Physiology OSPE CA2
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms

Anti A - Anti B - Anti D
1) What is the blood group?
2) Mention the type of agglutinogens in the red blood cells of this blood group
3) Mention the type of agglutinin in the plasma of this blood group
4) Which blood groups can receive blood from the subject
1) A negative
2) A antigens
3) B antibodies
4) A+ , A- , AB+ , AB-

Anti A - Anti B - Anti D
1) What is the blood group?
2) Mention the type of agglutinogens in the red blood cells of this blood group
3) Mention the type of agglutinin in the plasma of this blood group
4) Which blood groups can receive blood from the subject
1) O negative
2) no antigens
3) A and B antibodies
4) O+ , O- , A+ , A- , B+ , B- , AB+ , AB-

Anti A - Anti B - Anti D
1) What is the blood group?
2) Mention the type of agglutinogens in the red blood cells of this blood group
3) Mention the type of agglutinin in the plasma of this blood group
4) Which blood groups can receive blood from the subject
1) B positive
2) B antigens
3) A antibodies
4) B+ , AB+
Anti A - Anti B - Anti D
1) What is the blood group?
2) Mention the type of agglutinogens in the red blood cells of this blood group
3) Mention the type of agglutinin in the plasma of this blood group
4) Which blood groups can receive blood from the subject
1) AB positive
2) A and B antigens
3) No antibodies
4) AB+
What is the immediate hazard of blood transfussion?
Fever - Allergic reaction - Hemolysis
What are the delayed hazards of blood transfusion
Thrombo phlebitis - Sensitzation
What are the steps of blood coagulation in the common pathway
Clotting facts will change the prothrombin to thrombin which then converts fibrinogen into fibrin.
Define hemostasis
physiological process that stops bleeding at the site of an injury while maintaining normal blood flow elsewhere in the circulation
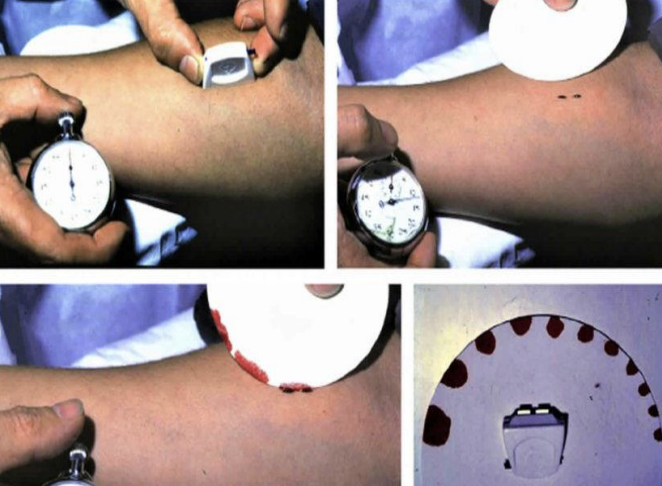
What is this experiment called?
What does it test?
Normal range?
If prolonged what is the case?
Duke method
Bleeding time
1 - 5 minutes
DIC - von williebrands disease
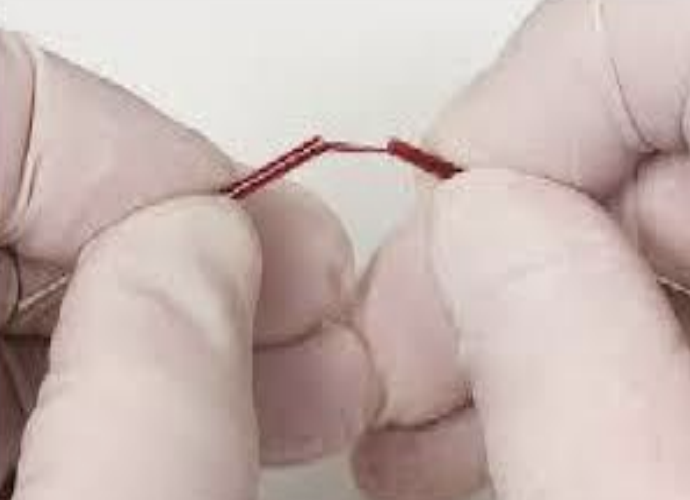
What is this experiment called?
What does it test?
Normal range?
If prolonged what is the case?
Capillary tube method
Clotting time
2-8 minutes
Pregnancy - cancer
What does HCV mean
Hematocrit
What does MCV measure?
average volume of the individual red cells in Femtoliter(fl).
What is the average MCV
80-100 fl
What is high MCV called
Macrocytic
What is low MCV called?
Microcytic
What is normal range of MCV called ?
Normocytic
What does MCH measure?
the content (weight) of the hemoglobin of the average individual red cell in a micro microgram (µµg) or picogram.
What is the normal range of MCH
27 - 33 picogram
What is high MCH called?
Hyperchromic
What is low MCH called?
Hypochromic
What is normal MCH
Normochromic
What does MCHC measure?
The average hemoglobin conc. per 100 ml of packed red cells in percentage.
What is the average range of MCHC?
32 - 36 g / dl
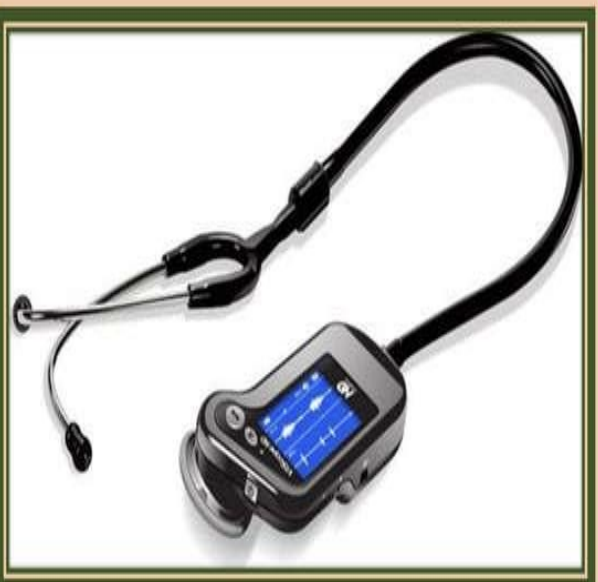
What is this?
What does it do?
Phonocardiograph
A phonocardiograph is a medical instrument used to record the sounds made by the heart during the cardiac cycle
When do we hear first heart sound?
When the AV valve closes (tricuspid and mitral valves) S1
When do we hear the second heart sound?
When the semilunar valves close (aortic and pulmonic valves) S2.
When do we hear the third heart sound?
Passive/rapid filling of the ventricles S3.
When do we hear the fourth heart sound
Active filling of the ventricles S4

What is this device
Sphygmomanometers
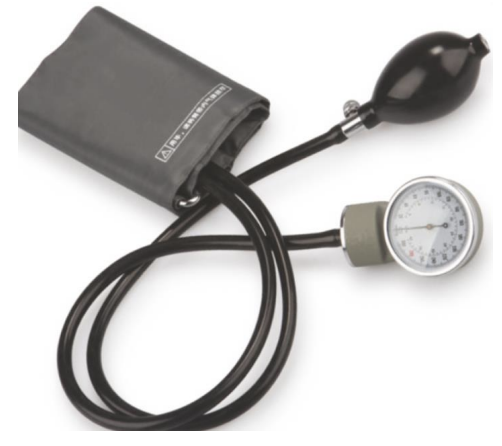

What is this device
aneroid Sphygmomanometers
Miss Y presented with a headache her BP is 140/90.
1) What is her Systolic BP ?
2) What is her diastolic BP ?
3) Calculate Her Pulse Pressure :
4) Comment on her Result ( Normal / Abnormal ) & why ?
5) Write 4 Precautions for accurate BP measurement
1) 140 mmHg
2) 90
3) Systolic - Diastolic = 140 - 90 = 50
4) Her result is abnormal since its high, the normal Blood pressure is 120/80
5) ensuring patient is relaxed before measurement, avoid stimulants
What are the factors the affect the capacity and volumes in different individuals
Age - Gender - Body size
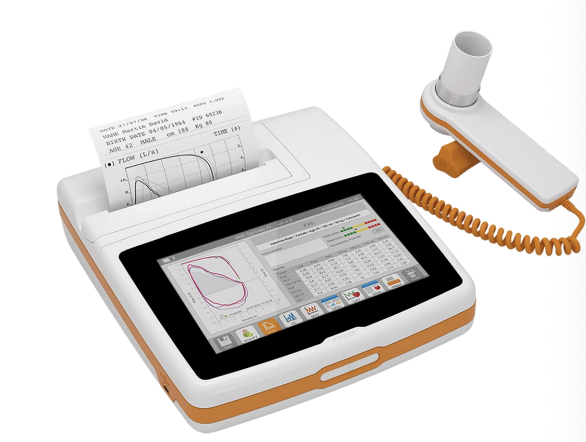
What is this device?
What does it measure?
Spirometry
lung function and volume

What is this device?’
What does it measure?
Peak flow meter
measures peak expiratory flow rate.
What does it mean by peak expiratory flow?
the maximum air flow achieved during maximum expiration after taking a deep breath.
What is the uses of Peak Flow Meter?
Evaluate treatment effectiveness
Diagnosis of obstructive airway disease
Asthma, COPD.
Normal values with the peak flow meter for males
400 - 800 L/min
Normal values with the peak flow meter for females
300 - 700 L/min
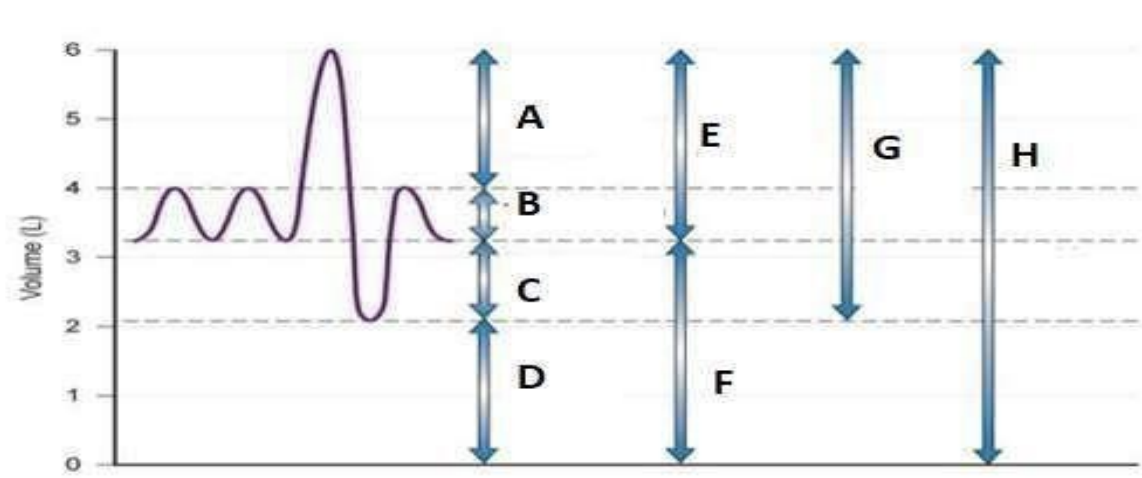
Label from A to H
A - Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
B - Tidal volume (TV)
C- Expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
D- Residual volume (RV)
E- Inspiratory Capacity (IC)
F- Functional Residual Capacity (FRC)
G- Vital Capacity (VC)
H- Total lung capacity (TLC)