MLS 332 Unit 2 Part 3 Erythrocyte Abnormalities
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
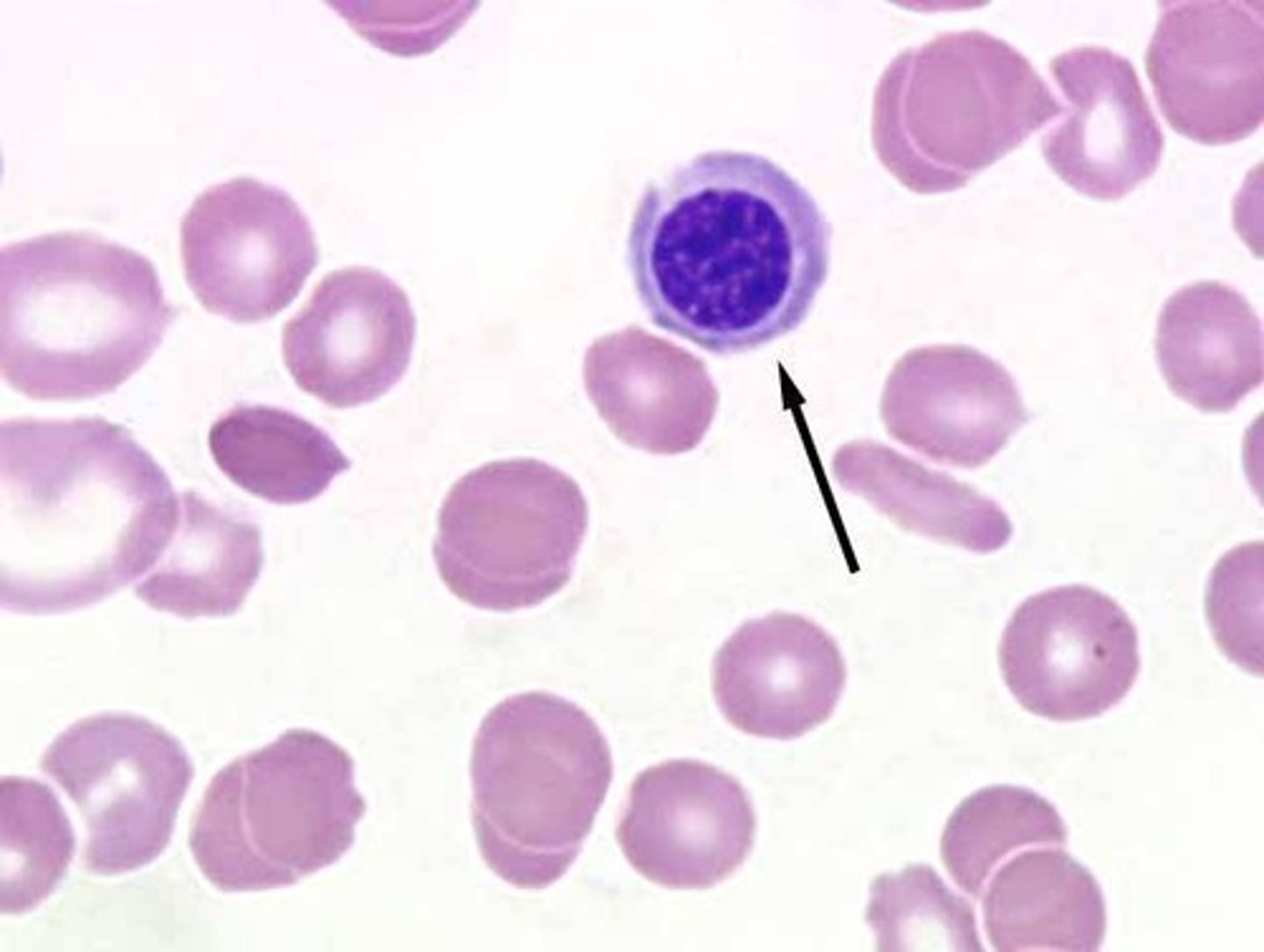
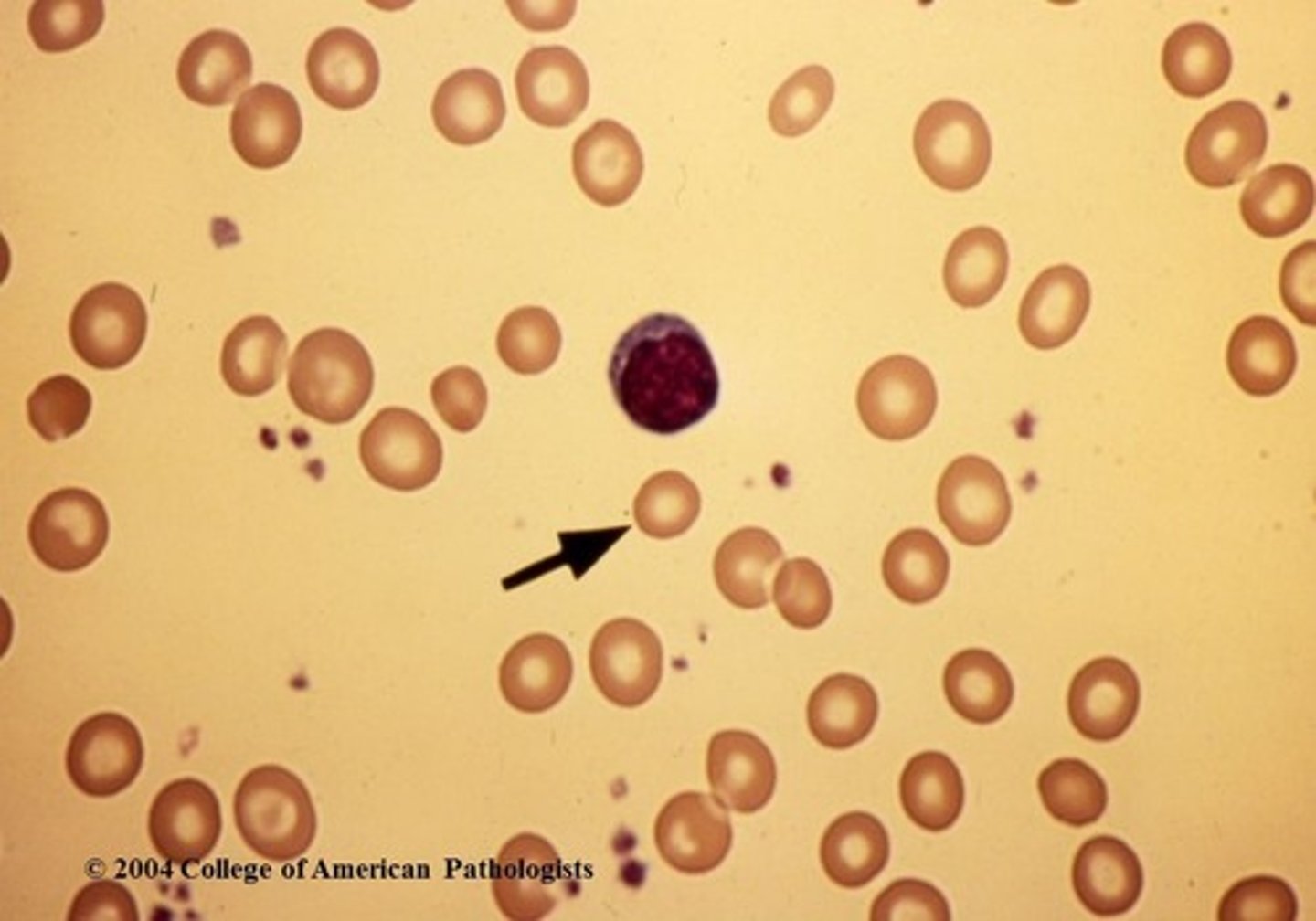
Microcytic RBC
small RBC
<80 fL
smaller than a small lymphocyte
–Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV)
•80-100 fL
•Correlates to size of the RBCs on a blood smear
How big does the cell look on the size
–Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH)
•28-34 pg - weight
average amount of hemoglobin in a RBC
–Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC)
•32-36 g/dL
•Correlates to hemoglobination on a blood smear
• Measures the concentration of hemoglobin in a given volume of packed red blood cells.
Poikilocytes
Change in Shape of RBC
Anisocytosis
–Variation in sizes of RBCs
–Correlates with RDW
• Red blood cell Distribution Width
*Do the Cells look uniform
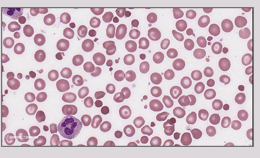
Normocytic RBC
normal size
(80-100 fL)
The same size as a small lymphocyte
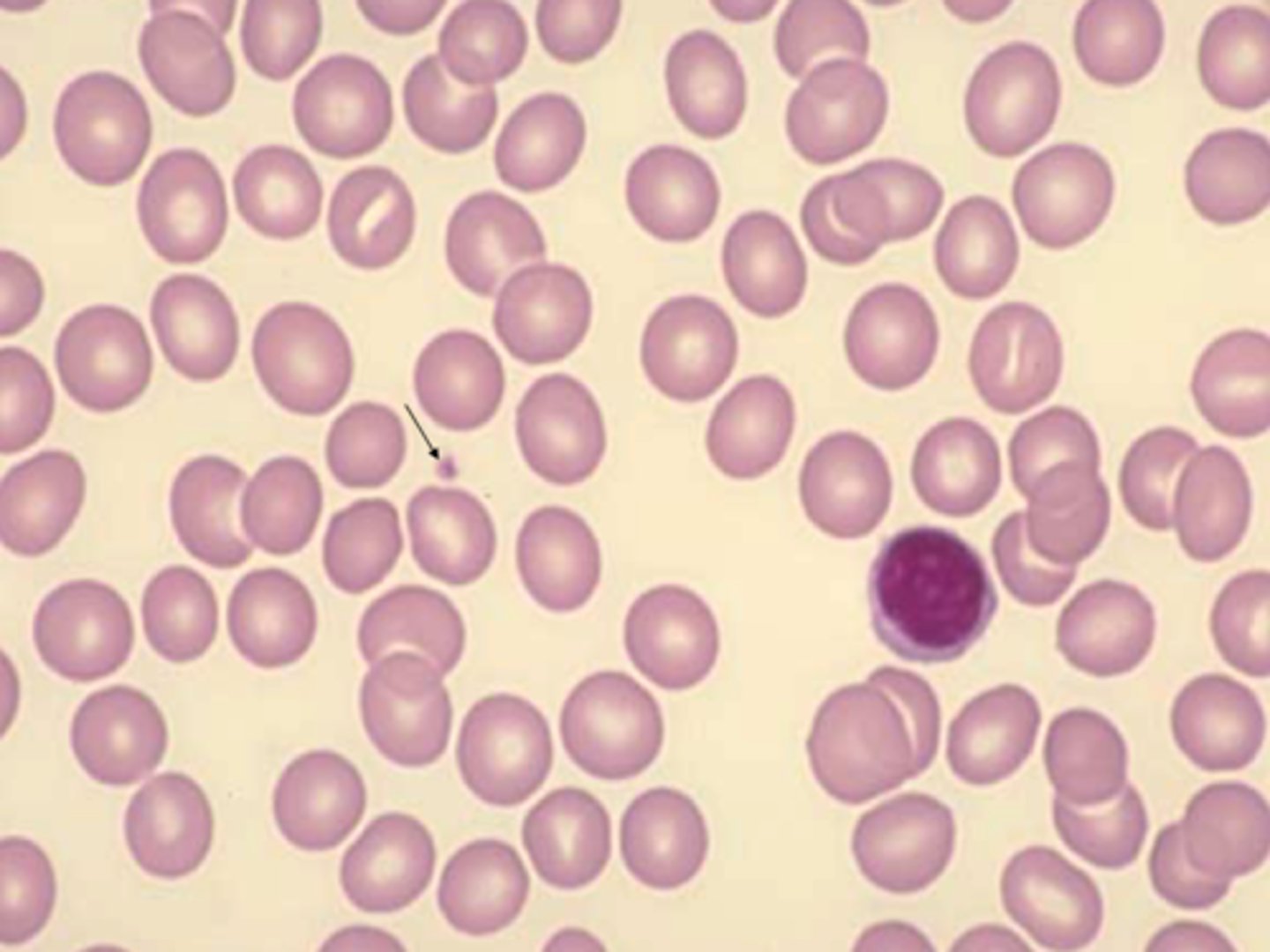
Macrocytic RBC
large RBC
(>100 fL)
Bigger than small lymphocyte
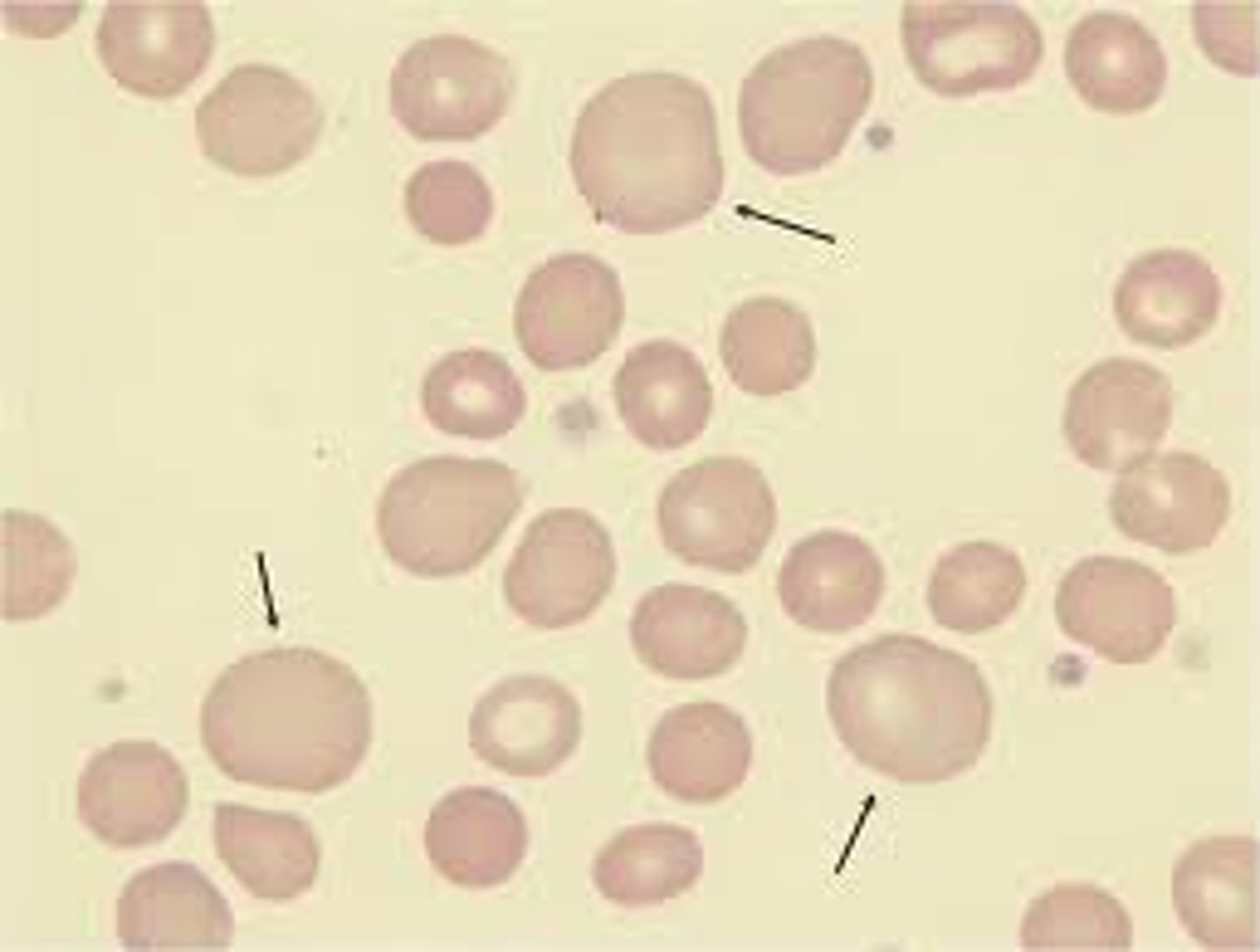
Hypochromic RBC
pale RBC (more white than pink)
The central pallor is the white part greater than one-third of the cell diameter.
Normochromic RBC
normal color (1/3 central pallor and 2/3 red part )
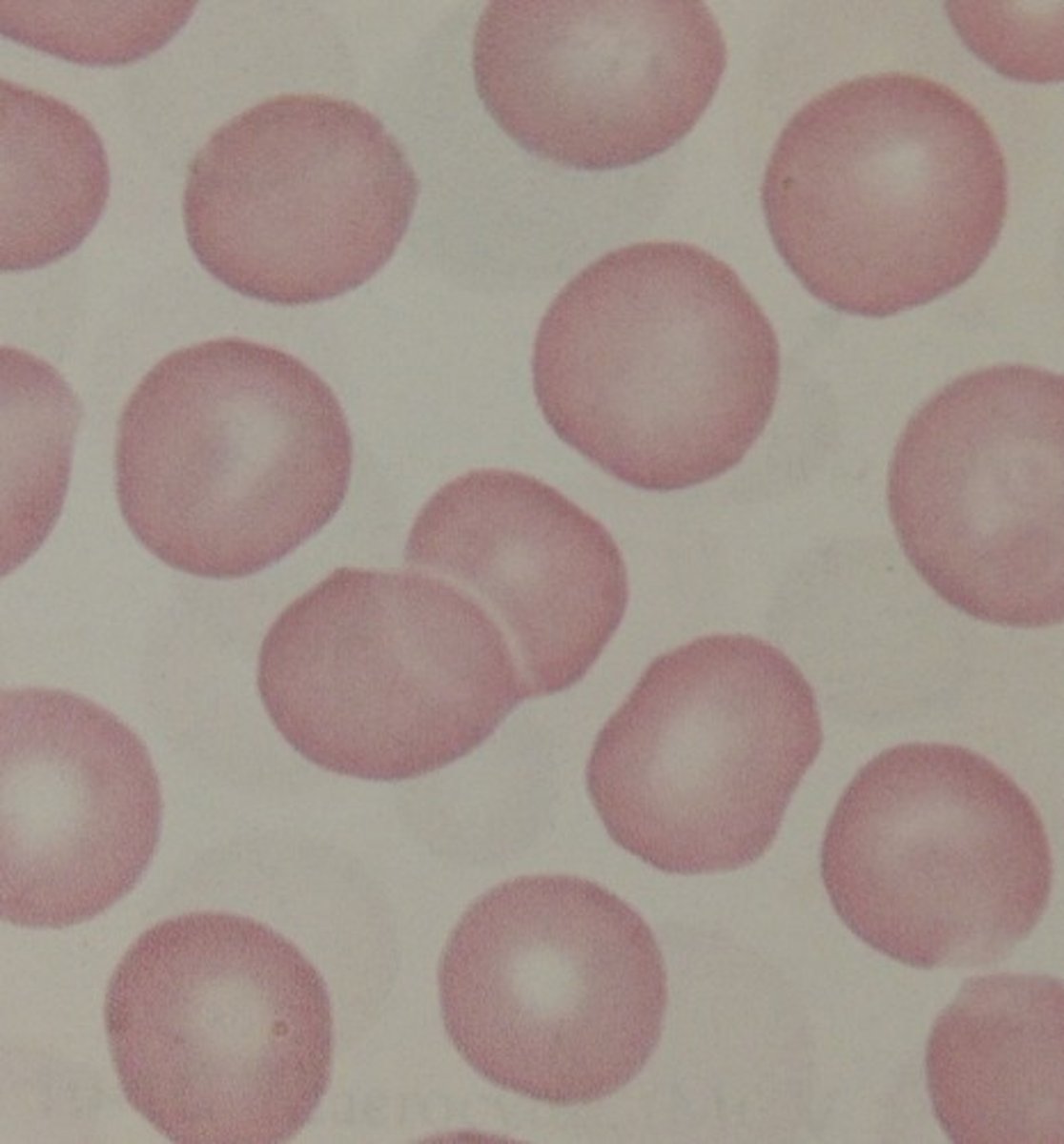
Spherocytic RBC
darker than usual (little or no central pallor)
Loss of cell membrane so a smaller surface area to the same amount of volume from a normal RBC
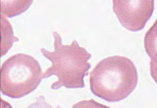
Acanthocyte Alternative Name
spur cell
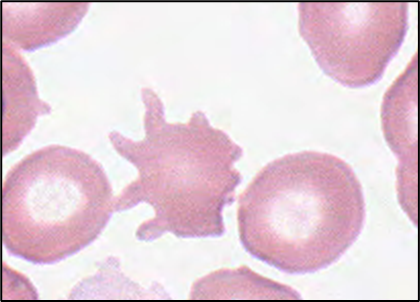
Acanthocyte Description
Red cells with spicules of varying length irregularly distributed over the surface; no central pallor
Acanthocyte Mechanism of Formation
Excess distribution of cholesterol in outer layer of membrane
Acanthocyte Associated Diseases
Abetalipoproteinemia, alcoholic liver disease, disorders of lipid metabolism, post-splenectomy - need to know yellow
Codocyte Alternative Name
target cell
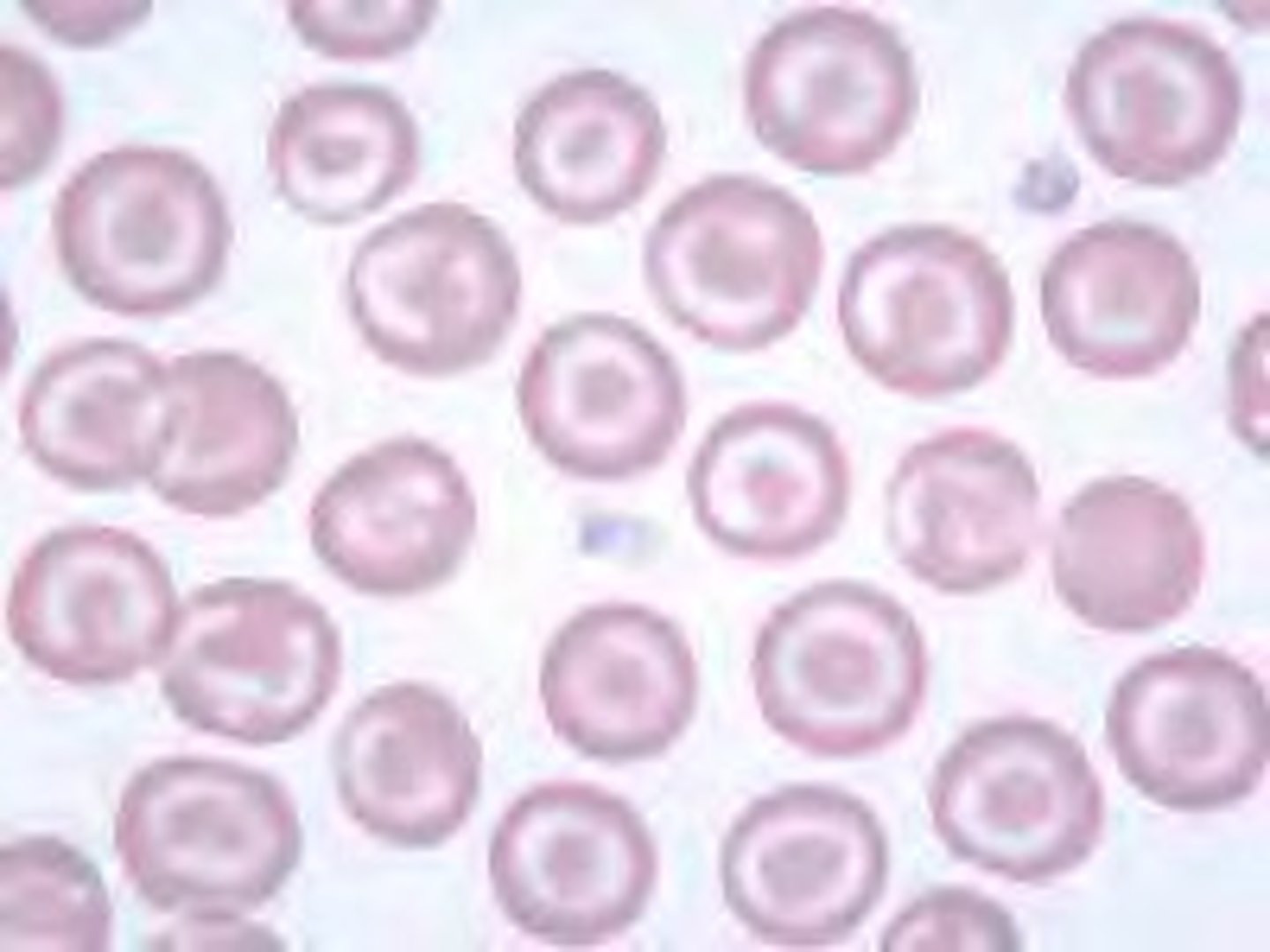
Codocyte Description
Thin and bell-shaped; on stained blood smears, appears as a target with a central bull's-eye, surrounded by a white zone and outer ring of hemoglobin
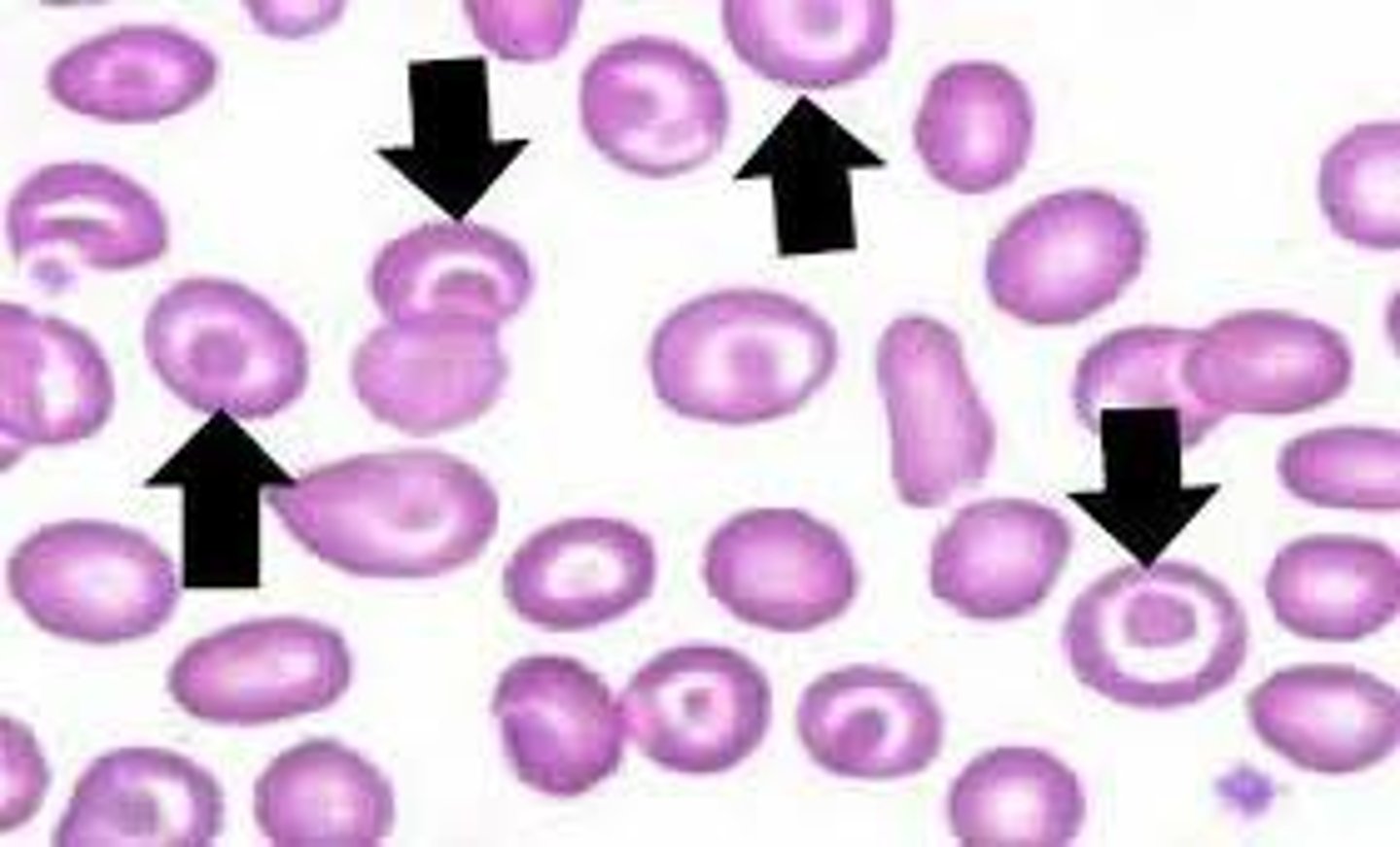
Codocyte Mechanism of Formation
Increased surface area-to-volume ratio
Codocyte Associated Diseases
Hemoglobinopathies, thalassemias, obstructive liver disease, iron deficiency anemia, splenectomy, renal disease, LCAT deficiency
Dacryocyte Alternative Name
Teardrop
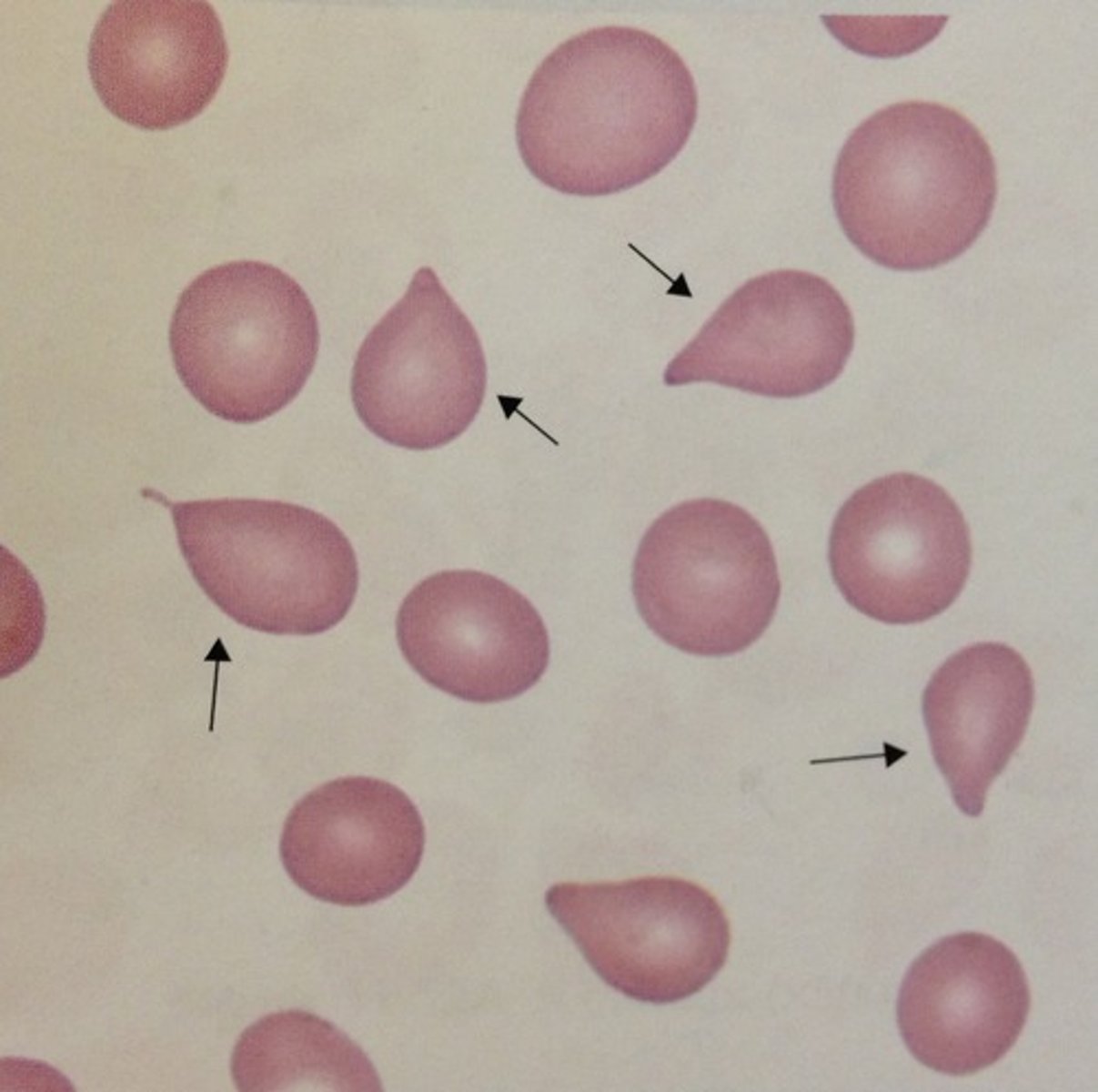
Dacryocyte Description
Round cell with a single, elongated or pointed extremity; may be microcytic and/or hypochromic
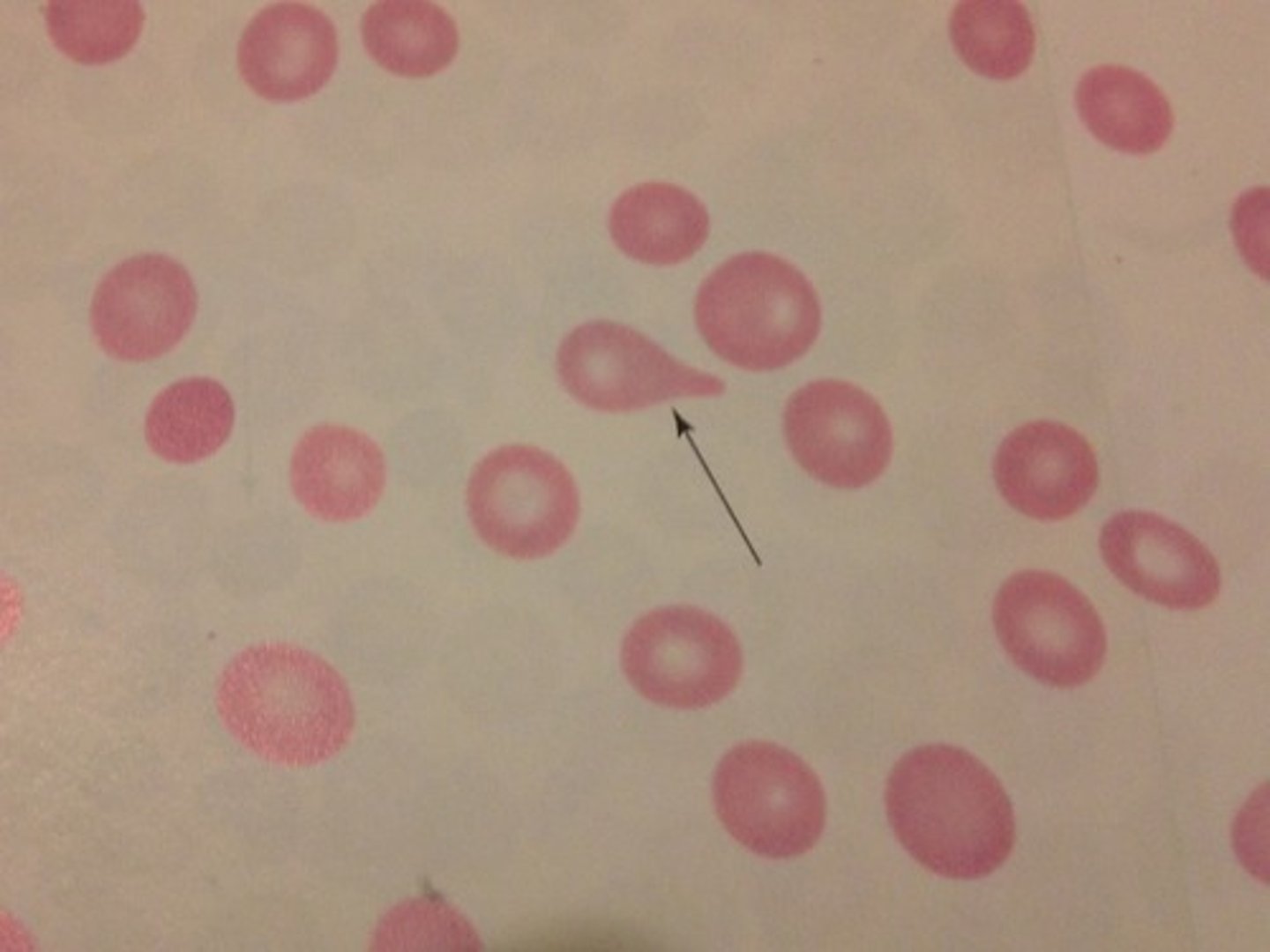
Dacryocyte Mechanism of Formation
Result of prolonged squeezing through a small space (e.g., spleen or fibrous bone marrow) - is stretched out to far
Dacryocyte Associated Diseases
Myelophthisic anemias, primary myelofibrosis (PMF), thalassemias, iron deficiency anemia
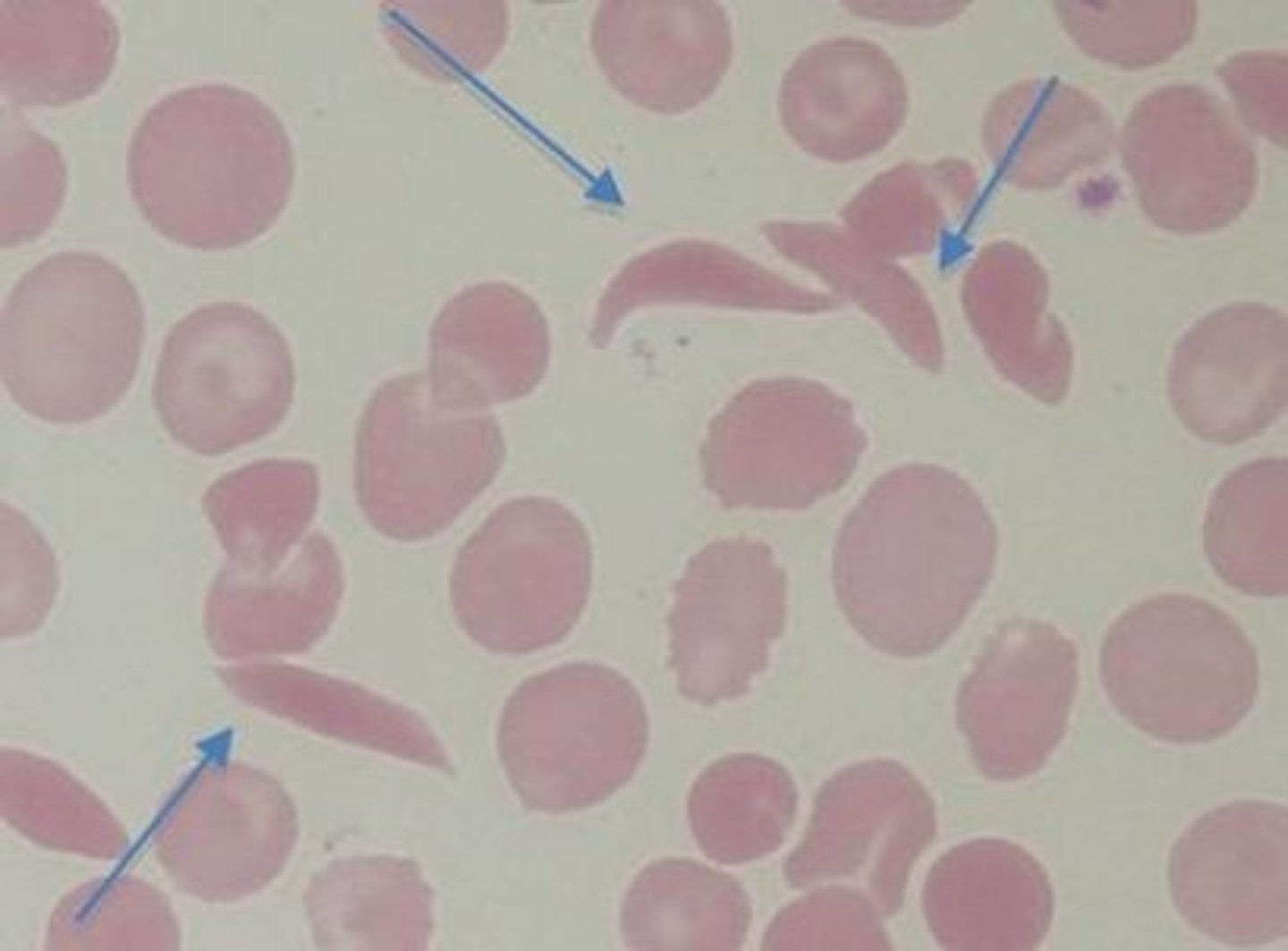
Drepanocyte Alternative Name
sickle cell - Is inherited and comes from the polymerization of Hemoglobin S
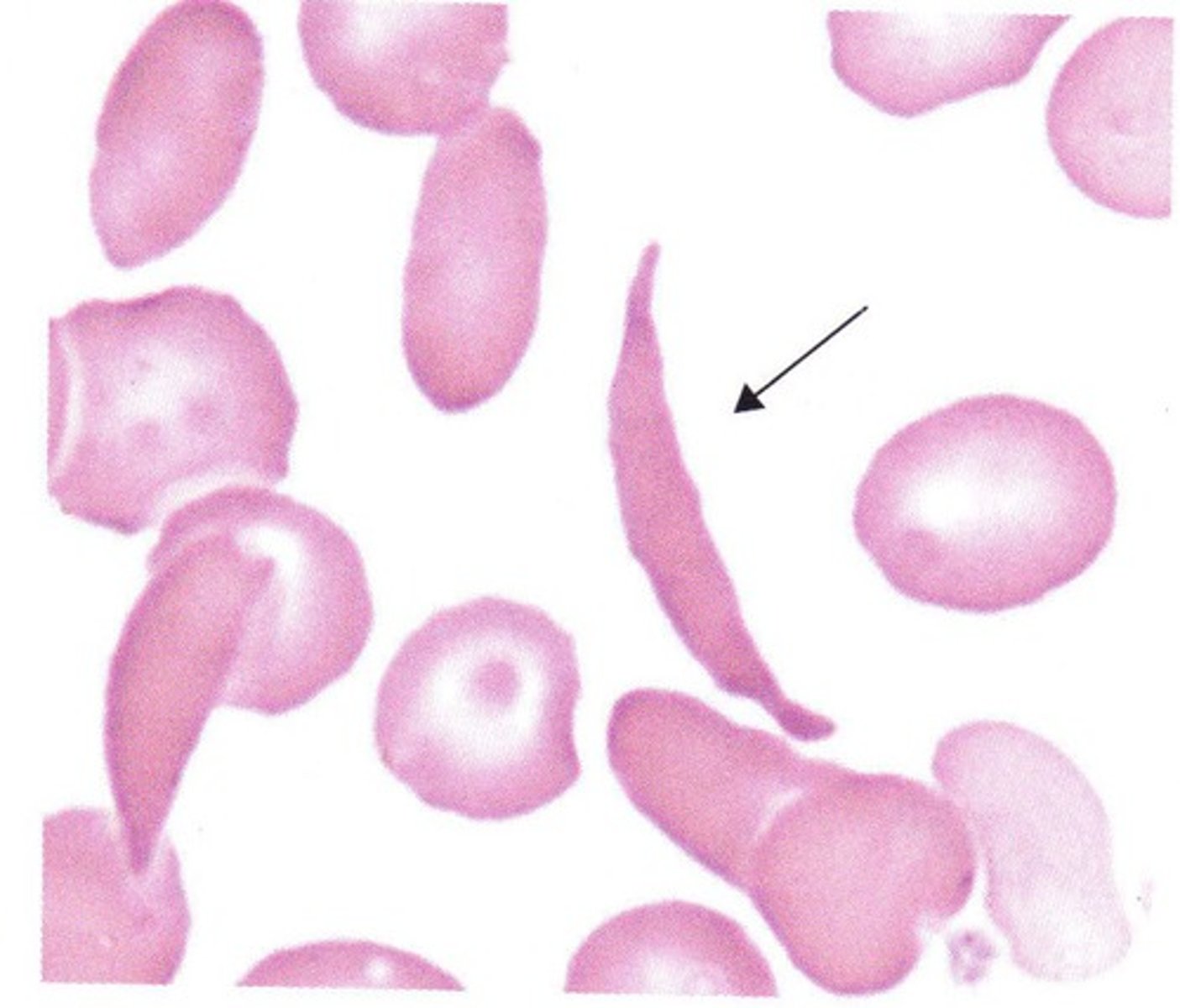
Drepanocyte Description
Contain polymerized hemoglobin showing various shapes; sickle-, crescent-, or boat-shaped
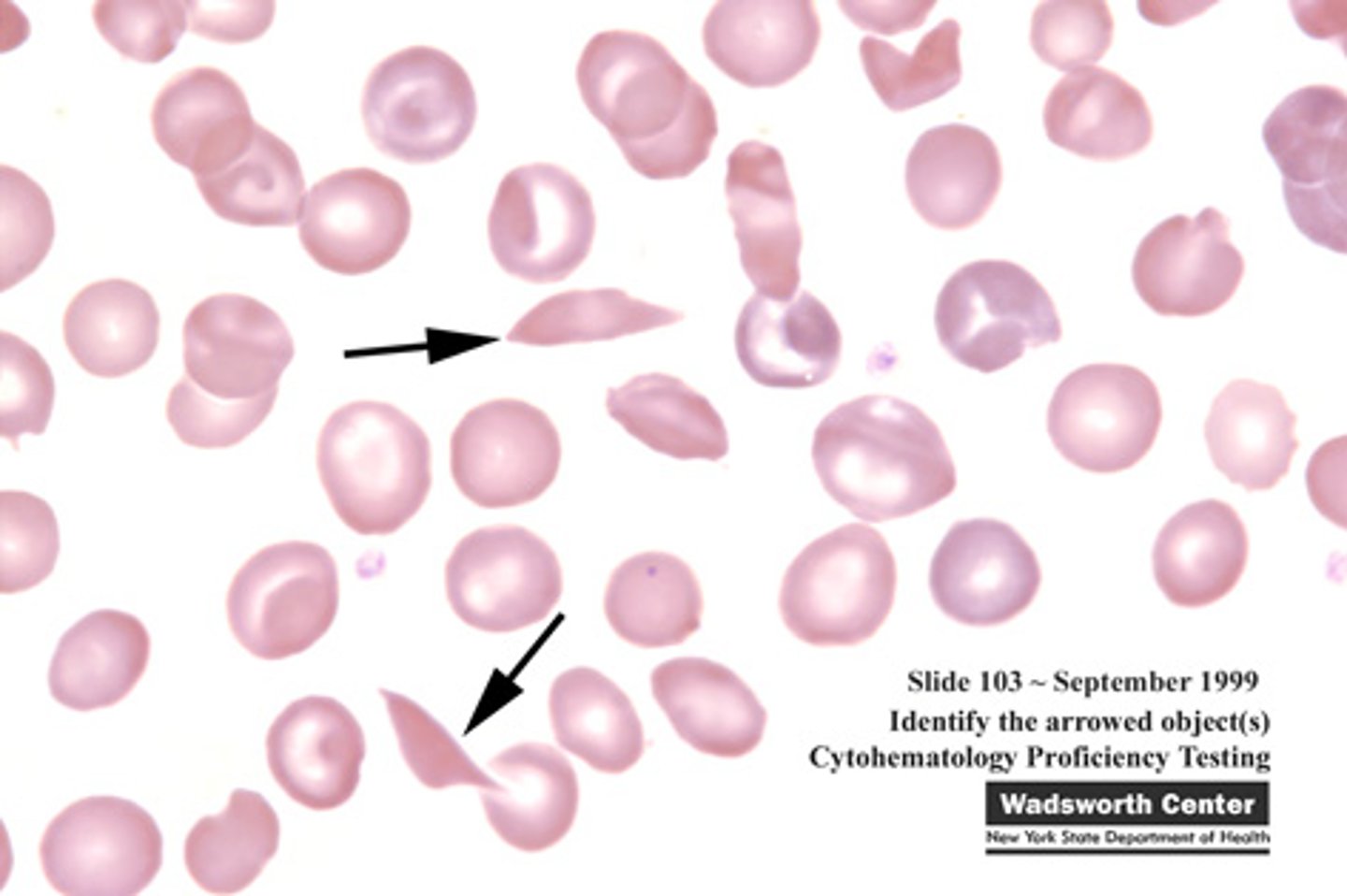
Drepanocyte Mechanism of Formation
Polymerization of hemoglobin S into rods stretches the cell and increased fragility
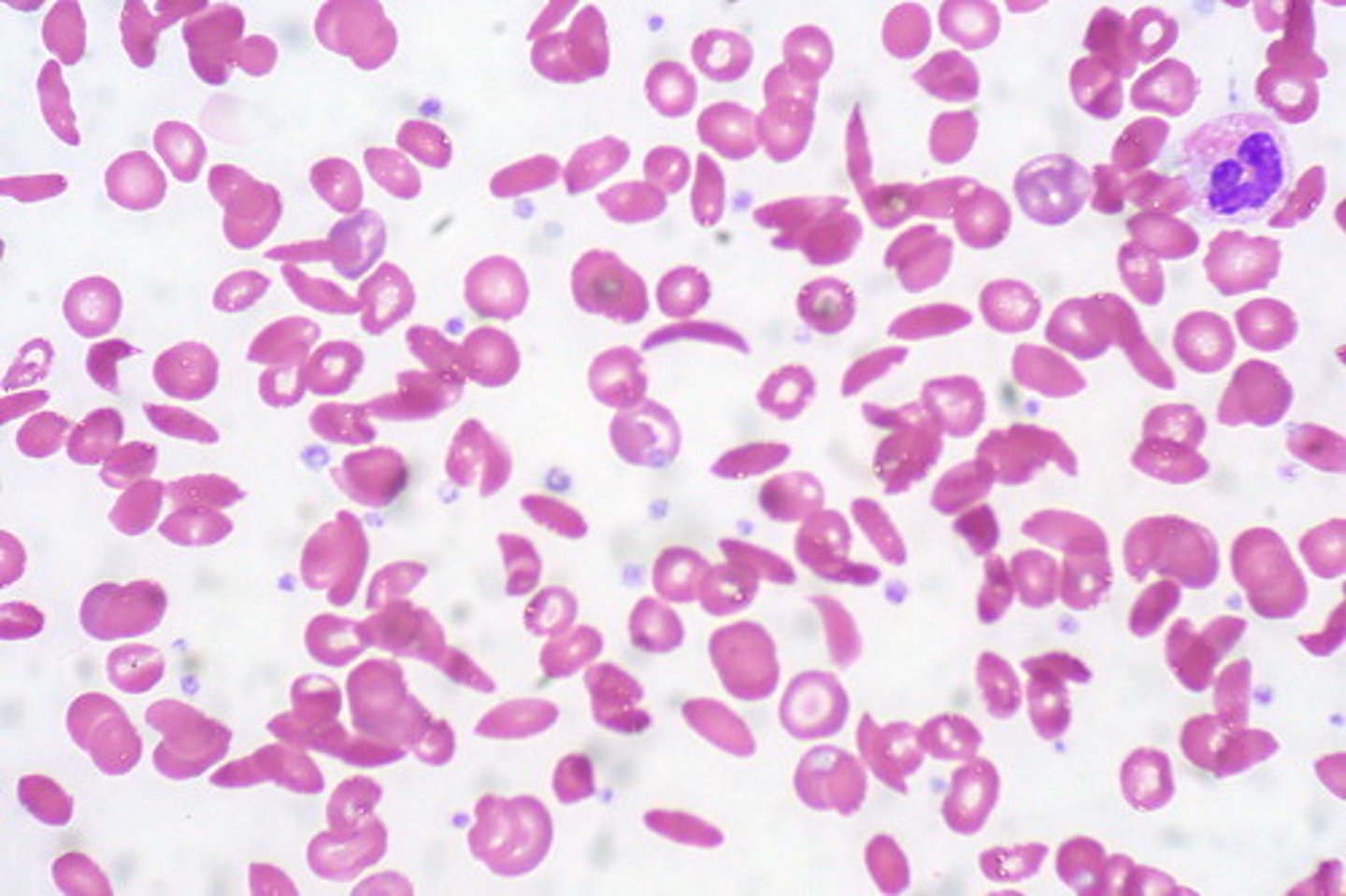
Drepanocyte Associated Diseases
Sickle cell disorders (Sickle Cell Anemia) is only inherited and needs to have hemoglobin S
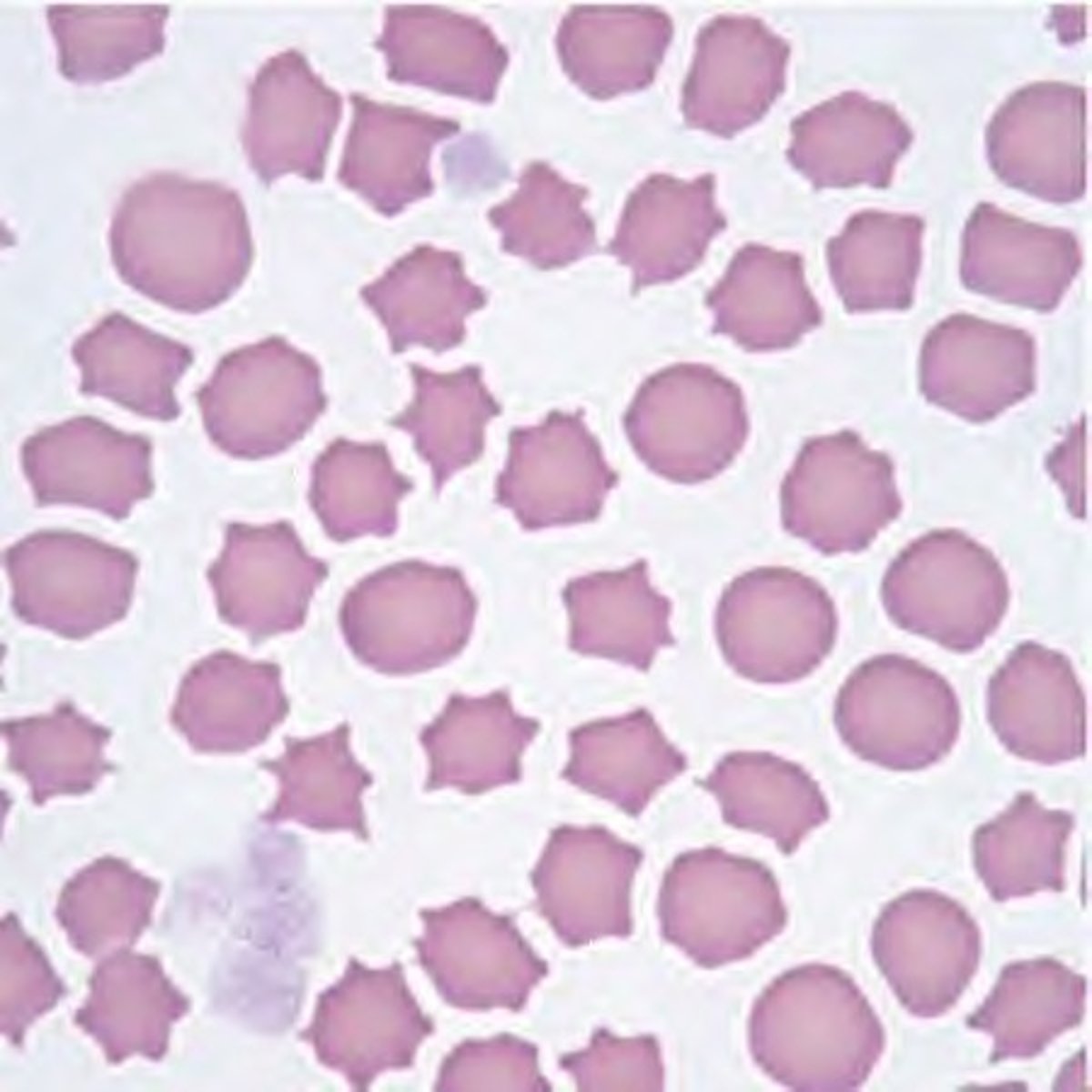
Echinocyte Alternative Name
spur cell
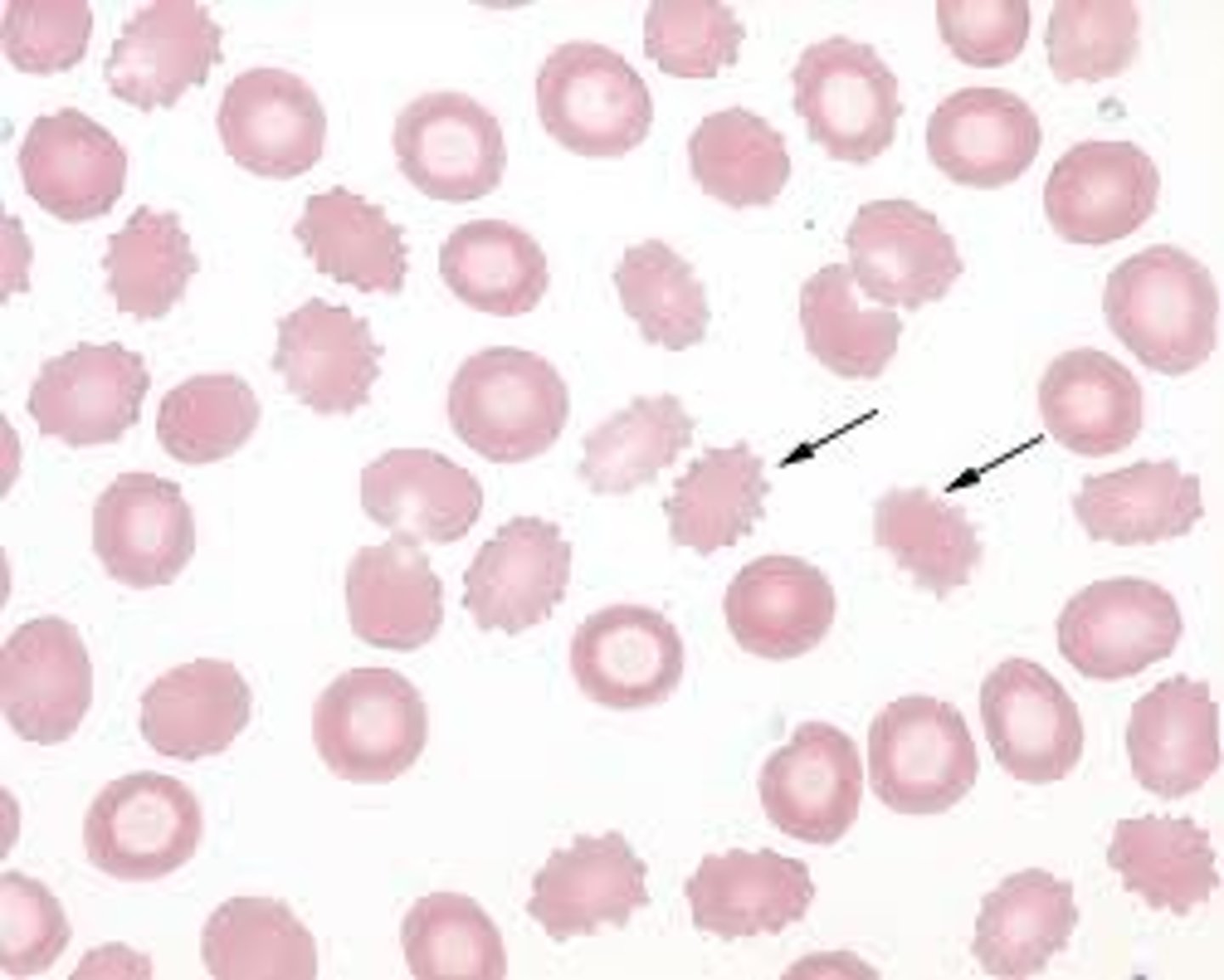
Echinocyte Description
Spiculated red cells with short, equally-spaced projections over the entire surface
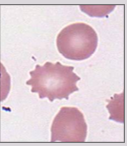
Echinocyte Mechanism of Formation
Increased area of the outer layer of membrane in comparison to the inner layer
Echinocyte Associated Diseases
Liver disease, uremia, pyruvate kinase deficiency, peptic ulcers, stomach cancers, heparin therapy
Elliptocyte Alternative Name
cigar cell
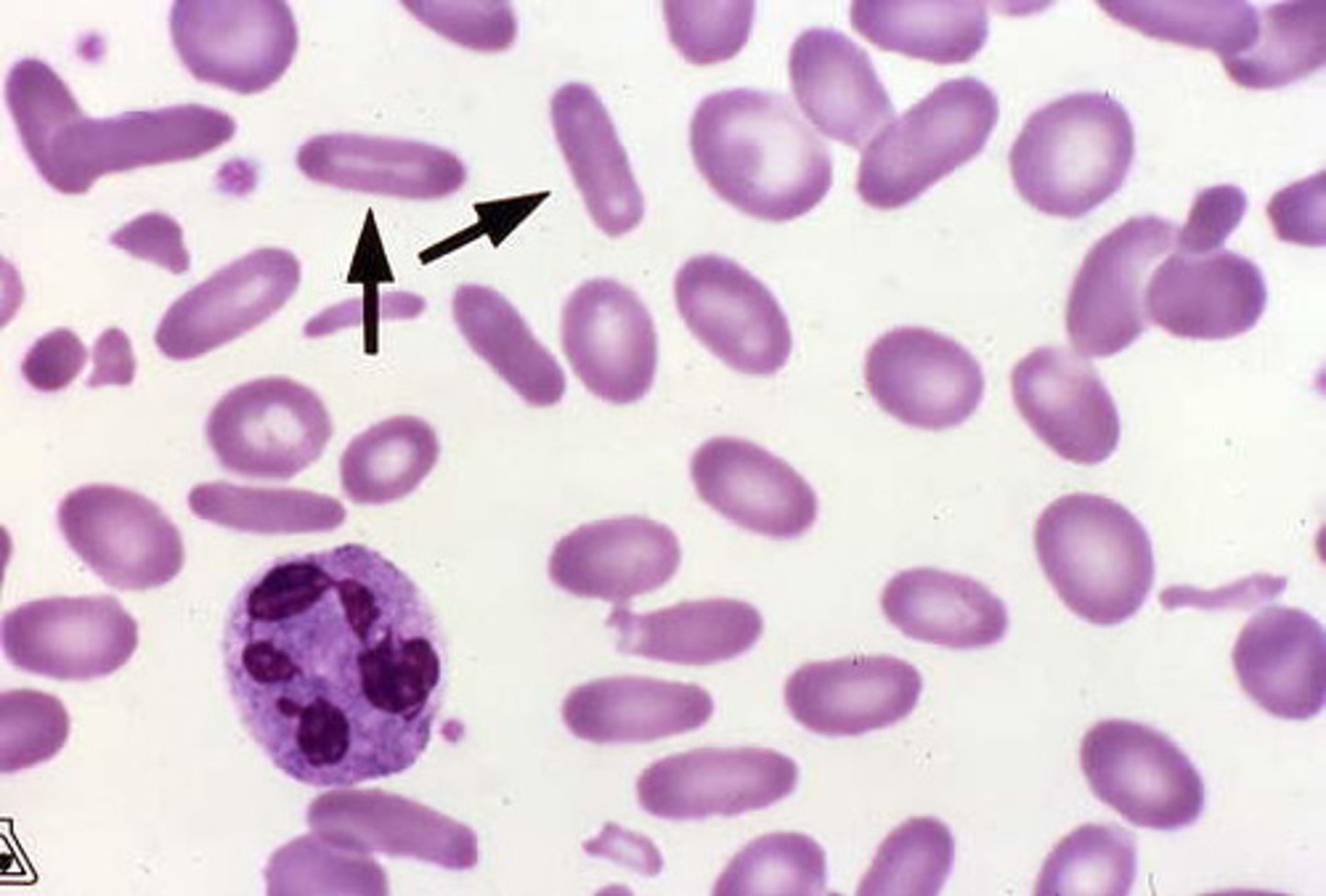
Elliptocyte Description
Elongated ellipsoid cell with parallel sides, and some have an area of central pallor, and some don’t, and hemoglobin at both ends
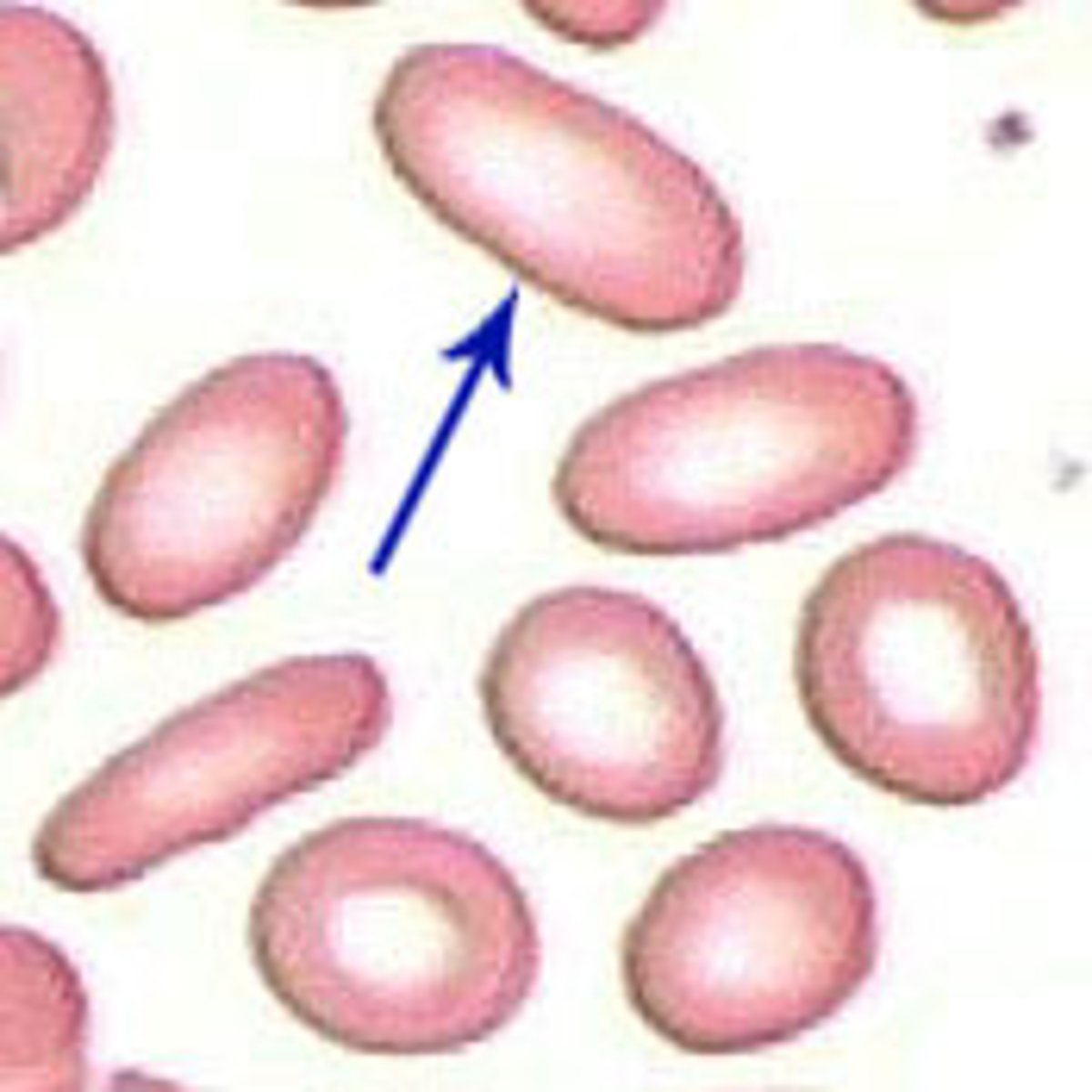
Elliptocyte Mechanism of Formation
Unknown; thought to be alterations in the membrane skeleton
Elliptocyte Associated Diseases
Hereditary elliptocytosis, iron deficiency anemia, thalassemia, anemia of chronic disease
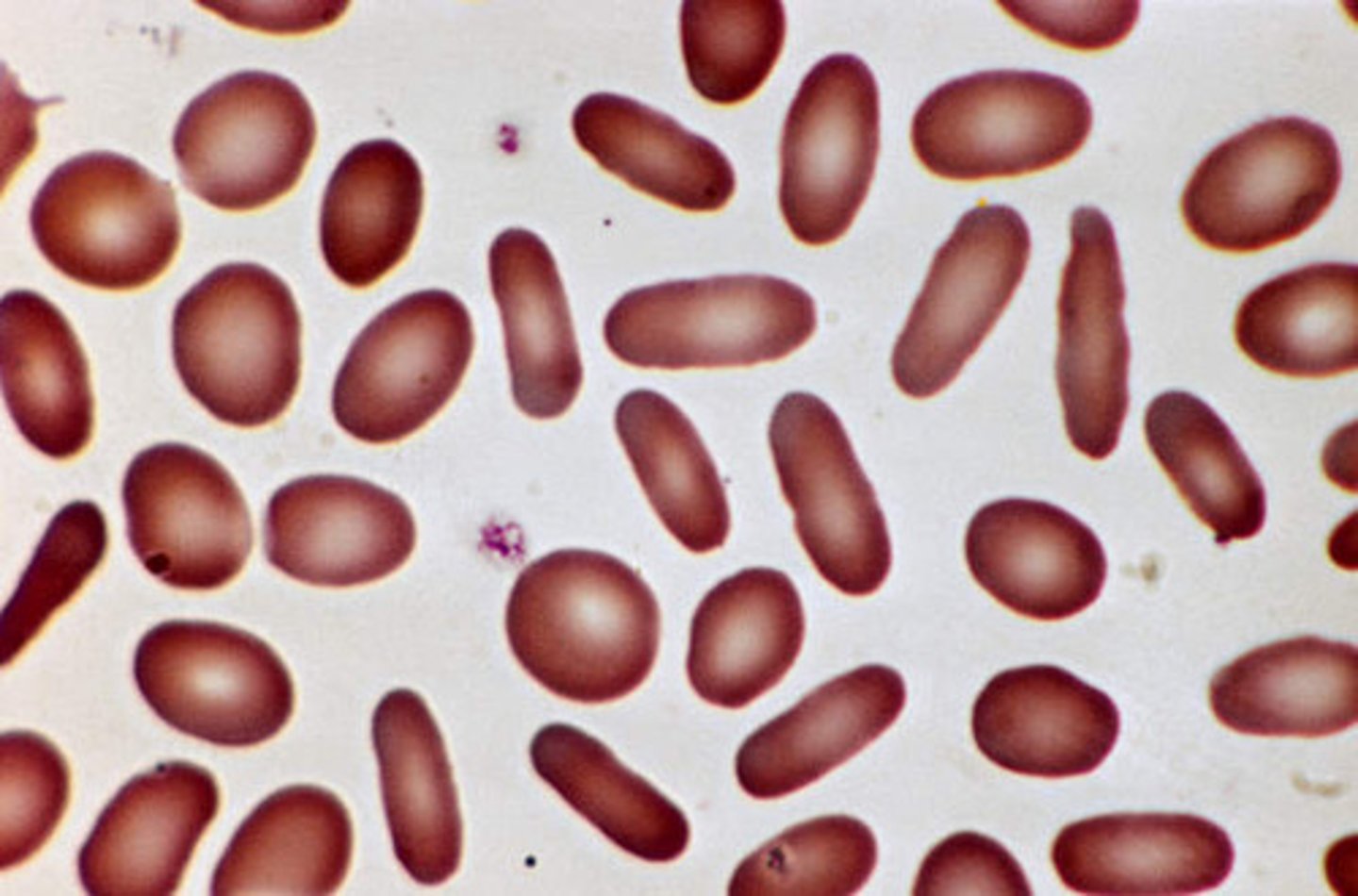
Oval Macrocyte Description
Slightly elongated macrocytic RBC; width is not continuous
Has to be bigger in size
Has to be oval shaped
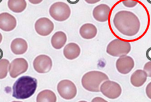
Oval Macrocyte Mechanism of Formation
Abnormal maturation and nuclear/cytoplasmic in the bone marrow asynchrony of developing bone marrow cells
Oval Macrocyte Associated Disease
Megaloblastic anemias
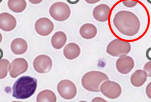
Schistocyte (fragment) Description
pieces of red cells; variety of shapes including triangles, commas
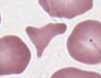
Schistocyte (fragment) Mechanism of Formation
mechanical damage to RBC
*The fragment is torn off and sealed back together
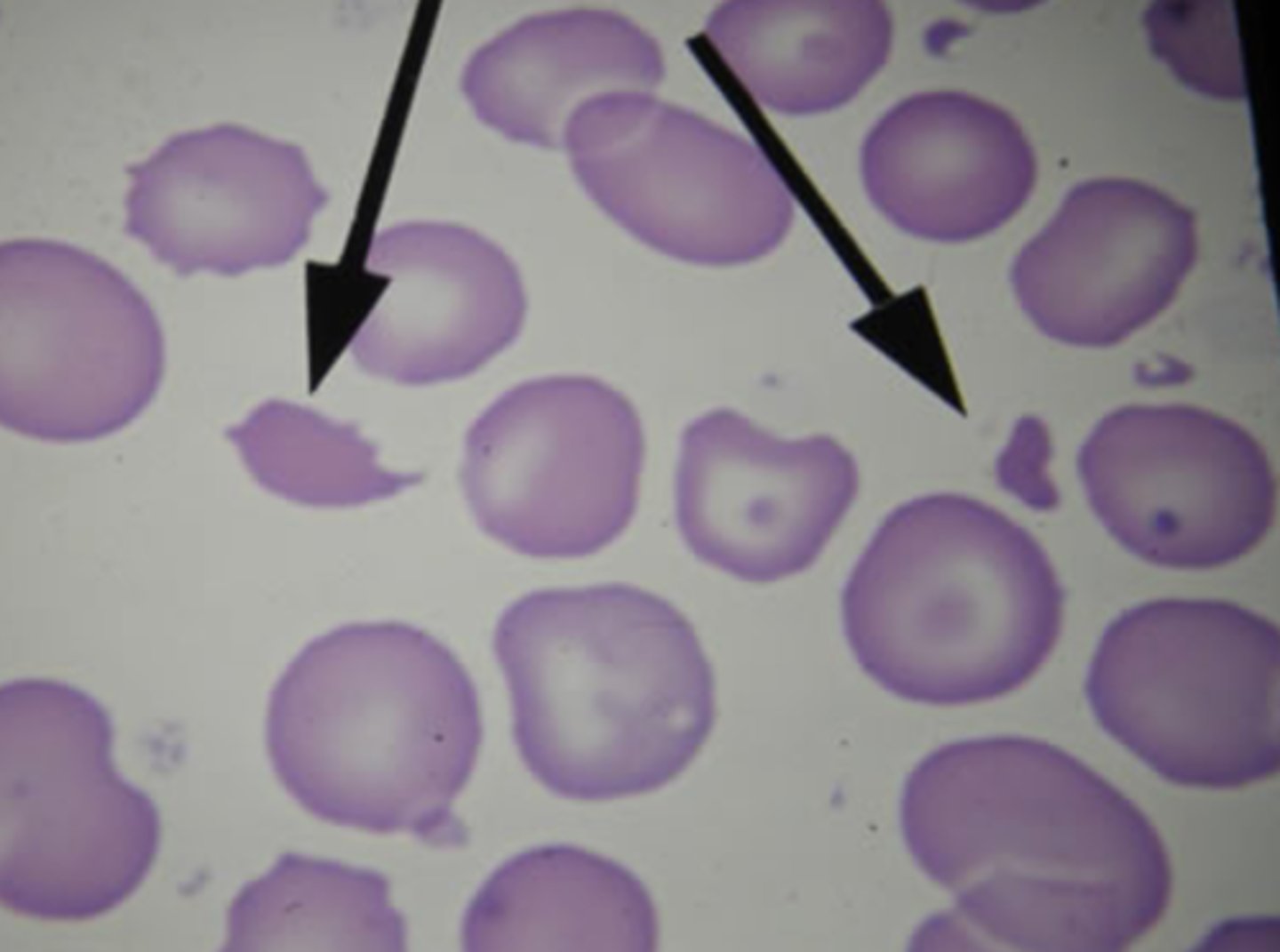
Schistocyte (fragment) Associated Diseases
Hemolytic anemias, intravascular hemolysis, and severe burns
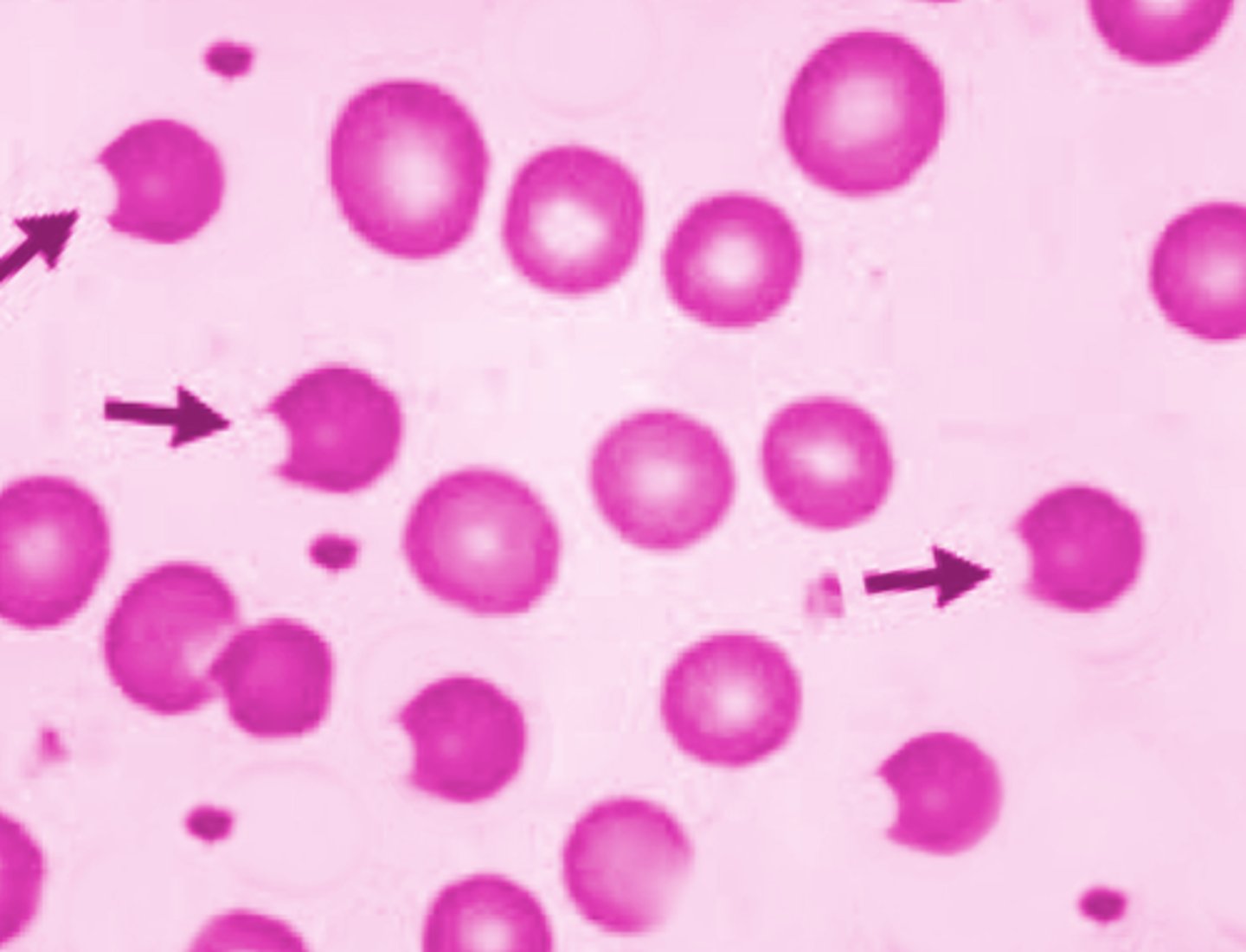
Schistocyte (bite cell) Description
RBC with one or two “bites” taken from it
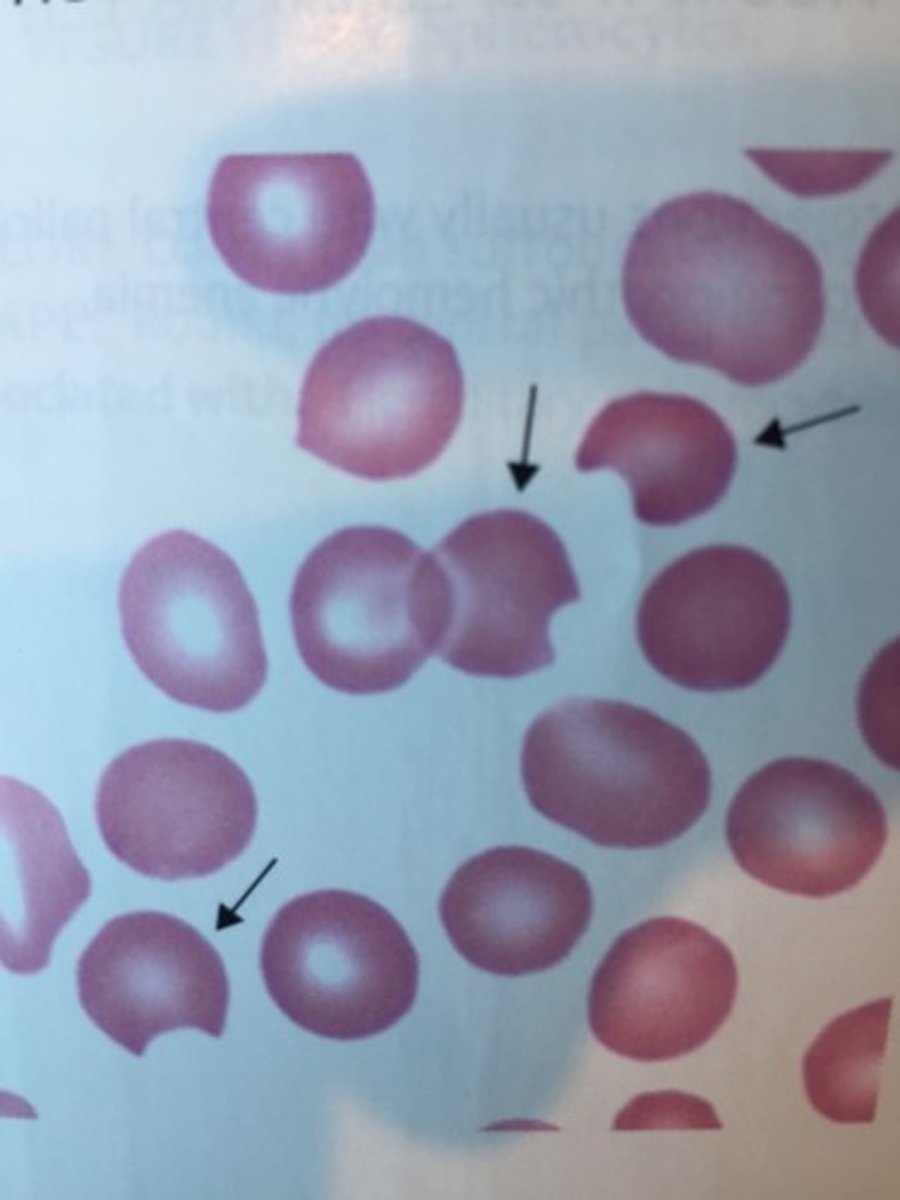
Schistocyte (bite cell) Mechanism of Formation
splenic pitting - because macrophages take a bite out
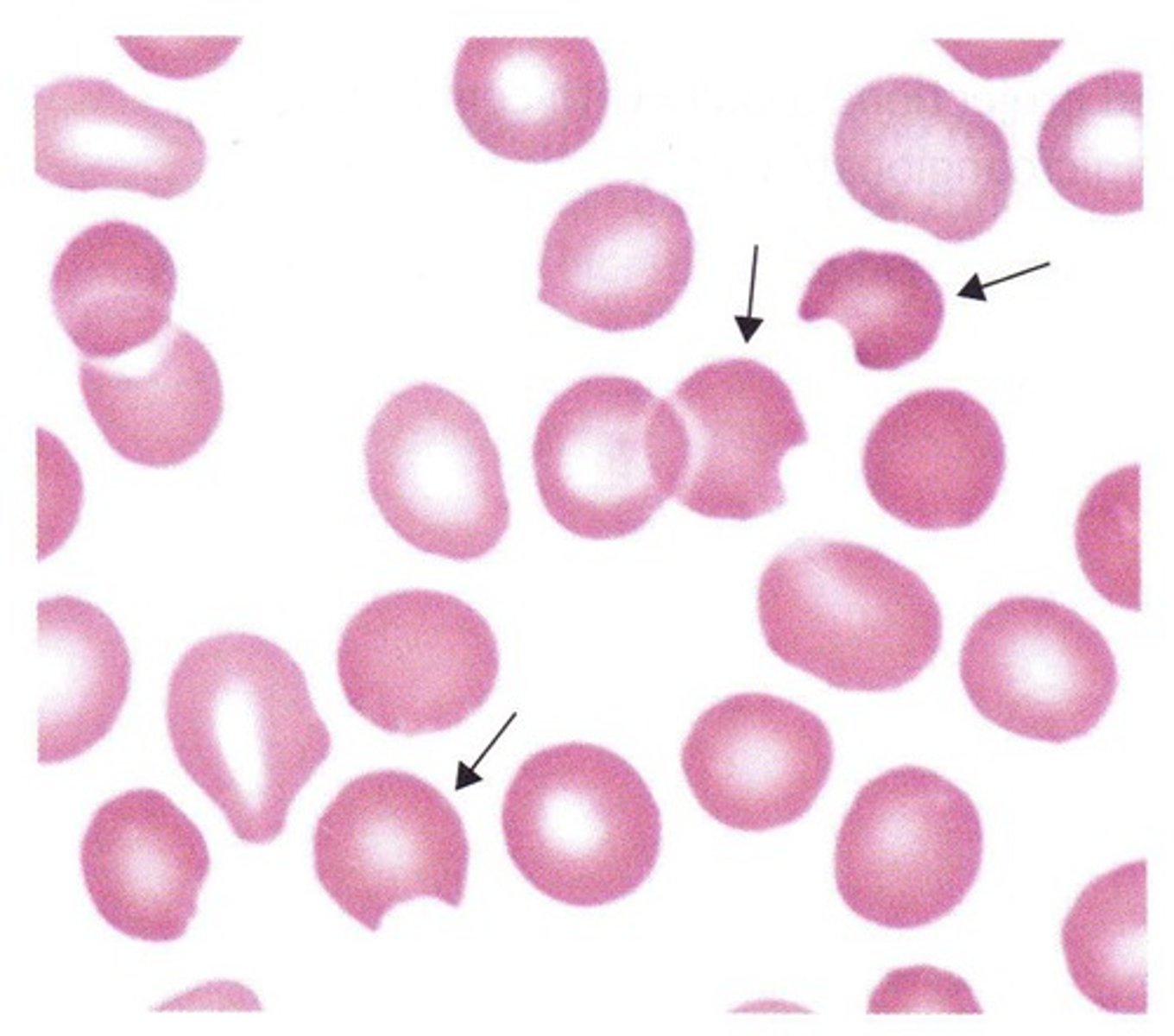
Schistocyte (bite cell) Associated Disease
G6PD deficiency so the red cell will build oxidized hemoglobin so a clump forms and macrophages bit the oxidized part out
Schistocyte (keratocyte) Description
"helmet cell"
Schistocyte (keratocyte) Mechanism of Formation
impalement of RBC on fibrin strand
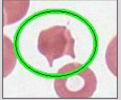
Schistocyte (keratocyte) Associated Diseases
hemolytic anemias and glomerulonephritis
Spherocyte Description
Spherocytic red cells with dense hemoglobin content; complete lack of central pallor
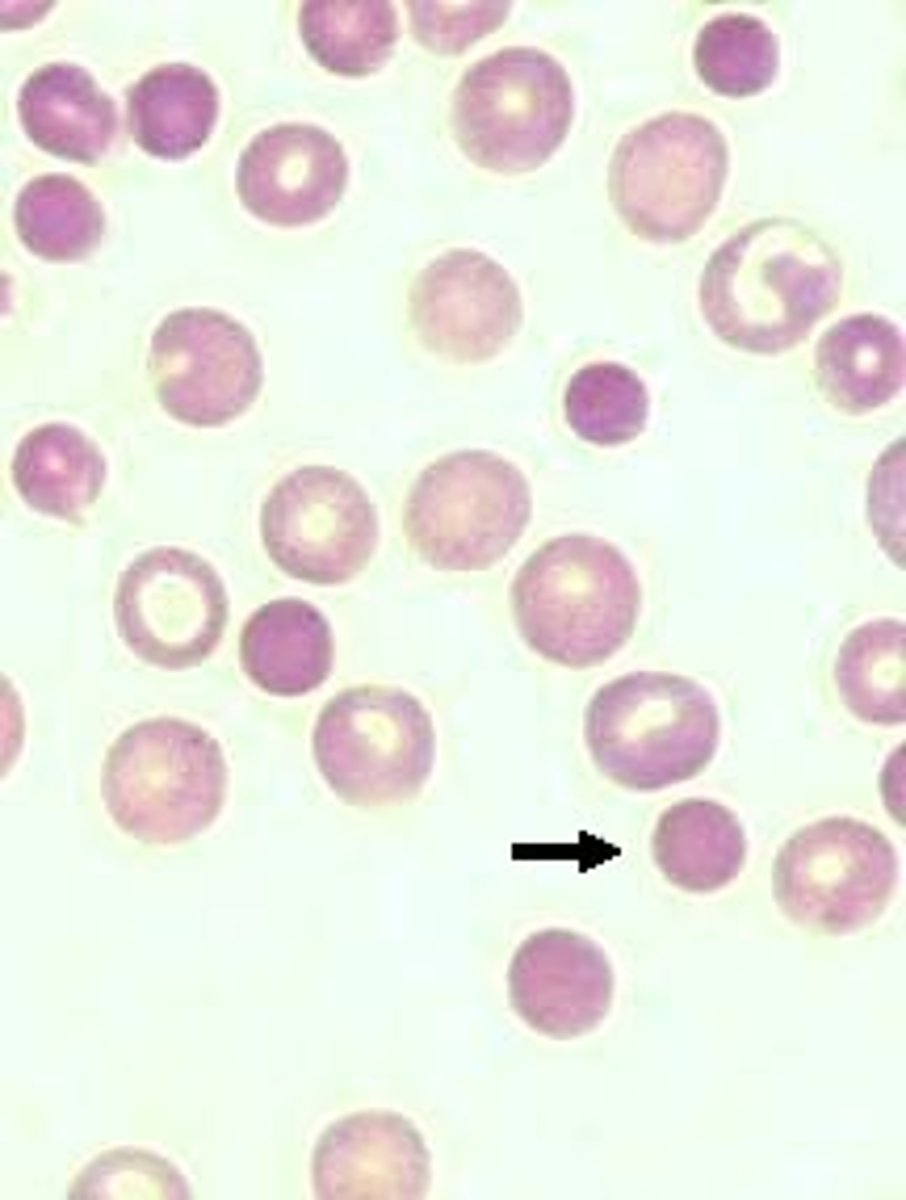
Spherocyte Mechanism of Formation
Decreased surface area-to-volume ratio
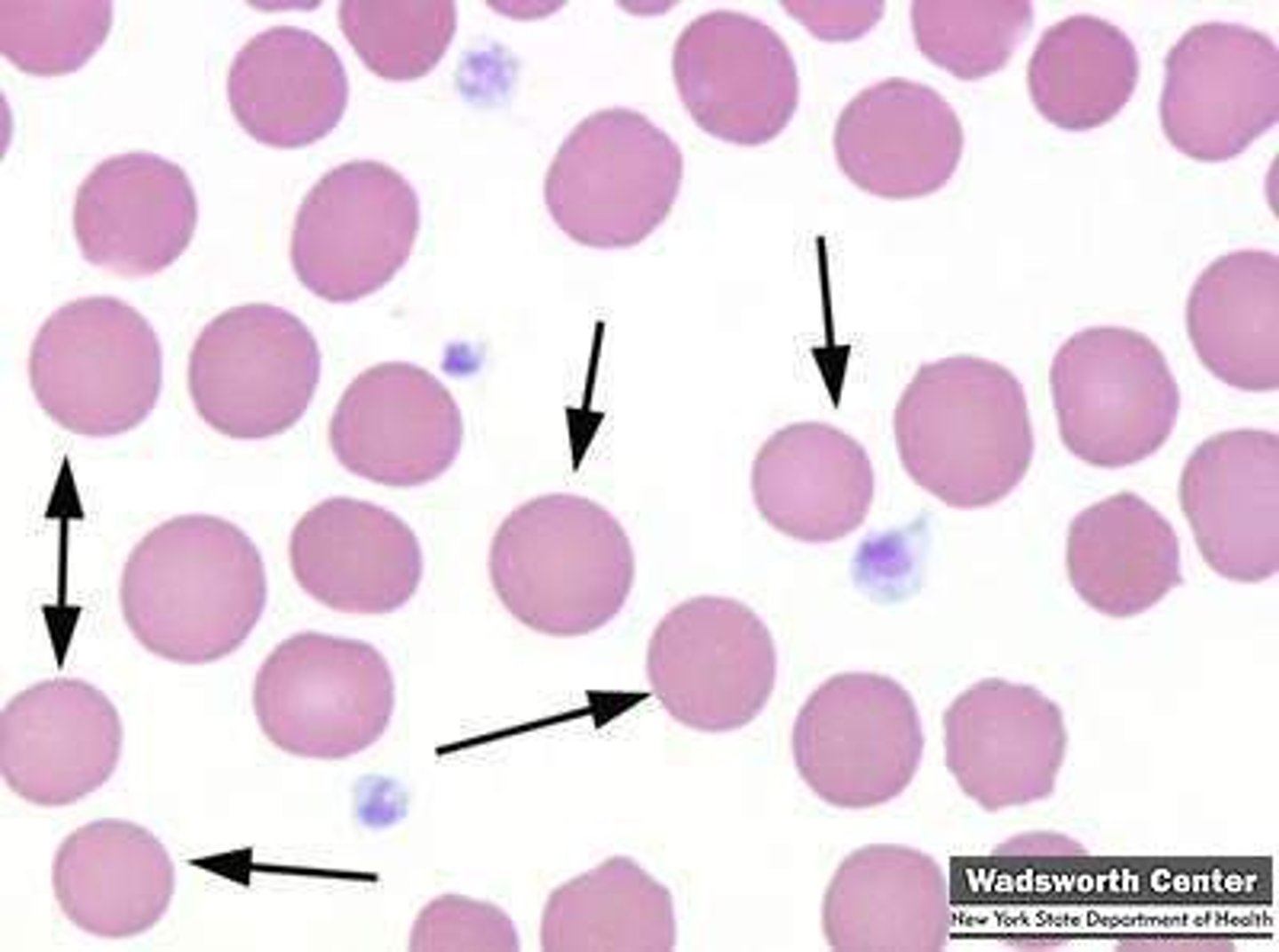
Spherocyte Associated Diseases
Hereditary spherocytosis, immune hemolytic anemias, severe burns
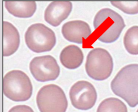
Stomatocyte Alternative Name
Mouth Cell - Uniconcave or cupshaped RBC; on stained smear has an oval or slit-shaped central pallor
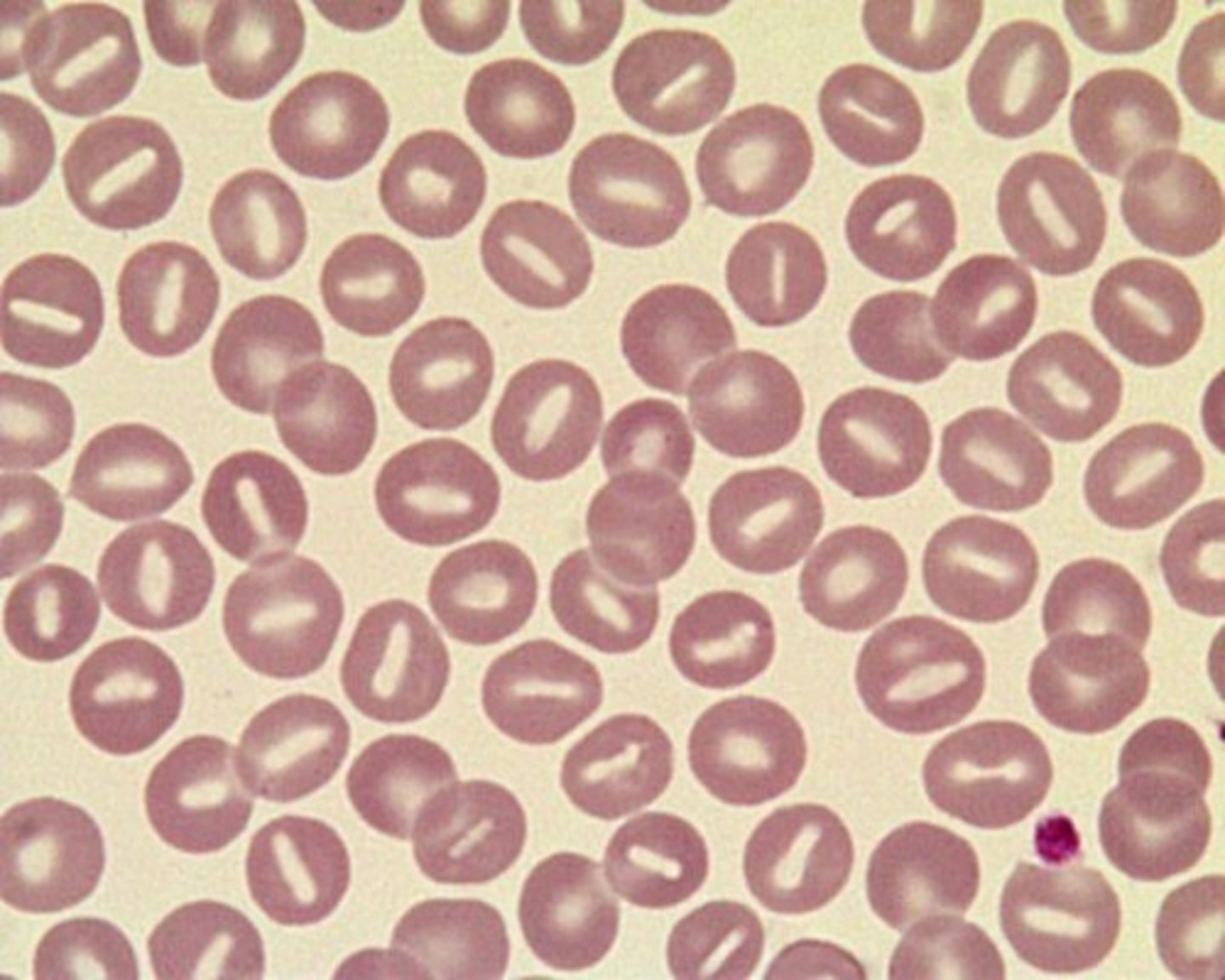
Stomatocyte Mechanism of Formation
Increased lipid content or area of the inner layer of cell membrane as compared to outer layer
Stomatocyte Associated Diseases
Hereditary stomatocytosis, lead poisoning, often artifact and stumble open it by chance
Basophilic Stippling Description
Round or irregularly shaped granules of variable number and size, distributed throughout the RBC
If you need to squint to see it than it not their
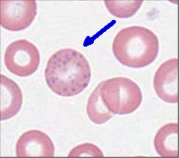
Basophilic Stippling Composition
Aggregates of ribosomes(RNA) and mitochondira
Basophilic Stippling Associated Diseases
Lead poisoning, thalassemia, anemias associated with abnormal hemoglobin synthesis (SIDEROBLASTIC ANEMIA)
Cabot Ring Description
Appear as a figure-8, ring, or incomplete ring. (very rare)
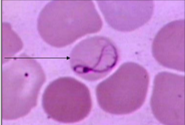
Cabot Ring Composition
Remnant microtubules of the mitotic spindle
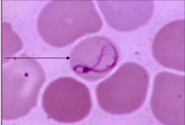
Cabot Ring Associated Diseases
Severe anemias and dyserythropoiesis
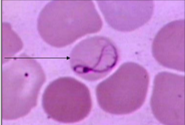
Howell-Jolly Bodies Description
Small, dark purple, round bodies located in the periphery of the cell; usually occur singly
*All Inclusion are in Red
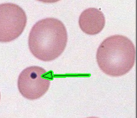
Howell-Jolly Body Composition
DNA inclusion
Howell-Jolly Body Associated Diseases
Post-splenectomy, megaloblastic anemias, functional asplenia, and severe anemia
Heinz Body Description
Bluish-purple round-shaped bodies of varying sizes, usually near cell membrane
(can't see on normal stain)
ONLY VISIBLE ON A SUPRAVITAL STAIN, NOT WRIGHT’S STAIN
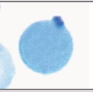
Heinz Body Composition
Denatured, precipitated hemoglobin that forms within red blood cells, often associated with oxidative stress
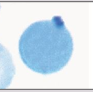
Heinz Bodies Associated Diseases
G6PD-deficiency, unstable hemoglobin disoders, oxidizing drugs/toxins, post-splenectomy
Pappenheimer Body Description
Grape-like clusters of bluish/purple aggregates, usually found in the periphery of the cell
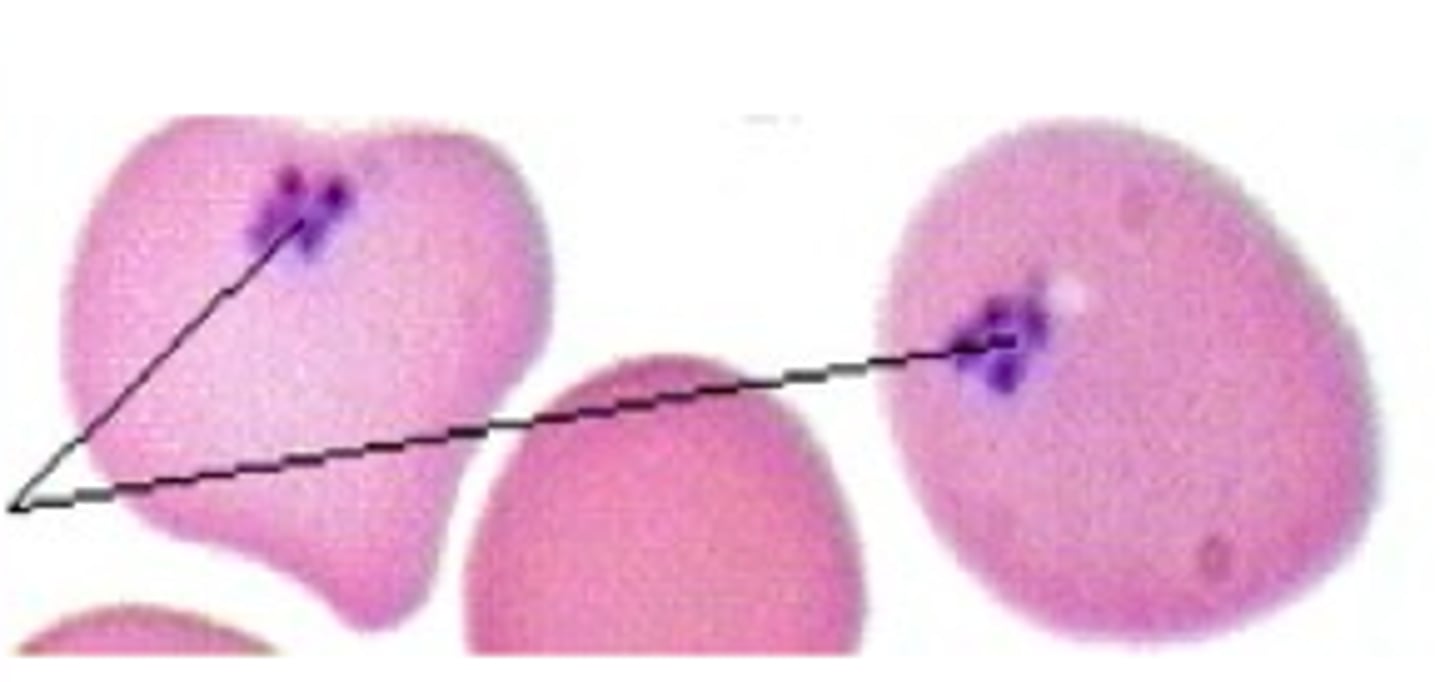
Pappenheimer Body Composition
Iron and Protein
Pappenheimer Bodies Associated Diseases
Sideroblastic anemia, thalassemia, other severe anemias (sickle cell anemia)
Hemoglobin C Crystal Description
dark red, hexagonal "crystals" within RBCs made out of hemoglobin C
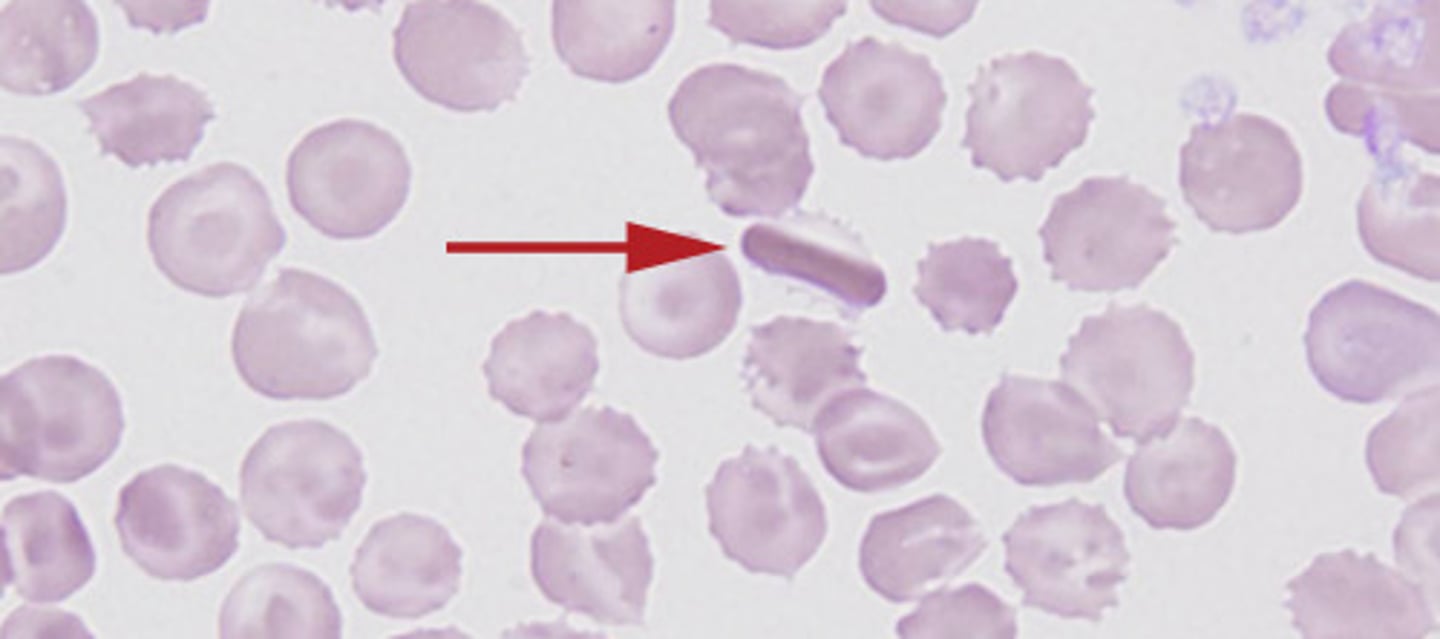
Hemoglobin C Crystal Mechanism of Action
Intracellular crystallization of hgb C
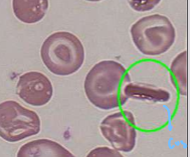
Hemoglobin C Crystal Associated Diseases
Hemoglobin C disease is Inherited
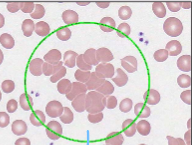
Agglutination Description
Rosette-like clusters of RBCs throughout the peripheral blood smear
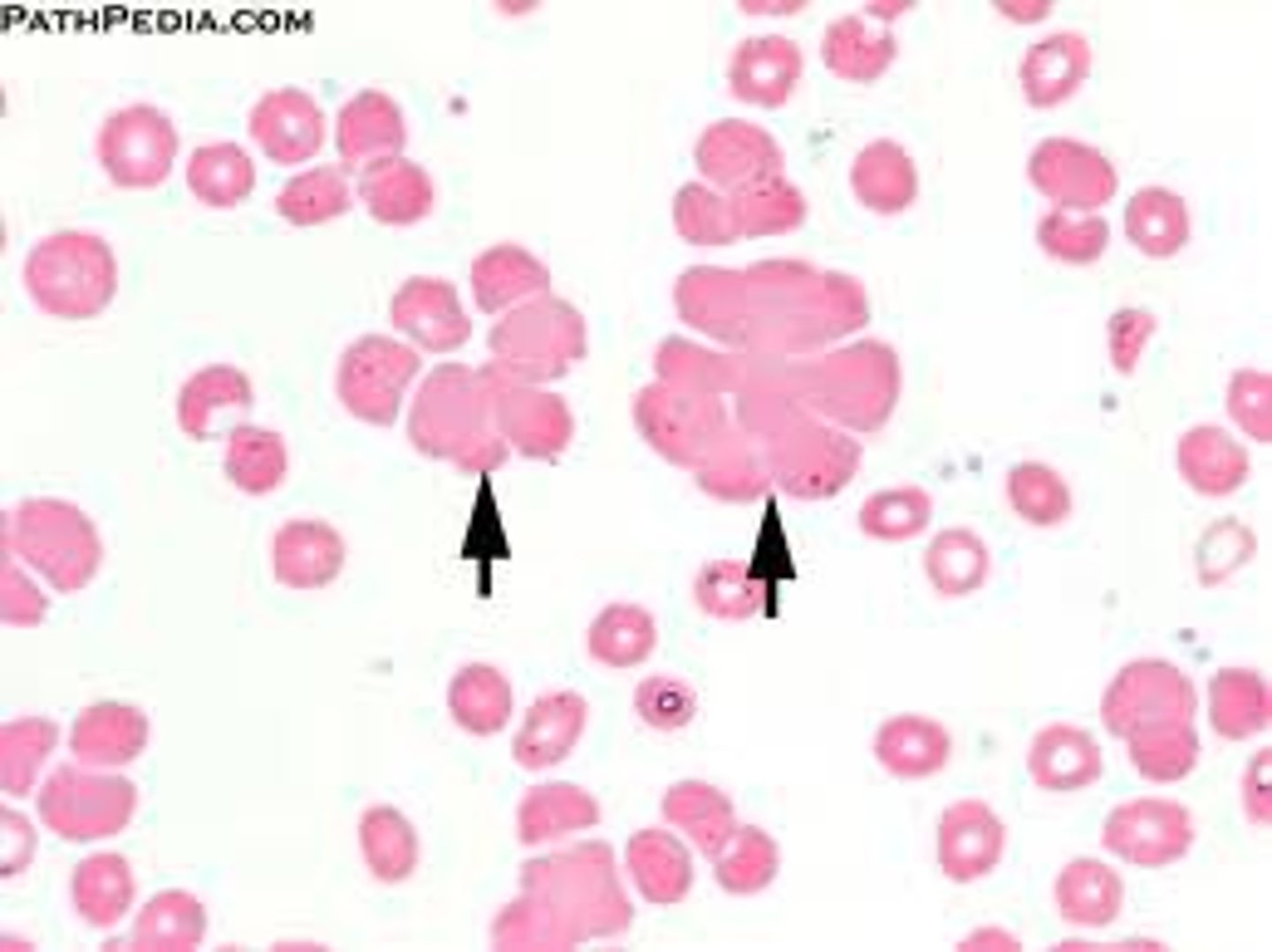
Agglutination Mechanism of Formation
Caused by antigen/antibody interactions between sensitized red blood cells
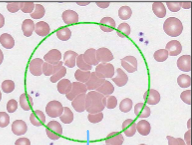
Agglutination Associated Diseases
Autoimmune Anemias
Rouleaux Description
RBCs stacked together in rows, appearing as a "stack of coins"
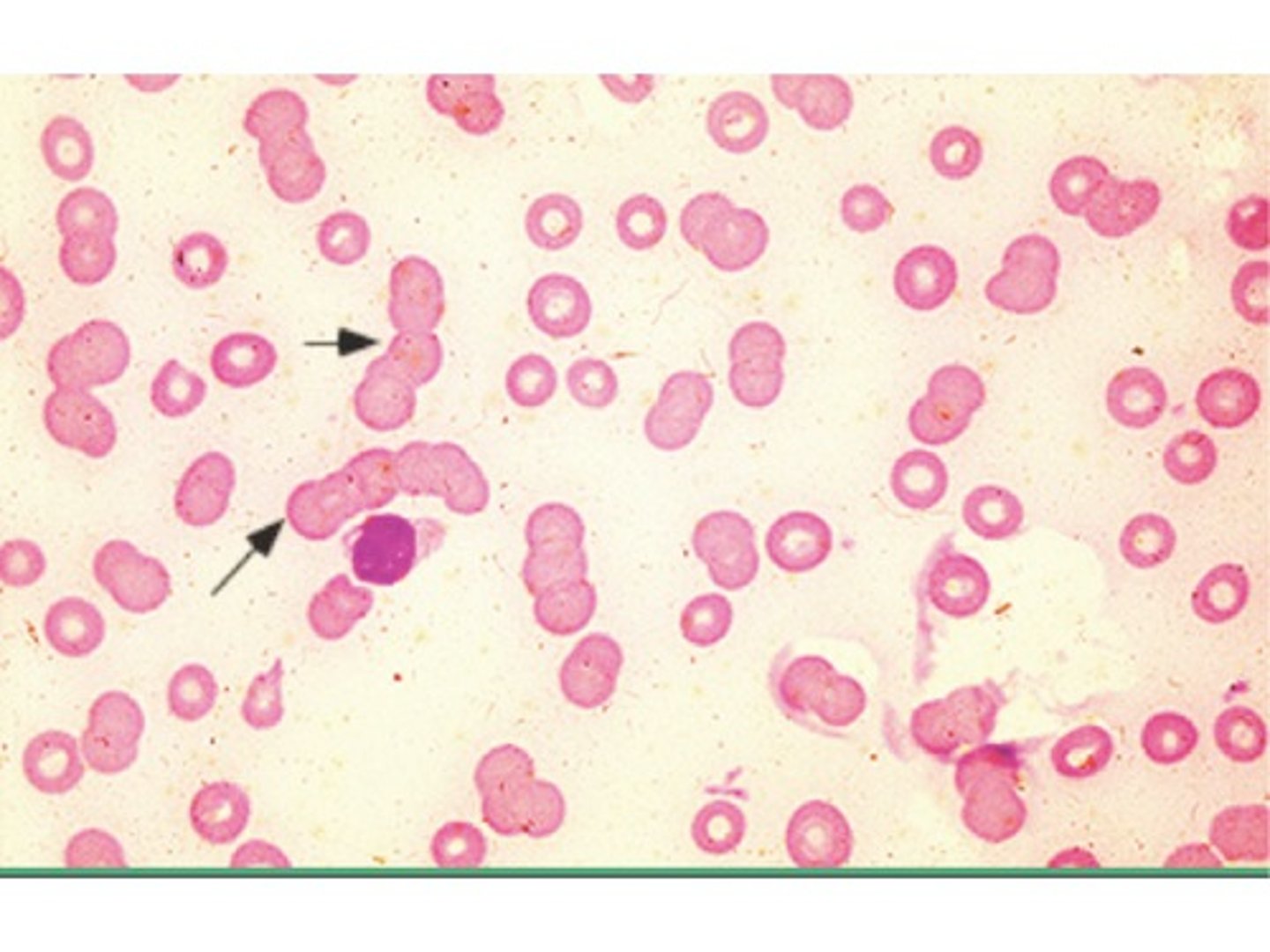
Rouleaux Mechanism of Action
Excess plasma proteins cause RBCs to be "sticky"
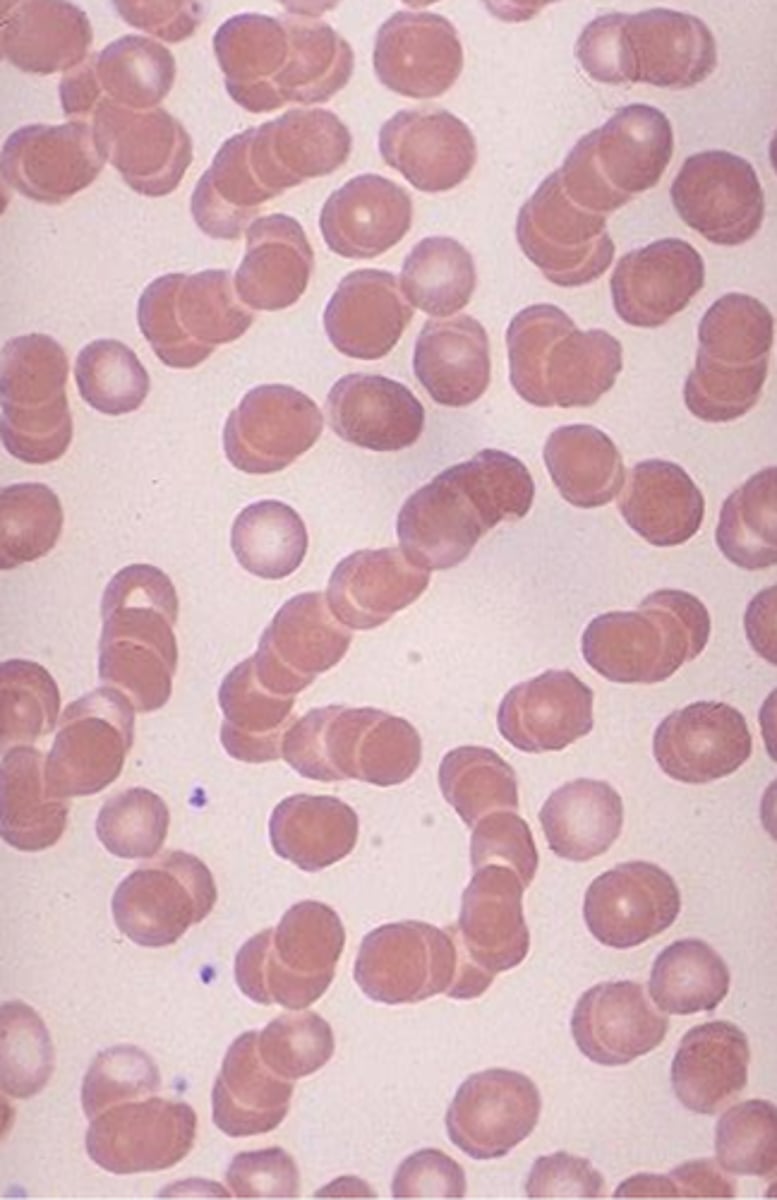
Rouleaux Associated Diseases
Multiple myeloma or other disorders associated with increased globulins/paraproteins
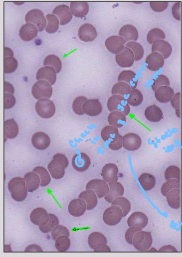
Babesia Description
ring-like organsims seen BOTH intracellularly and extracellularly
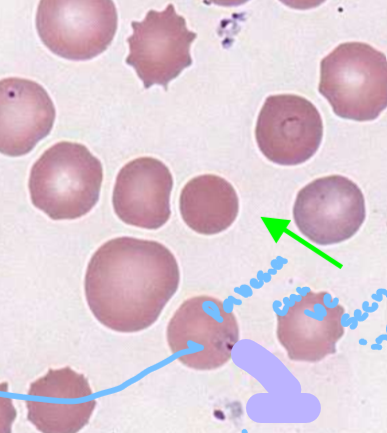
Malaria Description
ring-like organisms found only intracellularly, as well as in different stages
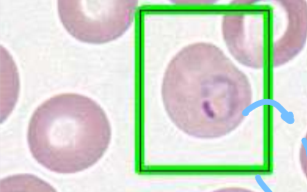
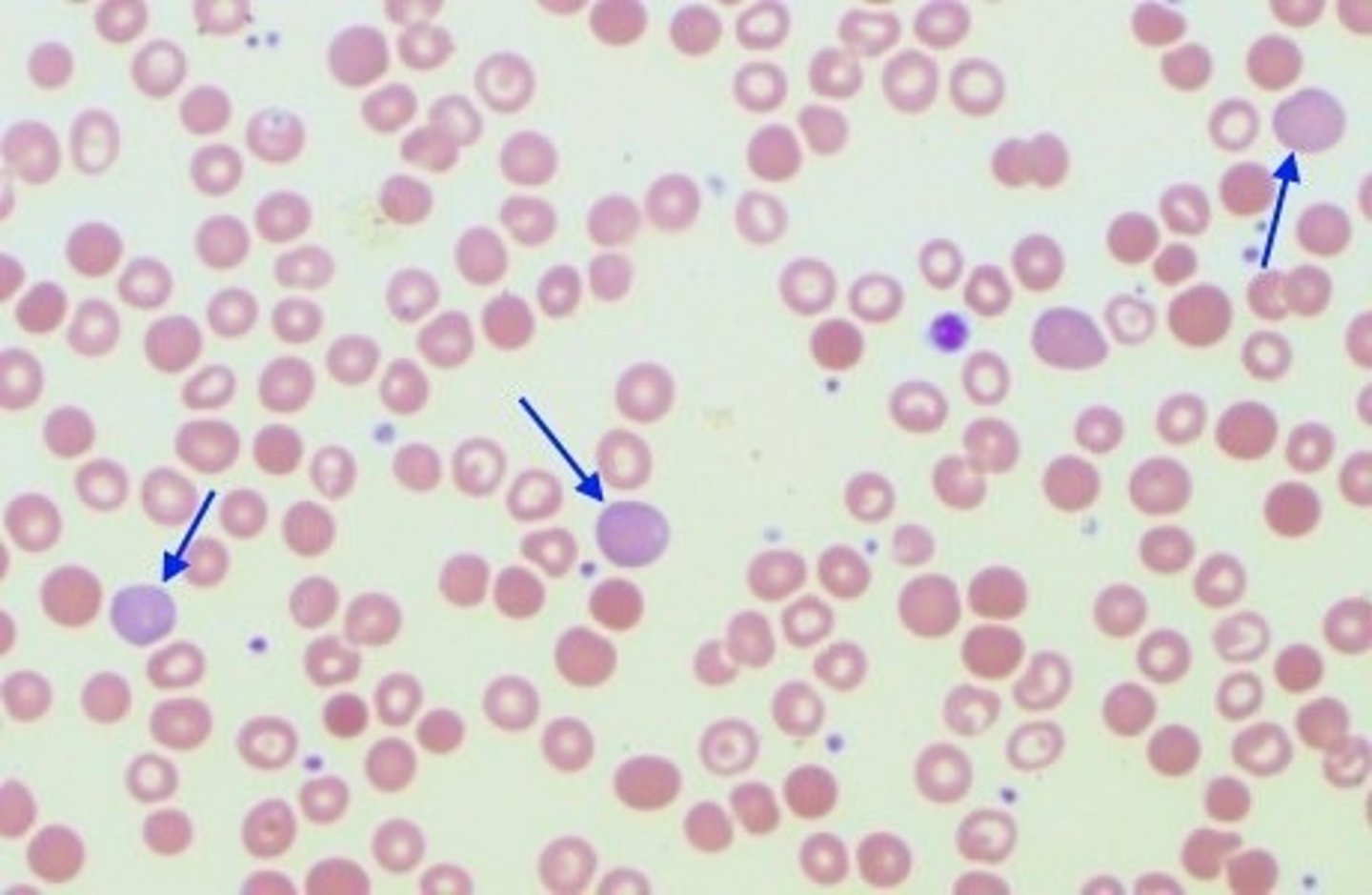
Polychromasia Description
Immature red blood cells that lack a nucleus but are larger in size than a mature red blood cell and have a purplish color
*the purplish color is picking up residual RNA up Azure B in Wright Stain )
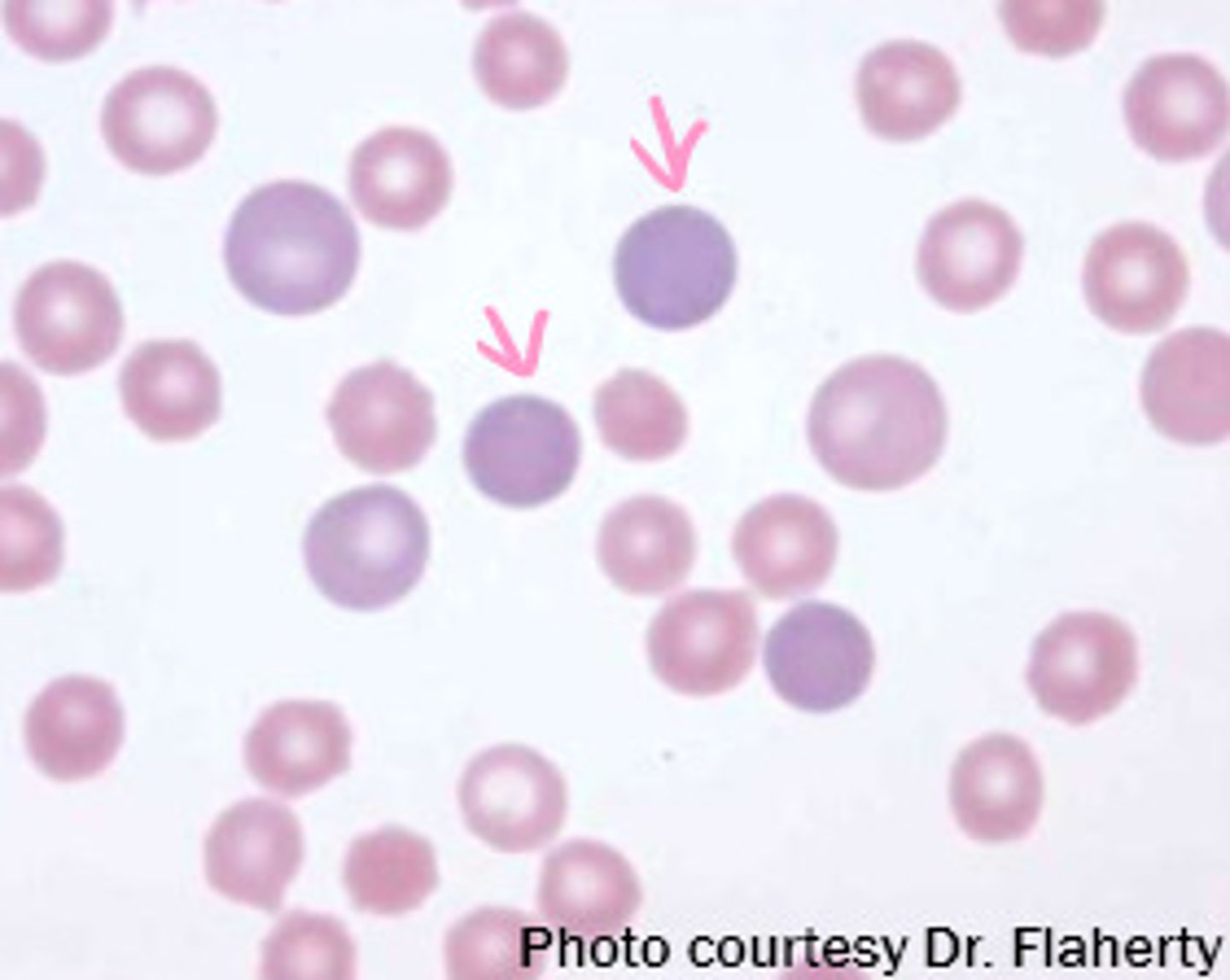
Polychromasia Mechanism of Action
Bone marrow releases red blood cell precursor earlier than is normal
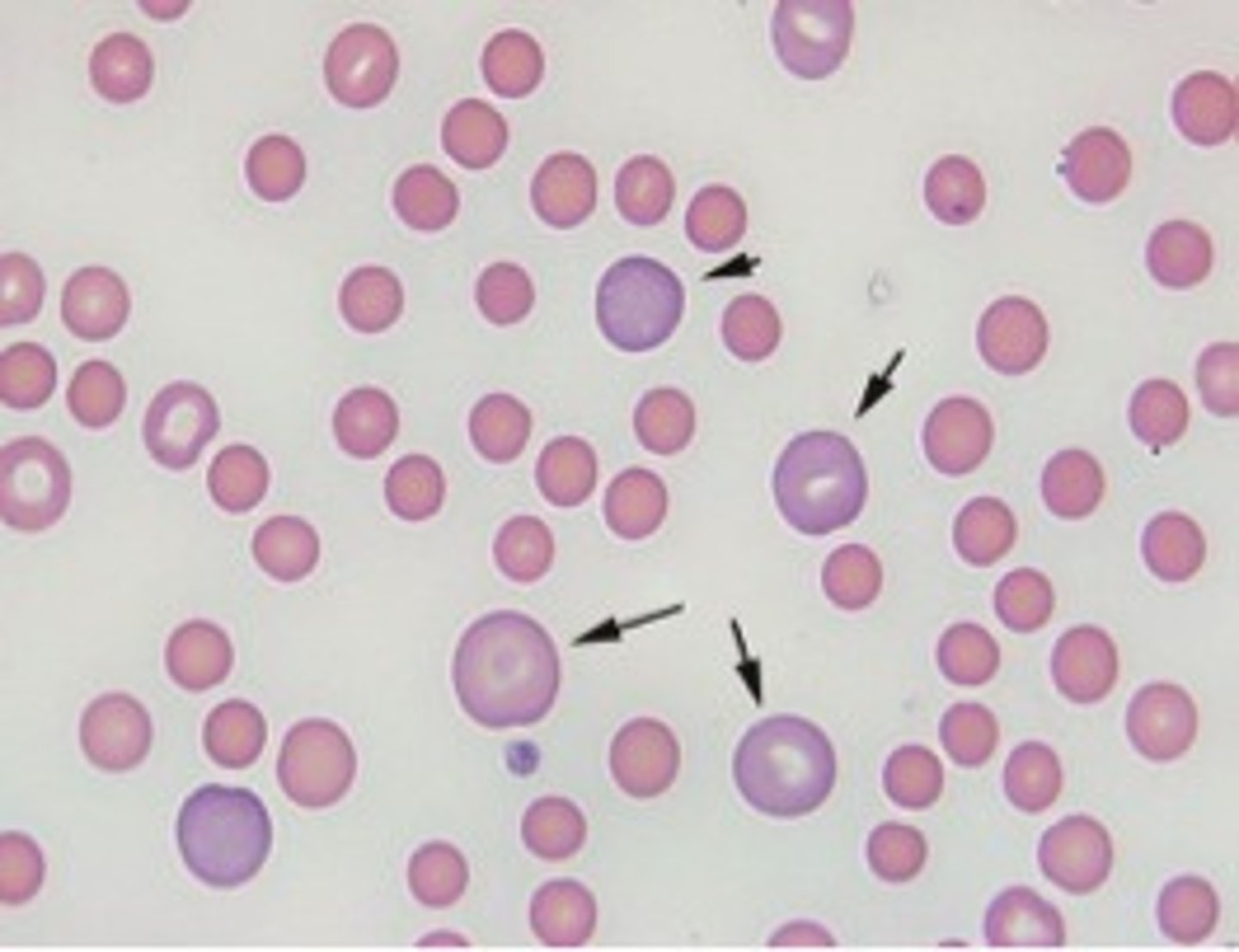
Polychromasia Associated Diseases
Various anemias, normal newborn
Nucleated Red Blood Cell (nRBC) Description
An immature stage of the erythrocyte that still has a nucleus. Normally not found in the peripheral blood of a healthy adult.
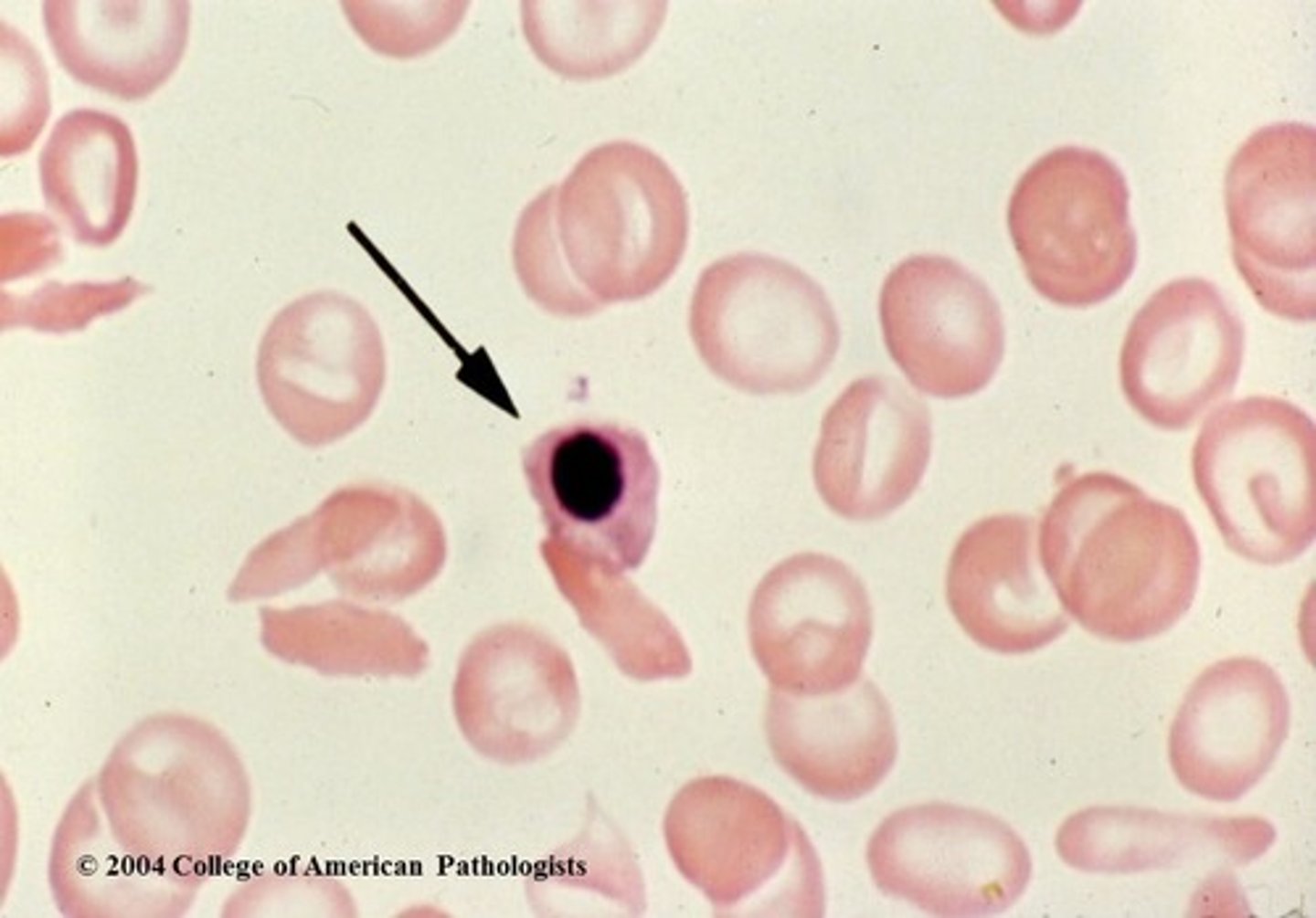
Nucleated Red Blood Cell (nRBC) Mechanism of Formation
Bone marrow releases red blood cell precursor earlier than is normal
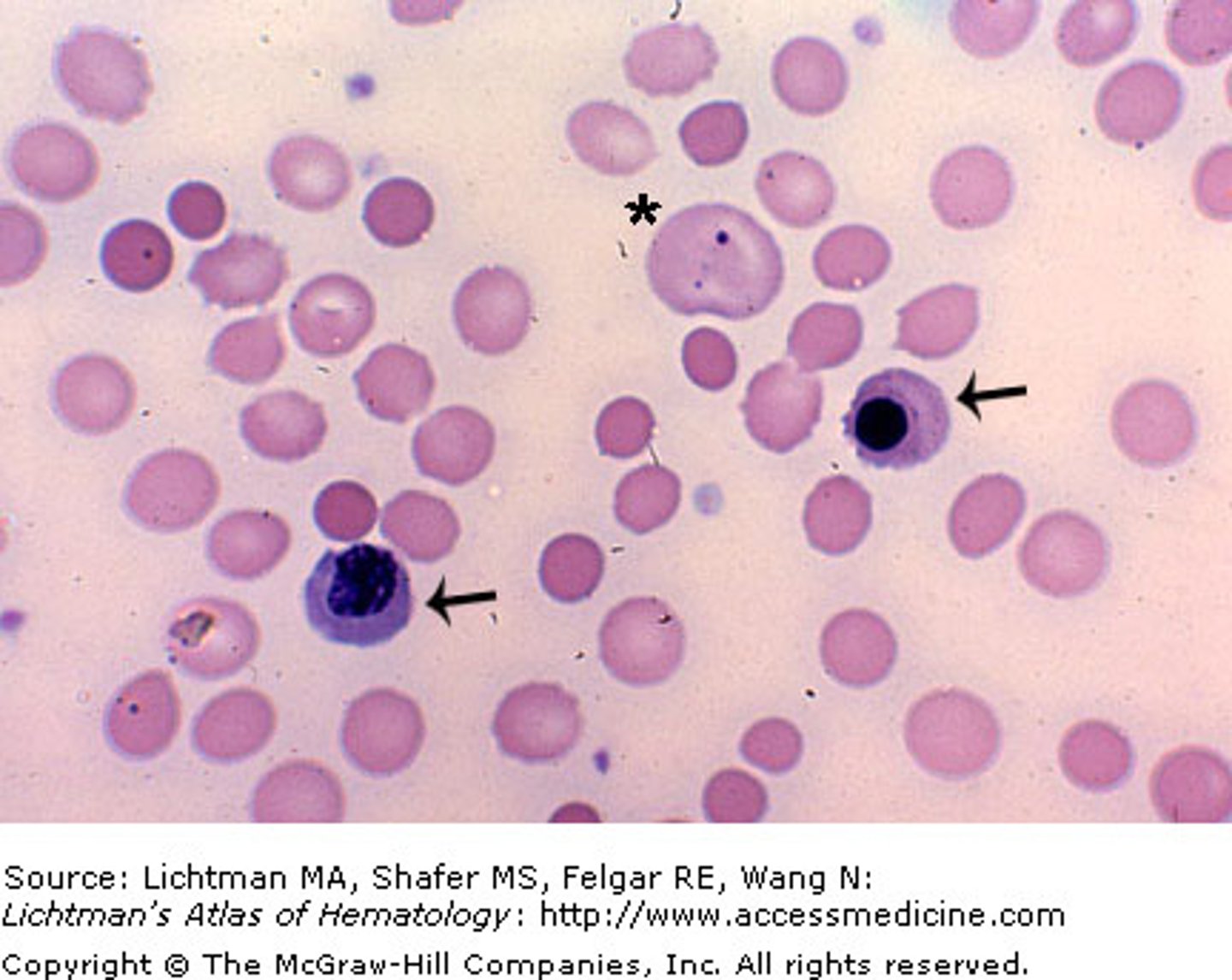
Nucleated Red Blood Cell (nRBC) Associated Diseases
Various anemias and normal newborn