Biology [Module 5:Muscle&Animal&Plant hormones]
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
hormones
-molecules that are secreted by endocrine glands
-chemical messengers carrying signals to specific target tissues
peptide hormones
—adrenaline,insulin,ADH,glucagon
-proteins that are non lipid soluble
-so cannot diffuse across the phospholipid bilayer
-so they would bind to complementary receptors on the plasma membrane of the target cell and they release a second messenger (cAmp) in cells
-cAMP activates enzymes to initiate a response
how is cAMP made
-adrenaline binds to a complementary receptor on plasma membrane
-this activates the G protein
-G protein activates the enzyme Adenyl cyclase
-Adenyl cyclase catalyses the conversion of ATP into cAMP
steroid hormones
-oestrogen and testosterone
-lipid soluble so can diffuse across the phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion
-in cytoplasm they would bind to complementary receptors on target cell to form steroid hormone receptor complex
-SHRC diffuses into nucleus and binds to DNA to initiate transcription
pancreas (endocrine gland)
-ductless
-produce an secrete hormones directly into the blood
pancreas (exocrine gland)
-ducts
-produces and secrets digestive enzymes
pancreas structure

increase in blood glucose
-detected by beta cells of the islet of langerhans
-secrete insulin into blood
-insulin detected by receptors on liver and muscle cells
-liver and muscle cells remove glucose from blood and convert it into glycogen
decrease in blood glucose
-detected by alpha cells in islet of langerhans
-secrete glucagon into blood
-glucagon binds to receptor on liver cells
-liver cells convert glycogen into glucose and release glucose into blood (glycogenolysis)
regulation of insulin secretion
-K+ channels open K+ ions diffuse out the beta cell
-when blood glucose conc is high glucose diffused into beta cell and is respired to produce ATP
-ATP blood K+ channels protein depolarising the mem(+) as k+ ions accumulate in the beta cell
-the depolarisation causes the ca2+ channels to open so ca2+ ions diffuse in
-signaling for vesicles containing insulin to fuse with the plasma membrane secreting insulin into the blood
symptoms of diabetes
-weight loss
-tiredness
-extreme thirst
-high blood glucose
if not managed:
-kidney failure
-blindness
-amputation
type 1
-insulin dependent
cause type 1
-auto immune response destroys beta cells
-antigen on beta cells are recognised as foreign so antibodies are produced to destroy them
treatment type 1
-insulin injection
-immunotherapy drugs
-reprogramming the immune system to stop attacking beta cells of the pancreas
type 2
-non insulin dependent
cause type 2
-receptors are no longer responsive to insulin
factors type 2
-obesity
-high sugar diet
-family history
treatment type 2
-less sugar diet
-medication
-low calorie soups
insulin treatment for type 1
-GM insulin
-less risk of rejection compared to pigs
-cheaper to produce
-stem cells
-can be used to produce new beta cells
auxins
-promotes cells elongation
-inhibitor lead abscission(leaf fall)
-inhibits growth of side shots
—uses:rooting powder
gibberelins
-promote seed germination and elongation of stems
—uses:sugar cane production
abscissic acid
-inhibits seed germination and growth ,stress hormone
-causes stomatal closure when the plant is stressed by low water
—uses:possibly seed bank
cytokinins
-promotes cell division
-prevents aging (senescence)
—uses cell tissue culture
ethene(gas)
-promotes fruit ripening/absiscion
-speed up fruit ripening
seed germination
-seed absorbs water
-embryo activated
-produces gibberellin
-which stimulates digestive enzymes to be activated that will break down energy storage molecules (starch,oil) which is respired to produce ATP
synergistic
work together
antagonistic
oppose one another
tropisms response
-growth response in a given direction
-towards the stimulus=positive
-away=negative
nastic response
non growth response to a stimulus in a given direction
how auxin causes positive phototropism
-auxin is produced at the tip of the shoot (apical meristem ) causing apical dominance
-root tip detected by the sunlight
-auxin moves to the shaded area=uneven distribution of auxin
-cells in the shaded area elongate more so bend towards the sunlight
effect of auxin on cell elongation in root tip
-cells in root to produce auxin
-they detect gravity
-uneven distribution of auxin with more auxin in the lower region of the roots
-where auxin inhibits cell elongation with the roots bending and growing downwards
skeletal muscles
tubular shape
striated
multinuclated
voluntary movemonts eg,
walking; movement of skeleton.
cardiac muscles
-tubular and branched
-striated
-one nucleus
-contracts to pump blood
smooth muscle
-spindle shape
-non striated
- one nucleus
-involuntary movement
-vasodilation of smooth muscle in arteries and veins
structure of skeletal muscle
-under the light microscope are seen as a bundle of muscle fibres (muscle cells)

structure of actin and myosin

similarities between cellulose vs skeletal
-hydrogen bonds
-bundles of fibres
-repeating units(beta glucose in cellulose,sacromere is skeletal muscle)
differences between cellulose vs skeletal muscle

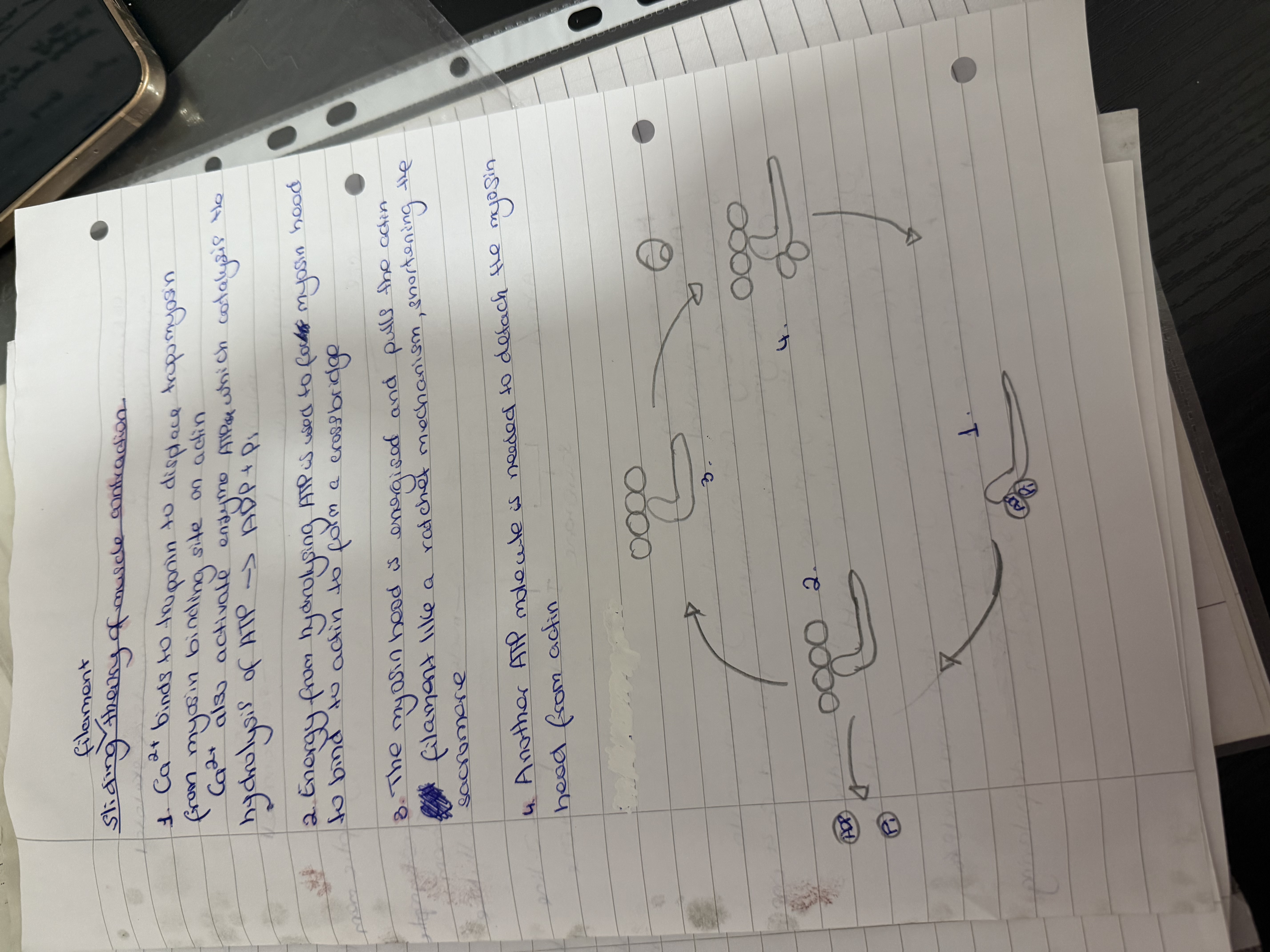
sliding filament theory of muscle contraction
neuromuscular junction
