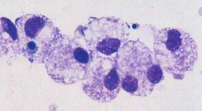
Dt: FNA w/ stringy fluid, non-degenerate neutrophils, macrophages
Tx: Sx excision of both glands + duct (mandibular + sublingual), marsupialization (pharyngeal/ranula)
excellent prognosis, but recurrence and infection possible
Rx management unsuccessful

Esophagus surgical considerations
Highest dehiscence risk
3 tissue layers: No serosa: poor healing
Segmental blood supply
No omentum
Constant motion
Tension at site
Dog Anatomy: striated entire length
Cat Anatomy: smooth in terminal ⅓ w/ involuntary contractions
Sphincters:
Upper Cricothyroid and thyropharyngeus muscles
Lower: Thickening of the muscularis layer, pressure, angle
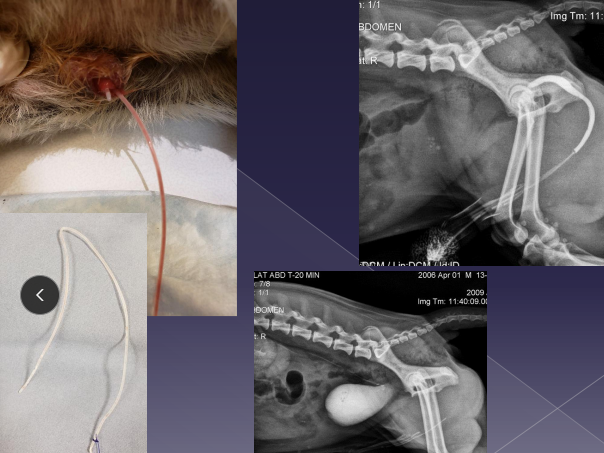
Esophageal Foreign Body
mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, and adventitia
Cs: retching, regurg, drooling, pawing at mouth, dysphagia, gagging, inappetence
Dt: rads, esophagoscopy
Tx: Endoscopic retrieval (#1), Push FB into stomach (gastrotomy), Esophagotomy
Comp: mediastinitis, pyothorax, pneumonia, sepsis, stricture, dehiscence
Esophageal Strictures
Et: prior injury, silent anesthesia regurge, oral tablet injury
Dt: contrast esophagram, endoscopy
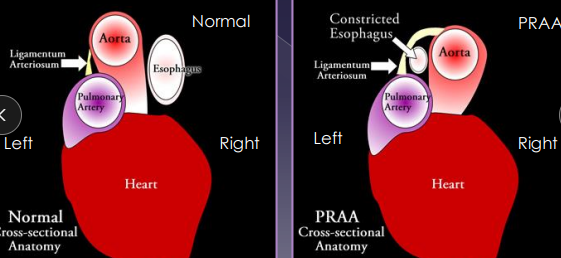
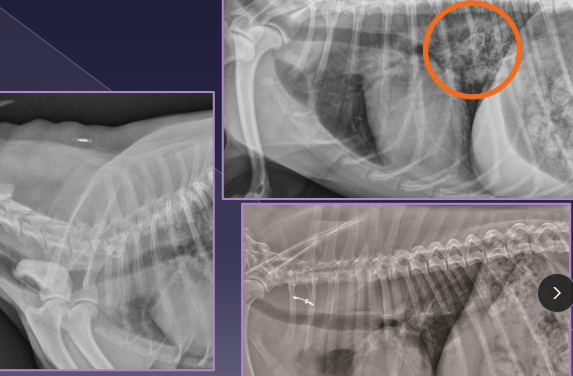
Vascular Ring Anomalies
Et: Persistent Right 4th Aortic Arch (PRAA), constriction at esophagus
Sig: young, GSD, Irish Setter, Boston, Siamese, Persian
Cs: solid food regurge, aspiration pneumonia(2ndary), failure to thrive, poor weight gain
Dt: contrast esophagram (enlarged @ base), CT/angiogram
Check for cranial megaesophagus
Tx: Sx at 10-12w (lig arteriosum division)
Fair to good prognosis
the fibrous remnant of the fetal ductus arteriosus
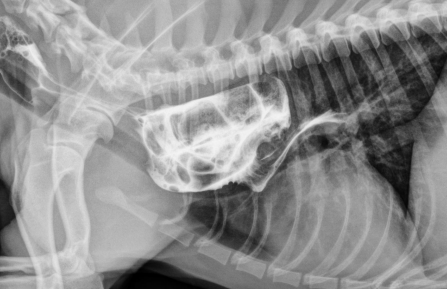
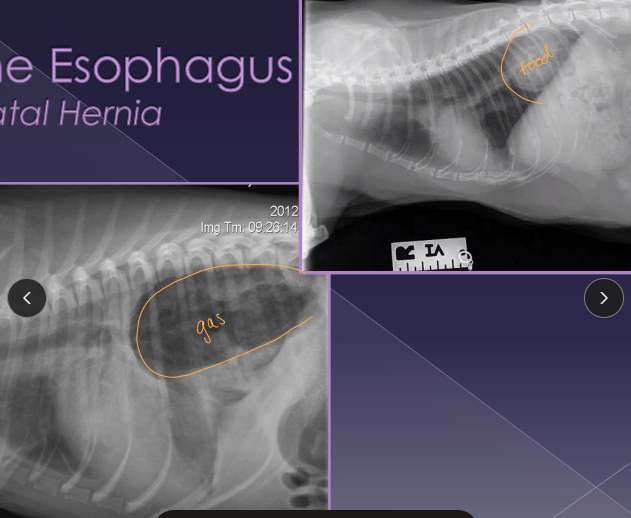
Hiatal Hernia
Et: stomach/abdominal esophagus through esophageal hiatus
Congenital (Phrenicoesophageal ligament laxity) , trama, brachycephalic syndrome, laryngeal paralysis, chronic vomiting
Sig: English bulldog, Shar Pei
Cs: inappetence, dysphagia, regurgitation, vomiting, weight loss, dyspnea
Dt: rads (may be normal), contrast gastroesophagram, fluoroscopy
Tx: antacids, sucralfate, metoclopramide, low-fat diet, elevate feeding, herniorrhaphy, esophagopexy, left-sided fundus gastropexy
Comp: persistent regurg, aspiration pneumonia
Refer out for Sx
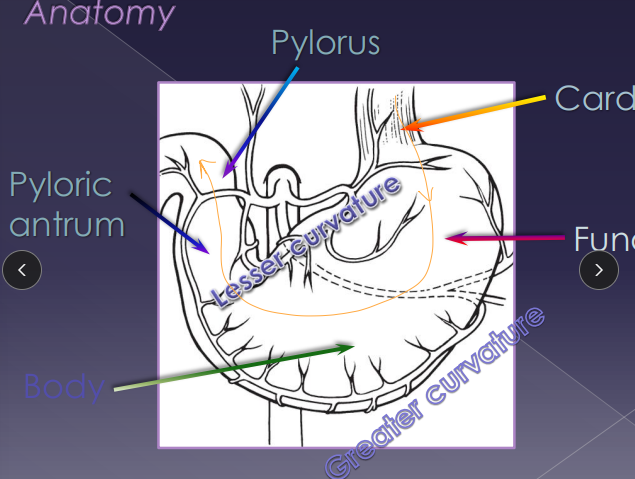
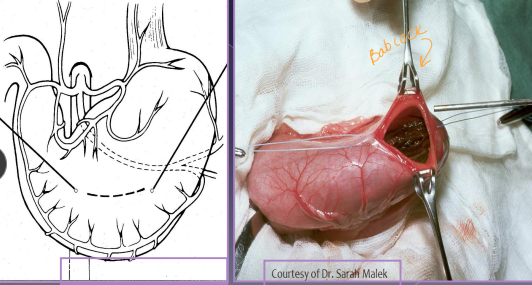
Surgical Considerations of the Stomach
4 layers
Serosa/muscularis (outer) + submucosa/mucosa (inner)
Healing: good
Lg blood supply, low bacti, acidic, rapid regen, omentum support
G+ antibiotics
Layers: four (serosa/muscularis +submucosa/mucosa)
Sut:
Avoid gastric spillage: suction, stay sutures
identify the body → for incision
Midway between greater and lesser curvature
Closure: 2-layer closure (Leak test not req)
Inner mucosa + submucosa: simple continuous
Outer muscularis + serosa: inverting Cushing/Lembert
Gastric Surgical Procedures
Gastrotomy: FB, gastric biopsy
Pack stomach w/ sponges and add stay sutures
ID body (between G+L curvatures) and use sharp insison
Orogastric tube: GDV
Place mouth gag and lube Semi-rigid tube
Flex neck ventrally, pass slowly till 13th rib
Trocarization: GDV
Puncture with 18 g needle at point of maximal tympany
Push opposite side of abdomen
Gastric Derotation: GDV
Stand on left, ventral midline incision, should see omentum over stomach
Right hand on pylorus dorsally, left hand on fundus
push on fundus and pull pylorus left then ventral then right
Insuasional Gastropexy: GDV
Inside right side of stomach (antrum) and right body wall (caudal 13th rib)
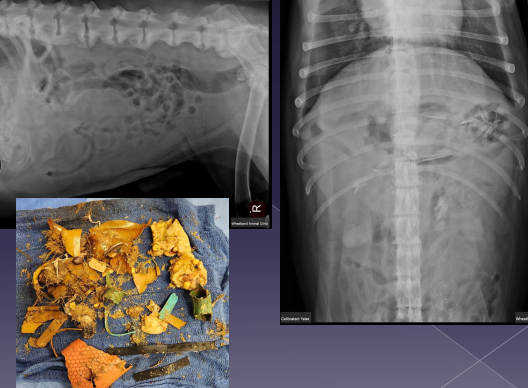
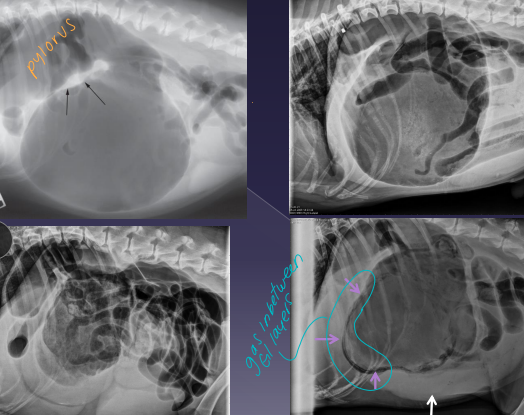
Gastric Foreign Body
Sig: history or suspicion of getting into things
Cs: vomiting, anorexia, dehydration, depression
Dt: contrast rads, US
Tx: Emesis (#1), Endoscopy (#2), Gastrotomy
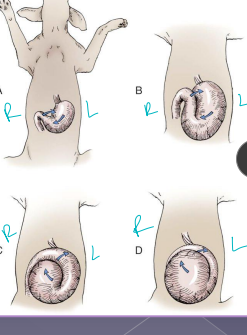
Gastric Dilatation-Volvulus (GDV)
Et: pylorus moves R → ventral → L → dorsal
mucosal damage, sepsis, portal vein obx + hypertension, vena cava obx, poor cardiac output
Sig: Deep-chested, Lg breeds, older, once-daily feeding, genetics, stress, exercise after eating
Cs: Retching, pain, distended abdomen, hypersalivation, VPC, shock, splenic congestion (often corrects on its own), hypoxia, acidosis, death
Dt: lactate trends, ECG (VPC), PT/PTT, RL rads w/ double bubble
Tx: gastric decompress (Trocarization, OG tube), right gastropexy, de-rotation, tube feed, famotidine, pantoprazole, mu opioids, fluids, O2
** Stand on left side, R hand pylorus, L hand on top of fundus - then rotate **
Tx arrythmias if: V tach >160-180. R on T, multifocal, pulse deficits
Emergency but good prognosis
NO NSAIDS or medical management
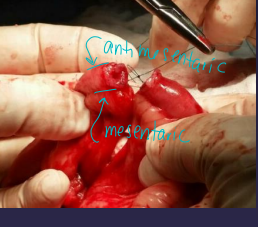
Considerations for Small Intestinal Surgery
Layers: all stuck together→mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, and serosa
Can resect < 70%
Ileum: antimesenteric artery
Duodenocolic ligament: anchors the duodenal flexure to colon
Proximal descending duodenum: common bile duct/pancreatic
Bacti: lots, lavage if spillage
Stabilization: fluids critical (#1)
obstruction/ileus → fluid sequestration → hypovolemia, shock, death
Rx: No NSAIDs, ampicillin + sulbactam
Sut: leak test req
Monofilament, 3-0/4-0
submucosa (holding), start at mesenteric border w/ appositional patterns (simple interrupted or continuous)
dont go 360 w/ continuous pattern, if unequal diameter angle sut on sm side
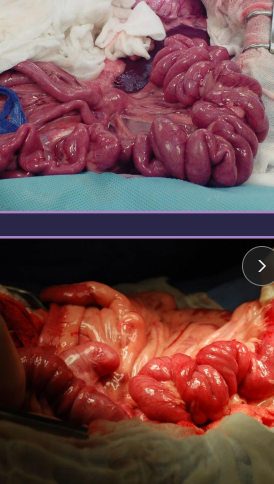
Small Intestinal Foreign Body
Common to anchor: pylorus (dog)
under tongue (cat)
Causes erosion into mesenteric border
Cs: vomiting, depression, anorexia, diarrhea, pain, dehydration, palpable mass, string under tongue (C), weight loss
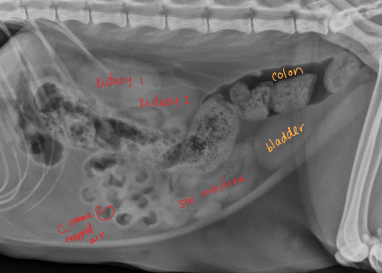
Dt: rads (stacking/bunching SI, pneumoperitoneum), US
Tx: gastroprotectants, Enterotomy (healthy bowel), R&A (damaged bowel), gastrotomy, (linear FB), fluids!!
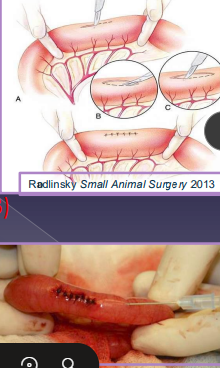
Small Intestinal Surgery Procedures
Enterotomy: FB, full tickness biopsy
Full exploration and isolate bowel w/ sponges
Incise on antimesenteric surface
Aborad to FB (#1) > Orad to FB > Over FB
Leak test (22g needle) and wrap incision in omentum
Resection & Anastomosis: resect devitalized bowl
Isolate diseased bowel
Ligate vessels and clamp
Carmalt (resected side, crushing), Doyen (remaining side, non-crushing)
Suture bowel, close mesenteric defect, omentalize
Can resect < 70%
Lavage!!! Lavage!!! Lavage !!!
Fish-mouth the smaller side: mix match sizes
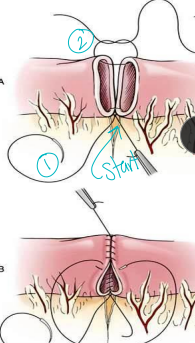
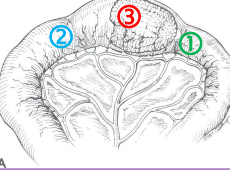

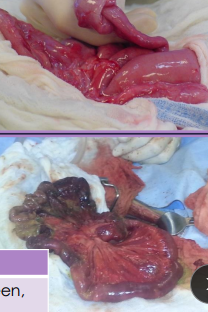
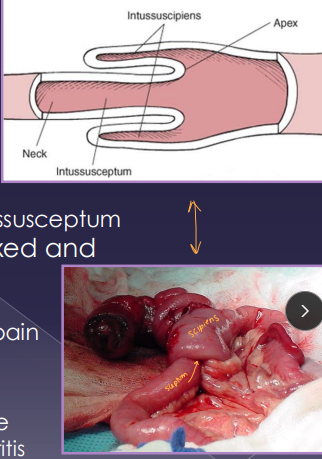
Intussusception
Et: Overlap of junctions of fixed & mobile bowel
Intussusceptum = proximal loop; Intussuscipiens = distal loop
Young: parasites, FB, viral enteritis
Old: neoplasia, infiltrative bowel dz, FB
Cs: diarrhea, anorexia, weight loss, pain
Dt: palpable tubular mass, radiographs (ileus),US
Tx: manual reduction (no adhesions), R&A (devitalized), SURGERY
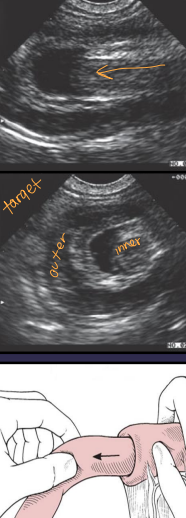
Large Intestine Surgical Considerations
Three segments: ascending, transverse, descending (longest part) left side
Cecum
True diverticulum
Cecocolic orifice
Ileocolic orifice
Healing: poor, high collagenase activity, high bacti load, high dehiscence risk
DON’T cut colon unless necessary
Bld supply: vasa recti
Sut: monofilament absorbable, taper needle
Always lavage, omentalize
Rx: Cefoxitin, Ampicillin/sulbactam + enrofloxacin + metronidazole, epidural, opioids
No enemas, NSAIDs, steroids
Post-op: Fiber (increases motility & healing), high-carb, low-fat diet
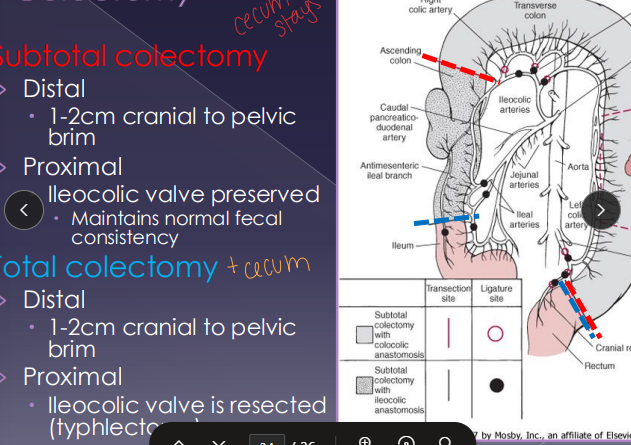
Surgical Procedures within the Large Intestine
Taper needle only
Typhlectomy: impaction, perforation, inversion, neoplasia
preserve ileocolic valve
Colotomy: biopsy, FB removal
Colectomy: megacolon, intussusception, ischemic injury, neoplasia, perforation
Subtotal: preserve ileocolic valve, better fecal consistency
Total: resect ileocolic valve and preform a typhlectomy
Closed anal sacculectomy: neoplasia, medical management fail
Catheterize, lateral skin incision, dissect sac, avoid caudal rectal nerve, ligate duct
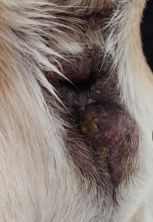
Neoplasia in the Rectum
Perianal gland adenoma
Et: Benign, arises from circumanal glands, related to androgen concentrations
Sig: Older, intact males
Tx: Castration causes regression
Adenomatous polyps
Et: Benign, intramural rectal mass, malignant transformation up to 50%
Tx: early Sx excision
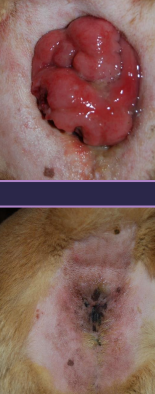
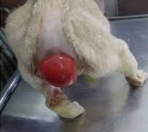
Rectal Prolapse
Et: parasites, enteritis, FB, dystocia, straining, genetic, sphincter laxity, prostatic dx, perineal hernia, recent butt sx
Incomplete: only rectal mucosa protrudes
Complete: all layers protrude
Sig: Manx, younger
Tx: cold saline, lubrication, sugar, purse-string anus over tube, Sx amp
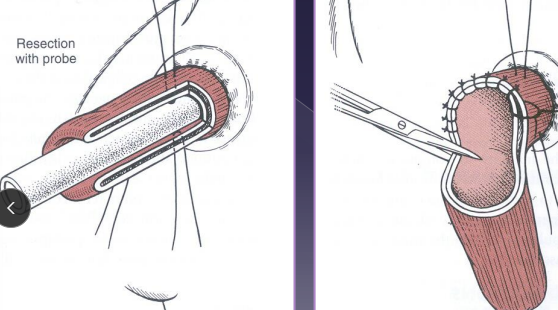
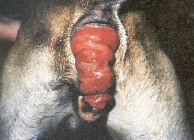
Anal Sac Diseases
Apocrine gland anal sac adenocarcinoma (AGASCA)
Et: Highly malignant, metastasis, sublumbar LN involvment → 50% mets @ time of diagnosis
#1 anal sac tumor
Cs: hypercalcemia, PU/PD, anorexia, bladder stones, lethargy
Sublumbar LN Located: L7, colon ventrally displaced (when enlarged)
Tx: Closed anal sacculectomy + excision of affected LN
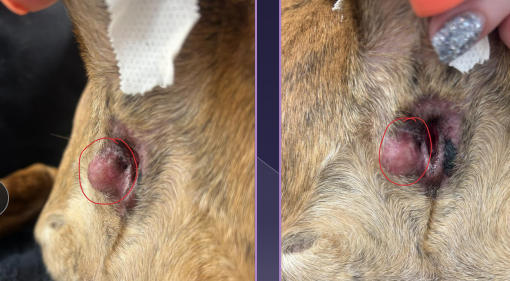
Anal sacculitis
Et: obstruction and infection
Sig: toy breeds, seborrheic dermatitis
Cs: soft stool, perineal irritation, tenesmus, constipation, dyschezia
Tx: regular expression, antibiotics, warm compress
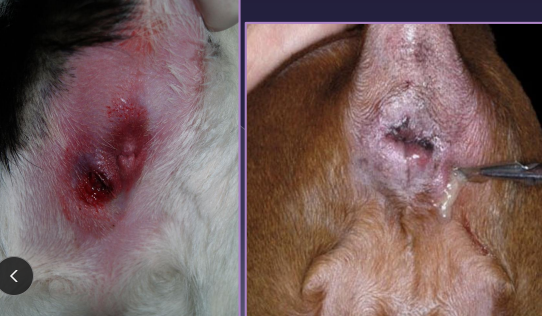
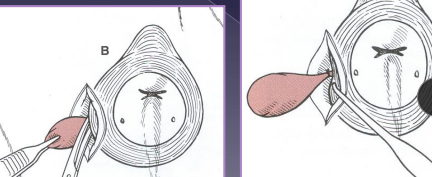
Closed anal sacculectomy
Why: anal sacculitis, neoplasia
Rx: anti-inflam and antibios pre-Sx
How:
Insert a foley urinary catheter (if needed) → infection, inflammation
Incise lateral aspect of anal sac and dissect sac from sphincter fibers
Avoid caudal rectal nerve
Ligate duct at orifice
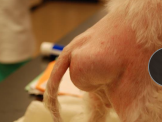
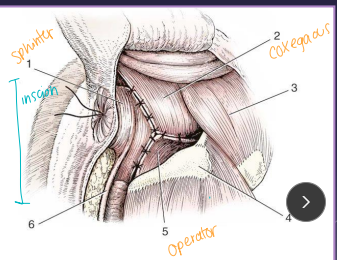
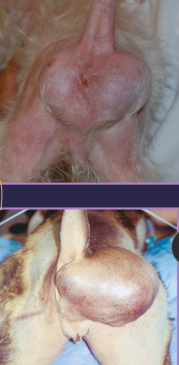
Perineal Hernia
Pelvic diaphragm: holds everything in
Coccygeus muscle
Levator ani muscle → pelvic floor
Sacrotuberous lig: dogs only
Et: abdominal contents herniate caudally
most common site due to levator ani atrophy → unilateral (dogs)
Cats: often bilateral
Sig: Corgi, Boxer, Poodle, Bouvier, Pekingese, Boston, Sheepdog, DSH, 10y, male > female
Cs: Perineal bulge, tenesmus, constipation, irregular stools
non-painful, incompletely reducible
Megacolon, perineal urethrostomy, trauma, perineal masses
Excess androgens and estrogens
Dt: rectal exam, contrast rads, US
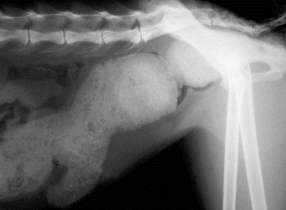
Tx: Sx (#1), Palliative: stool softeners, enemas, fiber
castration + herniorrhaphy: internal obturator flap, coccygeus of anal sphincter and sacrotuberous lig
stabilize bladder entrapment w/ catheterization/cystocentesis before Sx
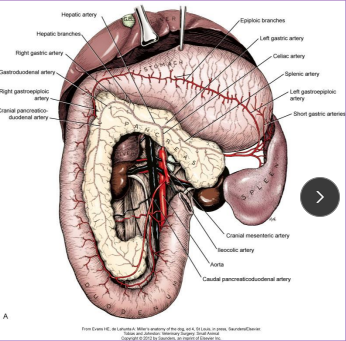
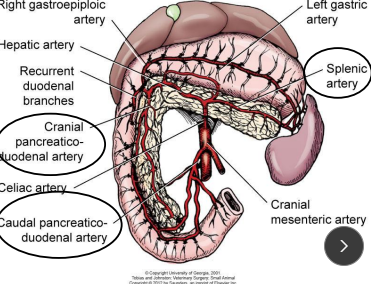
Pancreas surgical considerations
Body: descending duodenum
Left lobe: along greater curvature of stomach
Right lobe: closely with duodenum
Bld supply: Splenic a. (left limb), cranial pancreaticoduodenal a. (body, right limb, proximal), caudal pancreaticoduodenal a. (right limb, distal)
Cats: 80% single pancreatic duct, fuses w/ bile duct before entering duodenum
Dogs: Accessory pancreatic duct → minor, pancreatic duct → duodenal papilla (common duct)
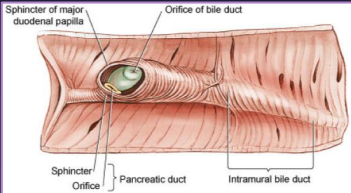
Pancrease Surgical Techniques
Biopsy: wedge, blunt dissection, guillotine, punch
Best site if diffuse = caudal/distal right limb
Partial pancreatectomy: abscess, neoplasia, biopsy
Remove distal limbs only, 75–90% resectable
avoid body = risk of blood supply/duct damage
Total pancreatectomy: very rare
Req duodenectomy, gastrojejunostomy, cholecystojejunostomy
Leads to loss of exocrine & endocrine fxn: req enzyme + insulin supp
Diseases of the pancrease
Pseudocyst
Et: Sterile(fluid filled), often from pancreatitis
Tx: partial pancreatectomy, drain + omentalize(fills hole) (#1)
Insulinoma
Cs: Severe hypoglycemia, seizures, metastasis
Tx: partial pancreatectomy, excise
metastasis 50% to liver and local lymph nodes: quickly
run a Insulin:glucose ratio - DX
Abscess → sterile, very common
Et: Rare, pancreatitis
Tx: excision, drain + omentalize, antibiotics
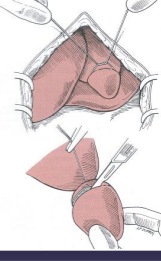
Surgical Techniques and Considerations of the Liver
Bld Supply: Portal v. (80%) > Hepatic a. (20%)
Biopsy: nonspecific path, high bile acids/ALP/ALT, storage dx, neoplasia
Guillotine: tie + excise distal
Punch: superficial, plug with gelfoam (vetsponge)
Laparoscopic: less invasive
Partial lobectomy: neoplasia, abscess, AV fistula, focal dx
Total lobectomy: resect at hilus w/ blunt dissection, sutures, stapling device
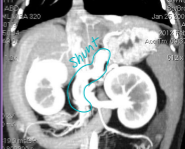
Liver Shunts
Et: genetic (single), acquired multiple (portal hypertension, cirrhosis)
Often seen with microvascular dysplasia, toxins circle systematically (ammonia)
Sig:
Single Congenital: toy breeds (Extrahepatic), Himalayans (Ex), → most common
Lg breeds (Intrahepatic)
Acquired multiple: older Lg breeds, cats
Cs: seizures, head pressing, dull mentation, post-prandial dullness, copper-colored irises(cats), straining, ammonium biurate stones
Dt: low BUN/cholesterol/albumin; high liver enzymes and bile acids; US, CT
Tx: Clavamox, lactulose, low protein diet, Keppra, Sx attenuation (ameroid ring, cellophane band)
Min. 2w medical tx even pre-Sx
Risk of portal hypertension, portal atresia w/ Sx
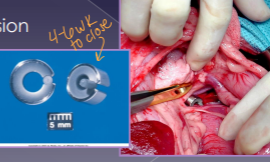
Extrahepatic Biliary Tract Obstruction
Et: pancreatitis, neoplasia, mucocoele, cholelithiasis, cholangitis
Cs: high bilirubin, hypotension, poor contractility, renal failure, coagulopathies, GI hemorrhage, intestinal bleeding
Tx: Sx
extremely Critical patients
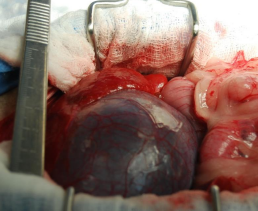
Surgical Techniques of the Gallbladder
Cholecystotomy: open GB, remove stones
Cholecystectomy: remove GB
Cholecystoduodenostomy: reimplant GB to duodenum/jejunum
if CBD diseased, GB healthy
Surgical Considerations of The Kidney and Urinary system
Pre Op: Min database, UA, ensure urine production 1-2 ml/kg/hr
Rx: penicillins, cephalosporins, enrofloxacin
NO: NSAIDs, aminoglycosides, tetracyclines, sulfonamides
Sut: Monofilament, absorbable, full-thickness (simple interrupted/continuous)
Suture can be calculogenic
Avoid lumen occlusion/stricture
Comp: Hypotension, pancreatitis, pancreatic duct cannulation, dehiscence, peritonitis, sepsis, DIC, choledochal dilation, re-obstruction
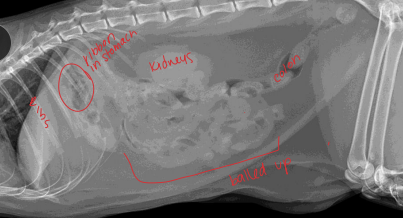
Anatomy: Retroperitoneal, ureter exits at hilus, right kidney higher + left mobile
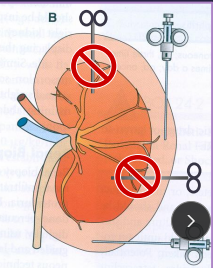
Kidney Surgical Considerations and Procedures
Biopsy: done at the cortex, avoid medulla cause of hemorrhage
Open surgical (#1): best hemorrhage control
US: risk bleeding, monitor fluids
Laparoscopic: min invasive, good visualization
Nephrotomy: explore pelvis, stone removal, hematuria, biopsy, partial nephrectomy
How: longitudinal incision in body, hemostasis critical, suture capsule
Comp: diminished renal function, urine leakage, stage if bilateral, temporary GFR reduction, renal failure
Nephrectomy: salvage; neoplasia, trauma, pyelonephritis, hydronephrosis, ureteral abnormality/trauma, ligation w/ OHE, ectopic ureter
How: confirm contralateral kidney GFR adequate pre-op
Free kidney from retroperitoneum
Double ligate renal a./v. (watch for multiple arteries)
Ligate ureter close and transect to bladder
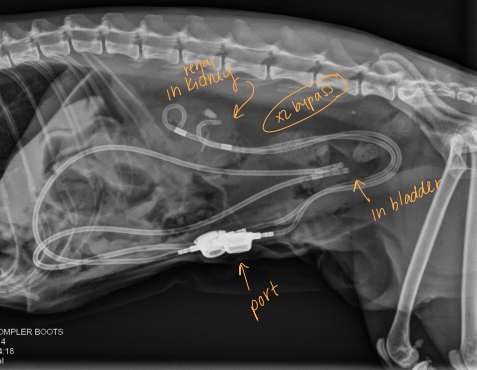
Ureteral Surgical Procedures
Subcutaneous ureteral bypass (SUB): Obstruction, cats
Replaces ureterotomy, pyelolithotomy
Place catheter from renal pelvis to bladder apex
Ureteral stent: for dogs w/ obstruction
Neoureterostomy: Intramural ectopic uterus
Do a cystotomy
Incise bladder mucosa into ureteral lumen
Create a new stoma then ligate distal portion of ureter
Cystoscopic laser ablation: min invasive for Intramural ectopic uterus
Insise between ectopic ureteral lumen and urethra/bladder
Ureteroneocystostomy: Extramural ectopic ureter
Ligate and transect distal ureter
Spatulate ureteral opening then reimplant ureter into bladder
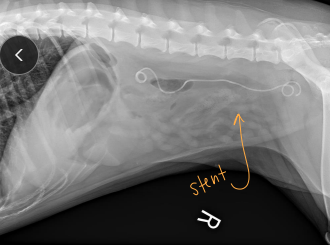
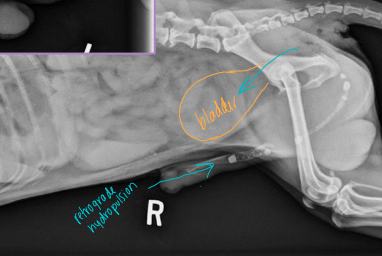
Ureteral Obstruction
Et: partial (stone, stricture), complete (stone, trauma, ligation, transection)
Cs: lethargy, anorexia, hydronephrosis, azotemia
urination possible unless bilateral
Dt: Rads + contrast, US
Tx: SUB (C), Ureteral stent (D)
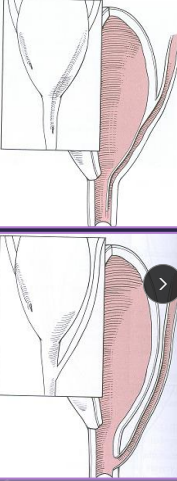
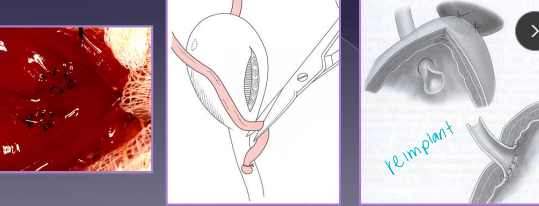
Ectopic Ureter
Et: empties abnormally, unilateral urethra most common
Intramural: tunnels submucosally, exits urethra/vagina
Extramural: bypasses bladder completely
Sig: young female, Husky, Golden, Lab, Newfie, Poodle, Bulldog
Cs: incontinence, urine scald, recurrent UTIs
Dt: azotemia, rads (stones), CT, cystoscopy (#1)
Tx: neoureterostomy (I), laser ablation (I), ureteroneocystostomy (E)
Comp: incontancence
Renal Neoplasia
Et: Primary tumors rare (malignant), renal tubular carcinoma (#1)
Metastasis to chest common
Tx: ureteronephrectomy
only if contralateral kidney fxn
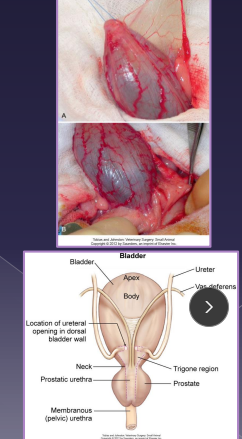
Surgical Conciderations of the Bladder
Healing: regains 100% strength in 14-21d, full re-epithelialization in 30d, 50% can be removed safely
avoid incisions near trigone
Urine sterile unless UTI
Sut: Full-thickness, monofilament absorbable
Simple continuous or interrupted,
single layer adequate, leak test req
Catheter: Not for routine, use if concern for leakage/repair integrity
Retrograde male, normograde female
Avoid bladder expression
Rx: fluids >24h
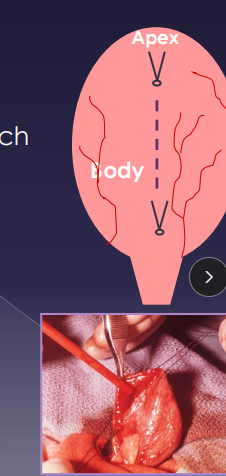
Surgical Principles of the Bladder
Leak test: saline infusion w/ 22g needle while occluding neck
Cystotomy: calculi, neoplasia, biopsy, polyp removal, ectopic ureter repair, cystopexy
Exteriorize & isolate bladder, place stay sutures at apex/body
Incise ventrally, suction urine and lavage
Partial Cystectomy: neoplasia, necrotic/traumatized bladder, lesions in apex/body
NOT for trigone issues
Cystopexy: perineal hernia, augment ureteral anastomosis
open or laparoscopic/lap-assisted
Bladder sutured to lateral body wall
Tube Cystostomy
Temp: Unstable patients w/ calculi obstruction, urethral trauma
Diverts urine until definitive procedure
Perm: neurogenic bladder, urethral obstruction, neoplasia
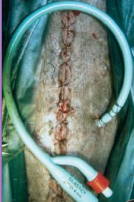
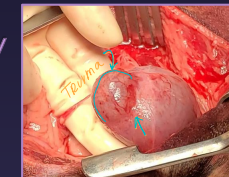
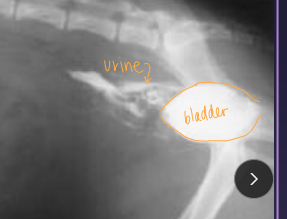
Uroabdomen
Et: blunt trauma (HBC), gunshot, surgery dehiscence, necrotic neoplasia
Cs: electrolyte imbalances, hyperkalemia, dehydration, hypovolemia, shock, uremia, death, abdominal distention
Dt: HCBC/chem (infection, azotemia), rads (loss of serosal detail), abdominocentesis (fluid Cr & K > blood levels), contrast cystourethrogram
Creatinine, potassium – higher than peripheral blood
Tx: ventral midline incision, ID defect, repair, lavage, drains, catheter
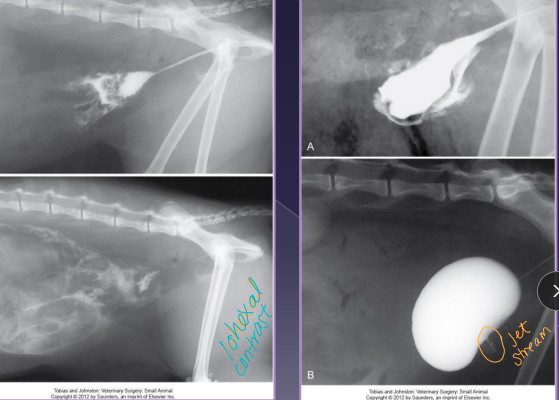
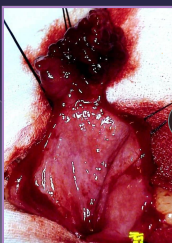
Bladder Neoplasia
Et: TCC (#1)→ @ trigone, SCC, adenocarcinoma, hemangiosarcoma, fibrosarcoma, leiomyosarcoma, benign tumors
Dt: rads, thoracic rads (mets), US, BRAF gene test, cystoscopy, traumatic catheterization
Tx: NSAID, chemo, tube cystostomy, sx (best long term)
Mostly medical
Urethral Disorders
Stones
Et: Bladder stones lodged in urethra
distal urethra, just proximal to os penis
Sig: Males > females
Tx: urohydropulsion, cystotomy
complete obstruction = EMERGENCY
Urethral Trauma
Laceration: usually heal w/ urinary diversion (catheter ≥ 7d)
Transection: primary anastomosis, urethrostomy
Urethral Prolapse
Et: excitement, chronic irritation, infection
Sig: Bulldogs
Cs: bleeding from urethra, visible prolapse
Tx: Urethral resection, Urethropexy, castrate
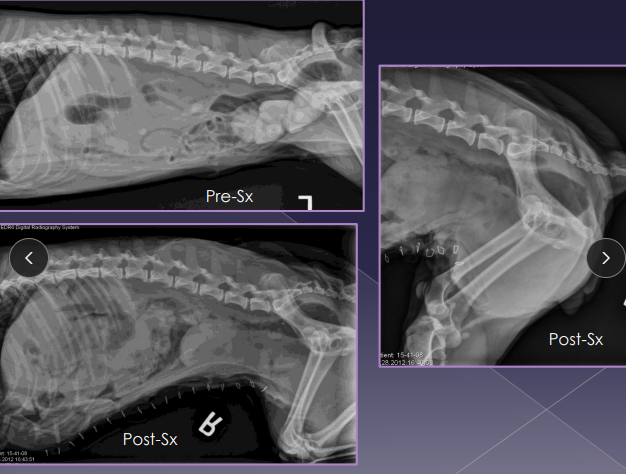
Urethral Surgery Procedures
Urohydropulsion: urethral stones, avoid Urethrotomy
Confirm stone position with rads, then push into bladder
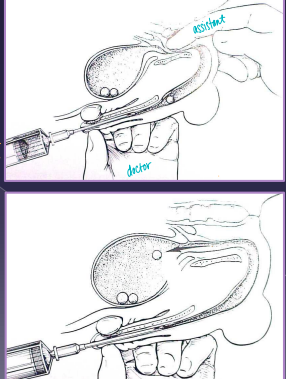
Urethrotomy: stone retrieval, FB retrieval, biopsy, neoplasia
Sharp midline incision over obstruction
Primary closure with apposition and place catheter
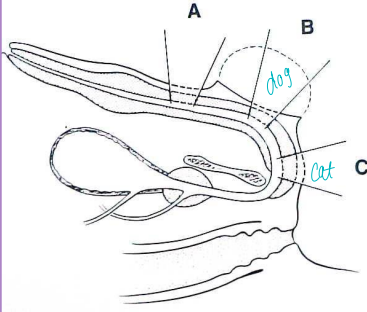
Urethrostomy: permanent stoma; Urethral obx, FIC, trauma, neoplasia, calculi
Perineal (C) or scrotal (D) incision, create stoma
Must dissect penis to bulbourethral glands (C) or stricture risk
Use a drain board to prevent urine scald, should fit hemostat box lock
A drain board is necessary to prevent urine scald
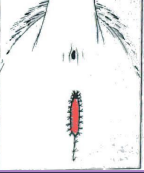
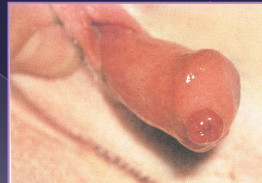
Urethral resection: urethral prolapse
excise prolapsed mucosa, amputate, suture to skin
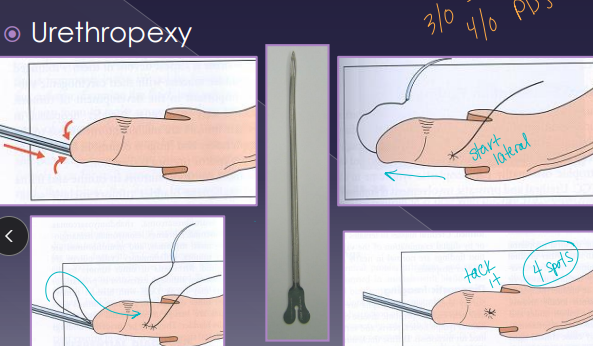
Urethropexy: urethral prolapse
reduce prolapse, place sutures proximally
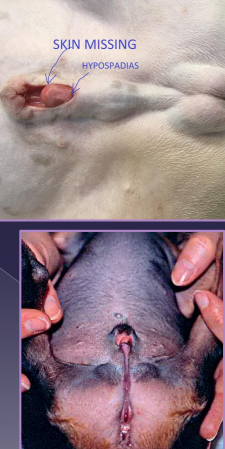
Penile Disorders
Hypospadias:
Et: congenital, urethral opening ventral/caudal to normal
Tx: preputial/urethral reconstruction
Phimosis:
Et: Congenital, trauma
Cs: inability to extrude penis, urine pooling, purulent discharge
Tx: enlarge preputial opening, new mucocutaneous junction
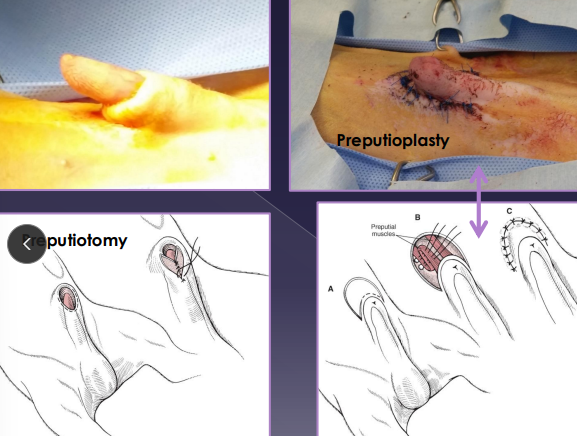
Paraphimosis:
Cs: penis remains extruded
Tx: reduce, preputial reconstruction, preputiotomy, phallopexy, partial penile amputation, castration
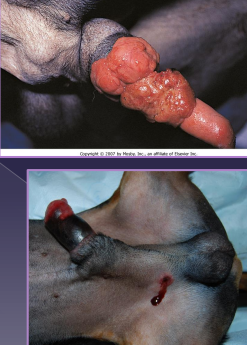
Penile Amputation
Why: neoplasia, trauma, congenital anomalies
How: scrotal urethrostomy + scrotal ablation