Magnetic Fields Questions
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms

A

In the presence of a suitably directed uniform magnetic field, charged particles move at constant speed in a circular path of constant radius. By reference to the force acting on the particles, explain how this is achieved and why it happens. (4 marks)
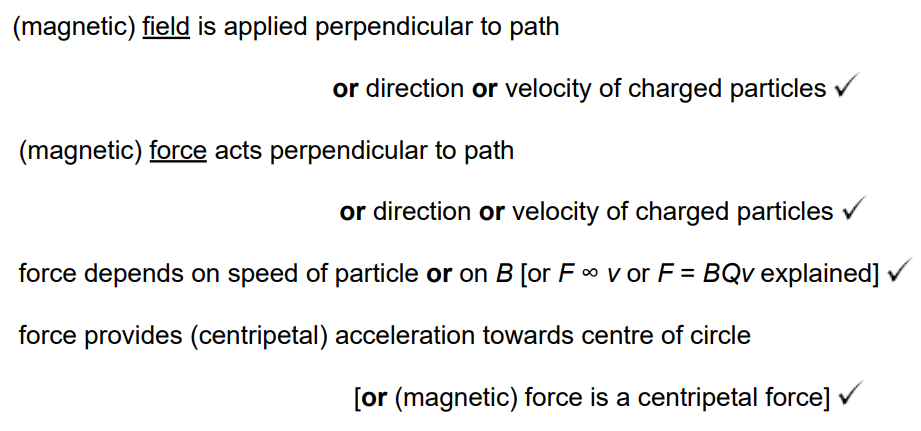
B

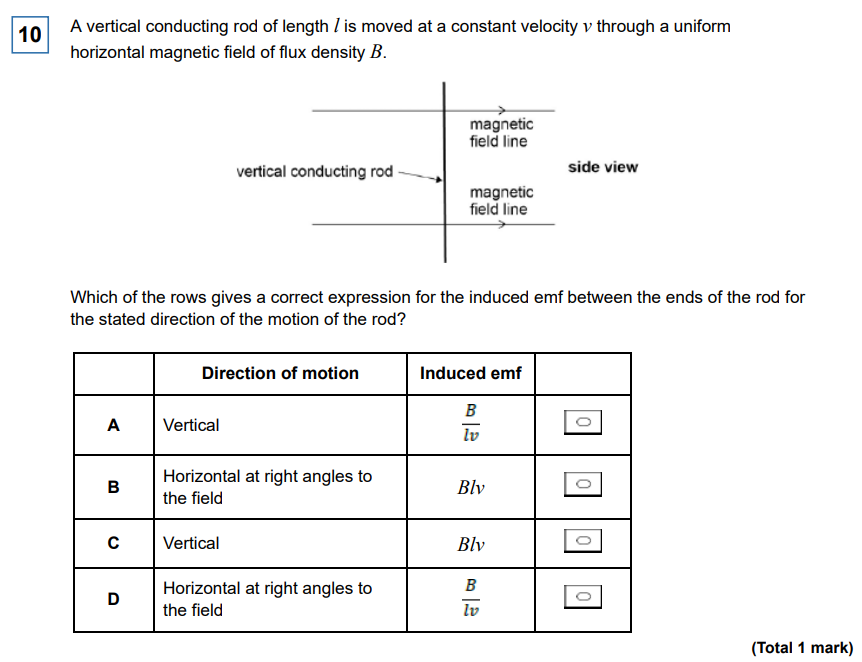
A
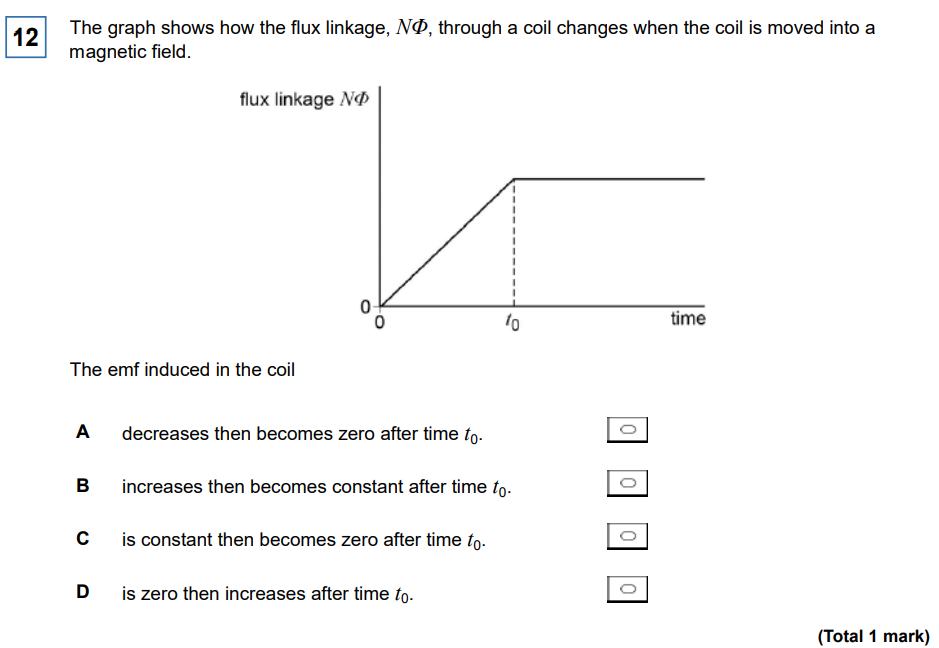
Think about the gradient (its linearly increasing graph so will have a constant graph.) C
Think Velocity-time graph (the gradient would explain constant acceleration… then 0 acceleration)
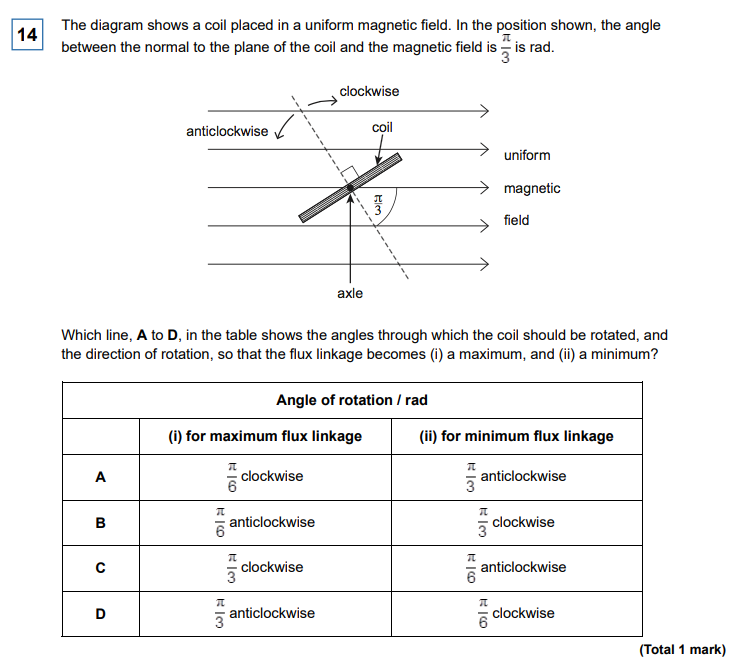
D

A
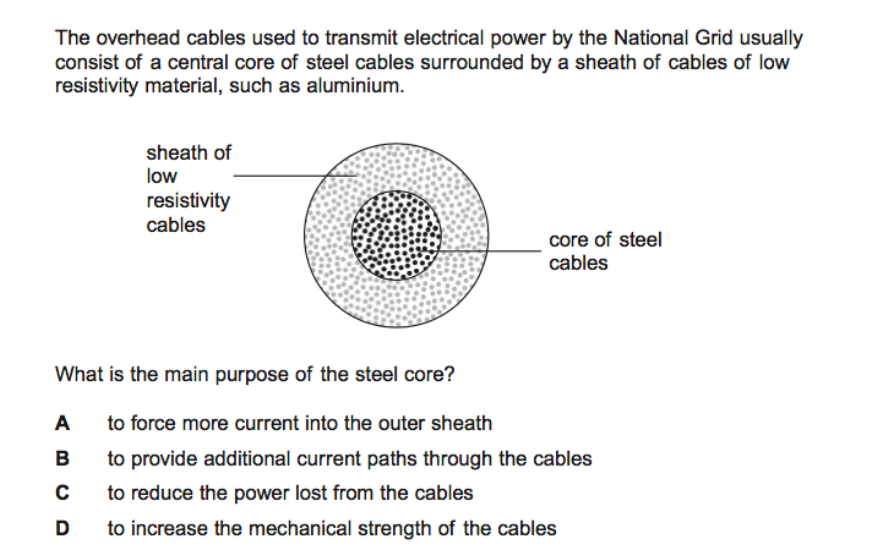
D

D
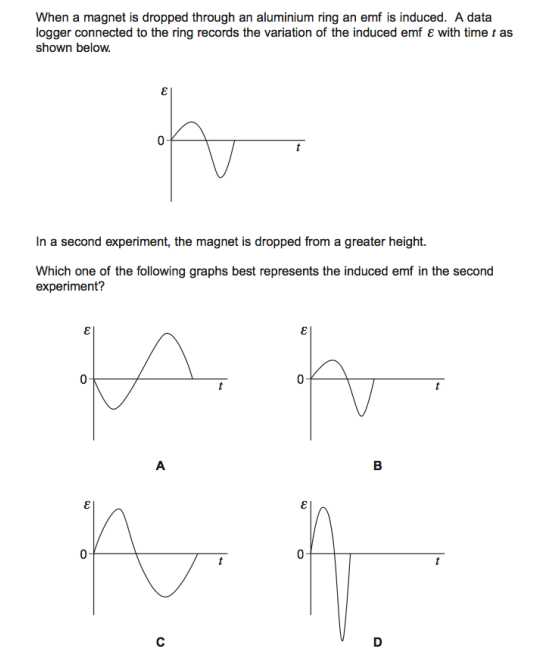
C
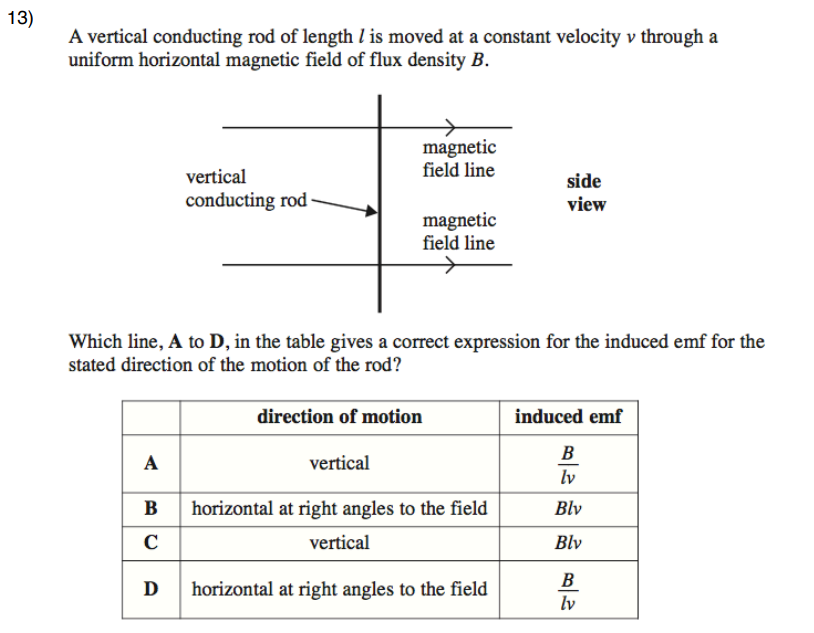
B (same as c?)
Explain why a particle is accelerating even when it is moving with a uniform speed in a circular path. (2 marks)
acceleration is (rate of) change of velocity
velocity is changing since direction is changing
State, in words, the two laws of electromagnetic induction. (2 marks)
emf ∞ rate of change of flux (linkage) (Faradays Law)
direction of induced emf (or current) ✔ is such as to oppose the change (in flux) producing it ✔
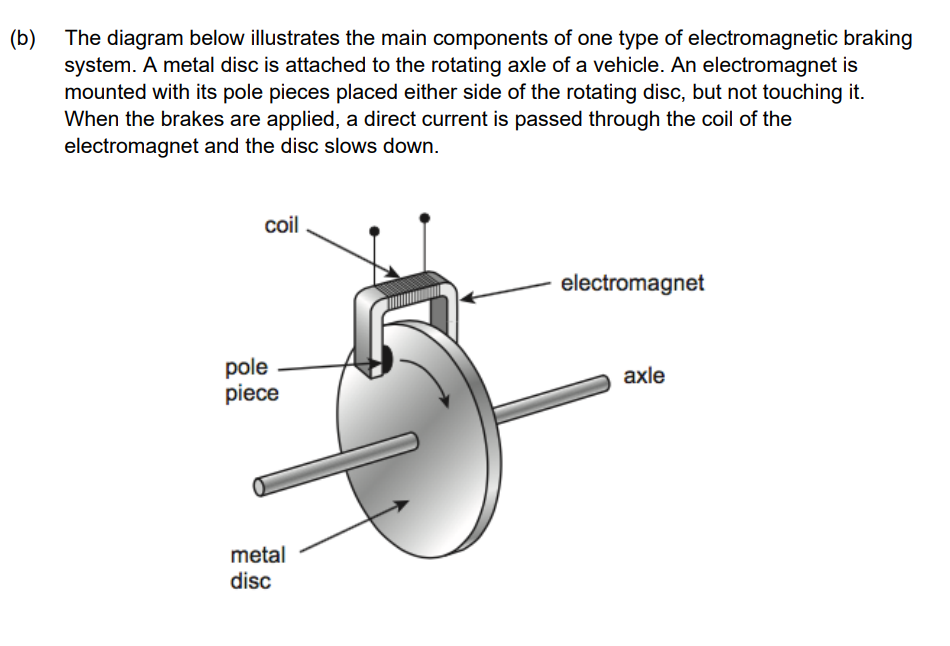
Explain, using the laws of electromagnetic induction, how a device acts as an electromagnetic brake. (3 marks)
Current in coil has its own magentic field.
Rotating disc causes a change in magnetic flux which induces an emf
Induced current interacts with magnetic field, causing a repulsion of like poles. (The induced emf generates eddy currents in the disc.
By Lenz’s Law, these currents create their own magnetic fields that oppose the change in flux.
This leads to a repulsion or braking effect, where the disc experiences a force resisting its motion.)
