SPED 308 Exam #1
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What best describes what happened to individuals with disabilities prior to 1970s?
-denied education and sent to psychological institutions; treatment was often cruel and dehumanizing
-law to include them was not created until 1975; when students were allowed in the schools, they were segregated
What key court cases and federal legislation have led to mandates for access to public education for children with disabiltities?
Federal Legislation:
IDEA: right for children to access education that meets the needs of students with disabilities
Section 504: expanded opportunities to kids who do not qualify for an IEP but need additional accommodations; emphasizes accessibility to programs and integration
Americans with Disabilities Act: extends civil rights to employment, public services, transportation, telecommunications
Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA): requires challenging content standards in math, reading, and science; allows students alternative testing, prepares students for higher education, requires SPED teachers to have proper certification, and how to prevent behavioral issues and adverse student behavior
Court Cases:
Brown vs. Board of Education: students not allowed to be separated, ending separate but equal in schools; used as a precedent for arguing for children with disabilities cannot be excluded from a public education (Zero reject, FAPE, Procedural Safeguards)
Pennsylvania association for Retarded Children v. Commonwealth of Pennsylvania: Sates must guarantee free public education to all children with intellectual disabilities ages 6-21 regardless of degree of impairment; must be in most integrated environment and parents have the right to participate in educational decisions of their child; states must engage in child find and preschool services must be provided to those with intellectual disabilities (FAPE)
Endrew F. vs. Douglas County School District: Expanded the meaning of FAPE
What are the 6 major principles of IDEA?
1) Zero Reject: no child is allowed to be excluded and must educate all children
2) Nondiscriminatory Evaluation: Tests must be administered in native language, there must be multiple tests to determine placement needs, and the tests must not discriminate on the basis of race, culture, or language
3) Free Appropriate Public Education (FAPE): Children must receive education at public expense to meet child’s needs, and IEP must be implemented
4) Least Restrictive Environment (LRE): Schools must educate children with disabilities with students without disabilities to the maximum extent appropriate and only be separated when the nature/severity of a disability can not benefit from a regular classroom
5) Procedural Safeguards: must protect the rights of children with disabilities and the parents (confidentiality, parental consent, due process)
6) Parent Participation and Shared Decision Making: parents and school must collaborate and have shared decision making
How are IDEA, Section 504 and Americans with Disabilities Act alike and different?
IDEA: federally mandated; focused on educational settings for ages 3-21; requires child to be identified under one of 13 disability categories
ADA: civil law; requires handicap access to buildings, transportation, equitable employment; how people with disabilities are accommodated for in society
504: if student does not qualify for IEP, they can receive reasonable accommodations to help support them
What is the process of special education? In other words, what steps need to be completed before and when an IEP is created?
Prereferral Intervention: support in the general education classroom where data is collected to see if student may need special education and has a disability; prevents child from going through IEP process if they do not need it; 3 tiers of support which gradually increase
Response to Invention (RTI) - academic support
Positive behavior interventions and support (PBIS) - behavioral support
Multifactored evaluation: meet and discuss tests and evaluations needed for child with parents; need parental consent, nondiscriminatory tests, ad multiple tests to get full picture of child’s abilities
Eligibility Determination: Results of testing discussed to determine need for special education, and which category of disability child qualifies for; must be LRE
Program Planning and IEP placement: meeting to design IEP and implementing it
Progress monitoring and review: add and change parts of the IEP to see what supports student needs; can occur throughout the year but must be done yearly at minimum
Reevaluation: must occur every 3 years where student repeats entire IEP process
What are some things that should be taken into consideration with regards to assessment and evaluation procedures for students from culturally diverse backgrounds?
ensure student is educated in their native language and include interpreter if needed
ensure cultural knowledge is there to prevent cultural bias
must have multifactored evaluation
does instruction show ‘disability’ is not a result of culture?
What are the major components of the IEP as specified by IDEA?
statement of child’s present level of academic achievement
statement of goals child needs to complete
description of child’s progress towards annual goals, measured by periodic reports
statement of special education and services and supplementary aid and program modifications
explanation of extent to which child will be educated with non-disabled kids
statement of accommodations necessary on state and district assessments or need for alternative assessments
date to begin services and modifications including frequency and duration and transition to adulthood if 16+
first IEP must be put into effect by age 16 and be updated annually
What is the process of developing the IEP and what are some considerations for implementing the IEP?
Considerations:
results of evaluation
parent’s perception of disability
language of child
strengths of child
Implementation:
consider LRE, progress monitoring, reevaluation
provide supports, assistive technology, put IEP into action
Who are the required members of an IEP team?
special education teacher
general education teacher
local education agency representative
parents
someone to interpret the results of tests
child when appropriate
any other person parent wants
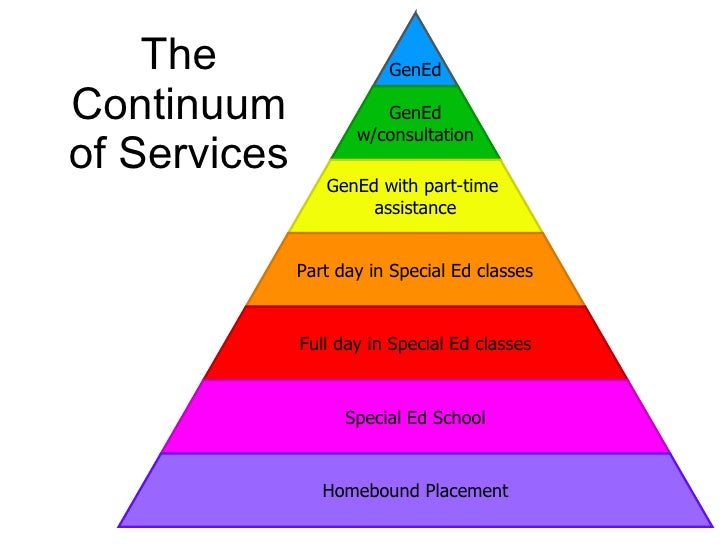
What is the continuum of services or continuum of alternative placements?
range of service options for students to receive services
general education classroom is not the best for every child; can be restrictive and harmful
What is co-teaching and the different models?
The general education and special education teachers work cooperatively together to coordinate curriculum and instruction, teaching a heterogeneous group of students in the general education classroom
Lead and Support: 1 teacher leads and 1 assists
Station Teaching: both teachers present different content at the same time to a group of students then switch groups and repeat the lesson
Parallel Teaching: both teachers teach the same material/ content to groups of students
Alternative Teaching: 1 works with larger group and 1 with smaller group
Team Teaching: shared responsibility for planning and instruction; both teach
What are some things that should be taken into consideration when working with families of students with disabilities?
person-first language
consider parent’s background, needs
consider if the parent is going through stages of grief
culture changes how parents perceive education and disability
communicate with families who speak other languages
parents have many roles/responsibilities to care for their child
must have parents’ consent to testing and implementation
What are the characteristics of students with Learning Disabilities?
a disorder in psychological processes involving understanding or in using language, spoken or written, which leads to issues in listening, thinking, speaking, reading, writing, spelling, or to do mathematical calculations
cannot be a learning issues as a result of visual, hearing, or motor disabilities or a result of emotional disturbance, environmental, cultural, or economic disadvantages
Dyslexia: difficultly reading, phonics, comprehension
Dyscalculia: difficulty solving/grasping math problems, lining up math equations, etc…
Dysgraphia: difficulty with writing where student has difficulty forming letters or writing in a specific place
problems often associated with listening, reasoning, memory, attention, focusing, processing visual and auditory things
What criteria is necessary to identify students with learning disabilities?
1) Discrepancy between intellectual ability (IQ) and academic achievement
2) exclusion criteria - student’s difficulty can not be a result of another known condition that can cause learning issues
3) a need for special education services
The reauthorization of IDEA in 2004 recognized the problems of the discrepancy approach to identification of learning disabilities. Based on the reauthorization of IDEA in 2004, in what ways can a local educational agency determine a child’s eligibility for special education under the specific learning disability category?
can use RTI to qualify a student through 3 tier system: Programing in general education classroom, supplemental intervention through small-group instruction, intensive instruction often as special education but can receive before special ed determination
use process to determine if child responds to scientific, research-based intervention as part of the evaluation
severe discrepancy between IQ and academic achievement can be used for qualification but not required
What strategies can be used when working with students who have Learning Disabilities?
Explicit/direct instruction: systematic approach to guided learning processes with clear statements on purpose, clear expectations, and demonstrations and feedback
Graphic organizers: visual-spatial arrangement of info with words and concepts connected to help students see relationships
Guided Notes: teacher prepared handouts to provide outline of lecture content, completed during class by writing key facts, concepts, or relationships
Note-taking strategies: provided cues to help organize information and combine new knowledge with prior knowledge
Mnemonics: develop ways student can easily remember steps to do something
Endrew F. V. Douglas County School district
Endrew had AuADHD and his progress was worsening in public school so his parents moved him to private school. When attempting to go back to public school, IEP was no sufficient to help him succeed so switched back to private school. Parents waned reimbursed tuition because it was not appropriate education for him → cornerstone to delivering appropriate education (specifically FAPE) and implementing an IEP that helps student succeed