PH BIO SCI 21 - 3. Lipids
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Lipids
This is known as a provide a major way of storing chemical energy and carbon atoms in the body.
Fats
surround and insulate vital body organs, providing protection from mechanical shock and preventing excessive loss of heat energy
Functions of fats include:
surround and insulate vital body organs
providing protection from mechanical shock
preventing excessive loss of heat energy
Phospholipids, glycolipids, and cholesterol
Basic components of a cell membrane
Cholesterol
Several ________ derivatives function as chemical messengers (hormones) within the body
Hormones
chemical messengers
Lipids are:
organic compounds found in living organisms
insoluble (or sparingly soluble) in water
soluble in nonpolar organic solvents
do not have
Lipids __________ a common structural feature that serves as the basis for defining such compounds.
solubility
Lipids are characterized based on ____________.
insoluble
All lipids are _________ in water.
Methods of subclassifying lipids
1. Biochemical function
2. Based upon whether or not saponification occurs in hydrolysis
5 Categories of Lipids
Energy-storage lipids
Membrane lipids
Emulsification lipids
Messenger lipids
Protective-coating lipids
Energy storage lipids
triacylglycerols
Membrane lipids
Phospholipids
Sphingoglycolipids
Cholesterol
Emulsification lipids
Bile acids
Messenger Lipids
Eicosanoids
Steroid Hormones
Protective-coating lipids
BIological waxes
Saponifiable lipids
Triacylglycerols
Phospholipids
Sphingoglycolipids
Biological waxes
Non Saponifiable Lipids
Cholesterol
Steroid Hormones
Bile Acids
Eicosanoids
Saponification
a hydrolysis reaction that occurs in basic solution
Saponifiable lipids
converted into smaller molecules when hydrolysis occurs
Nonsaponifiable lipds
cannot be broken up into smaller units since they do not react with water
Saponification classification system is widely used for
Lipid classification
Fatty acid
building block of lipids
energy-storage lipids (Triacylglycerols)
most abundant type of lipid
membrane lipids
second most abundant type of lipid
monocarboxylic acid
A fatty acid is a naturally occuring ______________, and always contain an even number of carbon atoms and have a carbon chain that is unbranched.
Characteristics of Fatty Acids
1. Unbranched carbon chain
2. Even number of carbon atoms in the carbon chain
3. Double bonds, when present, in a cis configuration
Short chain fatty acids
C4 and C6
Medium chain fatty acids
C8 and C10
Long-chain fatty acids
C12 to C26
no
Saturated fatty acids (SFAs) contain ______ double bond/s.
single bonds
A saturated fatty acid is a fatty acid with a carbon chain in which all carbon–carbon bonds are ________.
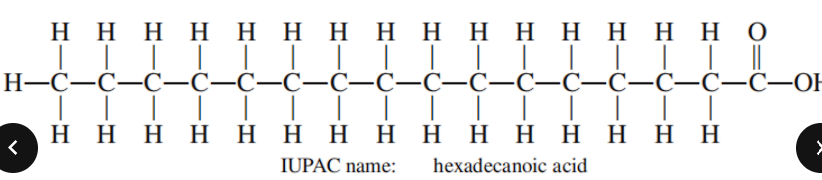
Common name of Hexadecanoic acid
Palmitic Acid
one
Monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) contain ______ double bond/s.
cis
In biochemically important MUFAs, the configuration about the double bond is nearly always ______, putting a rigid 30° bend in the chain, affecting the physical properties of a fatty acid.
two or more
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) contain ______ double bonds
Omega-3 fatty acid
An ___________ is an unsaturated fatty acid with its endmost double bond three carbon atoms away from its methyl end.
Omega-6 fatty acid
An _________________ is an unsaturated fatty acid with its endmost double bond six carbon atoms away from its methyl end.
The SFA 12:0 is known as
Lauric acid
The SFA 14:0 is also known as
Myristic acid
The SFA 16:0 is also known as
Palmitic acid
The SFA 18:0 is also known as
Stearic acid
The SFA 20:0 is also known as
Arachidic acid
The MUFA 16:1 ∆9 is known as
Palmitoleic acid
The MUFA 18:1 ∆9 is known as
Oleic acid
The PUFA 18:2 is also known as
Linoleic acid
The PUFA 18:3 is also known as
Linolenic acid
The PUFA 20:4 is also known as
Arachidonic acid
The PUFA 20:5 is also known as
EPA (Eicosapentaenoic acid)
The PUFA 22:6 is also known as
DHA (Docosahexaenoic acid)
MUFA
What is the type designation of this fatty acid? (SFA, MUFA, or PUFA)
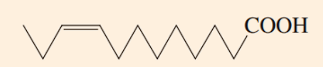
12:1 Fatty Acid
On the basis of carbon chain length and degree of unsaturation, what is the numerical shorthand designation for this fatty acid?
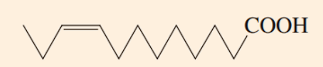
Omega-3 fatty acid
To which “omega” family of fatty acids does this fatty acid belong?
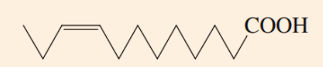
Delta-9 Fatty Acid
What is the “delta” designation for the carbon chain double-bond location for this fatty acid?
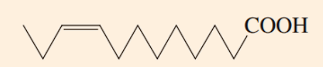
Which best describes the relationship of water solubility and carbon chain length?
Solubility decreases; carbon chain length increases
slight solubility
short-chain fatty acids have a _____________ in water.
insoluble
long-chain fatty acids are essentially __________ in water.
carboxyl group
The slight solubility of short-chain fatty acids is related to the polarity of the ____________ present.
Which best describes the relationship of melting point and carbon chain length?
As carbon chain length increases; melting point increases
The greater degree of unsaturation; the smaller the melting point
Which best describes the relationship of melting point and degree of unsaturation?
saturated
Long-chain ____________ fatty acids tend to be solids at room temperature
unsaturated
Long chain ____________ fatty acids tend to be liquids at room temperature.
bends
The ________ prevent unsaturated fatty acids from packing together as tightly as saturated fatty acids.