Special Segments of a Triangle
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Median
A segment who connects the vertex to the opposite side's midpoint. Medians from base angles of an isosceles triangle are congruent.
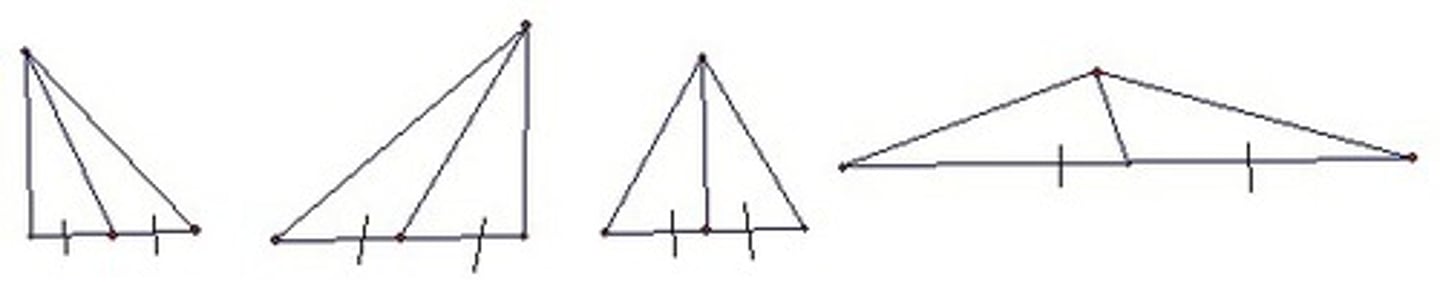
Altitude
A perpendicular segment that connects the vertex to the line containing the opposite side.
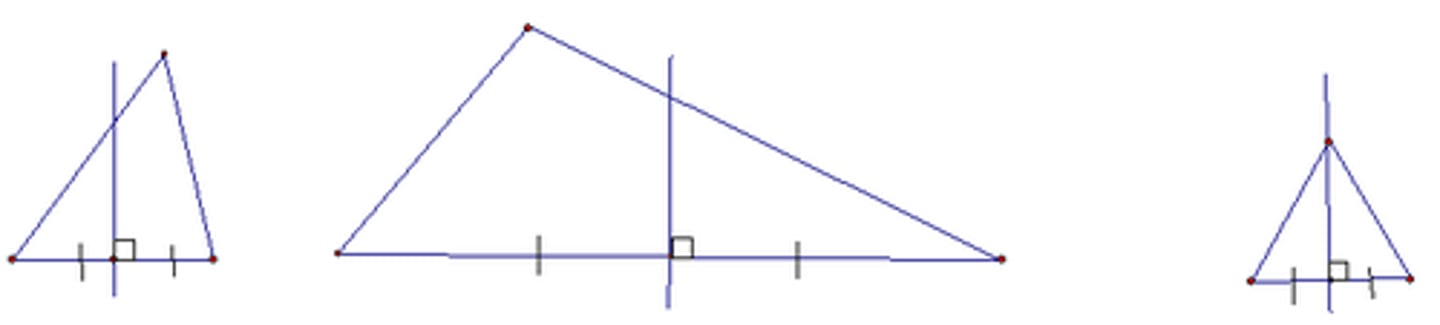
Perpendicular Bisector
A perpendicular segment that passes through the midpoint and does not have to pass through a vertex.
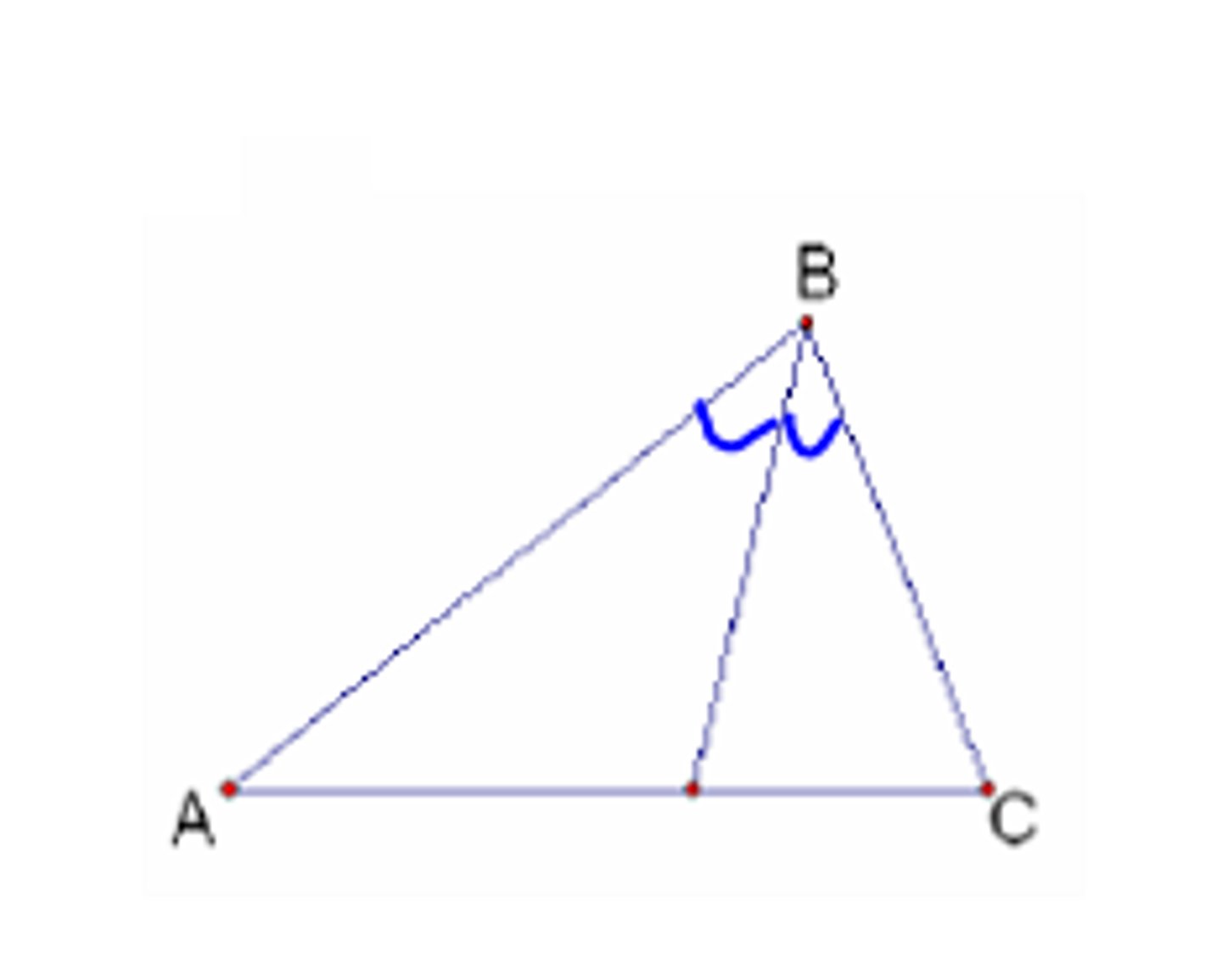
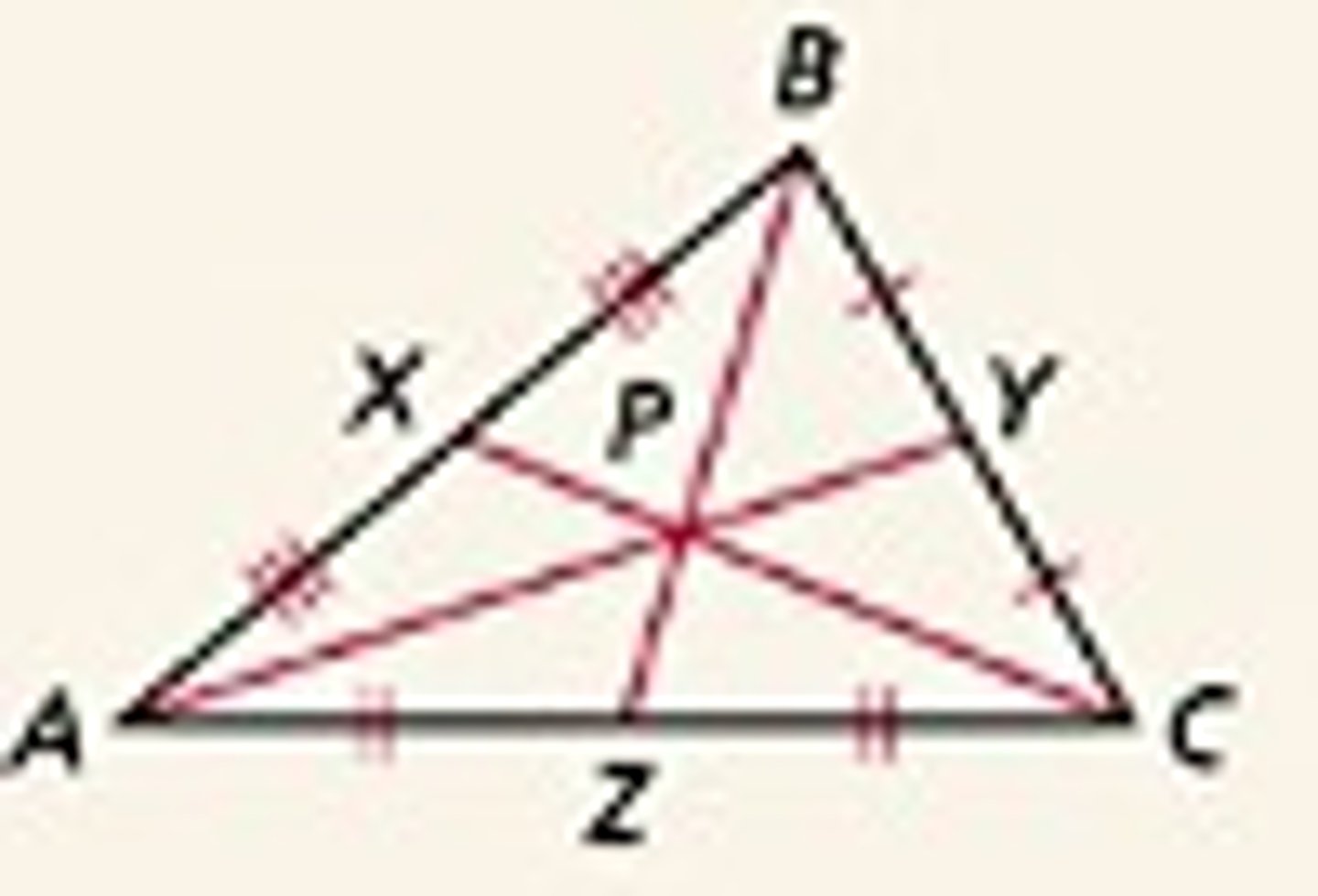
Angle Bisector
A segment that divides the angle into 2 congruent parts from the vertex.
Point of Concurrency
A point in which 3 or more lines intersect.
Circumcenter
The point where the 3 perpendicular bisectors of a triangle meet.
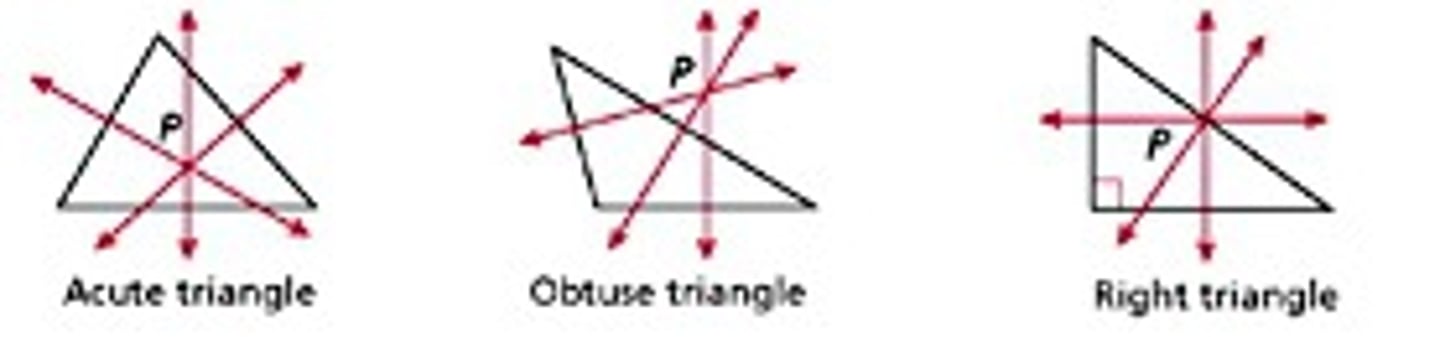
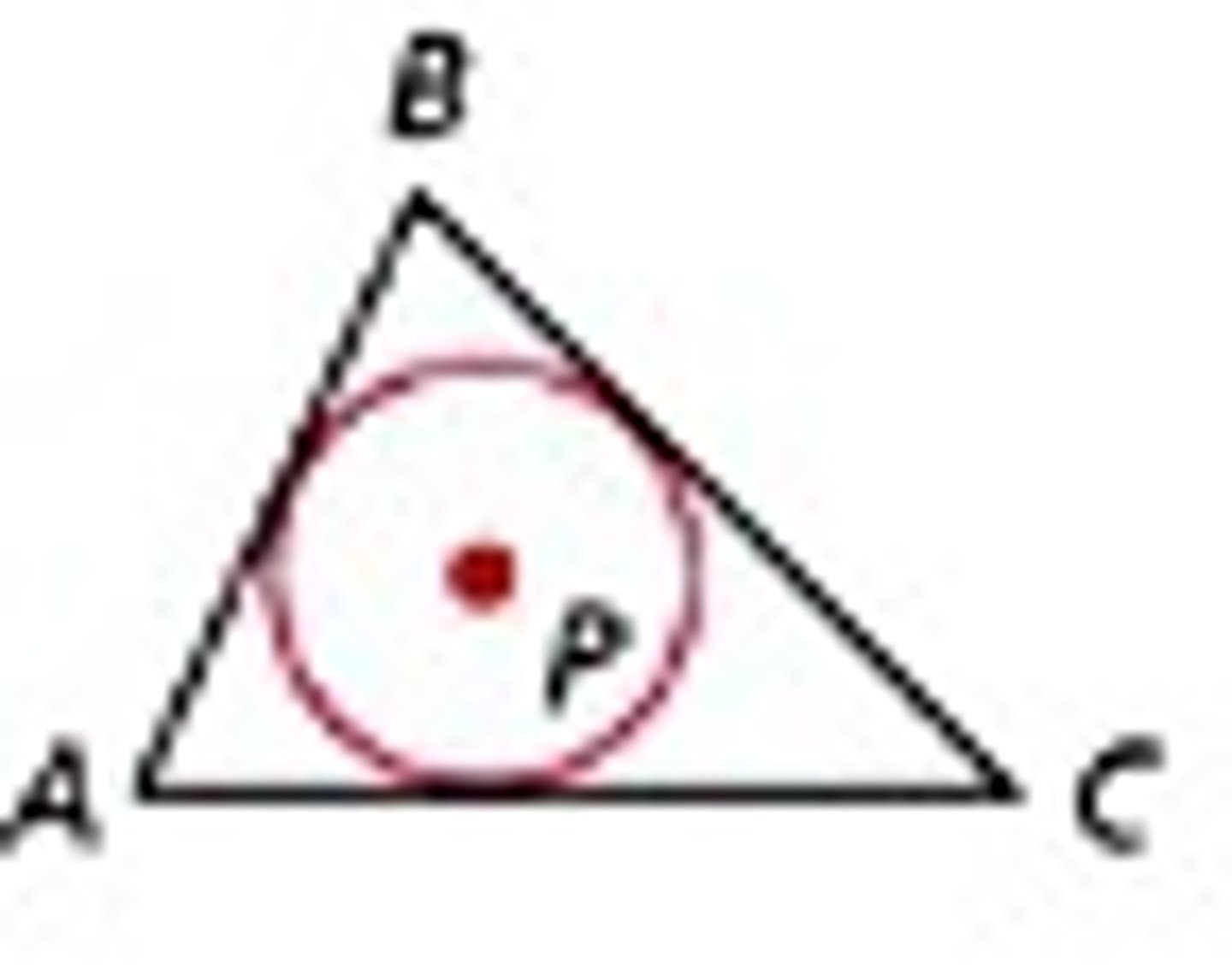
Incenter
The point where the 3 angle bisectors of a triangle meet and is always inside a triangle.
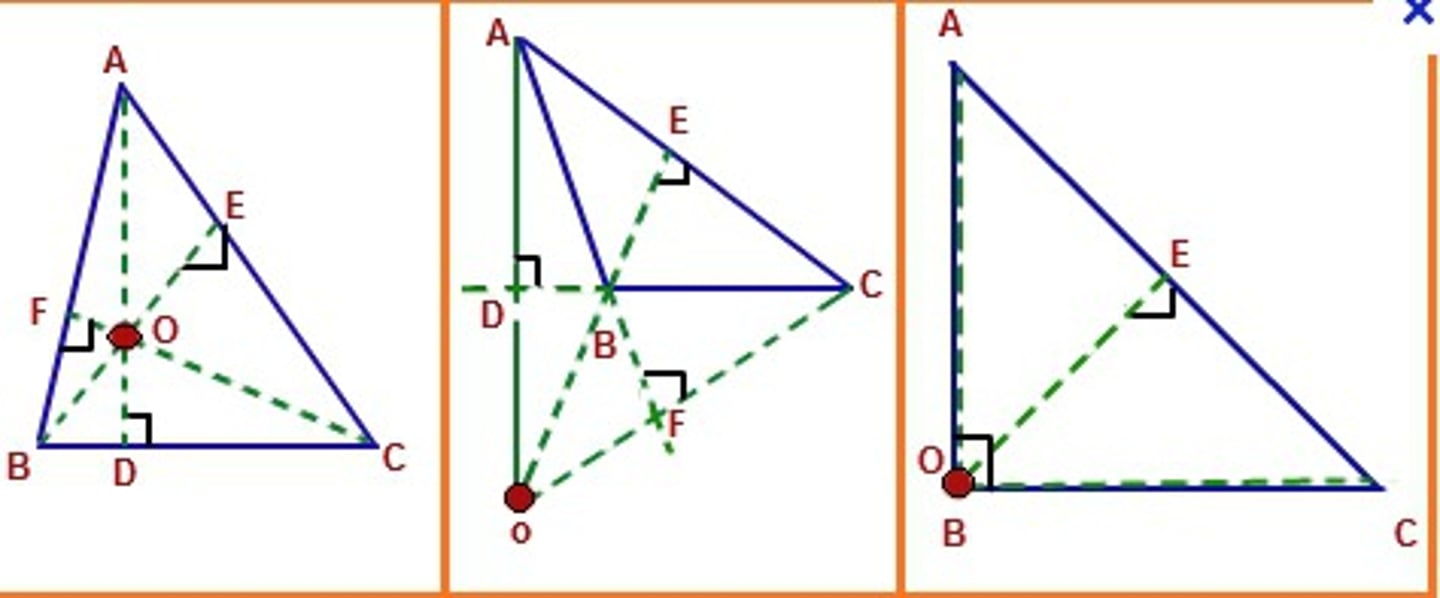
Orthocenter
The point where the 3 altitudes of a triangle meet. It can be located inside, outside, or on the triangle.
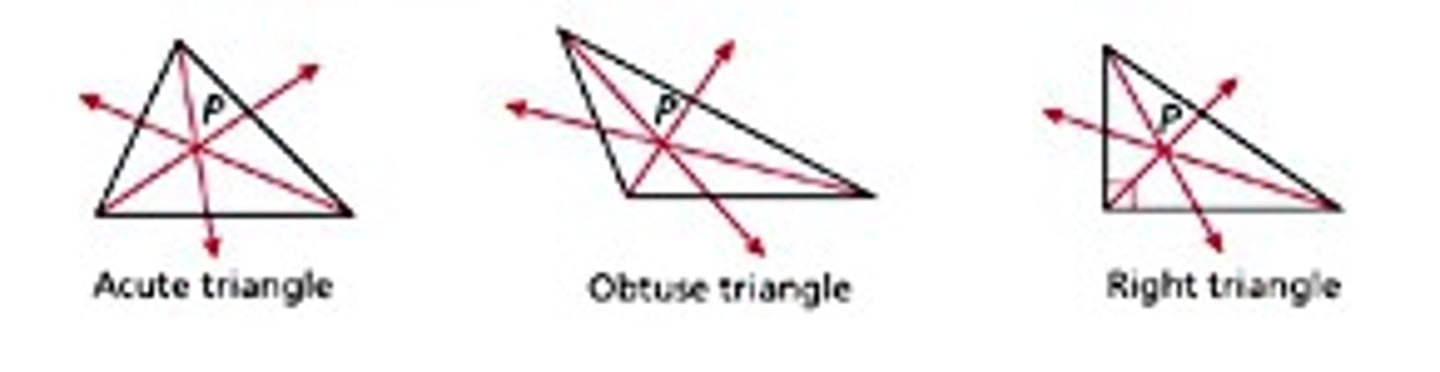
Centroid
The point where the 3 medians of a triangle meet.
Circumscribed
Every vertex of the polygon lies on the circle.
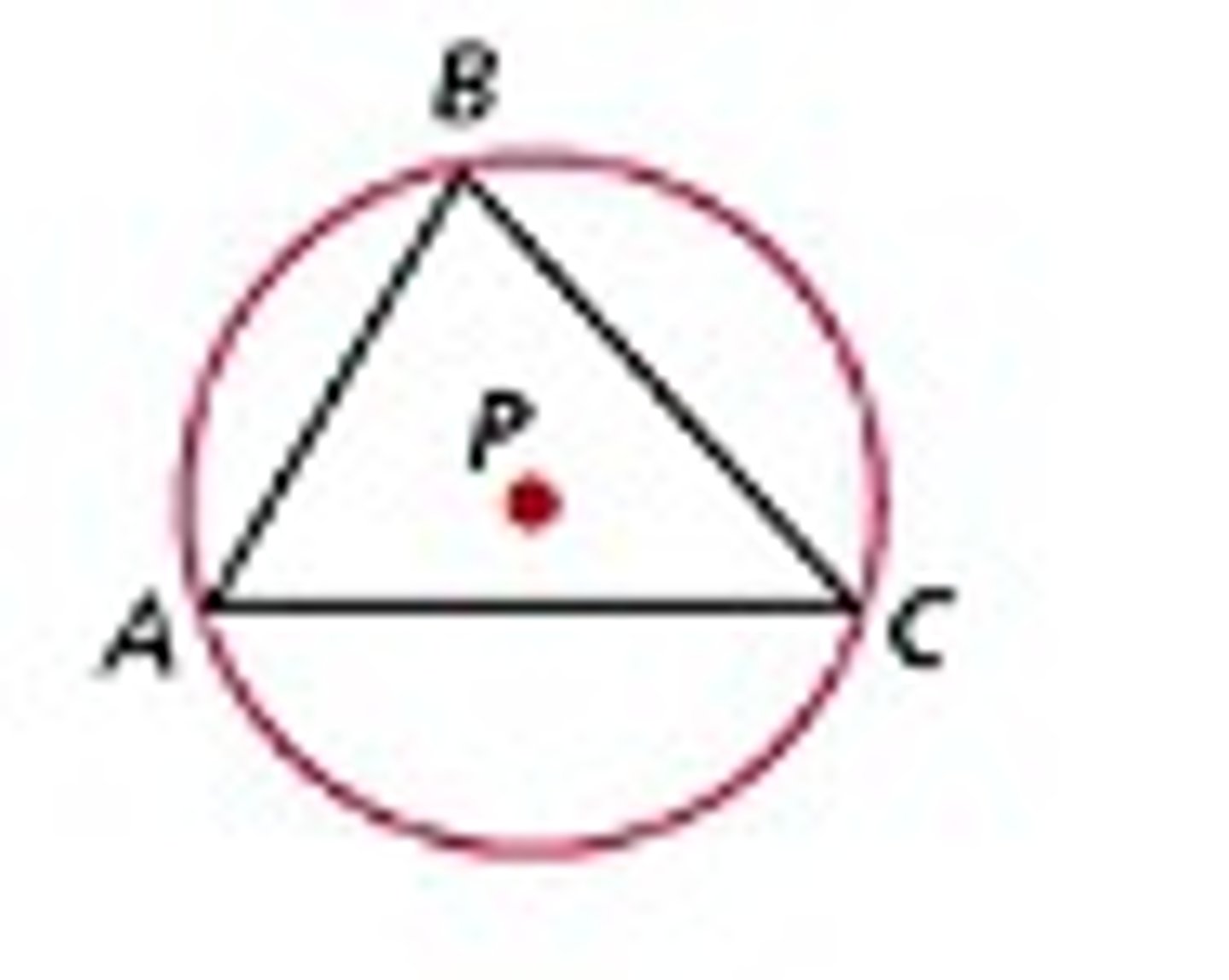
Inscribed
A circle in which each side of the polygon is tangent (touching) to the circle.
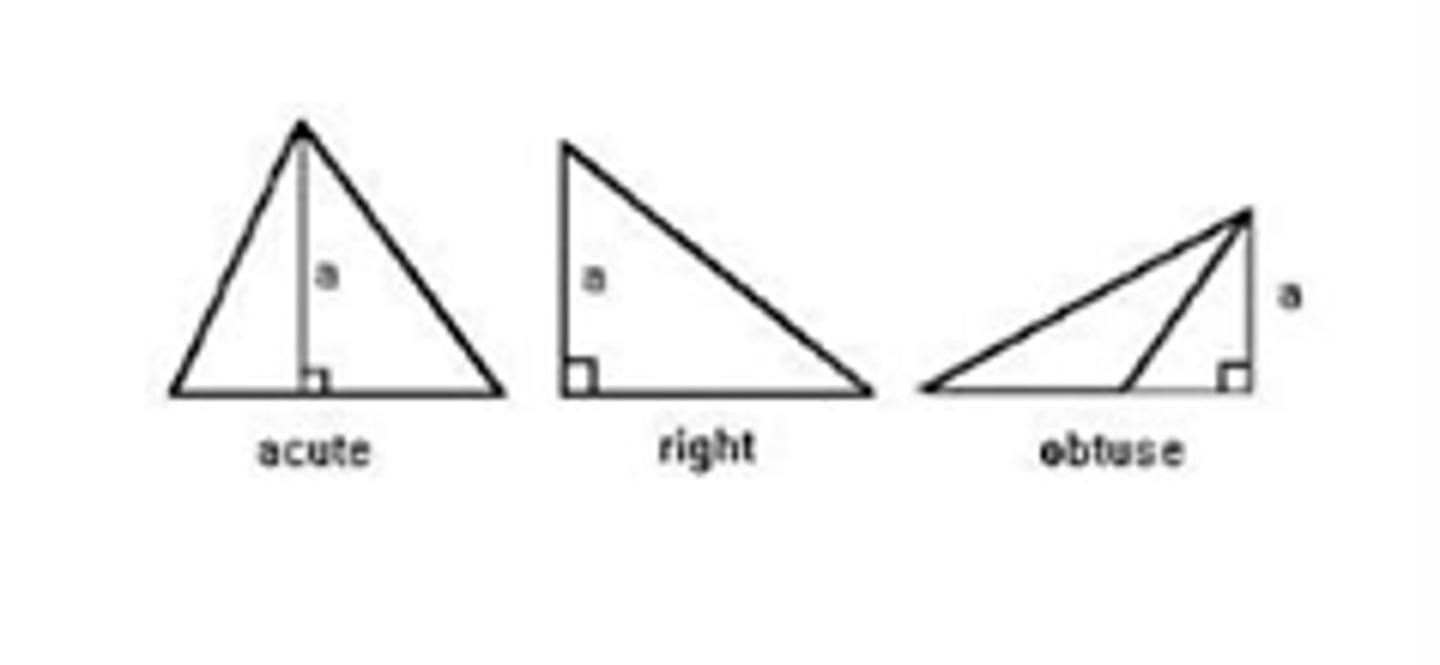
Cicumcenter Theorem
The distance from the circumcenter to each vertex is equidistant. It always meets inside an acute triangle. It meets outside an obtuse triangle.
Incenter Theorem
The incenter is equidistant from the sides of the triangle. It is always located inside the triangle.
Centroid Theorem
The distance from each vertex to the centroid is 2/3 the length of the median. (one piece is double the other) It is always located inside the triangle.
Altitude of a Right Triangle
They meet at the vertex of the right angle (on the triangle). 2 out of 3 altitudes are the legs.
Circumcenter of a Right Triangle
It is located at the midpoint of the hypotenuse.
Altitude of a Acute Triangle
Always meet inside
Altitude of an Obtuse Triangle
Lines containing the altitudes meet outside the triangle.
Perpendicular Bisector Theorem
If a point lies on the perpendicular bisector, then the point is equidistant from the endpoints of the segment.
Angle Bisector Theorem
If a point lies on the angle bisector, then the point is equidistant from the sides of the angle.
Isosceles Triangle Theorem
From the vertex angle, a perpendicular bisector is also a median, altitude, and an angle bisector.; With an acute isosceles triangle, all medians, perpendicular bisectors, altitudes, and angle bisectors meet inside.
Equilateral Triangle Theorem
Median, altitudes, Perpendicular bisectors, angle bisectors all meet inside the triangle and are all the same.
4 segments Theorem
The 4 segments for an equilateral triangle are the same and the 4 segments for an isosceles triangle are the same segments from the vertex angle.
Obtuse Triangle Outside Intersections
It has perpendicular bisectors and altitude intersections outside the triangle.
In what triangle are all four points of concurrence collinear?
Isosceles