Biology U3 AOS 1
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Nucleic Acids and Proteins
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Polypeptide
A linear organic polymer consisting of a large number of amino acid residues bonded together in a chain, forming part of (or the whole of) a protein molecule.
Polypeptide Synthesis
Ribosomes on rough endoplasmic reticulum (translation).
Protein Secretion
Synthesised, modified in ER tubules, sent to Golgi apparatus in vesicles, final modification in Golgi, transported to cell membrane in vesicles, exocytosis occurs (vesicle fuses to membrane to release protein).
Proteins
Determine structure and function of cells. Made up of amino acids in linear chains bonded together (20-22 total amino acids in the human body). One or more polypeptide chains joined together creates a protein.
Amino Acids
Joined by peptide (covalent) bonds (condensation polymerase reaction, involving a removal of water). Building blocks of proteins.
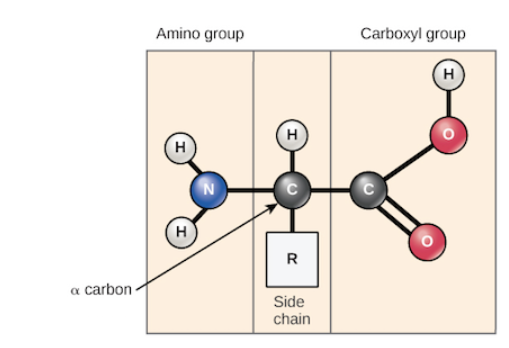
Proteins structure
Coded by genes, types of amino acids and how they bond/interact with one another impacts the structure/potentially the function of the protein also.
Primary: Linear structure of amino acid chains, strong covalent bonds between all of the amino acids.
Secondary: Folding of primary structure due to hydrogen bonds between the amine and carboxyl groups in the backbone. Forms alpha helices and beta pleated sheets.
Tertiary: Folding of secondary structure into a three dimensional shape or globular protein due to interactions between the side chains of amino acids (weak hydrogen bonds, strong covalent bonds, strong ionic bonds).
Quaternary: Two or more tertiary structures joint together to form a quaternary structure together eg. haemoglobin. Globular and functional.
Some proteins only have a tertiary or secondary structure.
Function of a protein impacted by:
pH, temperature, and other chemicals.
Proteome
Complete set of proteins made from the genome in a cell. Genes can make a large variety of proteins. The genome of all cells in an organism is the same however not all genes in a cell are used to make proteins (gene expression).
Diversity of proteins
Enzymes, hormones, antibodies, contractile proteins, structural. transport, receptor, storage.
Nucleic Acids
Code for the synthesis of proteins. Two types: Deoxyribonucleic acids (DNA) and Ribonucleic acids (RNA). Made up of monomers called nucleotides. Difference in the two is in the sugar group. Joined together in condensation reactions.
Five nitrogenous bases
Cytosine (DNA and RNA), Guanine (DNA and RNA), Adenine (DNA and RNA), Thymine (DNA), Uracil (RNA).
Strand of Nucleotides
HAs a 5’ end known as the phosphate group and a 3’ end known as the hydroxyl group.
DNA
Deoxyribose sugar group. Four bases: A, C, T, G. Two anti-parallel, complementary chains joined by base pairings. A=T two weak hydrogen bonds. C=G three weak hydrogen bonds. Double stranded DNA forms a double helix structure. DNA is coiled and wrapped around histones into chromosomes in eukaryotic cells.
RNA
Usually single stranded, shorter than DNA, contains a ribose sugar unit, contains uracil instead of thymine- still pairs with adenine.
Types of RNA
Messenger (mRNA), Ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and Transfer (tRNA).
Messenger RNA
Carries copy of DNA code out of the nucleus, formed in nucleus in transcription
Ribosomal RNA
Forms the structure of ribosomes, synthesised in the nucleolus, site of protein synthesis (translation).
Transfer RNA
Free floating in the cytoplasm, carries specific amino acids, involved in translation.
Triplet code
Each set of three bases of DNA codes for one amino acid, set of three known as a triplet or codon.
DNA code
Universal for all living things. Is referred to as degenerate/redundant as different codons code for the same amino acid.
In eukaryotic cells RNA modification occurs after transcription to form the mRNA
No RNA modification in prokaryotic cells
Eukaryotic Gene Structure
Promotor region- where RNA polymerase binds.
ATG: start triplet for amino acid code.
Exons: part of DNA that codes for amino acids.
Introns: part of DNA that doesn’t code for amino acids.
Stop triplet: end of amino acid code.
Transcription
Occurs in nucleus, DNA base sequence of a gene is copied into the form of RNA (single stranded). Three steps: Initiation, elongation, termination.
Initiation
RNA polymerase binds to promotor region of the gene. DNA unwinds into two seperate single strands.
Elongation
Termination