Generation and Transport of Electrical Energy - Week 5 - Overhead lines and cables video 1
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
what is the definition of an overhead line
an overhead line is any electrical line which is placed ABOVE GROUND and in OPEN AIR.
they are usually supported on a tower or wood pole and air is their insulation
what is the definition of a power cable
they are UNDERGROUND cables which are surrounded by insulation(not air insulation),
what is a “service span” with regards to overhead lines?
a span that connects a customer via an overhead line at 230V
what are two examples of overhead lines?
“service spans” at 230V
400kv double circuit steel tower transmission line managed by national grid.
what is the purpose of an overhead line/ power cable ?
to carry as much power as possible from point A to B
for overhead lines why do you need taller wooden poles for electrical lines which have a higher voltage rating?
because of electrical clearance.
the higher the voltage the more electrical clearance you need from ground.
what does electrical clearance mean with regards to overhead lines?
electrical clearance refers to the electrical isolation distance between the overhead line and ground.
why is there always going to be “sag” in the electrical line for an overhead line between the two wooden poles?
the line is never going to be at maximum tension due to ambient temperature conditions as well as the inherent temperature of the conductor.
this is because conductors expand when they gain heat meaning there is less tension
if an overhead line installation took place during summer what would you need to account for come wintertime?
you would put lines up with a little bit of sag. as when ambient temperature gets colder at winter the line will have increased tension and less sag. If you put line up in summer with barley any sag come winter it will have too much tension and will put stress on wooden poles and may cause them to snap.
why are the electrical lines not connected directly to the wooden poles but to an insulator?
insulator stops current flowing through wooden pole and straight to ground. this could cause flashover and even damage the wooden pole. the current instead flows over the wooden pole and into the next over headline in the sequence.
what are the 7 key design properties to take into account when installing an overhead line?

why are overhead line cables stranded instead of using a single solid conductor? and how are they they stranded.
it increases the flexibility.
they are stranded in a spiral to prevent unwinding of the strands
what materials are used for the conductor in an overhead line.
steel strands are in the middle of the conductor to provide mechanical strength.
aluminium strands are spiralled around the outside

what is the downside of stranding electrical conductors instead of using a single piece of conducting wire.
if the conductor is stranded in a spiral, then the length of the conductor needed will increase compared to a straight line, this increases resistance.
what is the most important cause of power loss in a transmission line?
resistance
what is the equation you need to remember for overhead lines which relates DC resistance and length
note the resistance changes with length and area and the resistivity of the material is temperature dependent.

what is skin effect with regards to AC current?
the tendency of AC current to become distributed within a conductor such that the current density is largest near the surface of the conductor and decreases exponentially as you near the centre of the conductor.
As you can see from diagram dc current has no skin effect and skin effect increases with increasing frequency
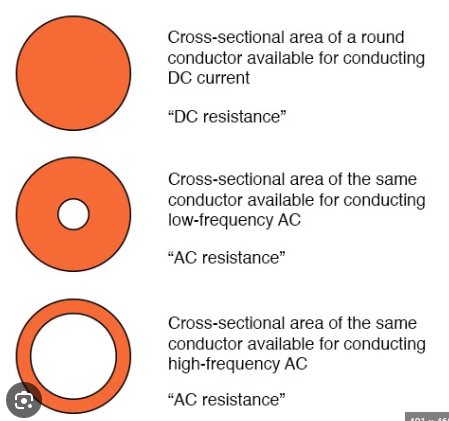
what are the three 3 things which influence the effective resistance in an overhead line?
spiralling
skin effect
proximity effect
what is the equation for DC resistance per meter at 20°C

what is the equation for the variation of resistance with temperature
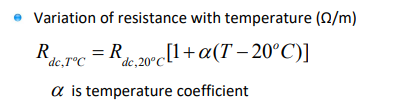
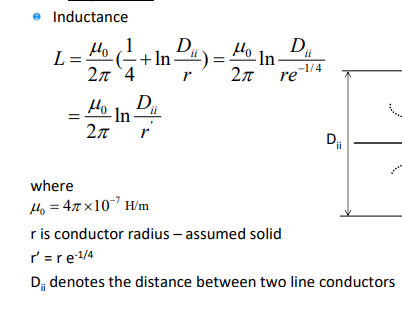
do thicker or thinner conducting lines have more or less inductance?
thicker conductors have less inductance
thinner conductors have more inductance
do longer or short conducting lines have more or less inductance?
longer lines have more inductance
shorter lines have less inductance
what is the equation for the inductance of a single phase transmission line
μ0 = the magnetic constant/ permeability of free space.
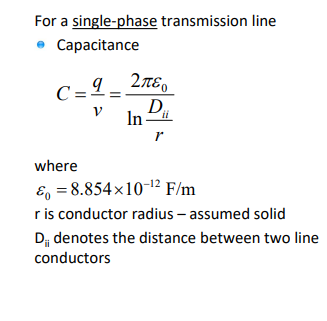
what is the equation to calculation the capacitance of a single phase transmission line
if there is a three phase overhead transmission line which has a balanced voltage and current at the sending end why does it become unbalanced at the receiving end?
what can be done to overcome this?
this occurs because of the geometric asymmetry between the 3 phase overhead lines.
transposition can be used to overcome this.
what is the benefit of transposing power lines?
it helps to reduce the overall system power loss
need to add last slide