Topic 1 - What is Economics
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What are the nine fundamental economic concepts
equity, sustainability, intervention, economic wellbeing, choice, scarcity, interdepencence, efficiency, change
What does ceteris paribus mean
all other things being equal
What is the economic problem?
All humans have needs and wants that the world cannot provide all these things for everyone: scarcity
What are the factors of production
land, labour, capital, entrepreneurship
What are positive statements
can be supported, refuted with evidence
what are normative statements
opinion based
Three central economic questions
What to produce, who gets what, how to produce
What is opportunity cost
trade off of next best option (choice)
What are economic goods
resources needed to produce
What are free goods
does not need scarce resources to produce
What is a centrally-planned/command economy
all economic decisions made by gov, no private owndership
What is a free market economy
all resources privately owned, and decisions are made by consumers and producers through price mechanism
What does the point beyond the PPC represent
impossible, unsustainable to maintain
What does the point within the PPC represent
inefficiency
How can the PPC grow (economic growth)
immigration, better technology, better education
What are the factors of payment
wages, rent, interest, dividends/profit
How can the PPC contract (economic contraction)
war, natural disaster, unemployment, disease
What is absolute scarcity
physical limitation of goods and services
What is relative scarcity
unequal distribution of resources, can be replenished, not geographically split (has oil, can’t mine oil)
What are consumer goods
finished products ppl buy
What are capital goods
tools to produce
Draw the circular flow of income
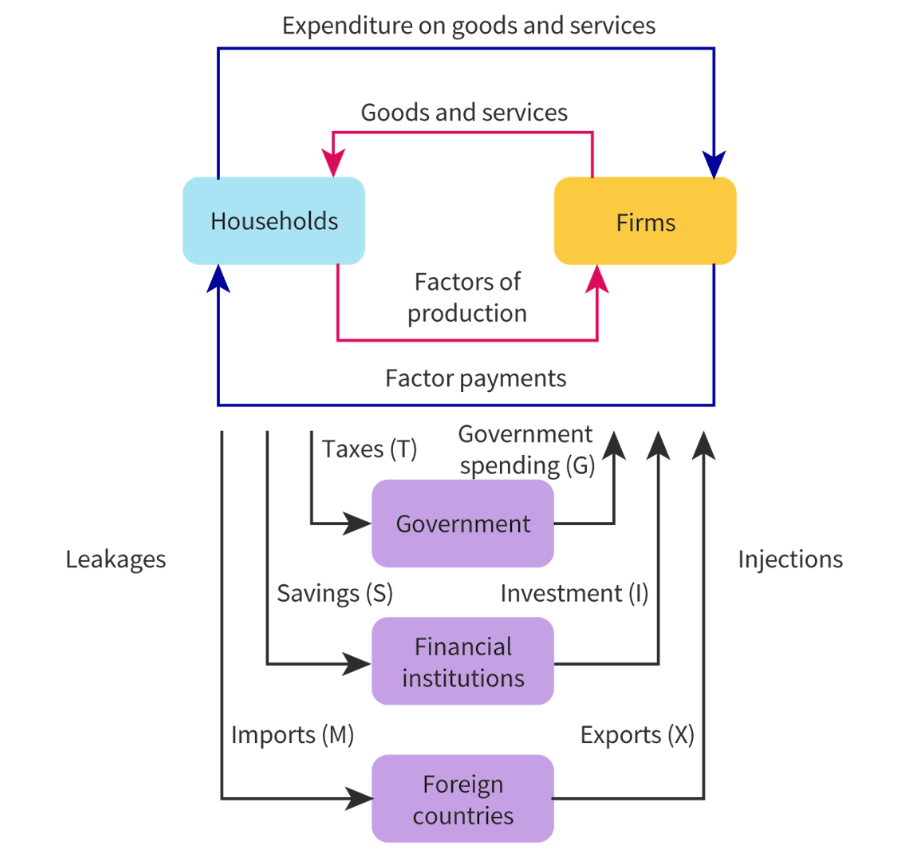
What happens to the economy when injections > leakages
growing, ppl’s standards of living increases
What happens to the economy when injections < leakages
contracting, ppl’s standards of living decrease
When is it economic equilibrium
leakages = injections
What is microeconomics
how individuals, firms, households, industries, governments, make economic decisions through the behaviour of consumers and producers
What is macroeconomics
The economy as a whole, aggregate, all production & expenditures of goods at a certain moment in time
What are transfer payments, example?
permanent leakages, like welfare
Who is the founding father of modern economics
Adam Smith