2. Organelles
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
endomembrane system
Internal organelles that are connected with the jobs of interacting in the synthesis, distribution, storage and export of molecules
Nuclear envelope, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, plasma membrane
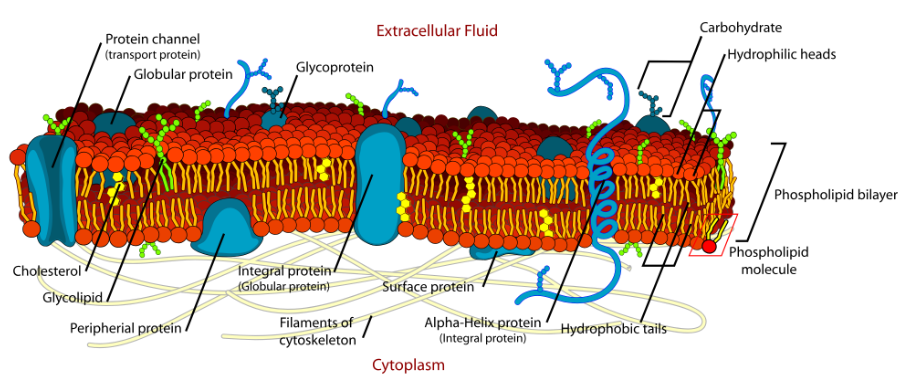
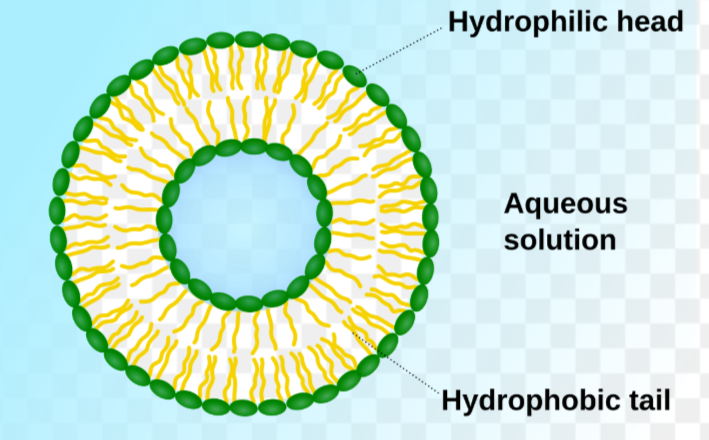
Cell Membrane/ Plasma Membrane
Biomolecules:
lipid bilayer made up of two layers of phospholipids (move laterally) w/ cholesterol (lipid) that adds structure + lil carbs hang
proteins: throughout membrane
Transport: moving molecules through membrane
cross: water?
enter: food, molecules (glucose), gasses (o2, Co2)
exit: proteins, wastes, gasses (o2, Co2)
Signal transduction: insulin
and more (for later)
all cells
Function:
to regulate the transport of materials entering + exiting cell, protection, fixed environment
selective permeability: some substances pass through easier than others
Fluid Mosaic Model: hydrophilic regions of proteins that interact w/ water as outer region + hydrophobic regions of proteins in nonaqueous environments as inner region
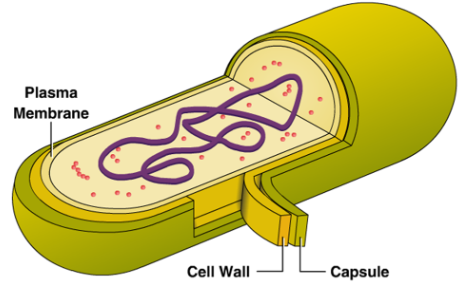
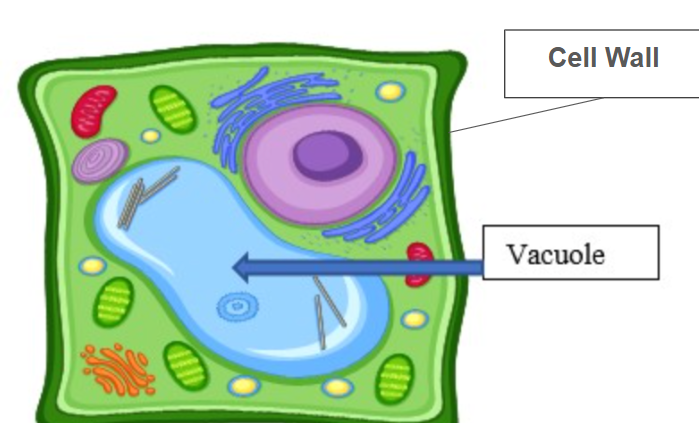
Cell Wall
Biomolecules:
?
all except animal (just plant)
Function:
rigid outer barrier surrounding cell membrane
Cytoplasm
Biomolecules:
gelatinous liquid comprised of water, salts and other organic compounds that fills the cell
all cells
Function:
Transports, protects, maintains cell shape and structure, stores macromolecules + acts as host of metabolic processes. Also maintains optimal environment for cellular organelles
Cytoskeleton
Biomolecules:
protein filaments + tubules = microscopic network in cytoplasm
all cells
Function:
maintains shape of cells + provides organization (ex: motor proteins)
centrosomes: used as transport when cell is dividing
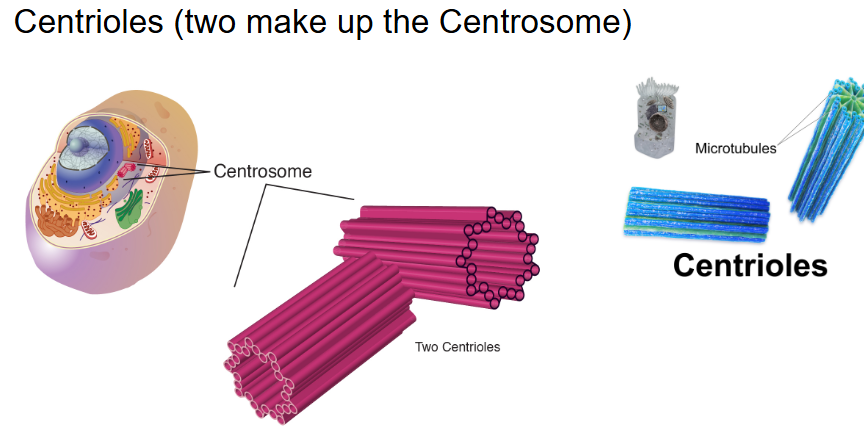
Centrioles/Centrosome
Biomolecules:
proteins = parried barrel-shaped organelles located in the cytoplasm of animal cells near the nuclear envelope
centriole + centriole = centrosome
only eukaryotic + animal cells
Function:
help to determine the location of the nucleus and organelles in the cell + organize cells for division + support/skeletal system
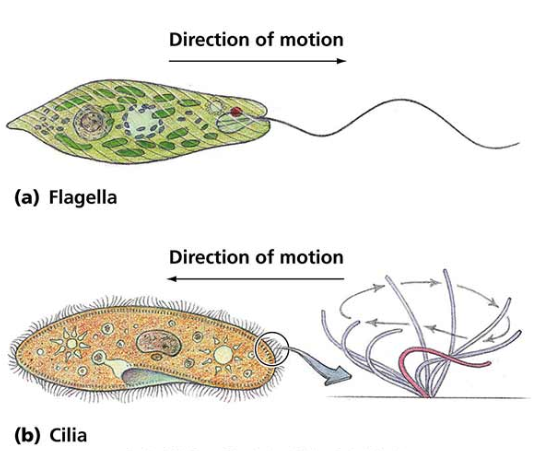
Flagella + Cilia
Biomolecules:
made of proteins called microtubules = long wavy structure that extends from plasma membrane
both euk + prok, only animal cells
Function:
used to move entire cell
cilia: moves molecules and lipids past cell membrane (often in animal) only euk
flagella: facilitates movement in certain single cell organisms (sometimes in animal) (on the outside of cell) prok + euk
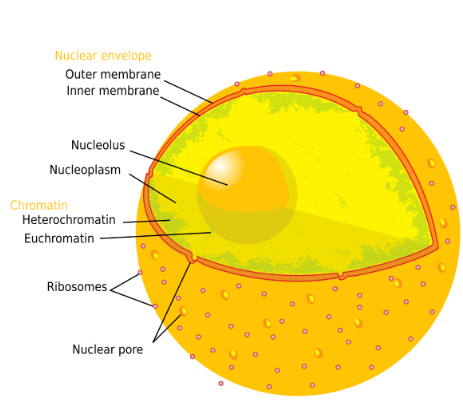
Nucleus + Nucleolus
Biomolecules:
Nucleus: nucleic acids (DNA + RNA) + phospholipids (membrane-bound structure) that includes the nucleolus
Nucleolus: nucleic acids (DNA + RNA) spherical structure inside cells nucleus
only euk, plant + animal cells
Function:
Nucleus: store genetic info
Nucleolus: manufactures ribosomes (begins protein composition)
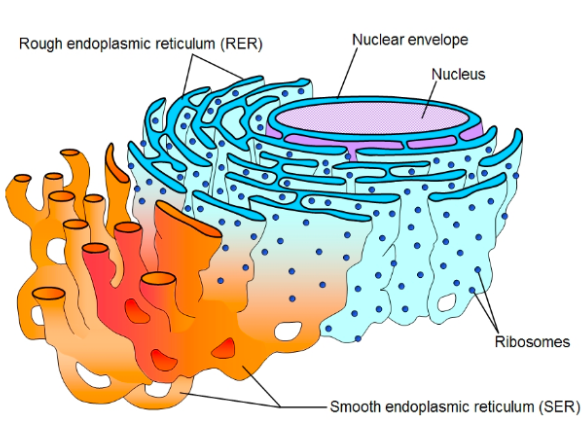
Ribosome
Biomolecules:
nucleic acids (RNA), protein, little spheres on rough ER or in cytoplasm
all cells
Function
2nd step of protein synthesis (linking amino acids into polypeptides)
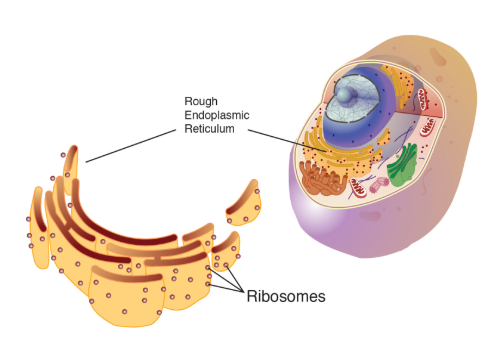
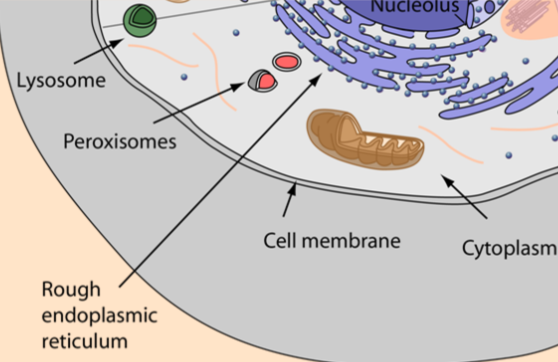
Endoplasmic Reticulum (rough + smooth)
Biomolecules:
Rough endoplasmic reticulum: proteins = layer type structure around nucleus + ribosomes
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum: proteins = layer type structure around rough ER
only eukaryotic, plant + animal cells
Function:
Rough ER: protein folding (3rd step)
Smooth ER: help produce lipids
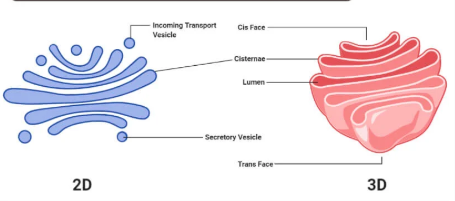
Golgi Apparatus
Biomolecules:
proteins = series of smooth, stacked membranes
only eukaryotic, plant and animal cells
Function:
transport, sort and modify proteins + lipids if needed (step 5) (a carbohydrate tail, adding a phosphate group, etc)
package then transport into vesicles
Vesicles
Biomolecules:
phospholipid shell + cytoplasm like liquid = membrane sacs
only eukaryotic, plant + animal cells
Function:
transport substances into and out of cell, often proteins (steps 4 & 6)
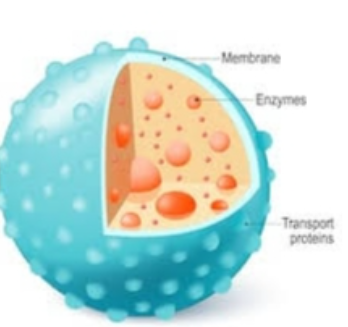
Lysosome
Biomolecules:
phospholipid bilayer = membrane, small container within cytoplasm
transport protein = let molecules thru
eukaryotic, animal (rarely plant) cells
Function:
use enzymes to break down general waste (used materials in cytoplasm) (hydroylsis)
Peroxisome
Biomolecules:
phospholipids = single membrane-bound vesicles
proteins = structure
only eukaryotic, (rarley plant) + animal cells
Function:
uses enzymes to break down fatty acids + amino acids
neutralize harmful toxins so they don’t damage cells
ex: contain catalase for neutralization of hydrogen peroxide
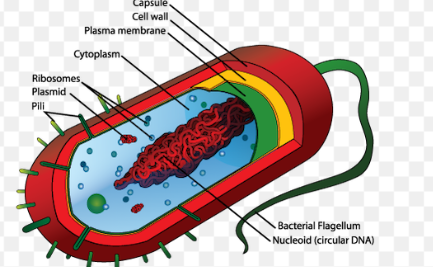
Capsule
Biomolecules:
proteins + carbohydrates = along cell wall
only prokaryotic
Function:
layer on the outside of cell wall that protects cell + stores nutrients
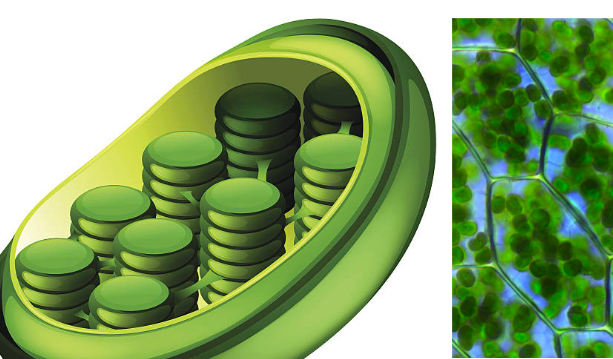
Chloroplast
Biomolecules:
organized by internal membranes into diff compartments
one compartment holds thick fluid called stroma (contains chloroplast DNA, ribosomes, and enzymes)
only eukaryotic, plant cells
Function:
conduct photosynthesis: Carbon Dioxide +H2O →(add sunlight) Glucose + Oxygen
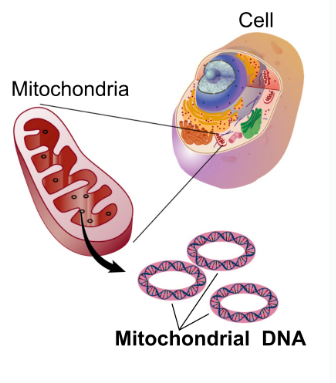
Mitochondria
Biomolecules:
double membrane structure, tiny
proteins = ribosomes
only eukaryotic, plant + animal cells
Function:
make energy by breaking down food (glucose) using oxygen → stored as ATP
powerhouse of the cell
Central Vacuole
Biomolecules:
lipids + proteins
only eukaryotic, plant + animal cells
Function:
stores water, nutrients, and waste
plant cells: large and in center
animal cells: multiple smaller and only temporary space for waste + chemical reactions
Nucleoid
Biomolecules:
nucleic acids = irregularly shaped region
only prokaryotic cells
Function:
stores all or most of the genetic material for cell
microtubules
straight, hollow tubes, assist cell shape and movement
microfilaments
solid rods, assist cell shape and movement