"tHiS cOuLd Be On BoArDs"
1/180
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
181 Terms
radiolucent
more crystals are exposed, less dense, black
radiopaque
no crystals are exposed, more dense, white
latent image to visible image
chemical reaction takes place, latent image is immersed in chemicals, energized silver halide crystals are removed (reduction)
selective reduction into black metallic silver
what does the fixer solution do?
removes unexposed silver halide crystals
what are developing agents?
chemical solutions used to convert a latent image on xray film to a visible image
hydroquinone and elon
what prevents oxidation?
antioxidants, sodium
accelerator
sodium carbonate
restrainer
potassium bromide
fixing agent
clearing agent
-sodium thiosulfate or ammonium thiosulfate
-removes all unexposed or underdeveloped silver halide crystals from the emulsion
preservation
sodium sulfite
hardening agent
harden and shrink the gelatin
potassium alum
acidifier
neutralizes the alkaline developer
acetic acid
thermometer
used for the developer
optimum temperature is 68-70 degrees
film hangers
hold films
keeps films clean and dry
unexposed receptor
film appears clear
digital appears white

film exposed to light
film appears black

overexposed receptor
film and digital appears dark or high in density
excess time, kilovoltage, or milliamperage
underexposed receptor
film or digital appears light or low in density
inadequate time, kilovoltage, or milliamperage
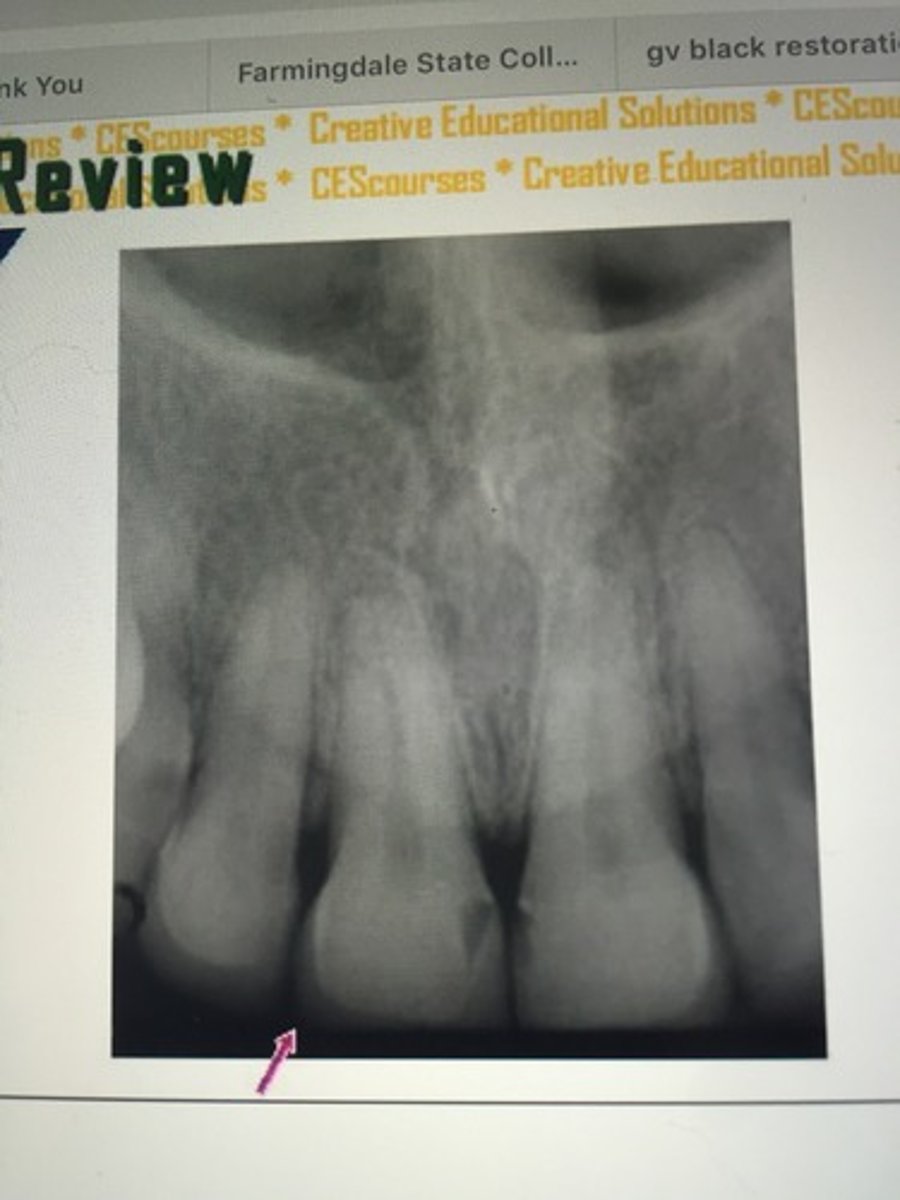
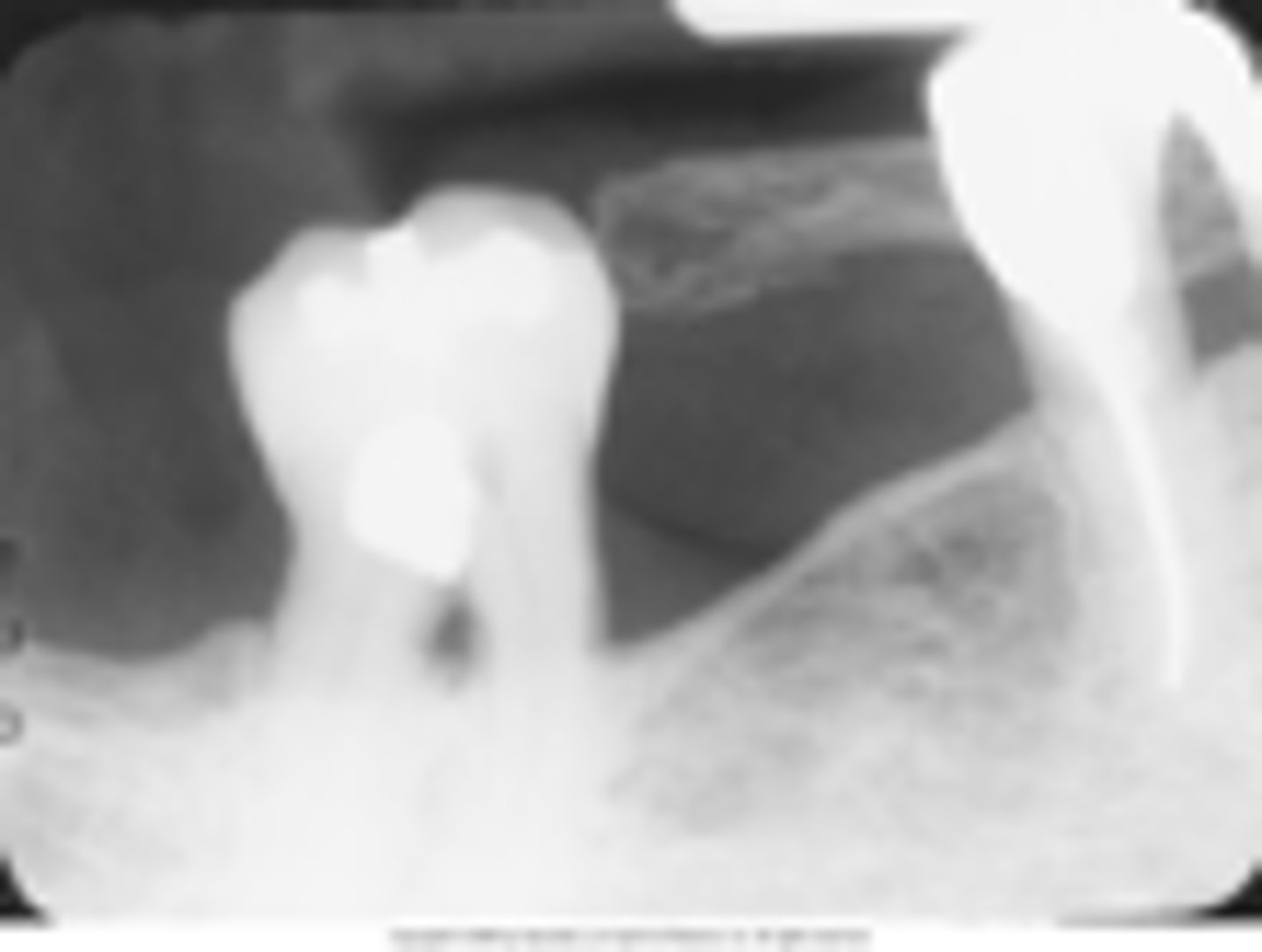
absence of apical structures
receptor not positioned to cover apical region of teeth
bite block not placed on the teeth being exposed
dropped receptor corner
edge of receptor not placed parallel to occlusal plane
bite firmly on bite block
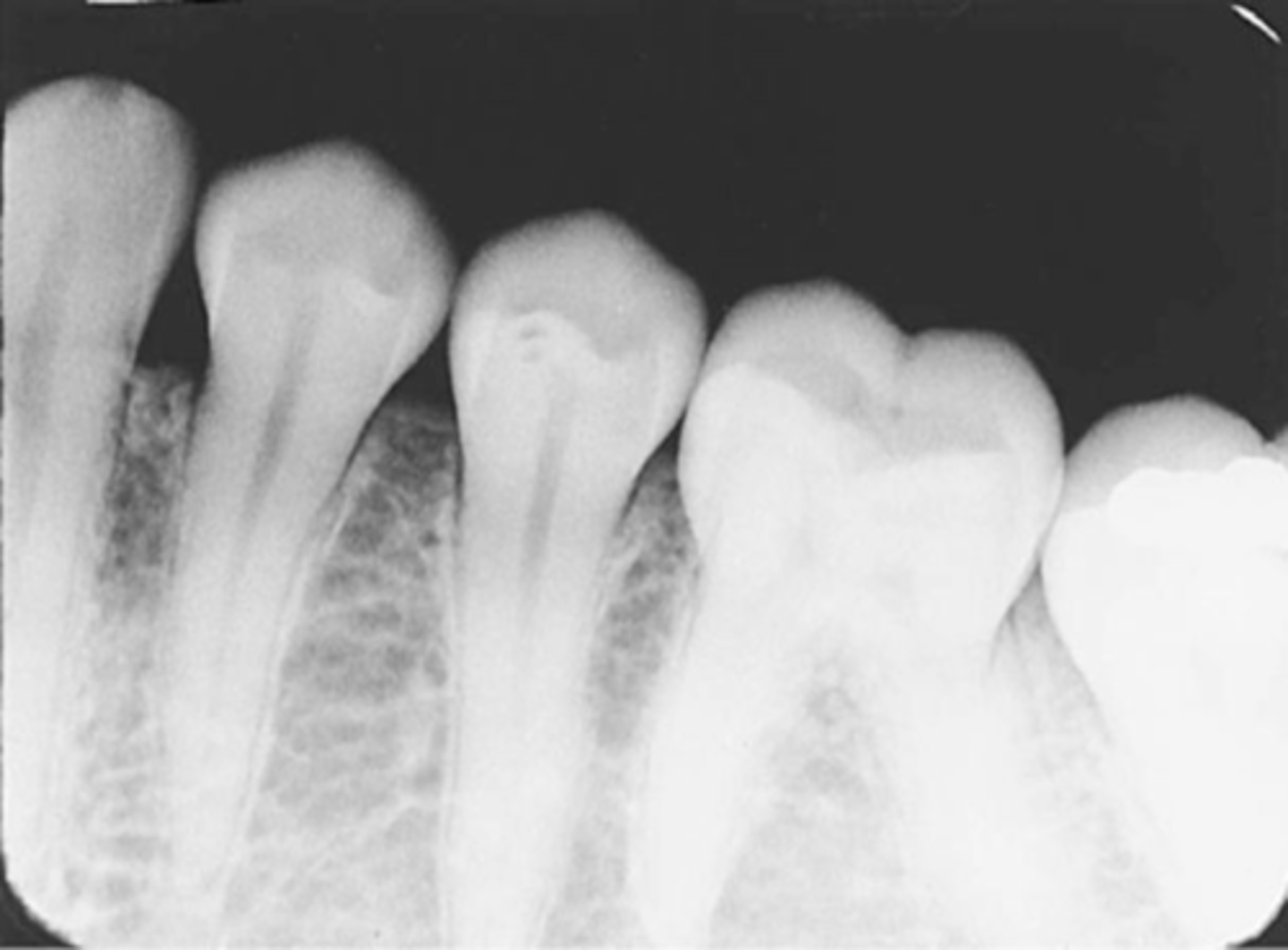
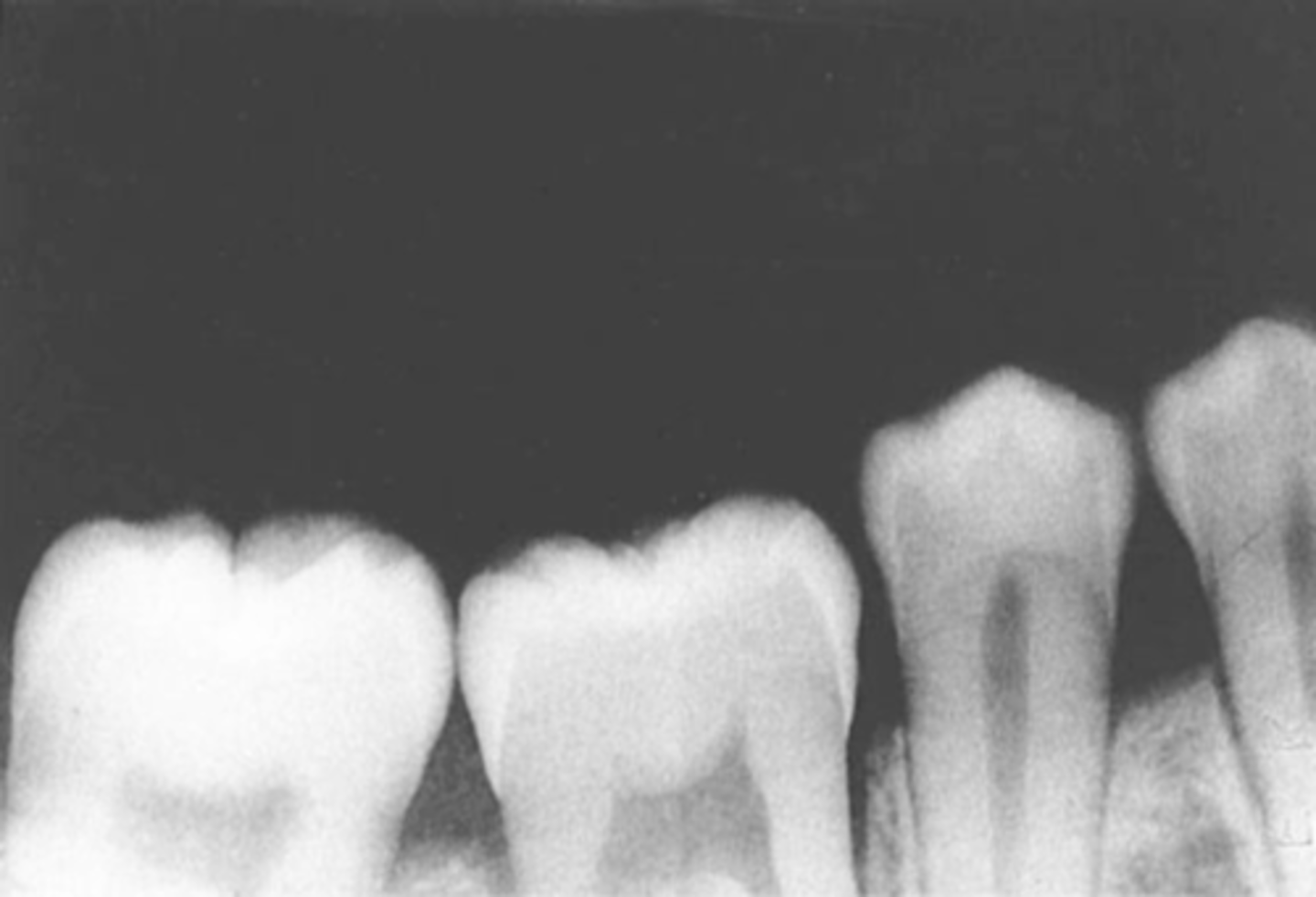
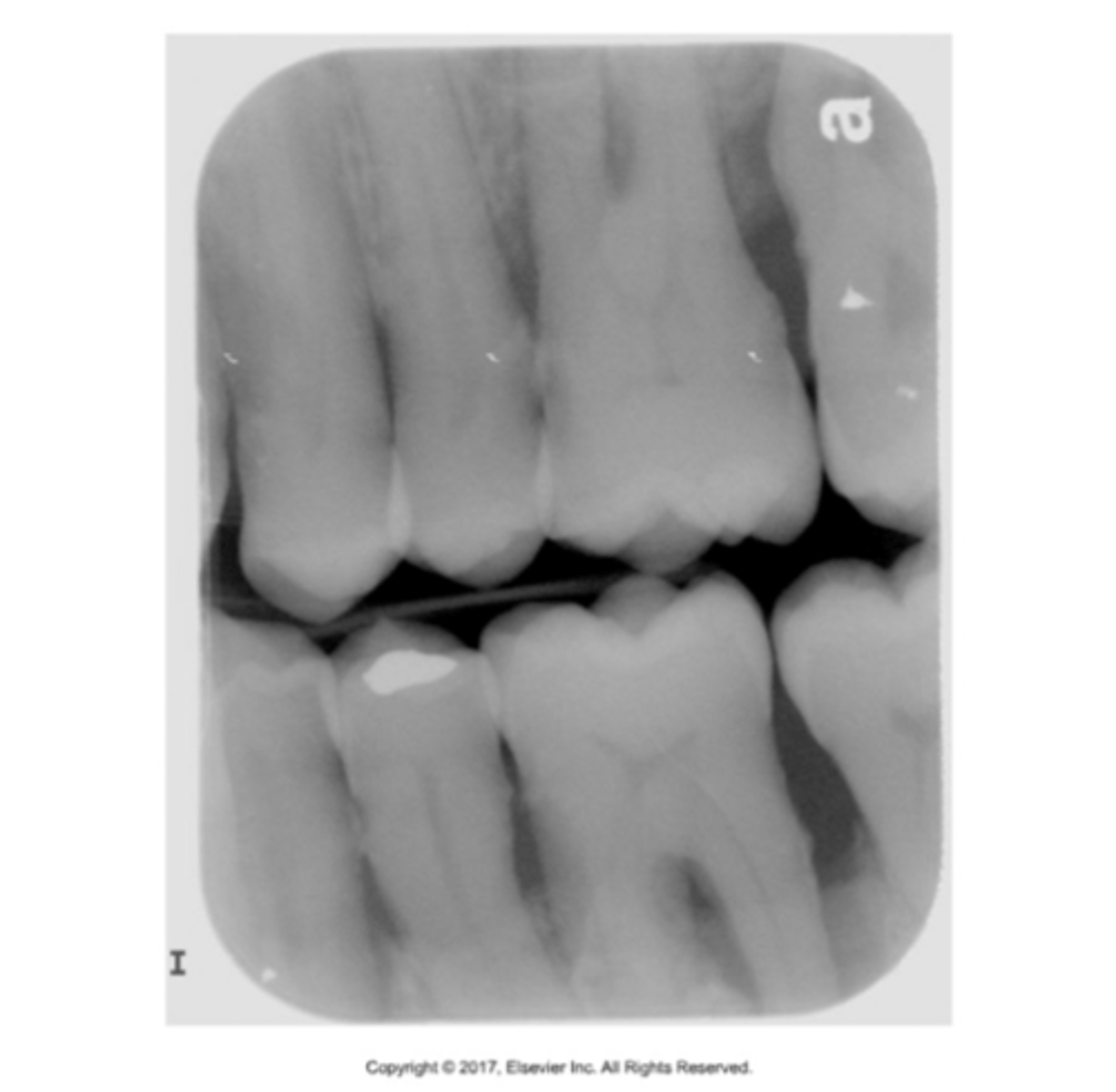
overlapped contacts
contacts are overlapped
central ray not directly through the interproximal spaces
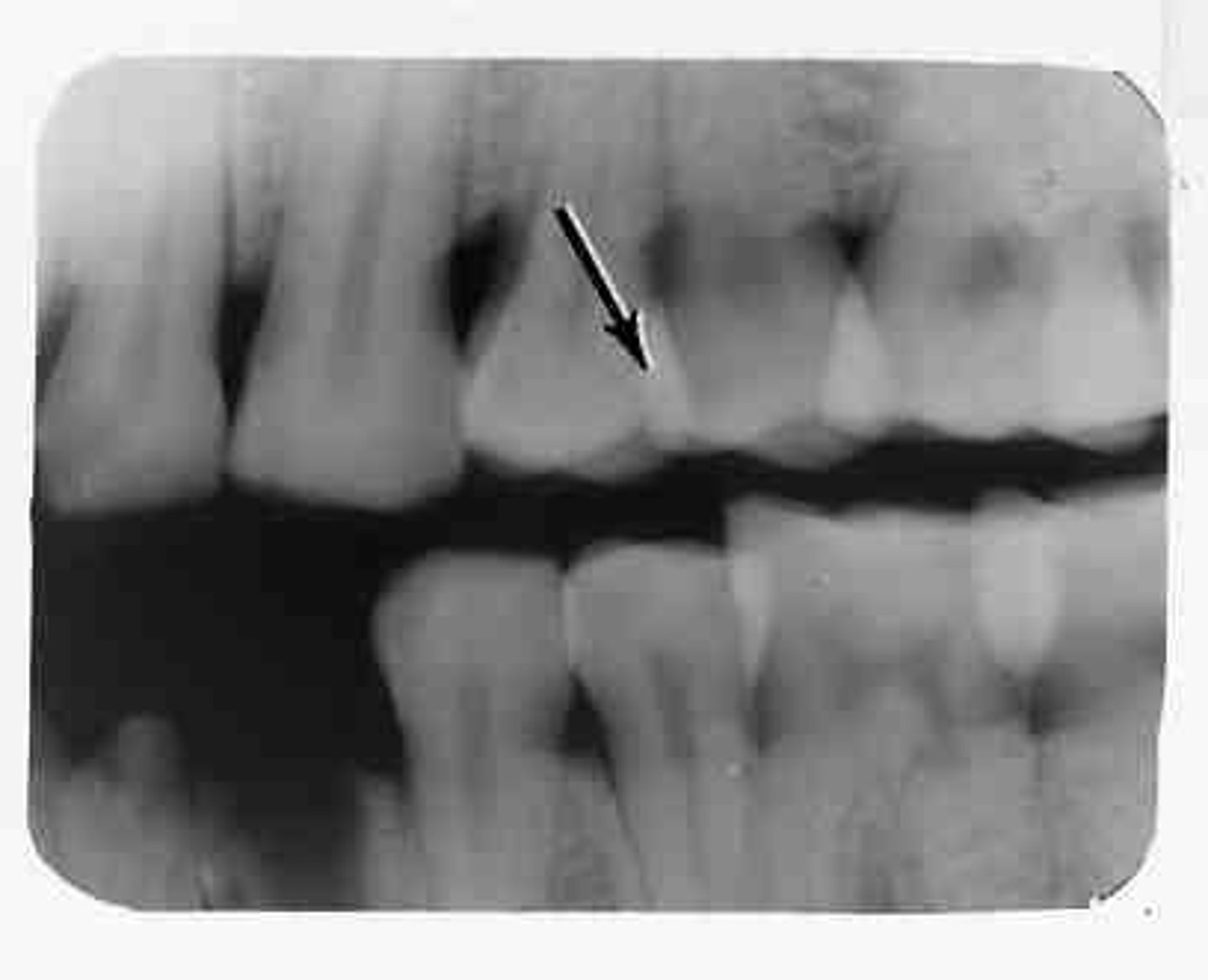
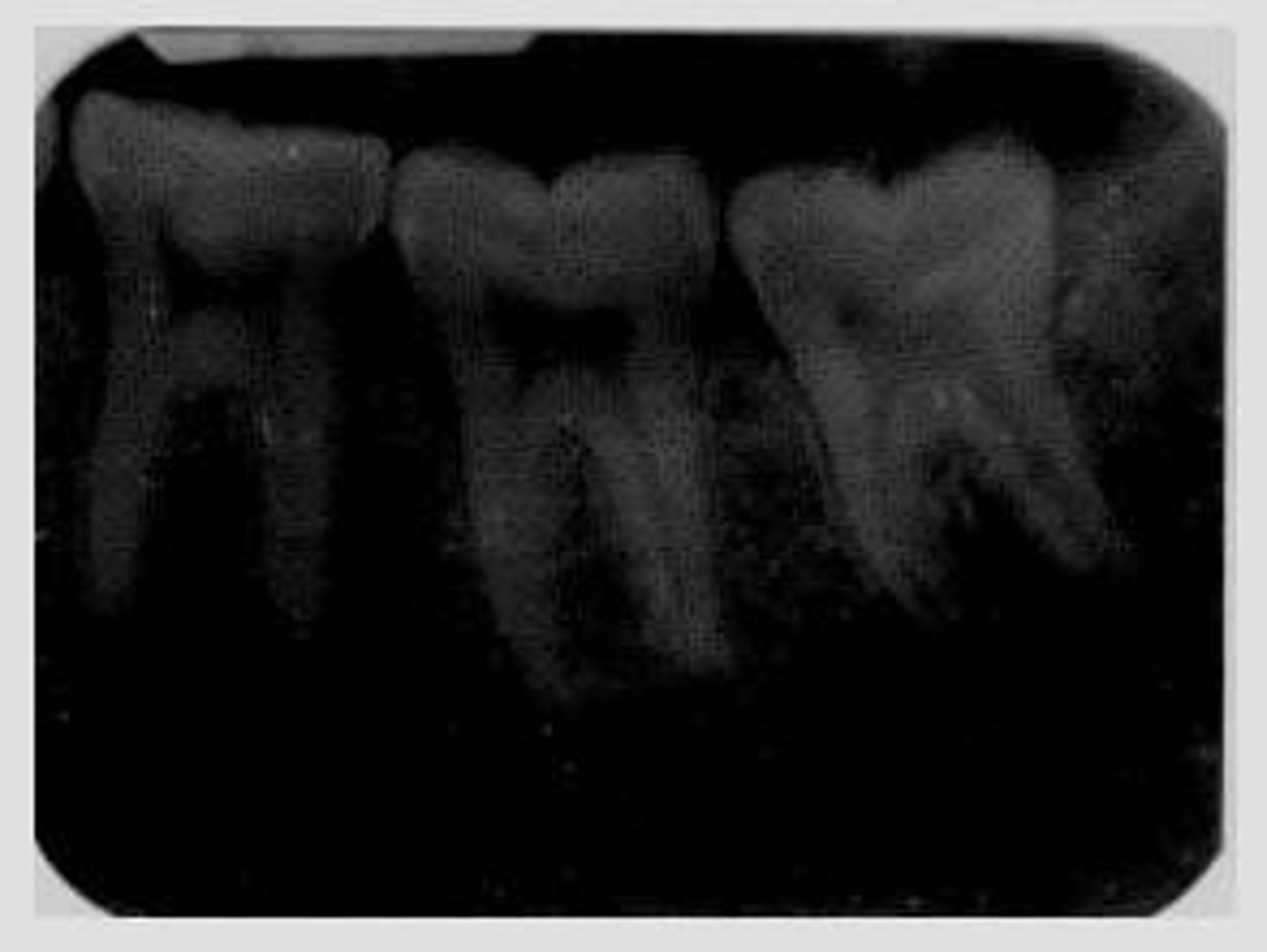
foreshortened images
teeth appear short with blunted roots
caused by too steep vertical angulation
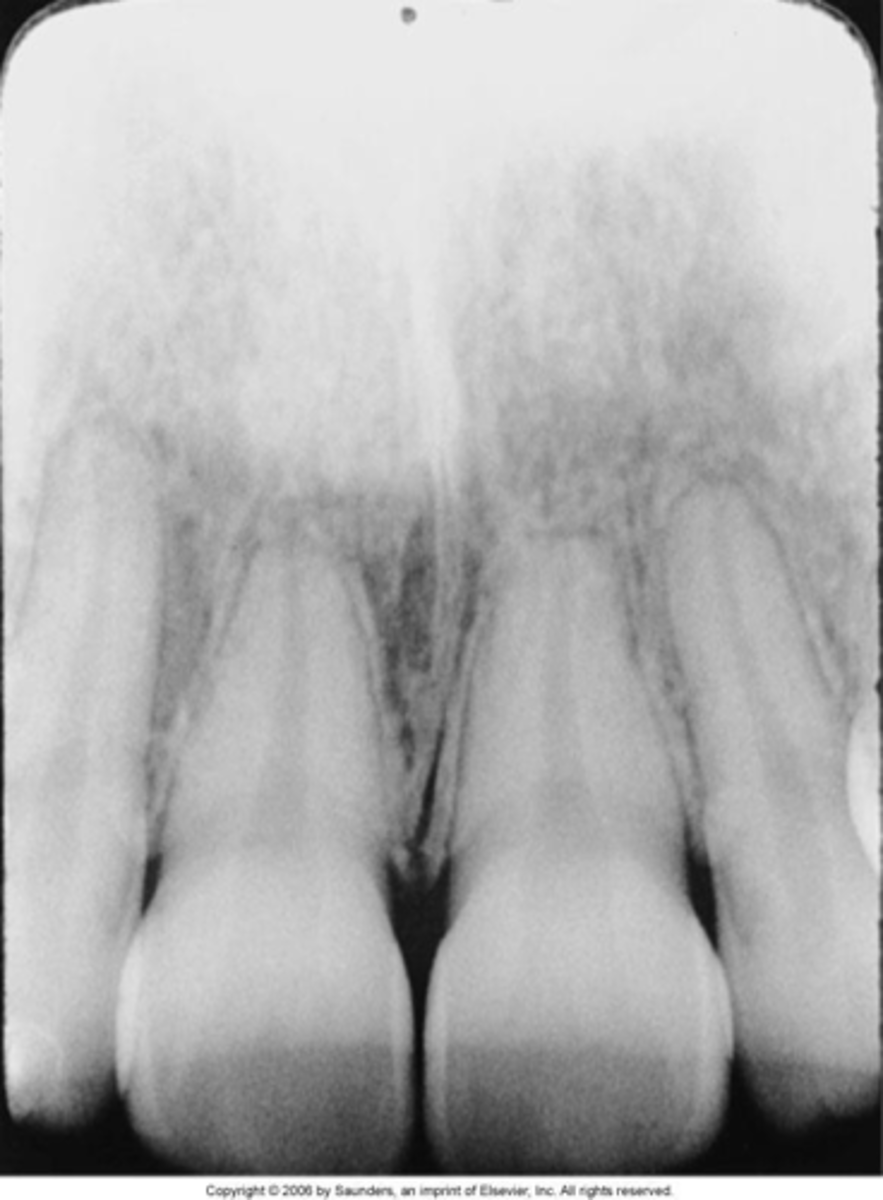
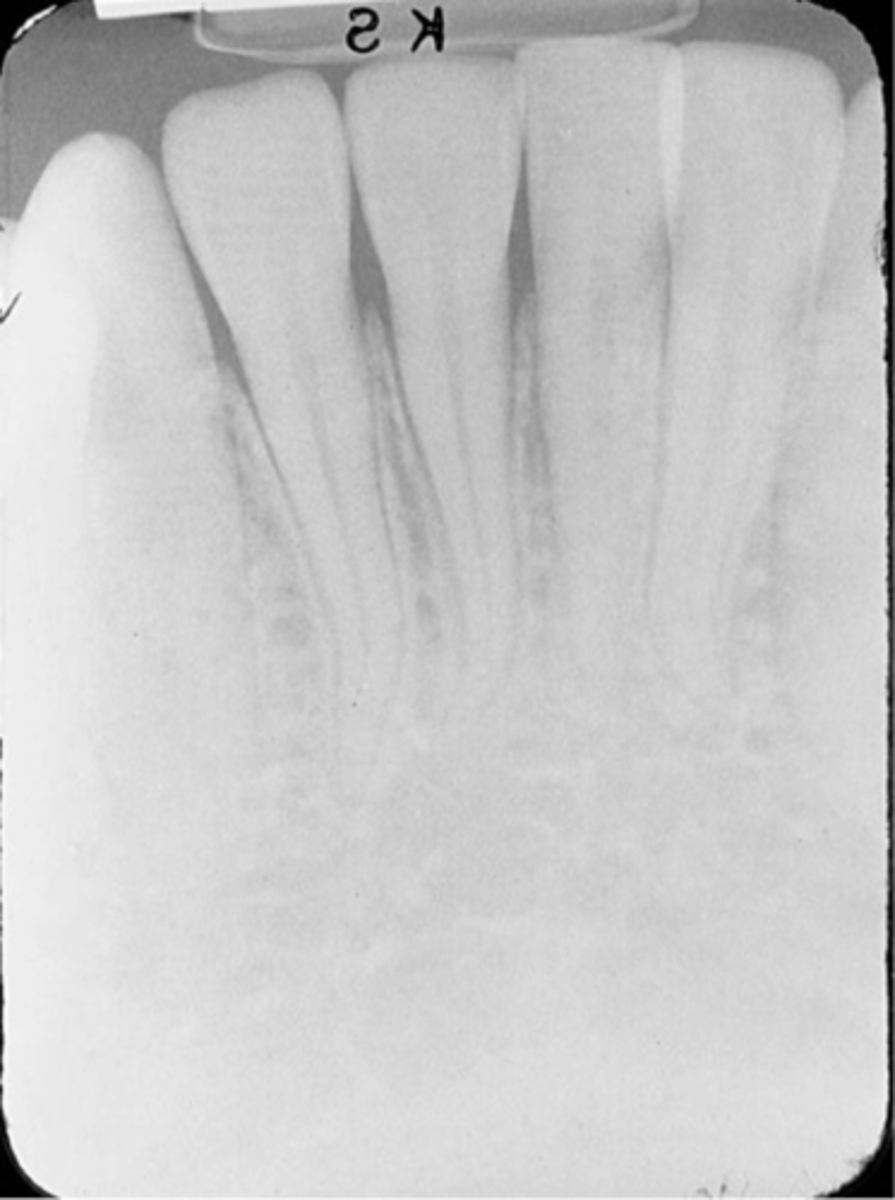
elongated images
teeth appear long and distorted
vertical angulation too flat
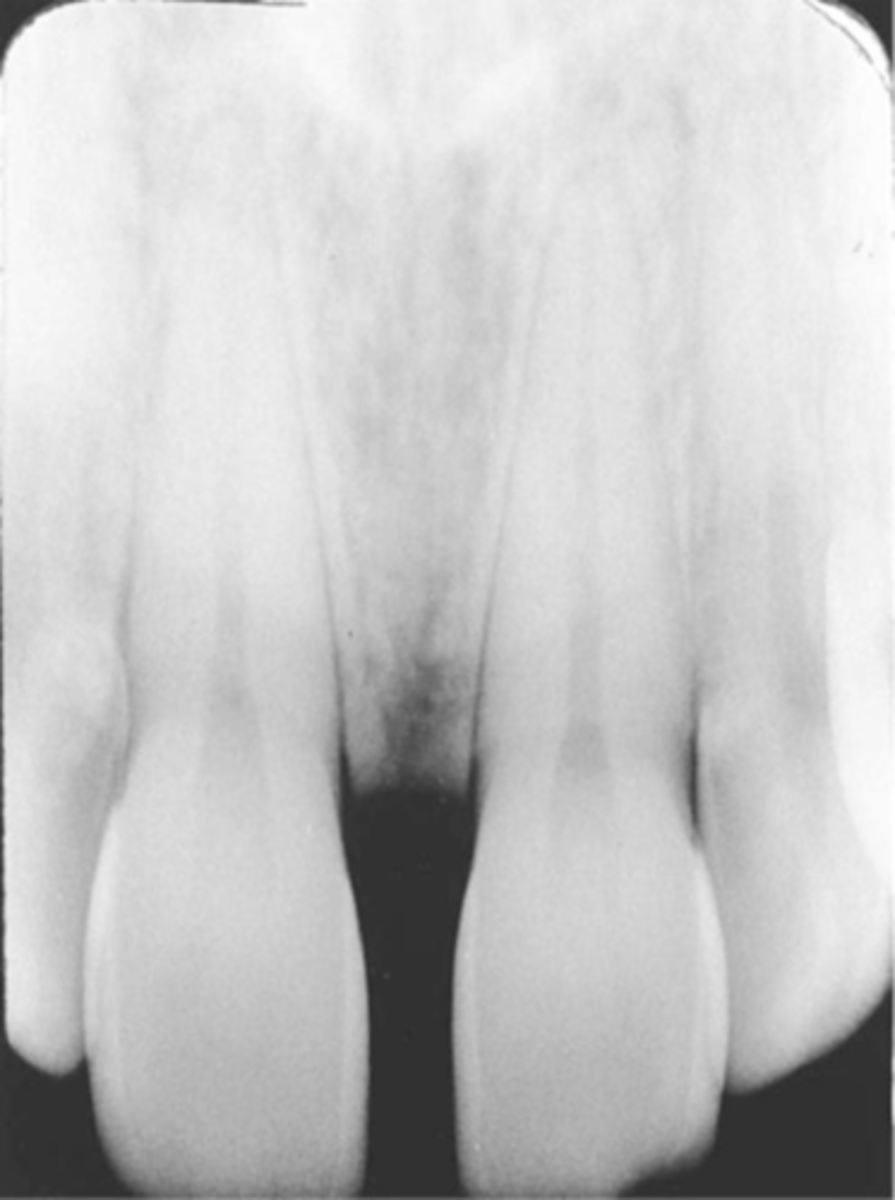
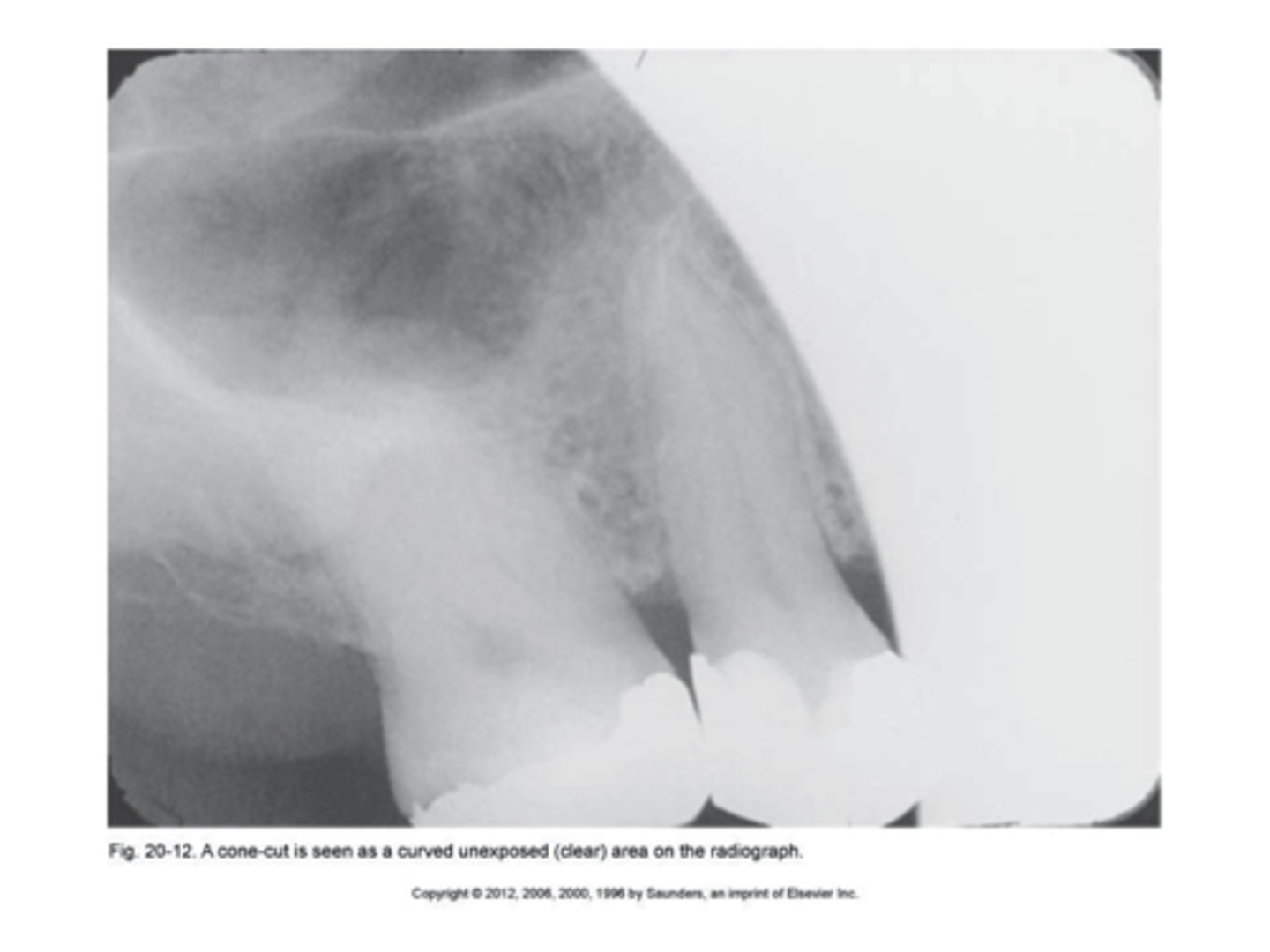
cone cut with beam alignment device (PA)
clear or white unexposed area
PID was not properly aligned with the beam alignment device
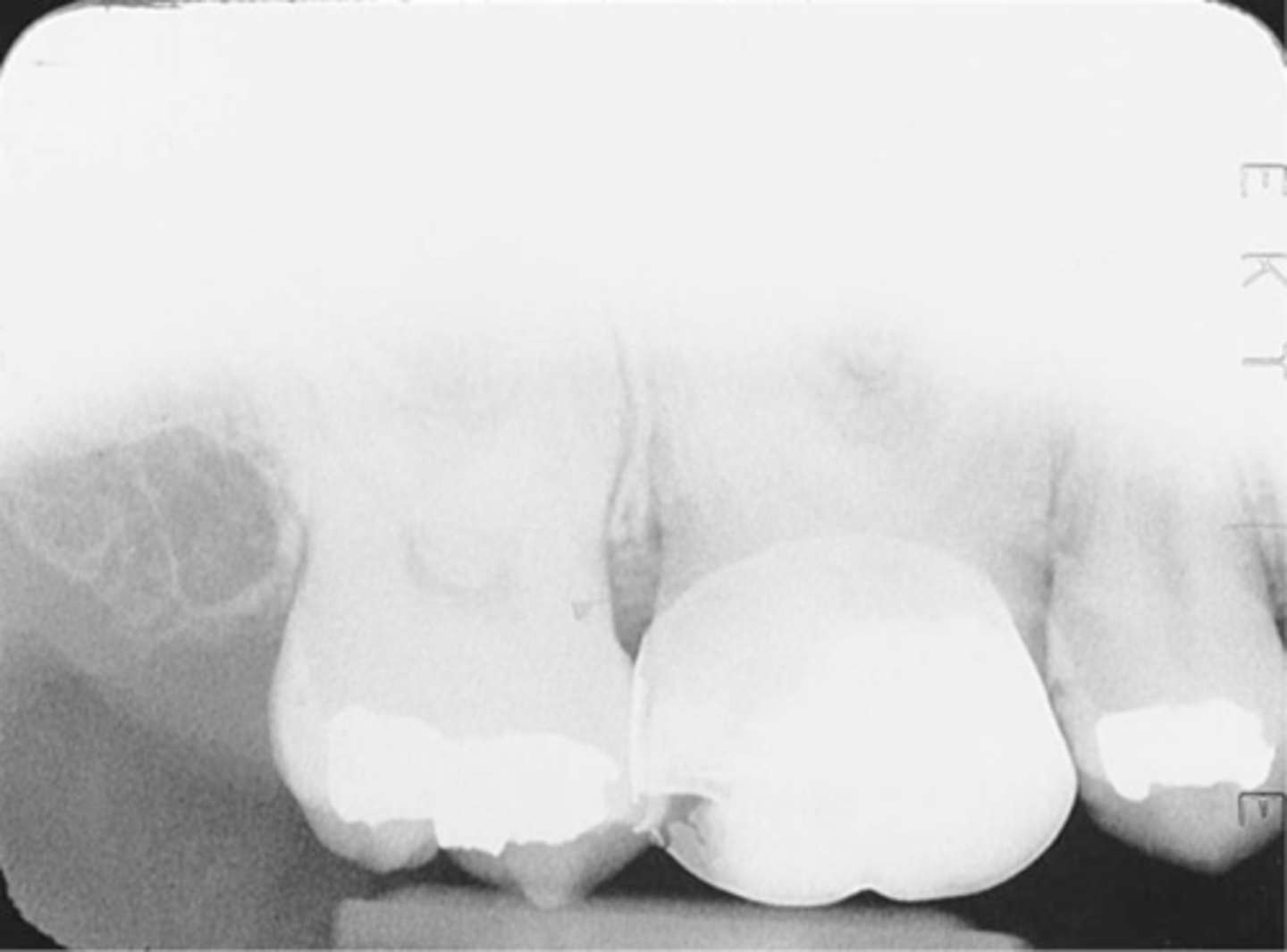
cone cut without beam alignment device (PA)
bisecting technique when a beam alignment device is not used
a clear or white unexposed area
PID was not directed at the center of the receptor
make sure PID is directed over the center of the receptor
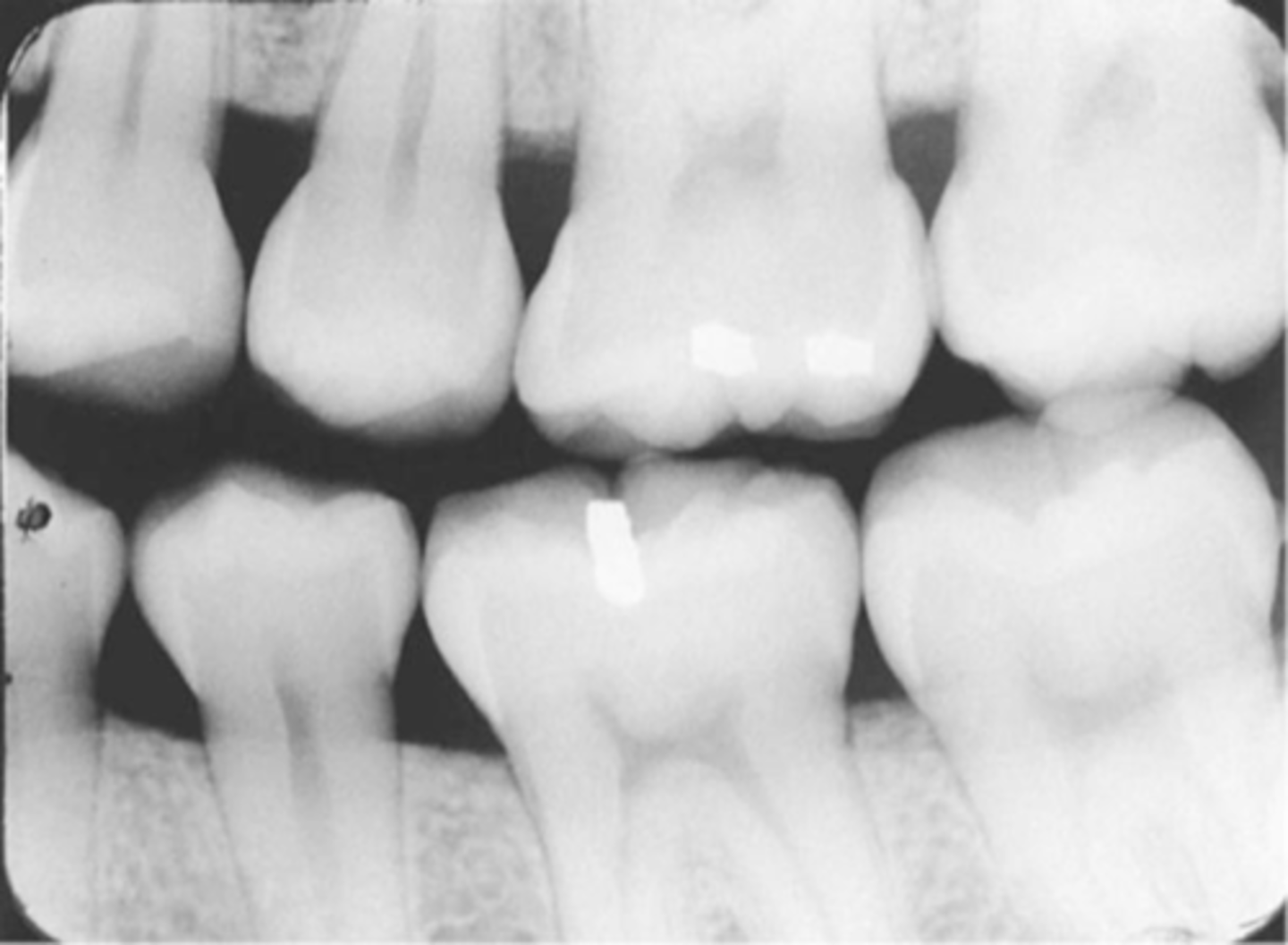
incorrect placement of premolar bite wing
distal surfaces of the canine are not visible of the image
receptor too far back
make sure anterior edge of receptor is at the midline of the mandibular canine
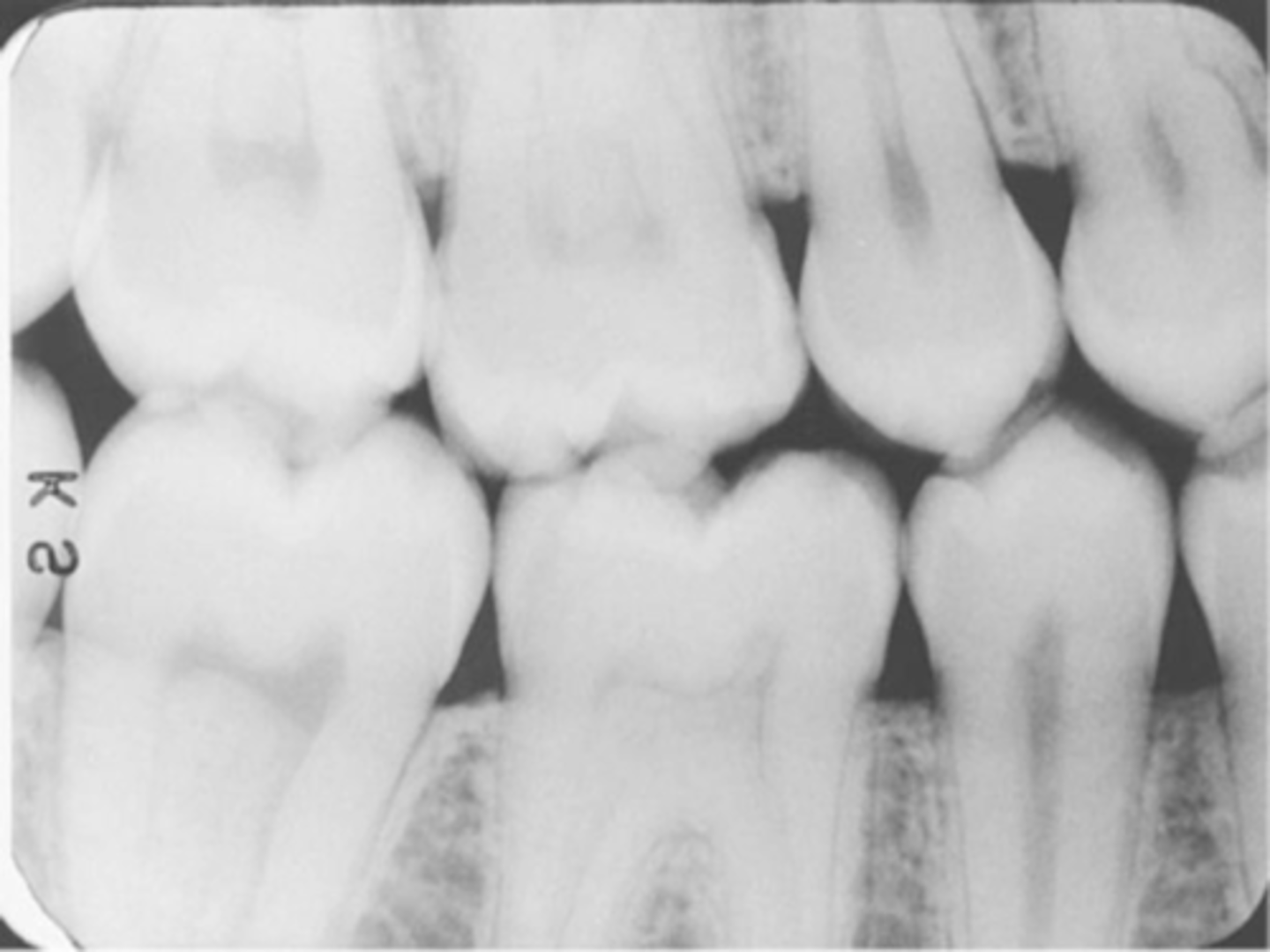
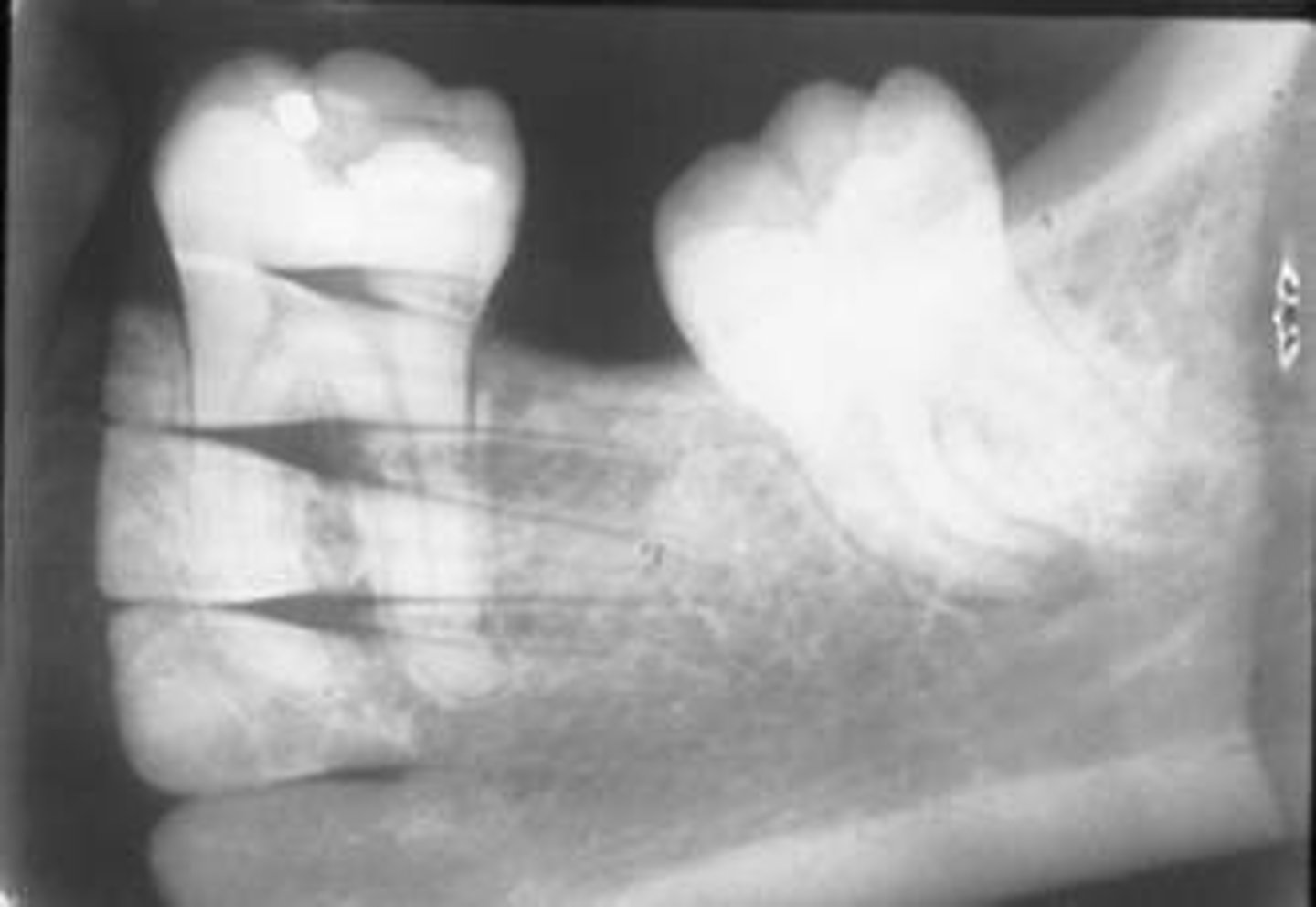
incorrect placement of molar bite wing
third molar regions not visible on the image
receptor too far forward
make sure anterior edge of the receptor is at the midline of the mandibular second premolar
center the molar bite wing over the mandibular second molar
distorted image
incorrect vertical angulation
vertical angle was negative
use +10 degree angle when using bite tab
cone cut with beam alignment device (BWX)
clear or white rounded unexposed area
PID was not properly aligned with the beam alignment device
cone cut without beam alignment device
clear or white rounded unexposed area
PID was not directed at the center of the receptor
make sure PID is directed over the center of the receptor
bending
occurs with paralleling, bisecting, or BWX
appears stretched
because of curvature of patients hard palate or rough excessive handling
creasing
occurs with paralleling, bisecting, or BWX
thin radiolucent line with film
thin white line with PSP digital receptor
do not over manipulate the receptor
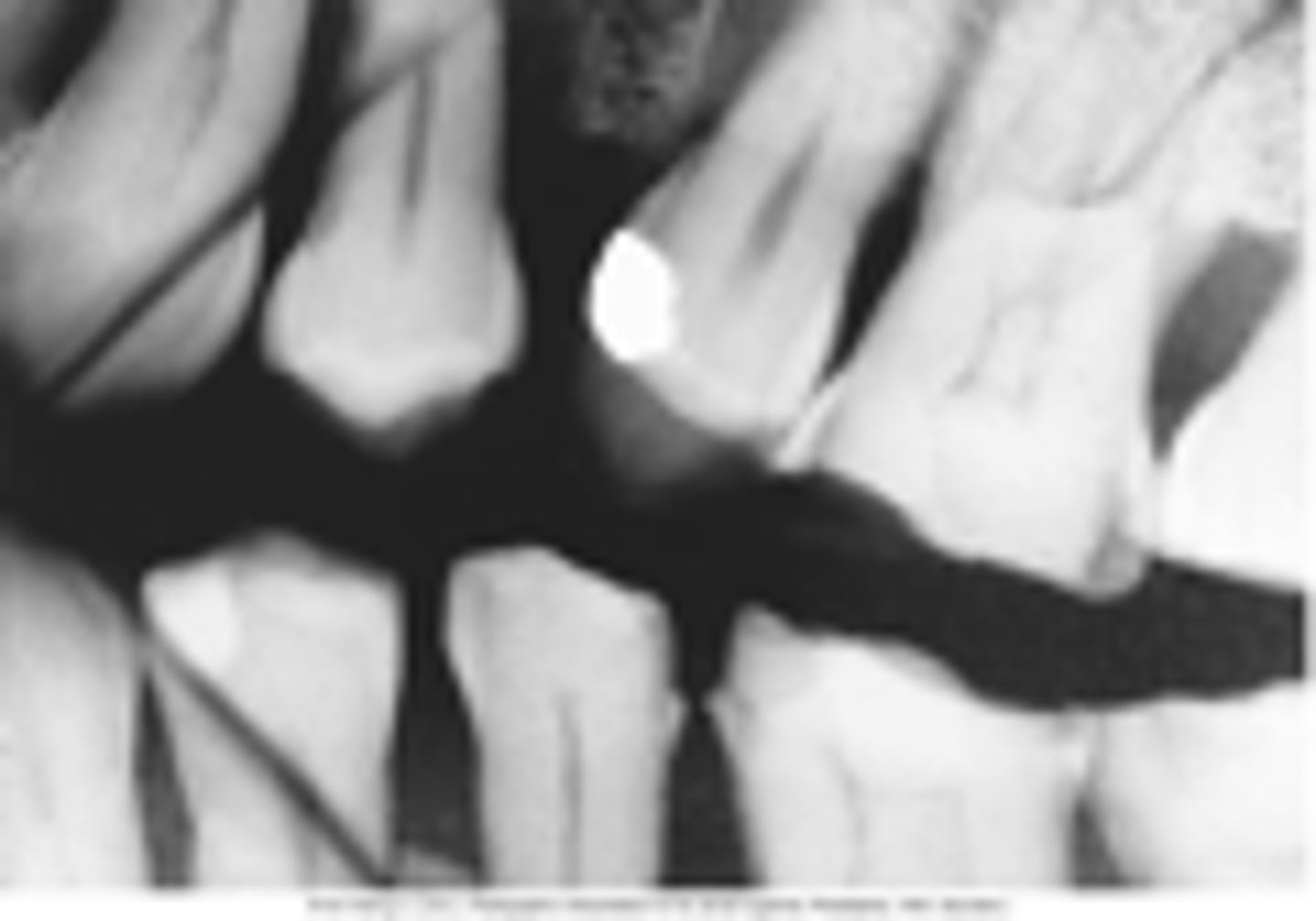

debris accumulation
take care to keep sensor clean
correct infection control procedures followed
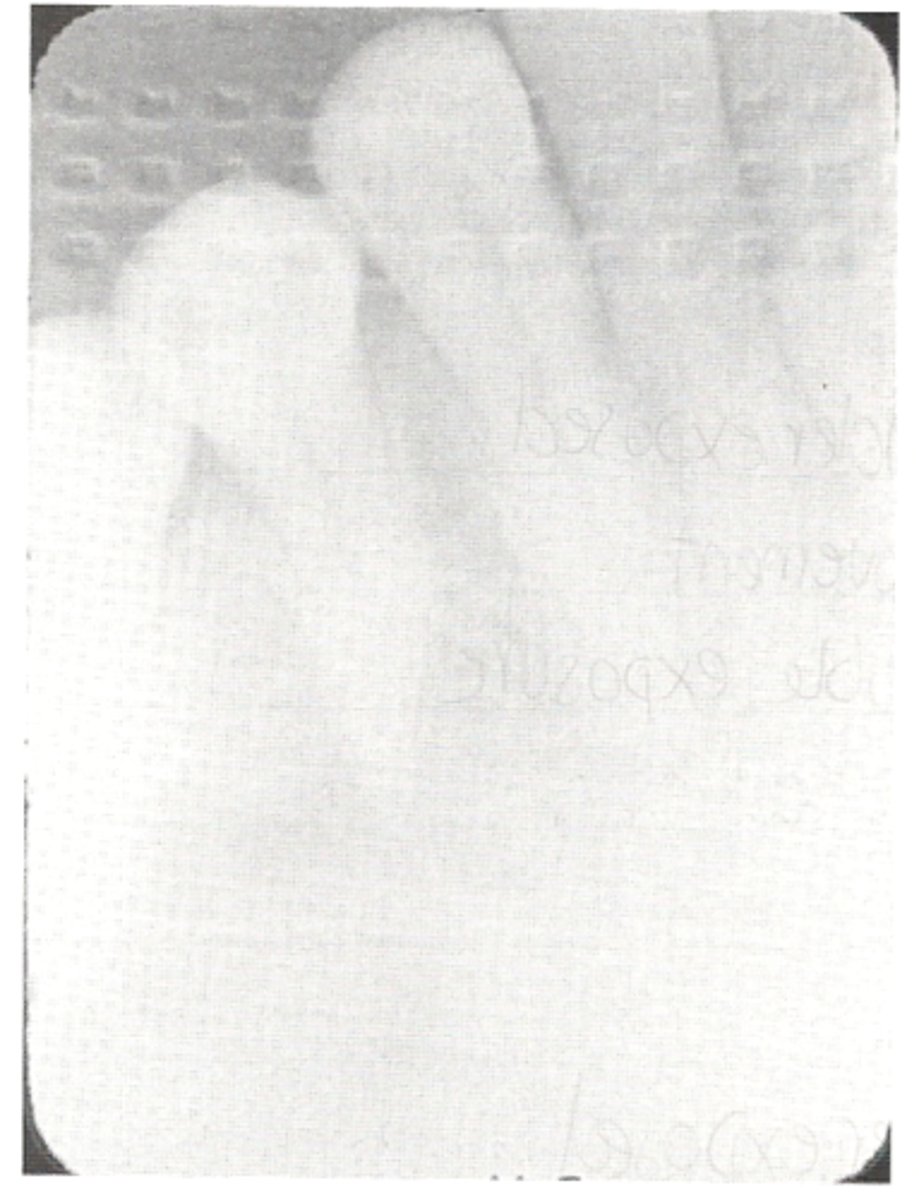
phalangioma
patient holds the receptor
image of the finger
double image
image appears dark with superimposed structures
always separate exposed and unexposed receptors
blurred image
movement of tubehead, receptor, or patient
stabilize patients head with headrest and instruct to keep still

reversed
with film: light image with herringbone pattern
with sensor: no image produced
with PSP digital plate it is difficult to identify
always place the receptor with the proper side towards the tubehead
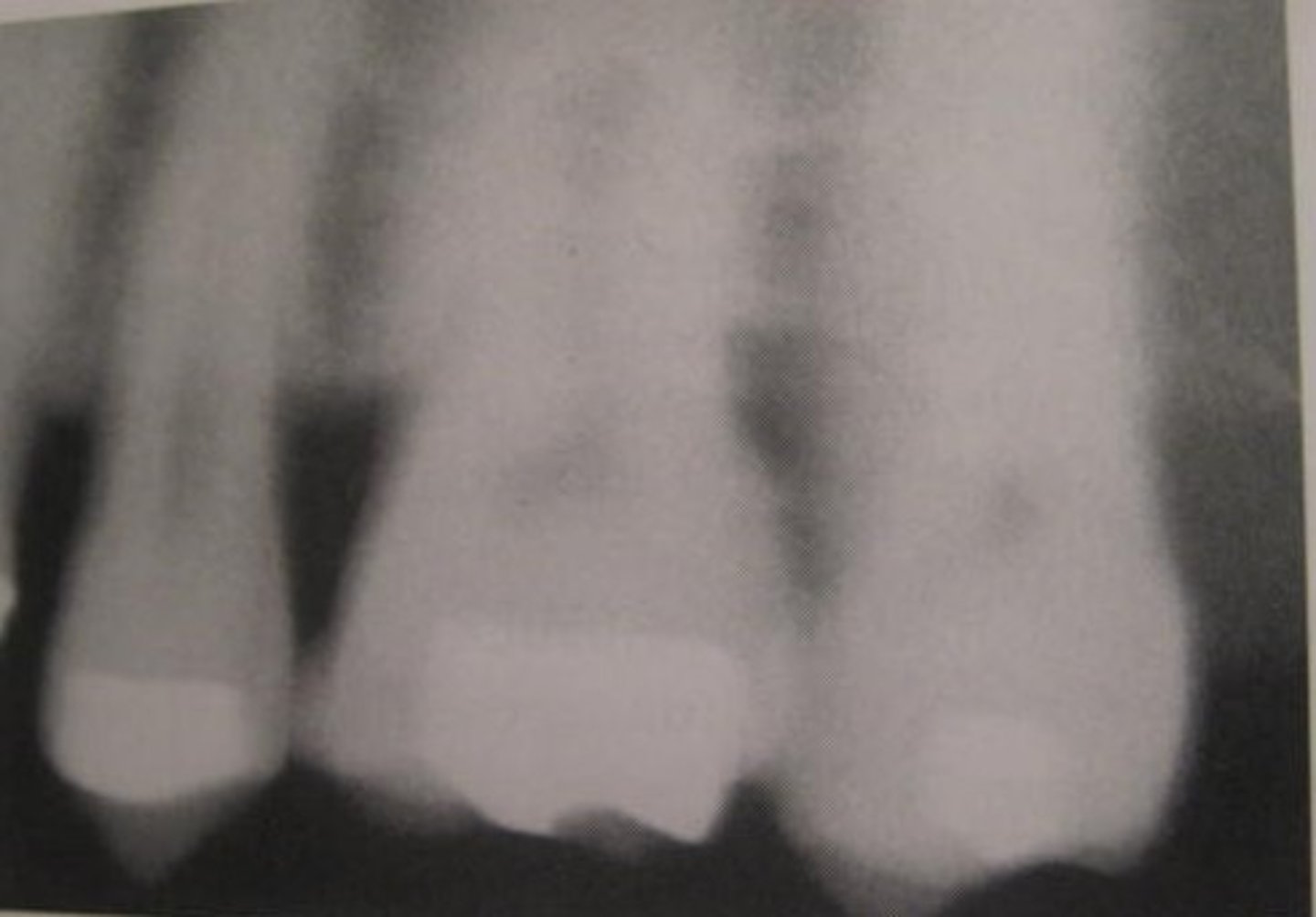
receptor placement
absence of apical root structure
dropped receptor corner
tomography
imaging technique that allows the imaging of one layer, or section, of the body while blurring the images of structures in other planes
conforms to shape of dental arch
image receptor and tubehead rotate in opposite direction around center or rotation
focal trough
the layers of the dental arch that remain in focus
teeth are positioned into the focal trough
objects inside focal trough are clear
real image
true image to size and shape
ghost image
an artifact on a dental image produced when a radiodense object is penetrated twice by the x-ray beam; radiopaque
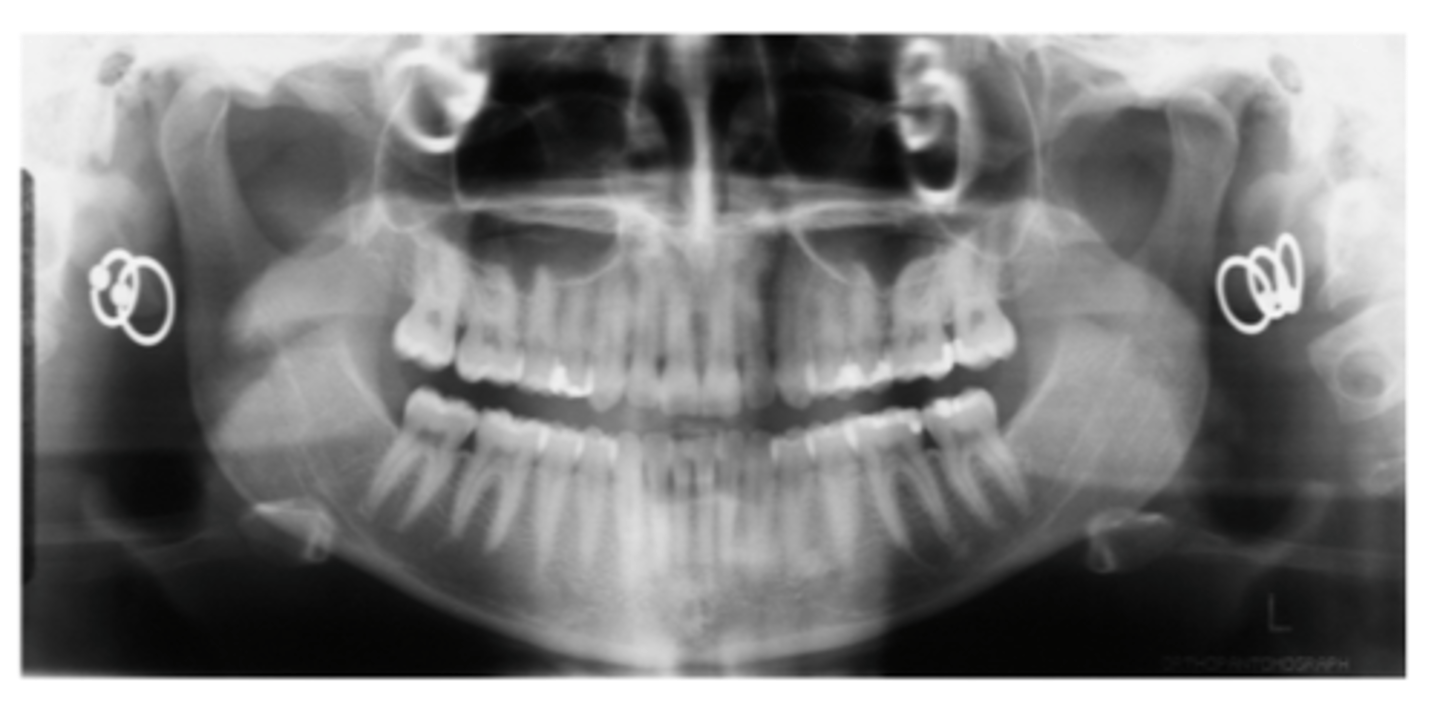
double image (PAN)
has the same proportions as the real image and is located in the same location on the opposite side
which collimator do you use on PAN?
vertical slit collimator
equipment for panoramic
-x-ray tubehead
-head positioner
-exposure controls
-exposure switch
-vertical slit collimator
what does the vertical slit collimator do?
restricts radiation
green light
rare earth
blue light
calcium tungstate
intensifying screen
increases the intensity of radiation on the film
film is placed between two intensifying screens
cassette
holds the films
calcium tungstate
emit blue light
paired with blue film
rare earth
emit green light
recommended in panoramic
paired with green film
static electricity
caused by removing film from box or cassette too quickly, creating static discharge
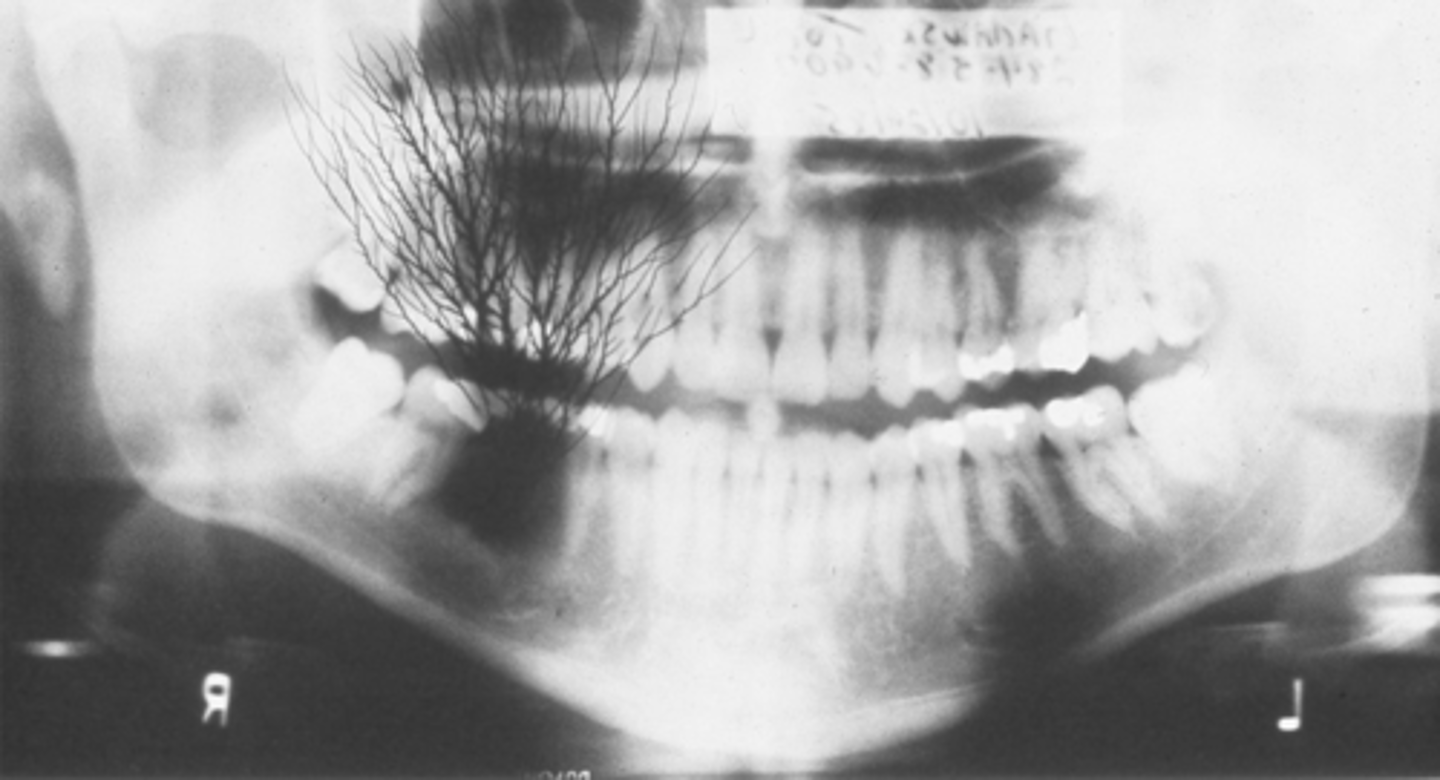
complete denture
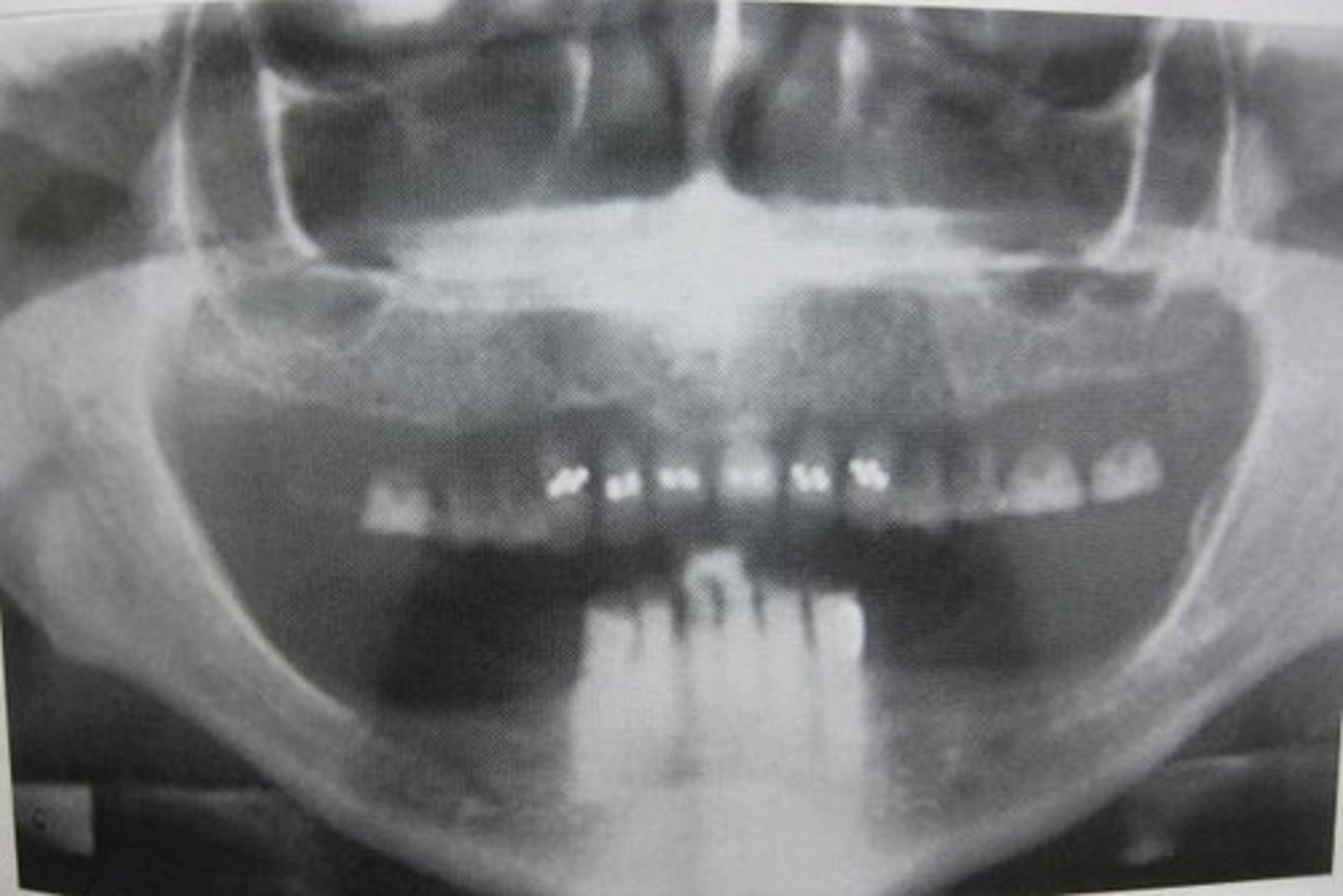
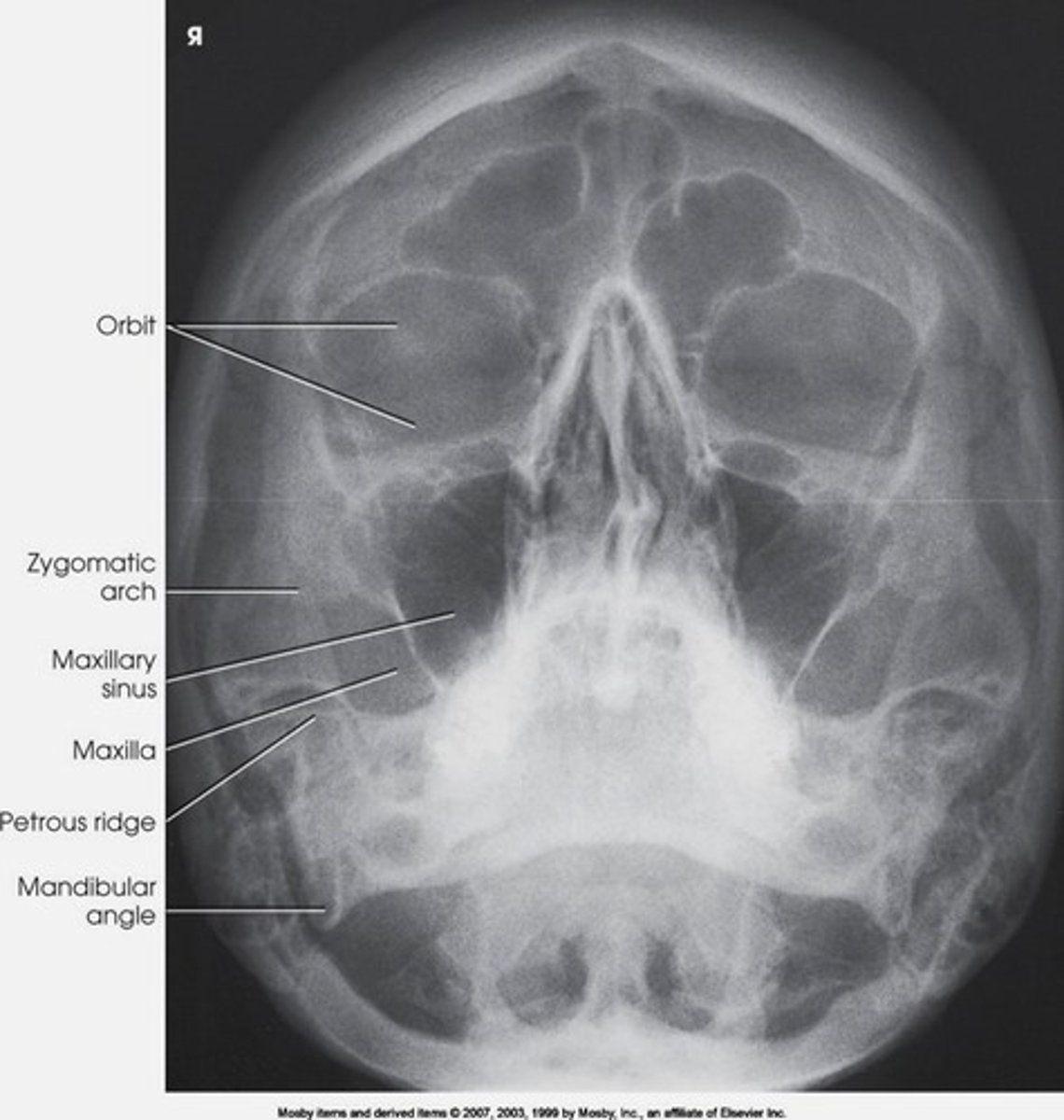
waters projection
shows maxillary sinuses
xray beam directed from behind head
clark's rule or buccal object rule
requires 2 radiographs
all factors remain the same for the second exposure except that tube is shifted 20 degrees mesially/distally
-the buccal object will appear to have moved in the opposite direction from tube shift
-the lingual object will appear to have moved in the same direction from tube shift
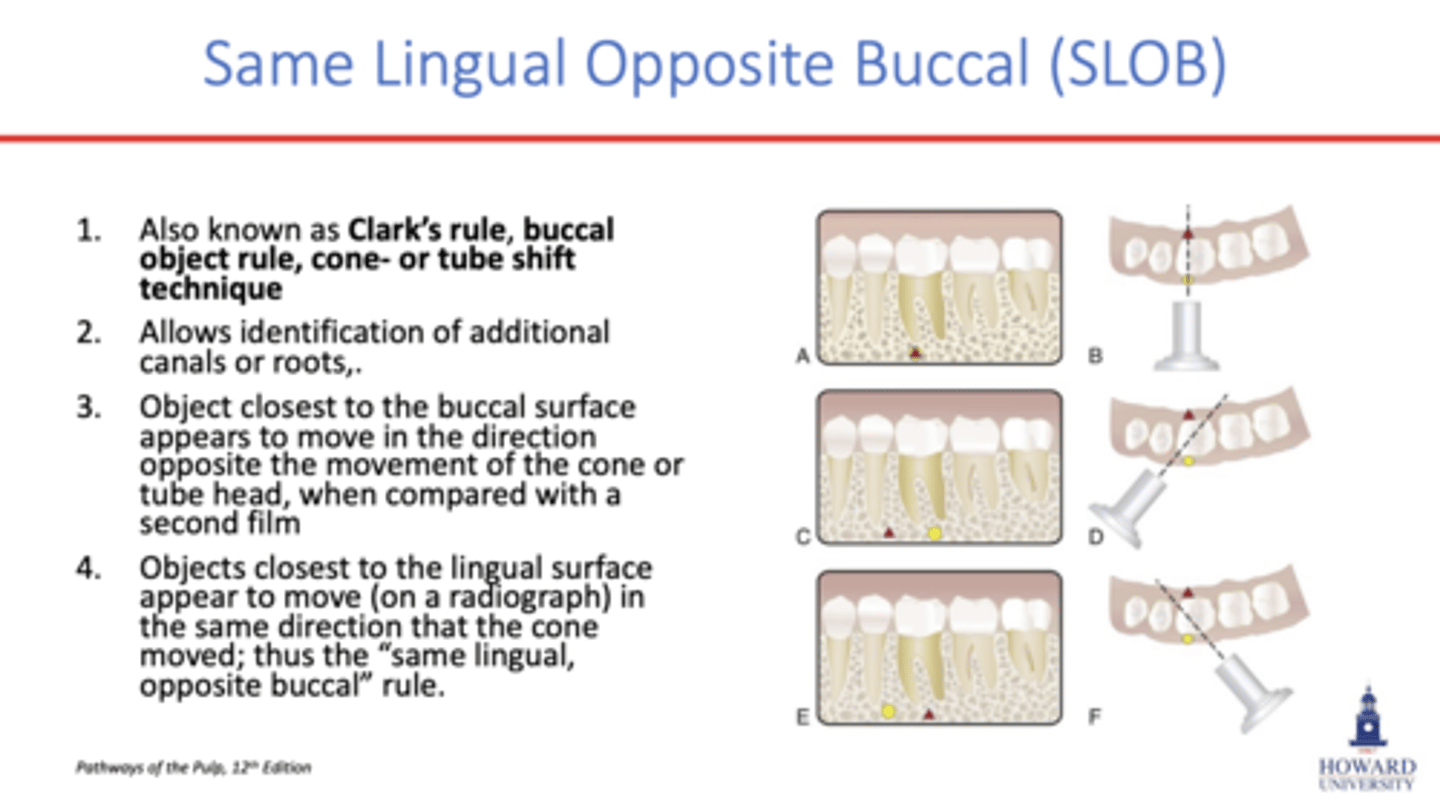
SLOB
same lingual, opposite buccal
arrested
carious lesion that has not progressed, hard surface with a dark color
primary
occurs on a surface that has not been previously affected
rampant
widespread lesions that start off as chalky white and may increase in size over a short period of time, they include several teeth and often multiple areas of one tooth
incipient
very early lesion that has not broken through the enamel surface, does not have to be restored right away
recurrent
occur on surface adjacent to a restoration, a continuation of the original lesion
sharps container
-warning label
-closed
-durable
-no leakage
when recapping you must use ---- method
scooping method
how much epinephrine to treat anaphylaxis?
1:1000 = 1mg/ml
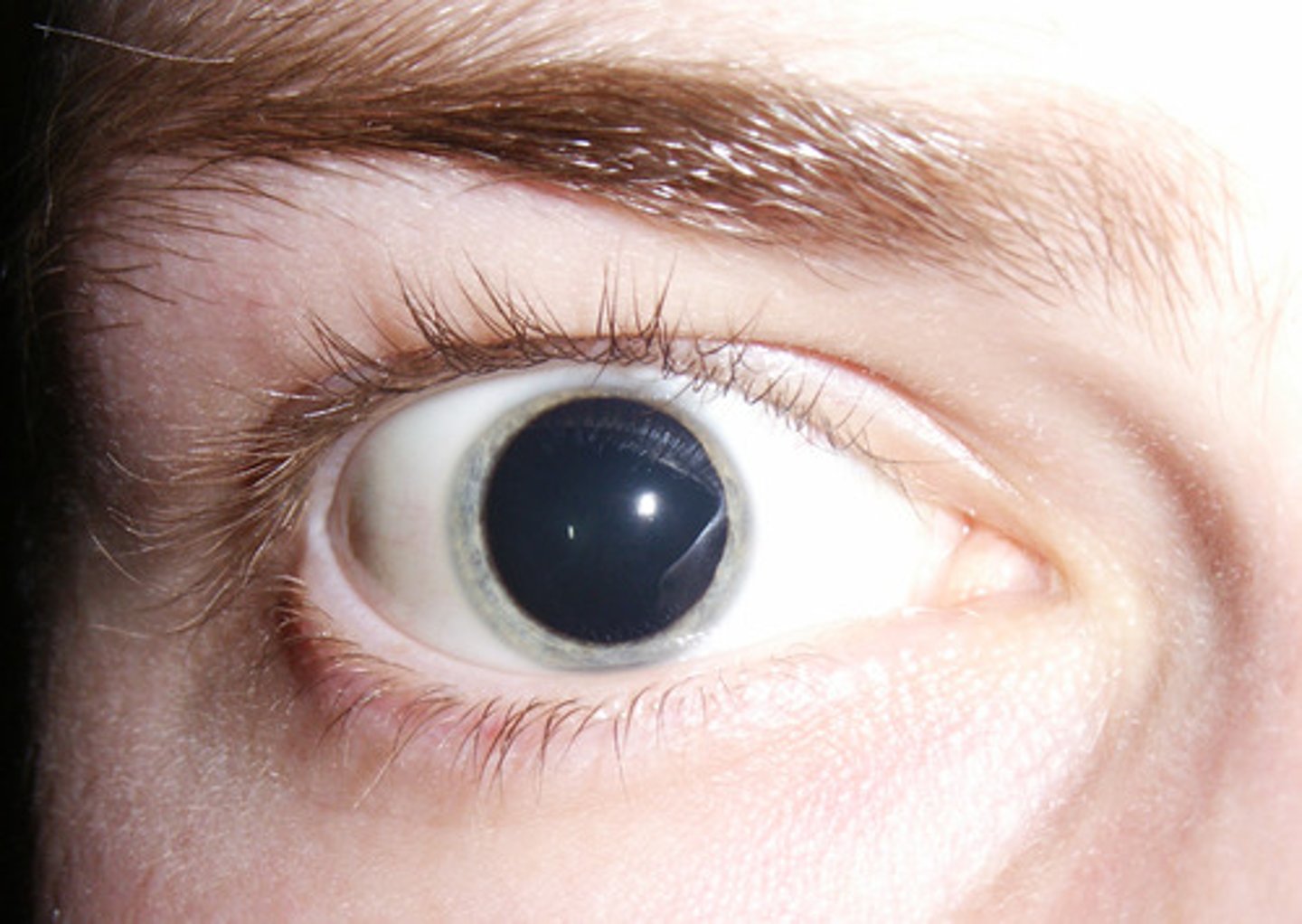
mydriasis
dilation of the pupil from excess sympathetic drug actions
how old are patients when their 3rd molars are developed?
in utero
atrial fibrillation
occurs when the normal rhythmic contractions of the atria are replaced by rapid irregular twitching of the muscular heart wall
periogard and peridex
chlorhexidine gluconate
.12 concentration with 15% alcohol
ADA seal
what is the mechanism of action for periogard/peridex?
bactericidal (kills bacteria)
most substantive mouthrinse (continues to be active)
no overgrowth of opportunistic organisms (candida)
broad spectrum non specific action
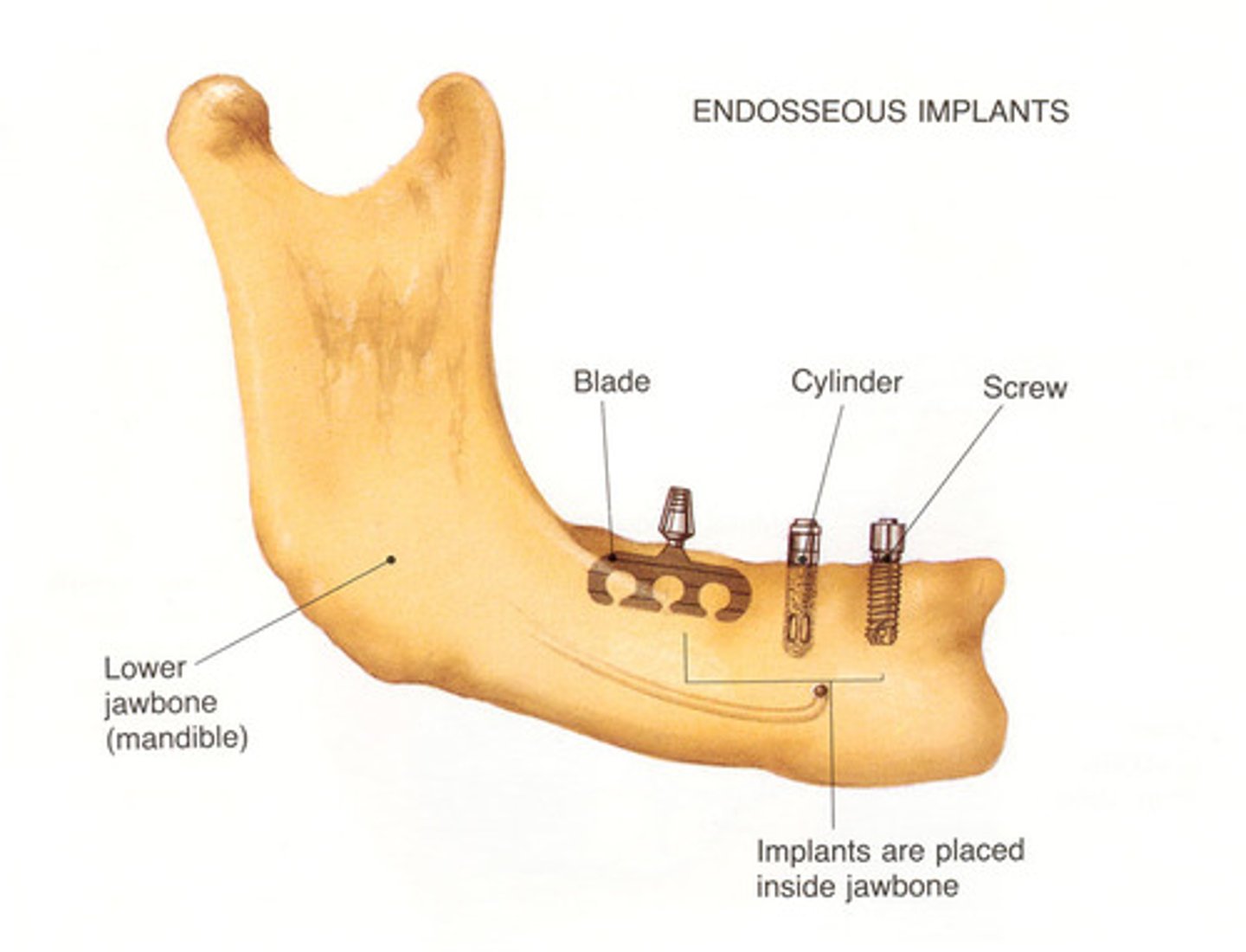
endosseous
placed within alveolar bone
based on concept of osseointegration
consists of 3 parts: fixture, abutment, prosthesis
most effective
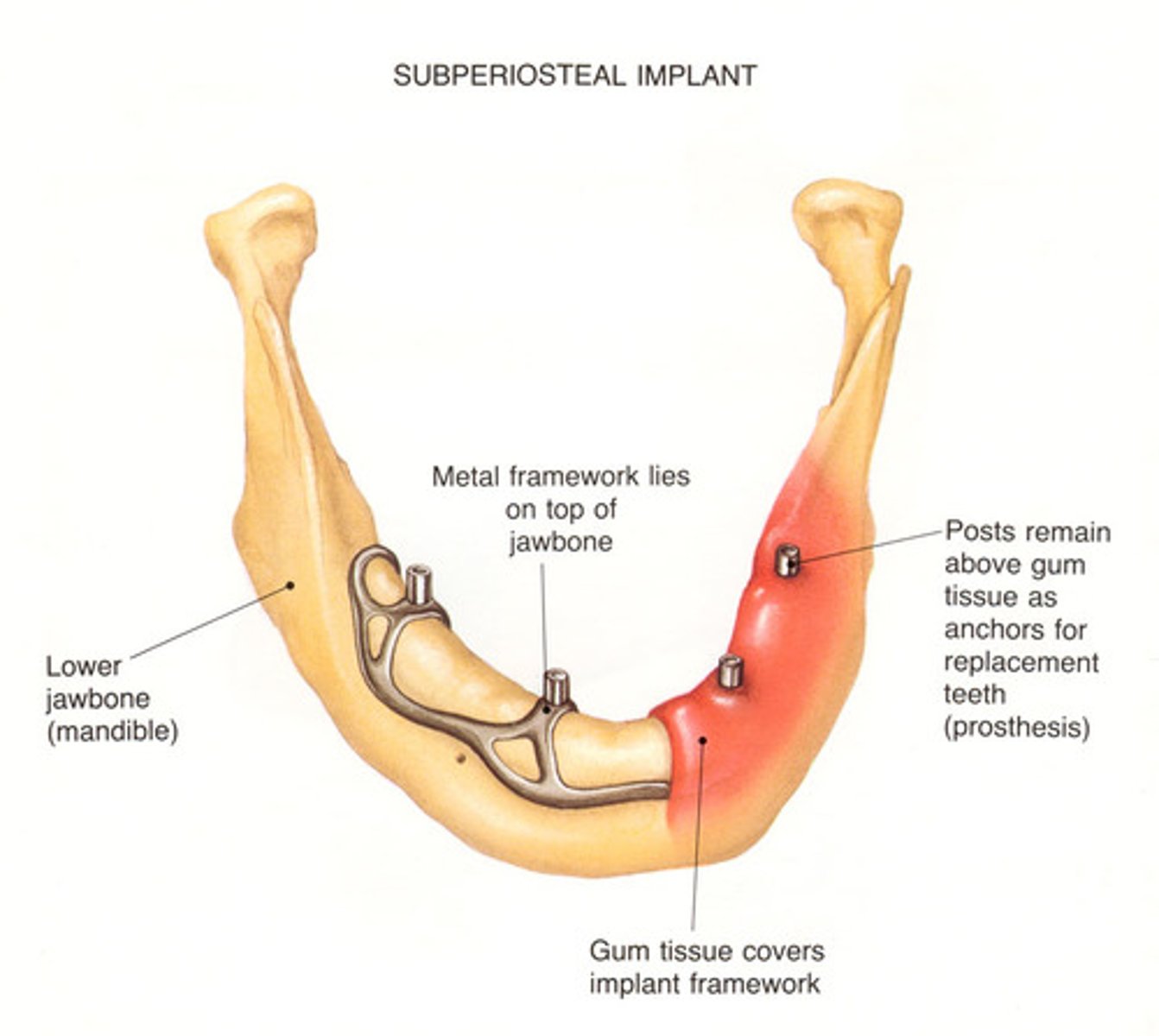
subperiosteal
rests directly on bone under soft tissue
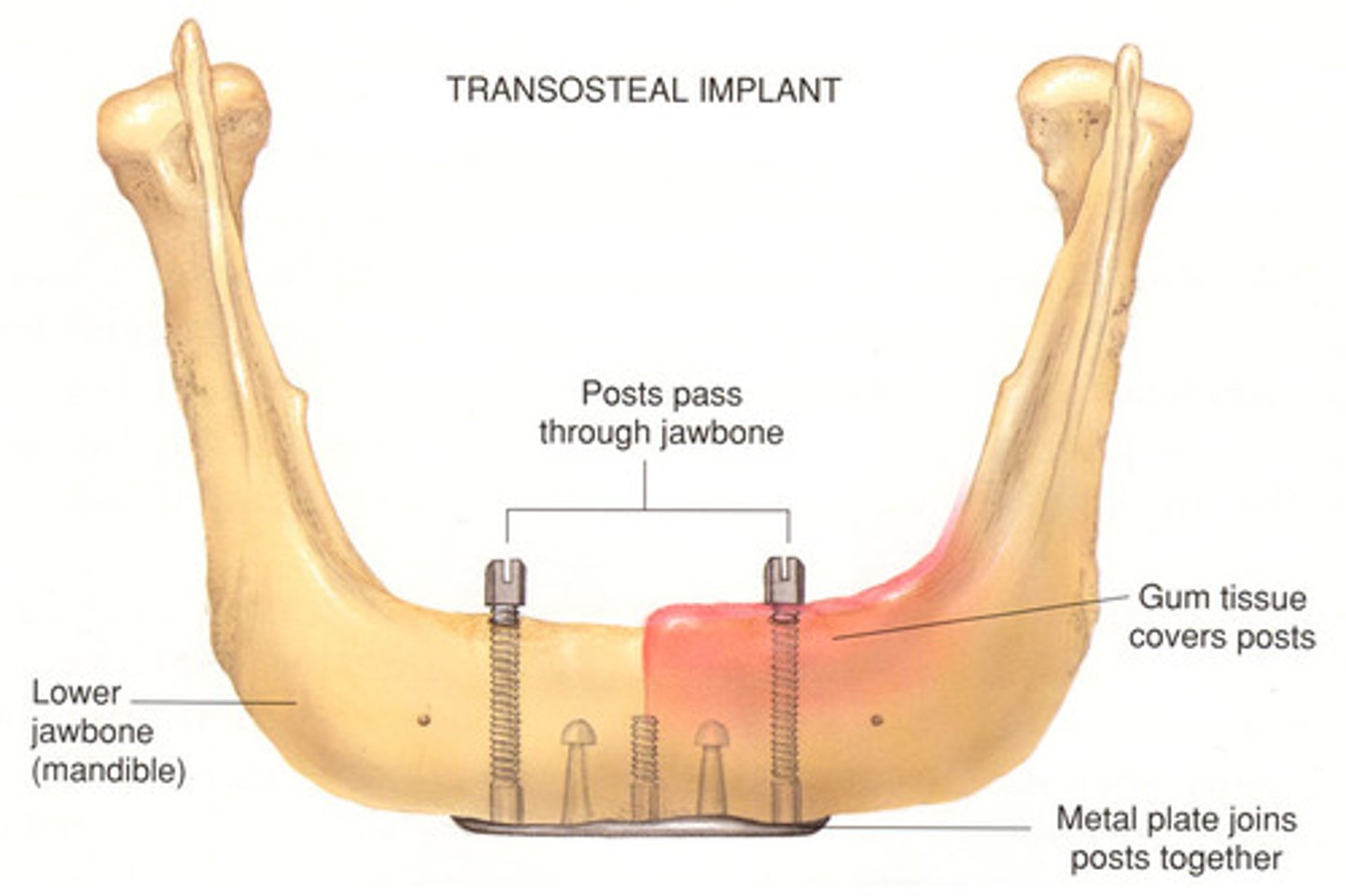
transosteal
horizontal support soft tissue
used for patients with atrophic mandible
bone grafting
implantation or transplantation of bone tissue from another part of the body or from another person to serve as replacement for damaged or missing bone tissue
needed when proposed implant site lacks adequate amount and quality of bone
autograft
bone from yourself
allograft
bone from cadaver
xenograft
bone from animal (cow, pig)
alloplast
synthetic bone-like material
what is used to fill root canals?
gutta percha (zinc oxide)
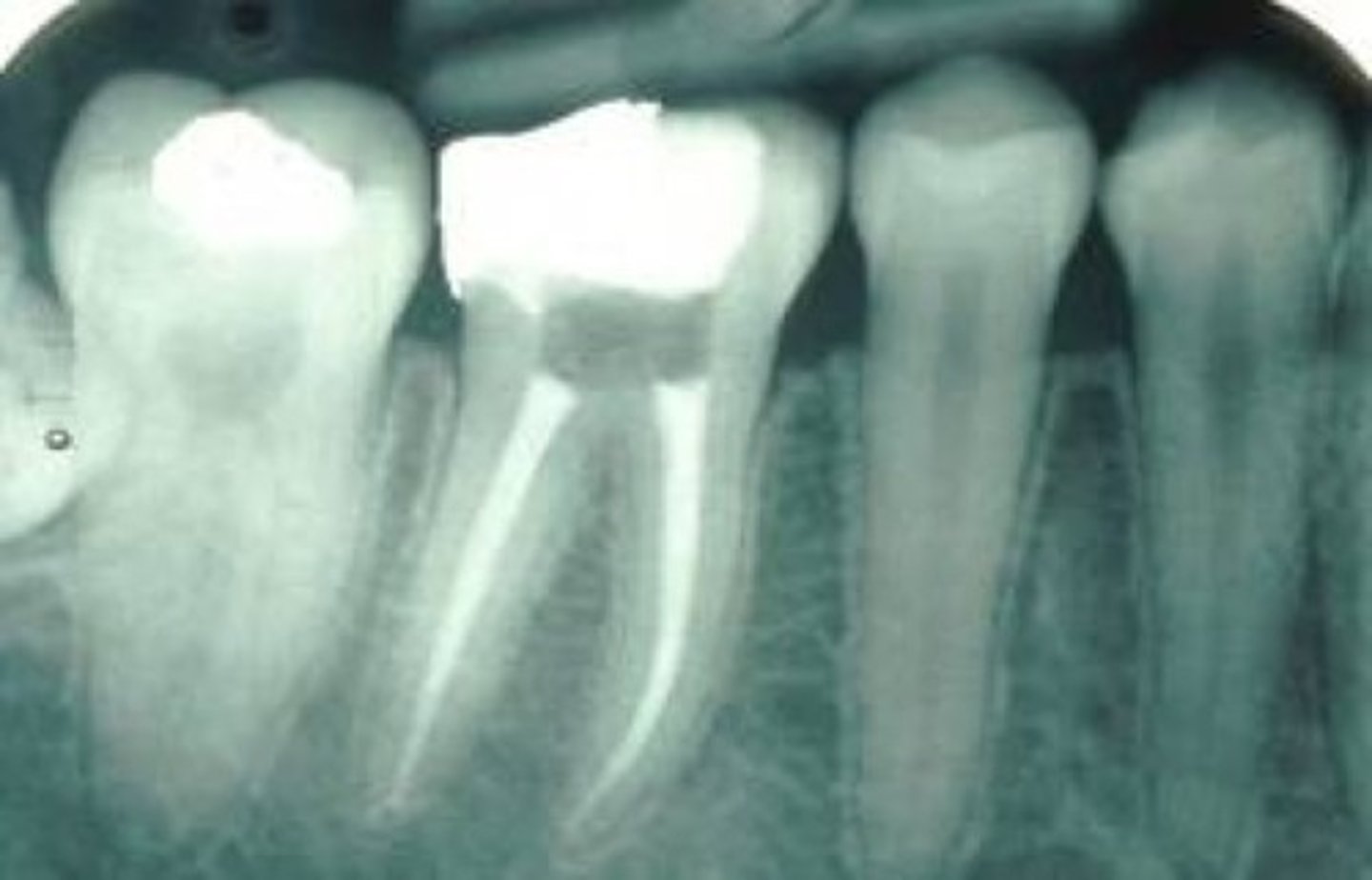
silver point
radiopaque
what do you NOT use prior to composite placement?
ZOE
place a protective layer of ---- on the pulpal wall
calcium hydroxide
MOD amalgam
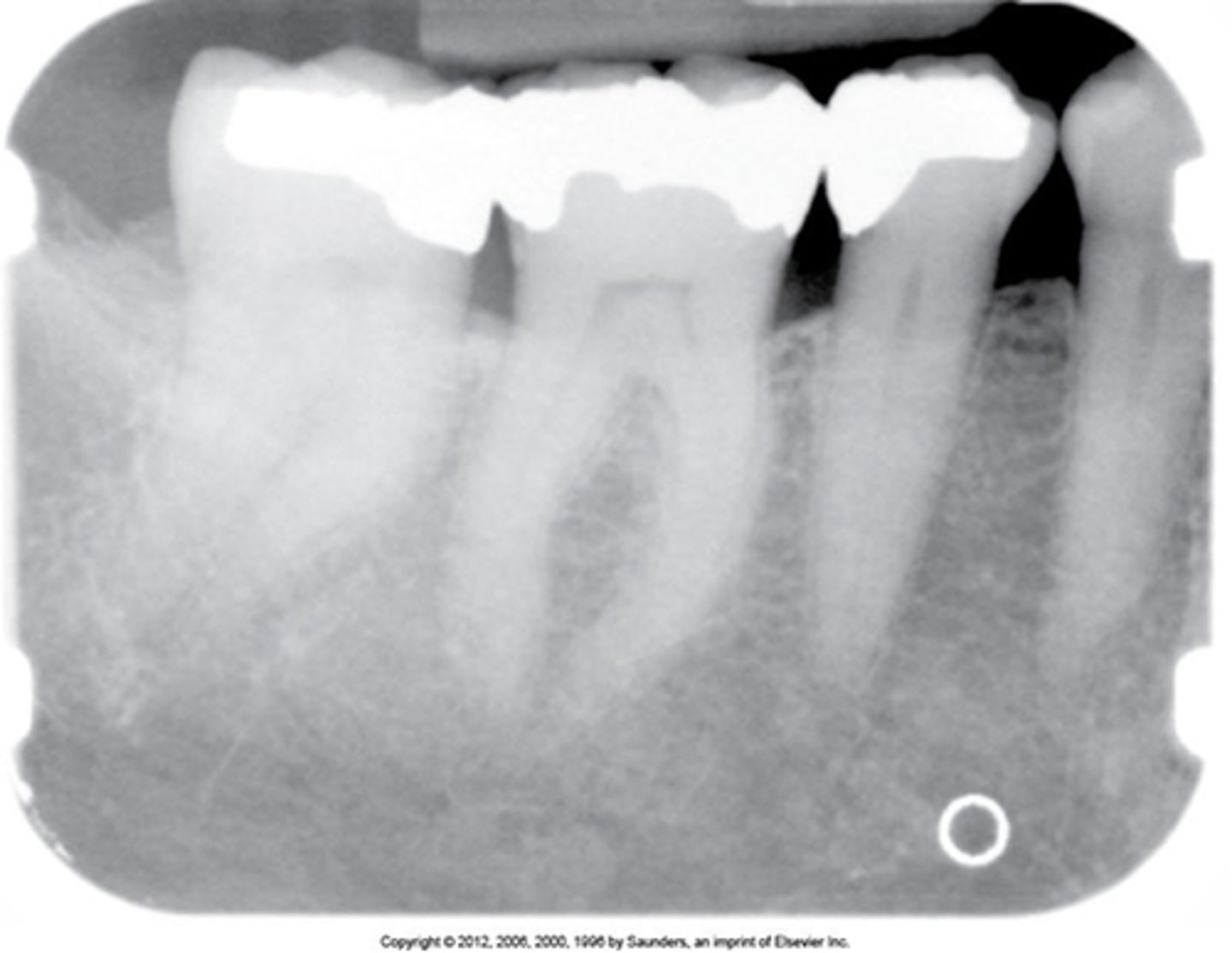
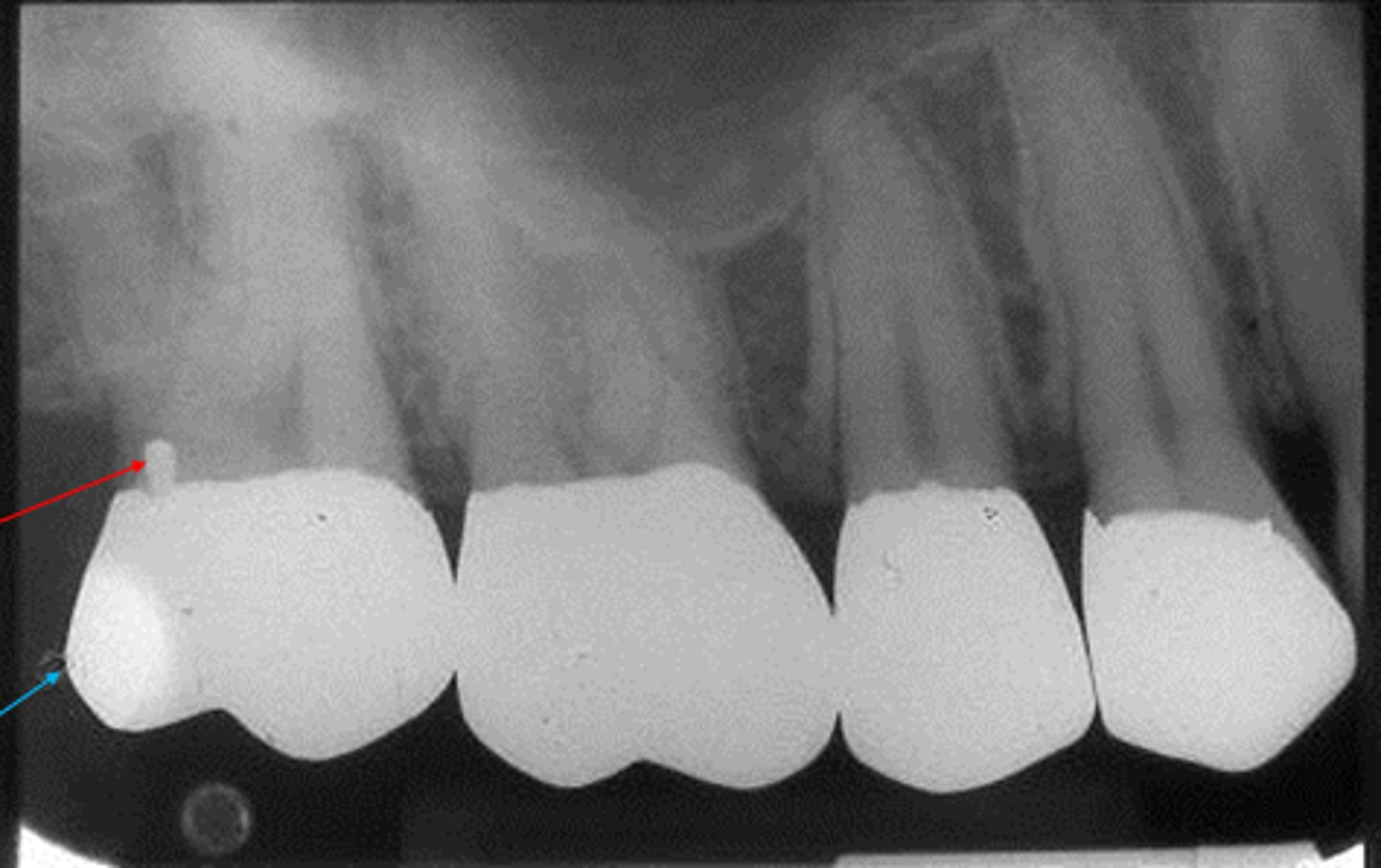
overhang
overhang
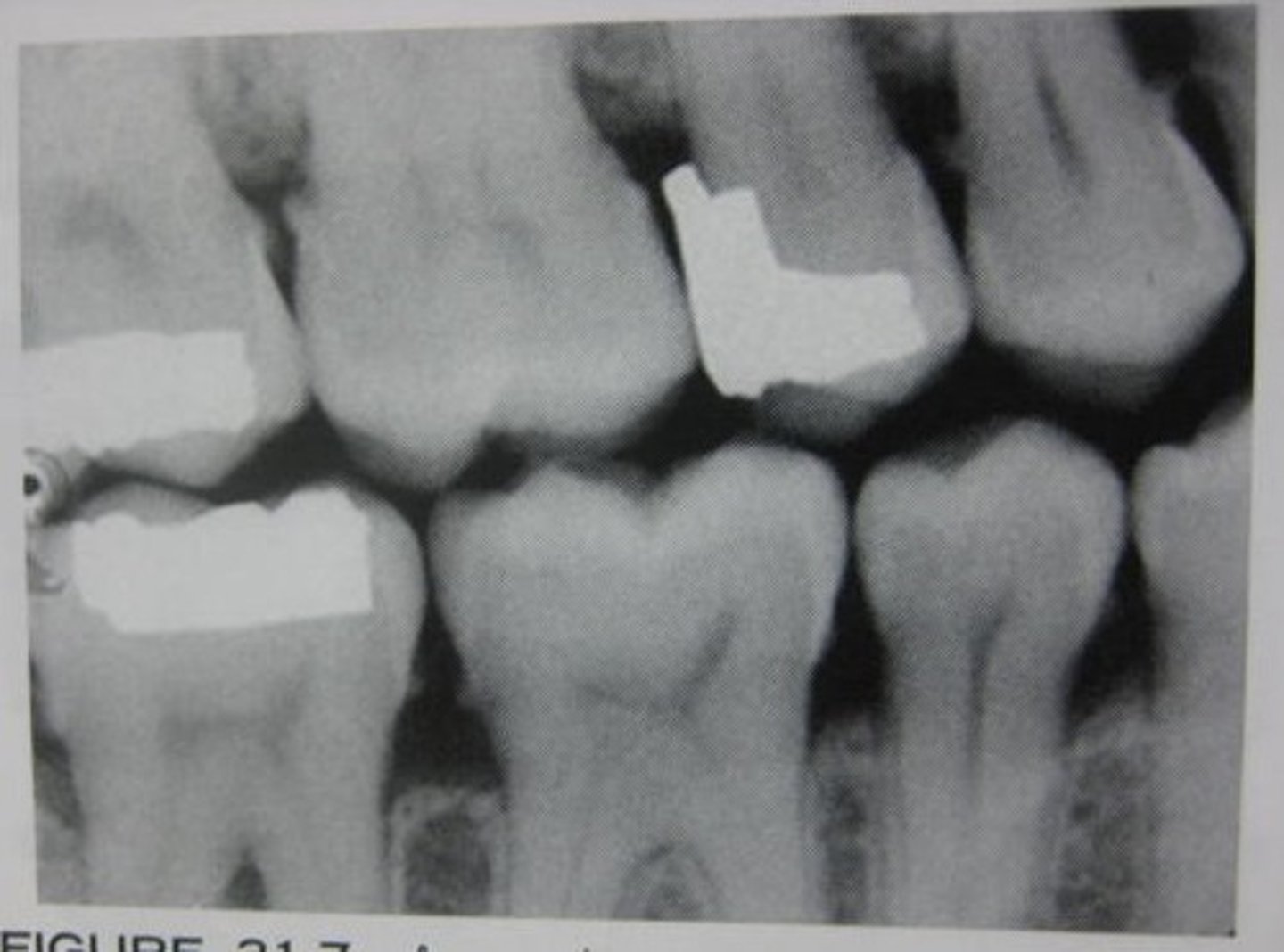
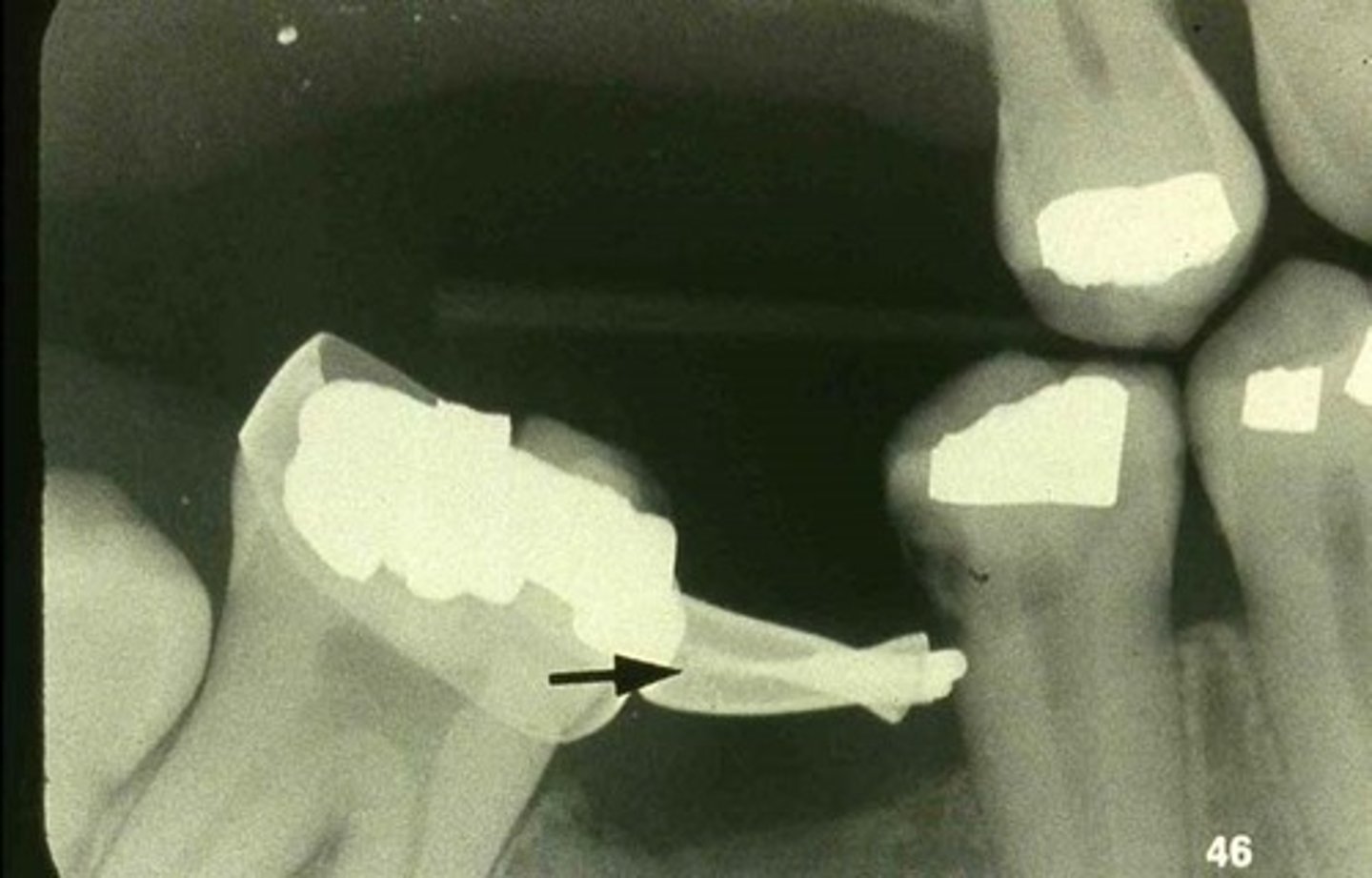
PINS
prior to composite filling
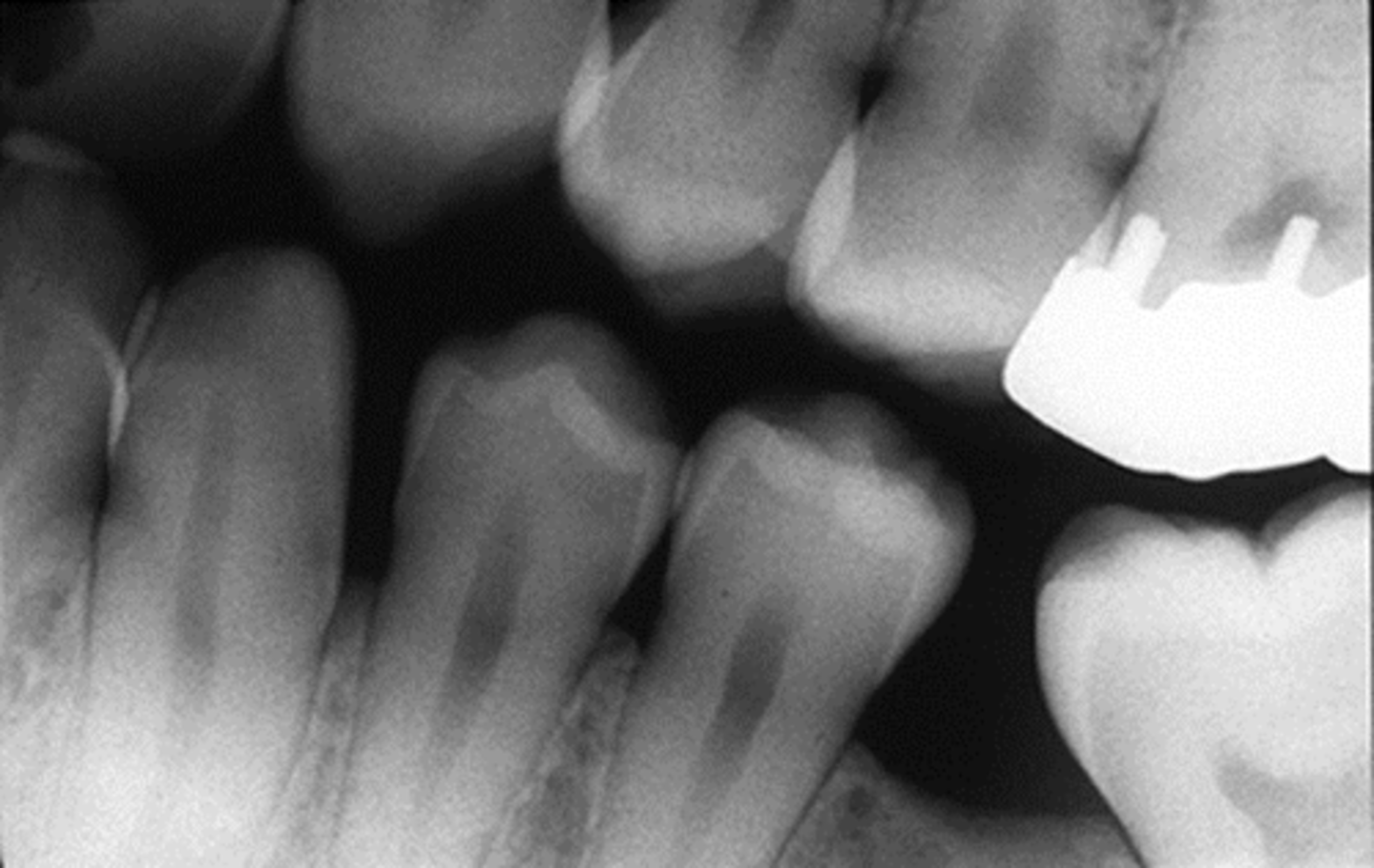
decay
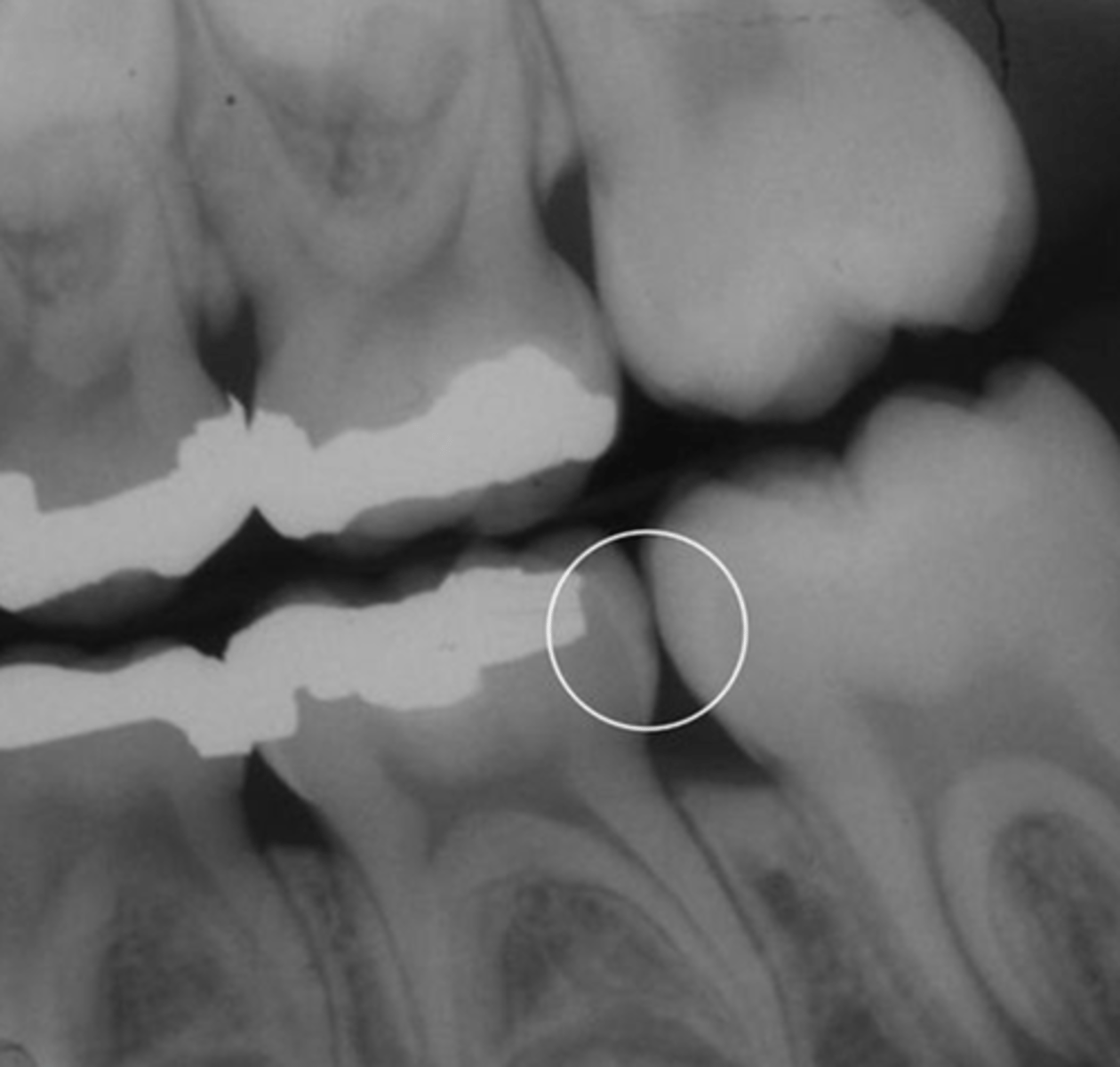
gold crown
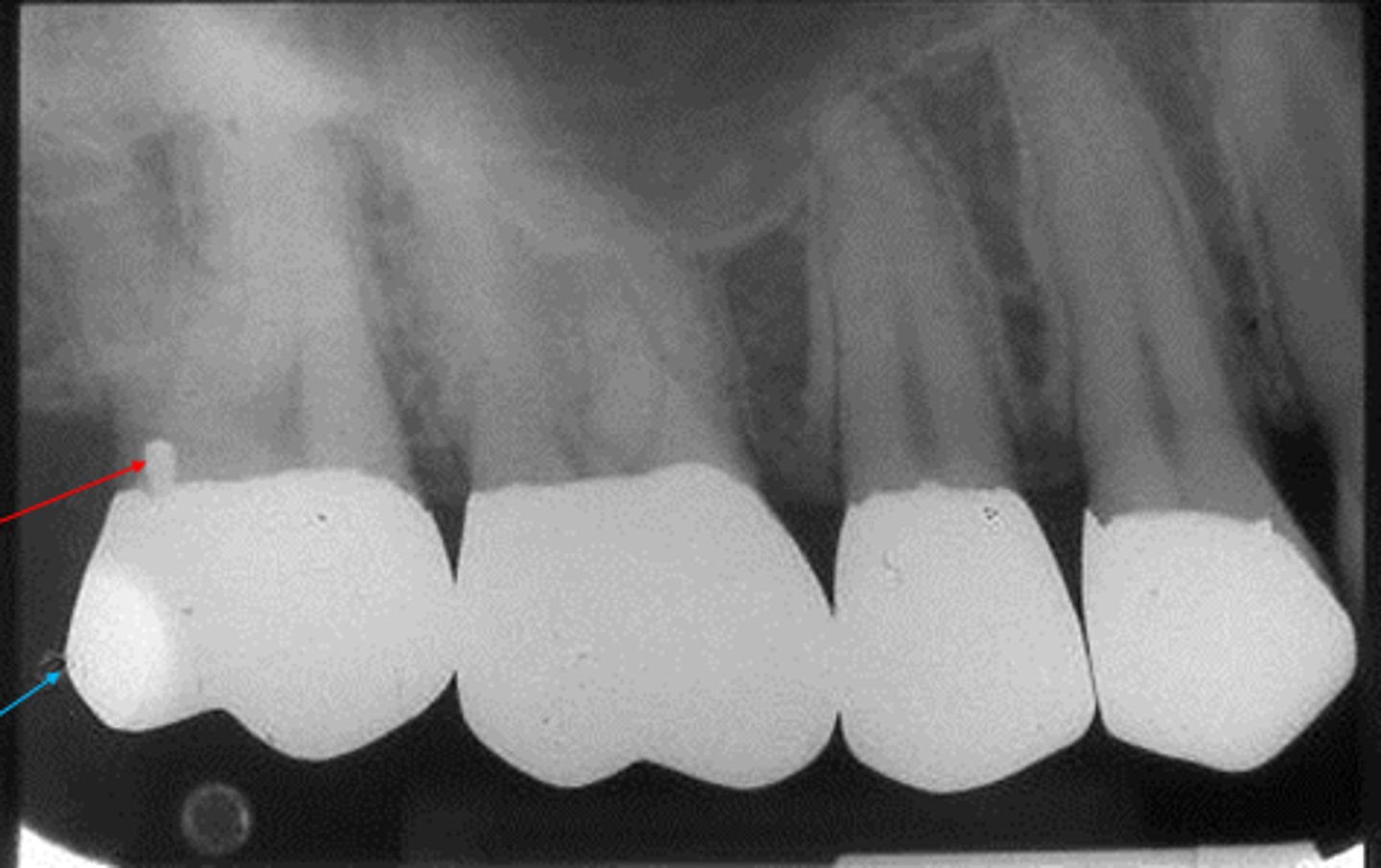
porcelain crown
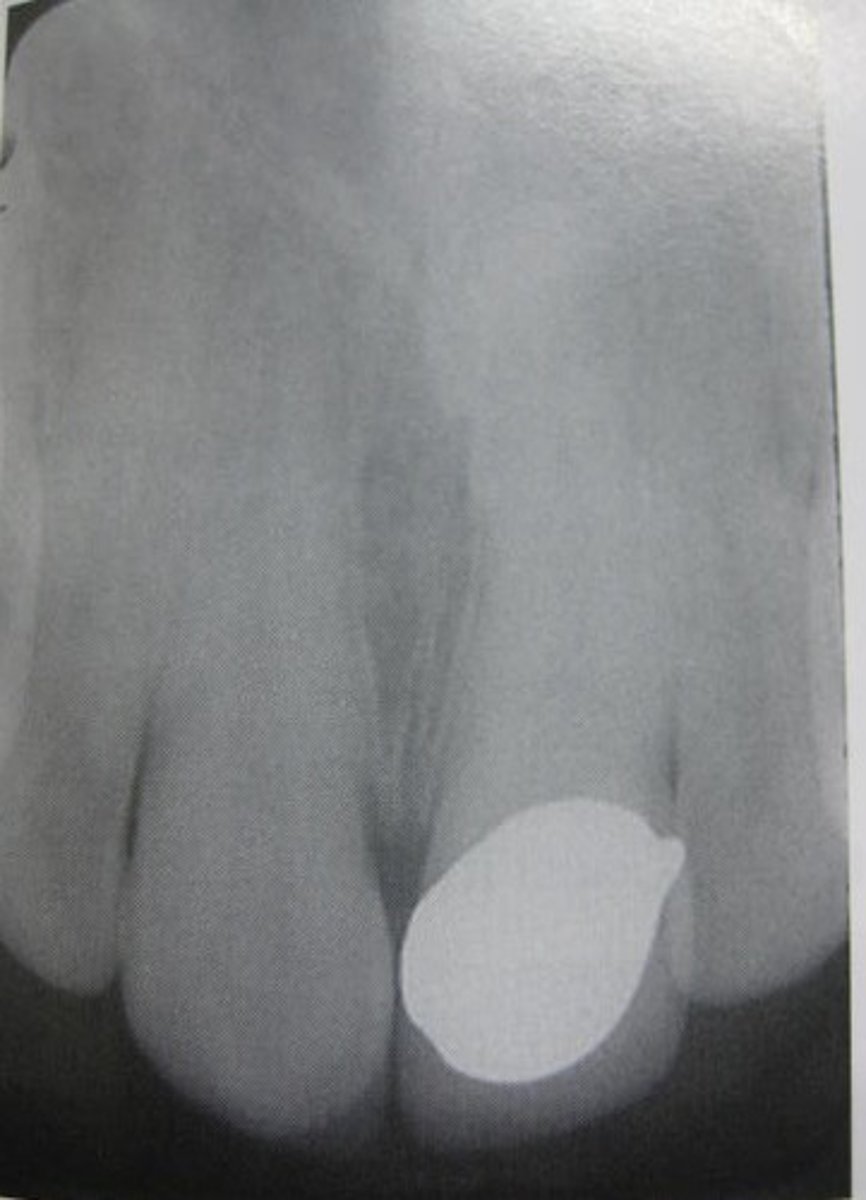
gold crown with post
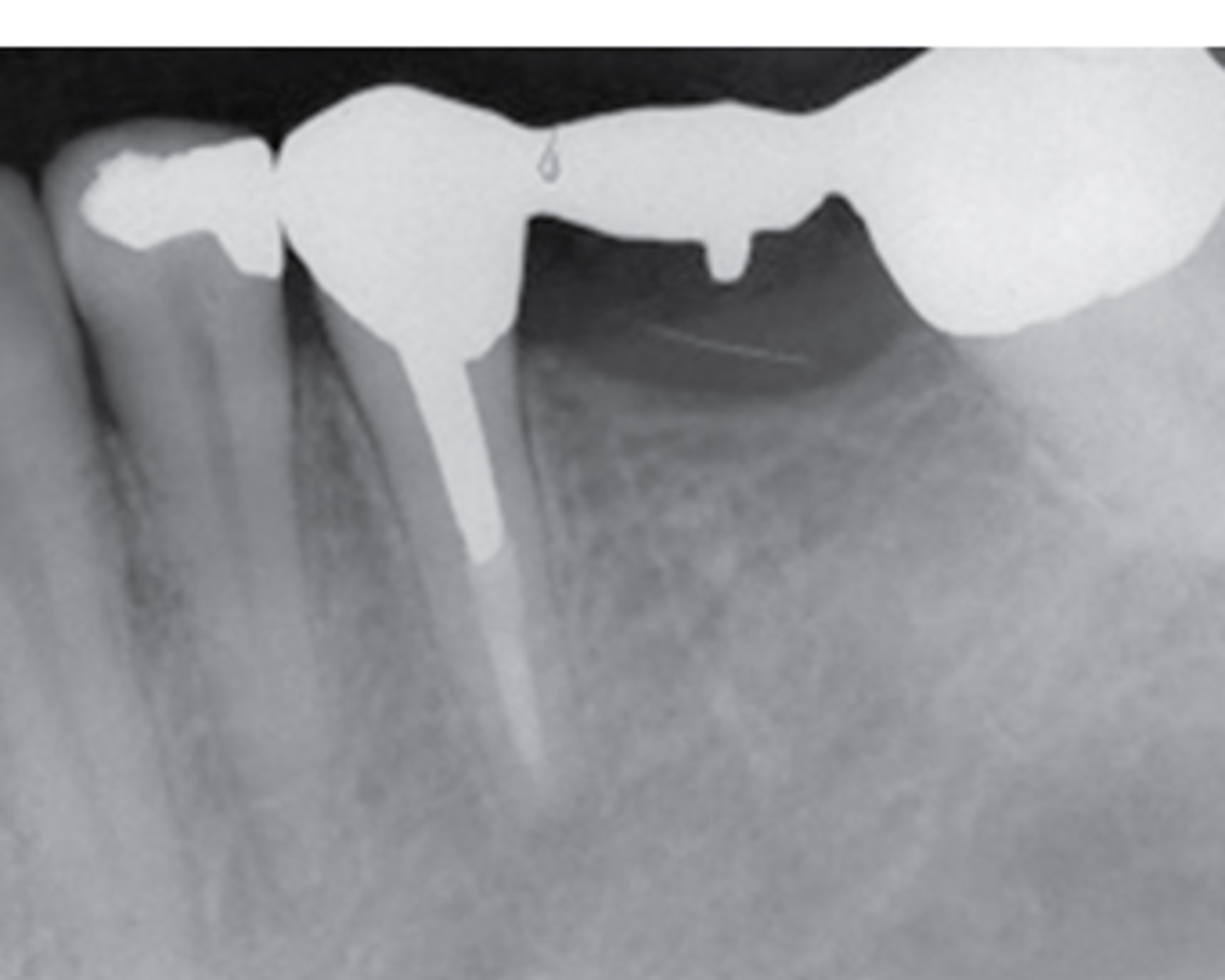
calculus
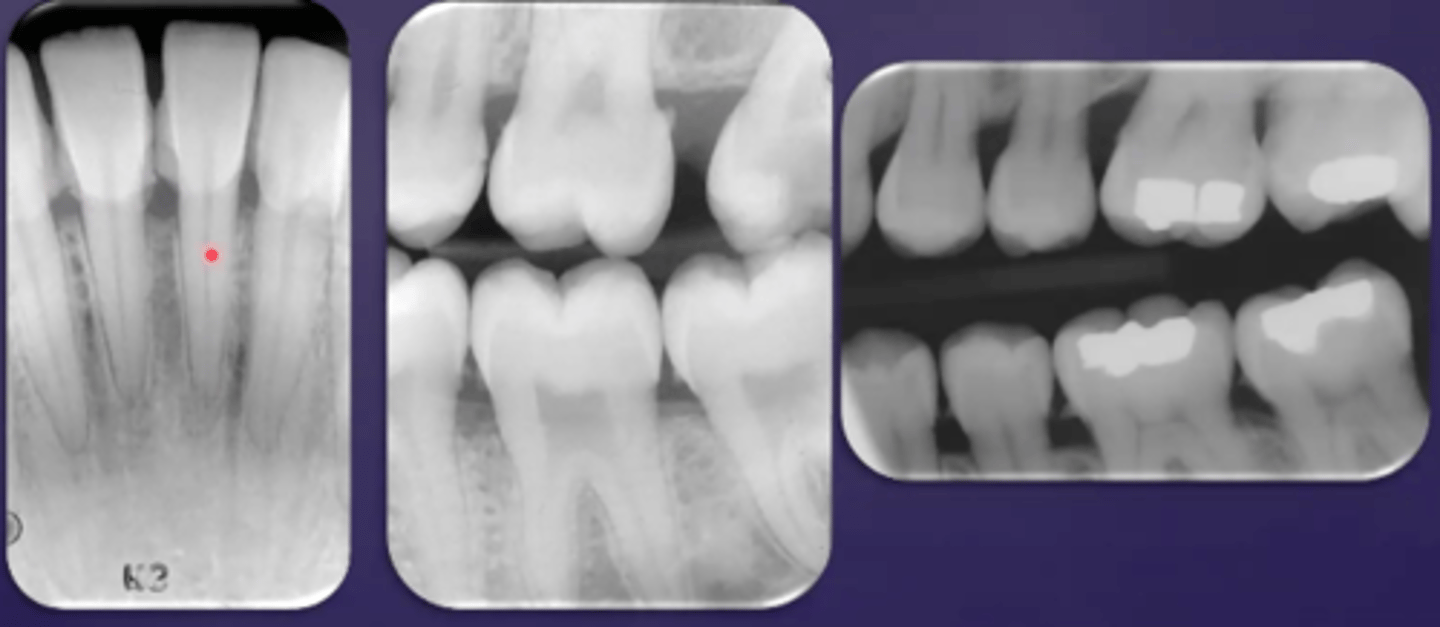
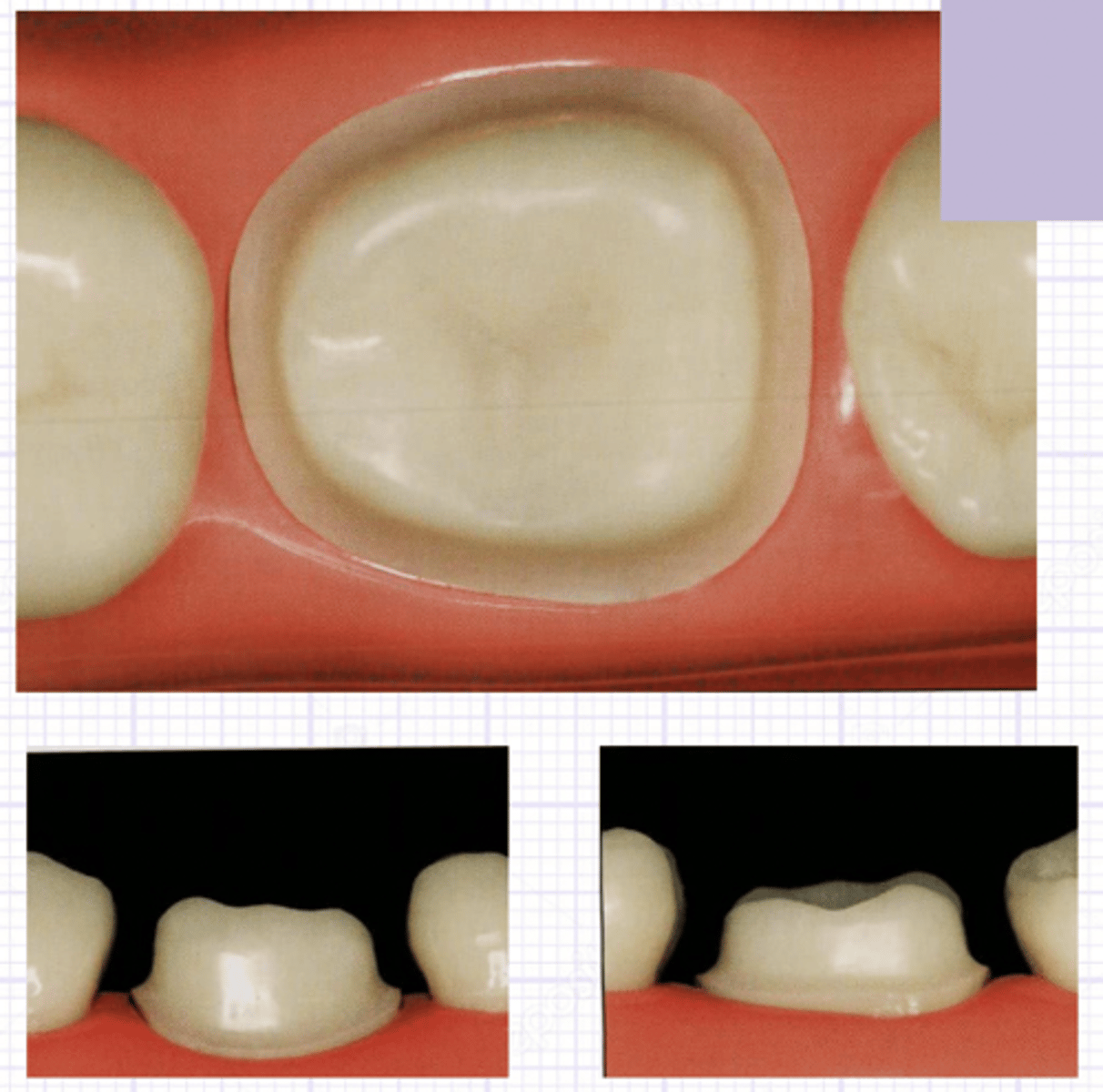
crown prep
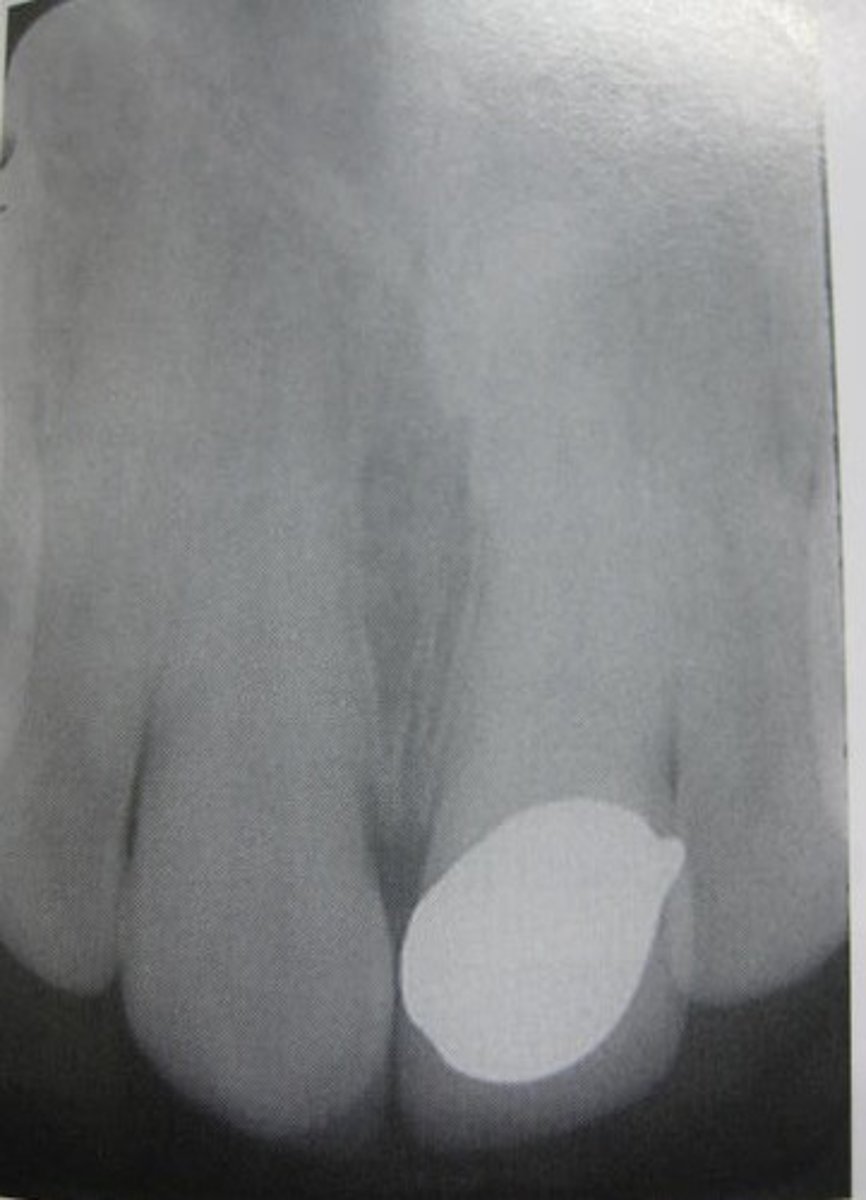
porcelain fused to metal radiograph
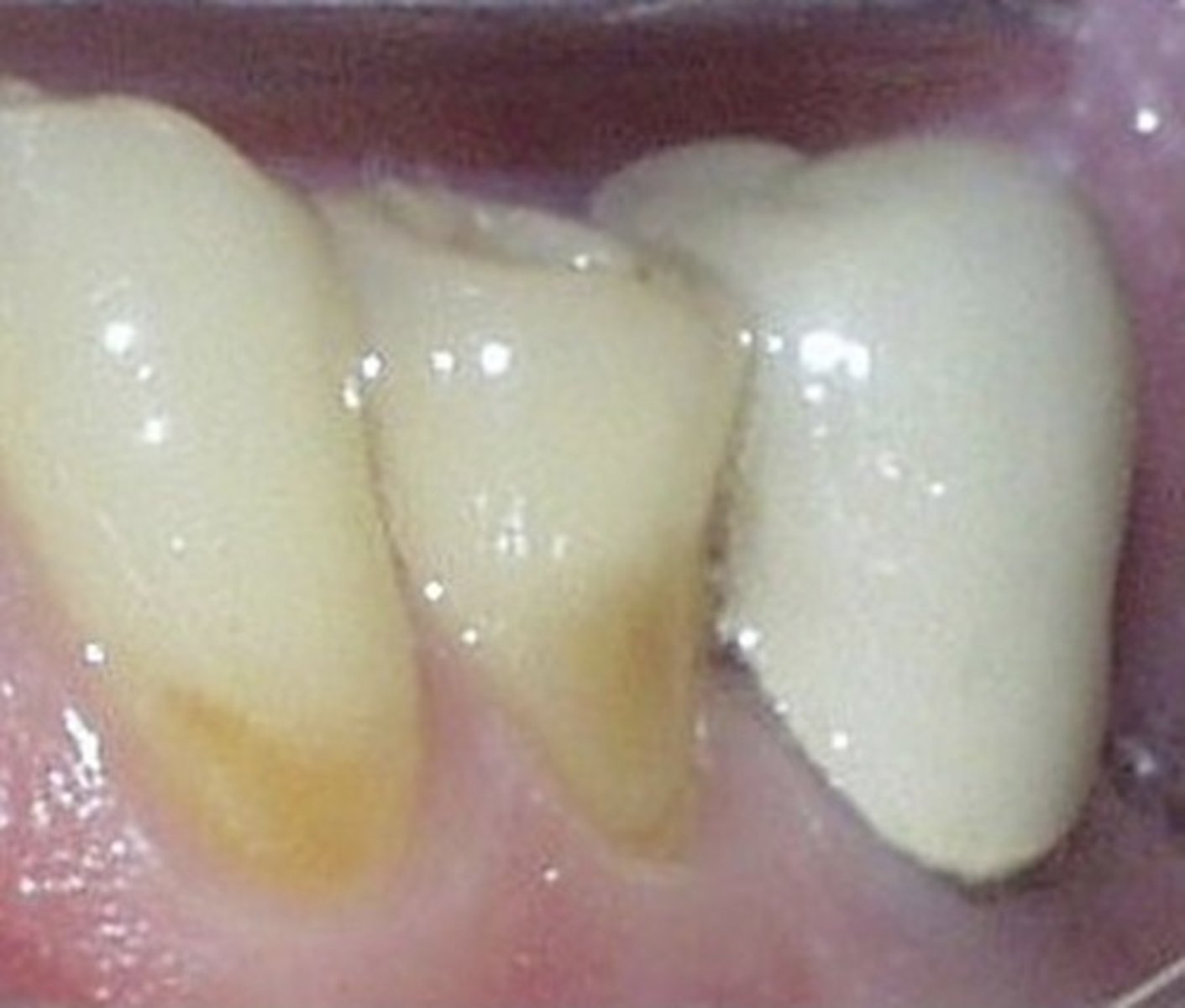
porcelain fused to metal image
cubic zirconium
symmetrical
stainless steel crown
on primary tooth
cheaper
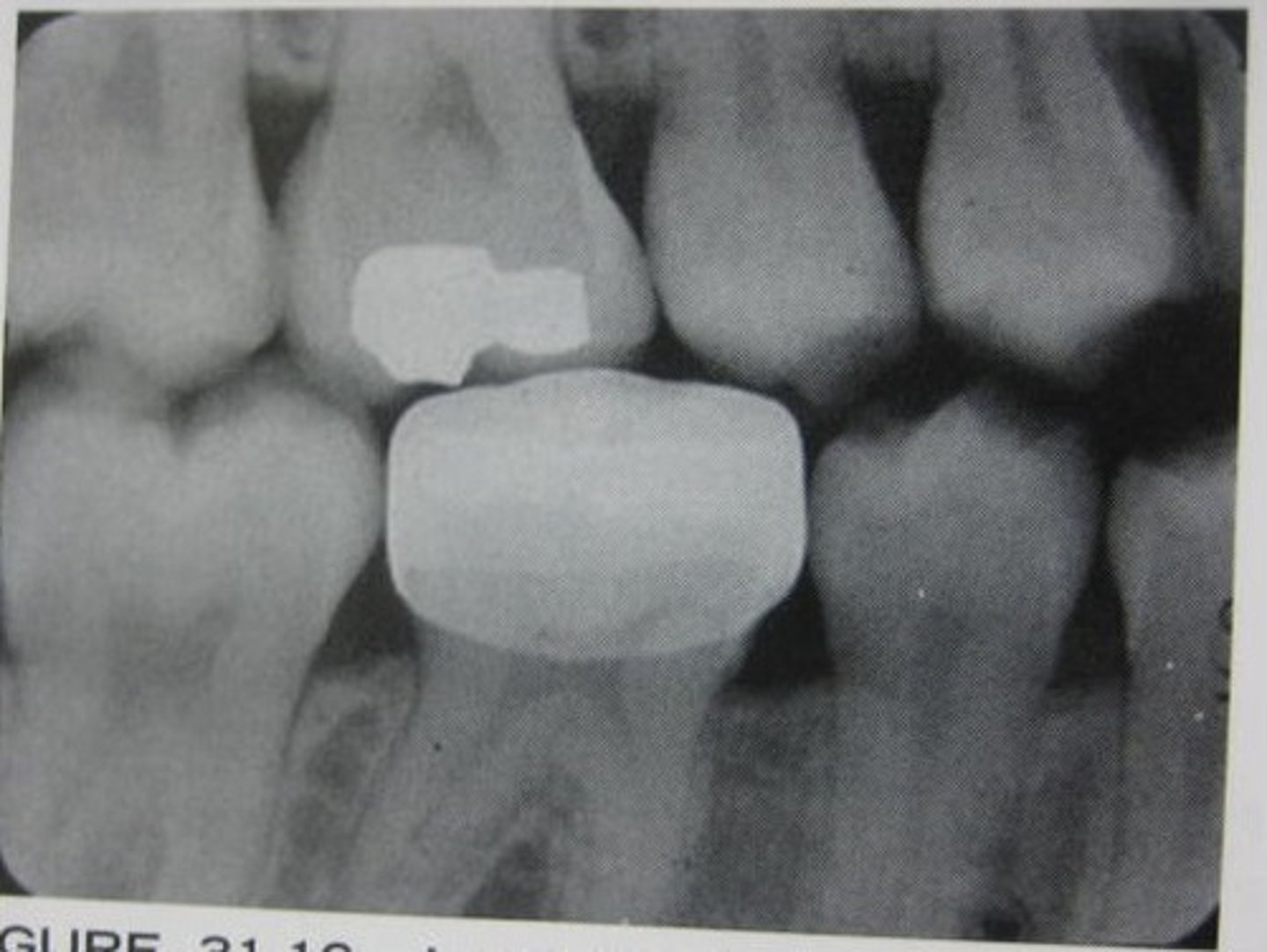
stainless steel space maintainer
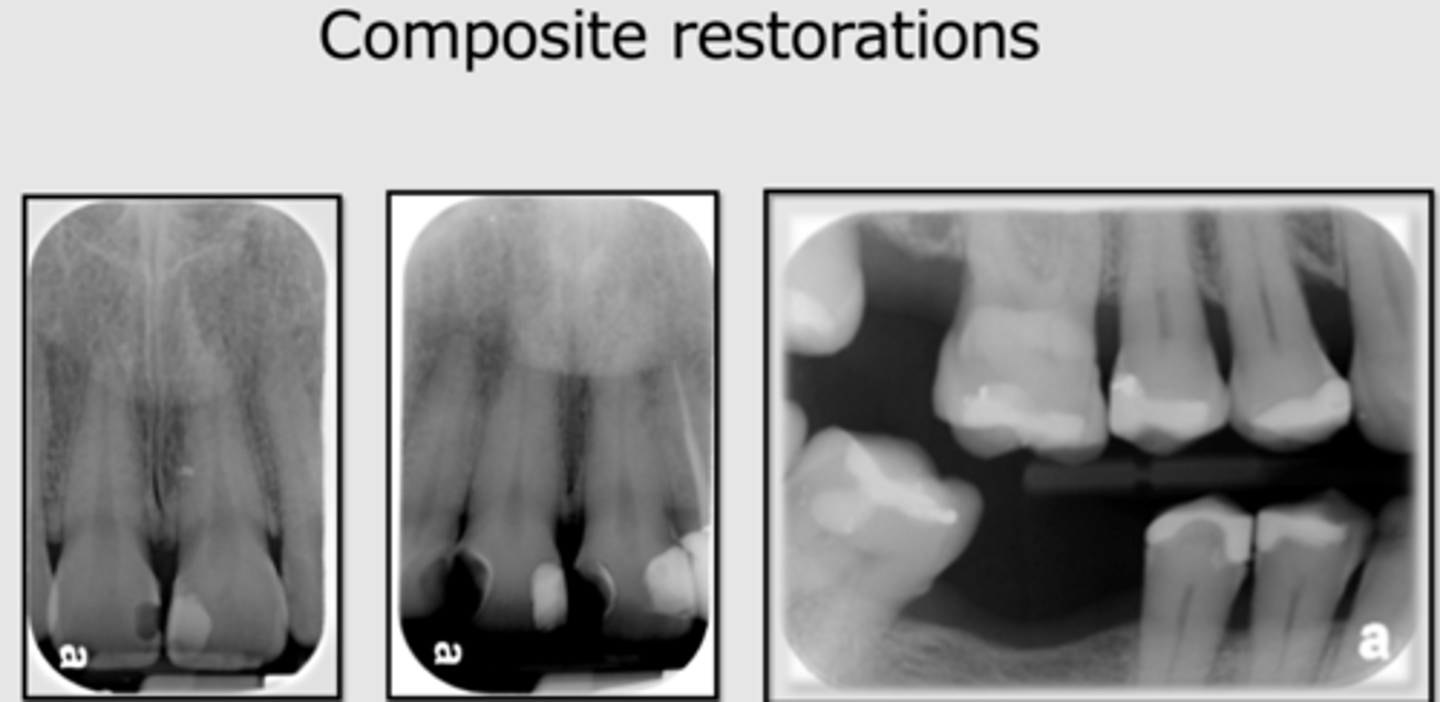
composite
full gold crown with pins
all porcelain crown
veneer