Respiratory System: Alveoli, Ventilation, and Regulation
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
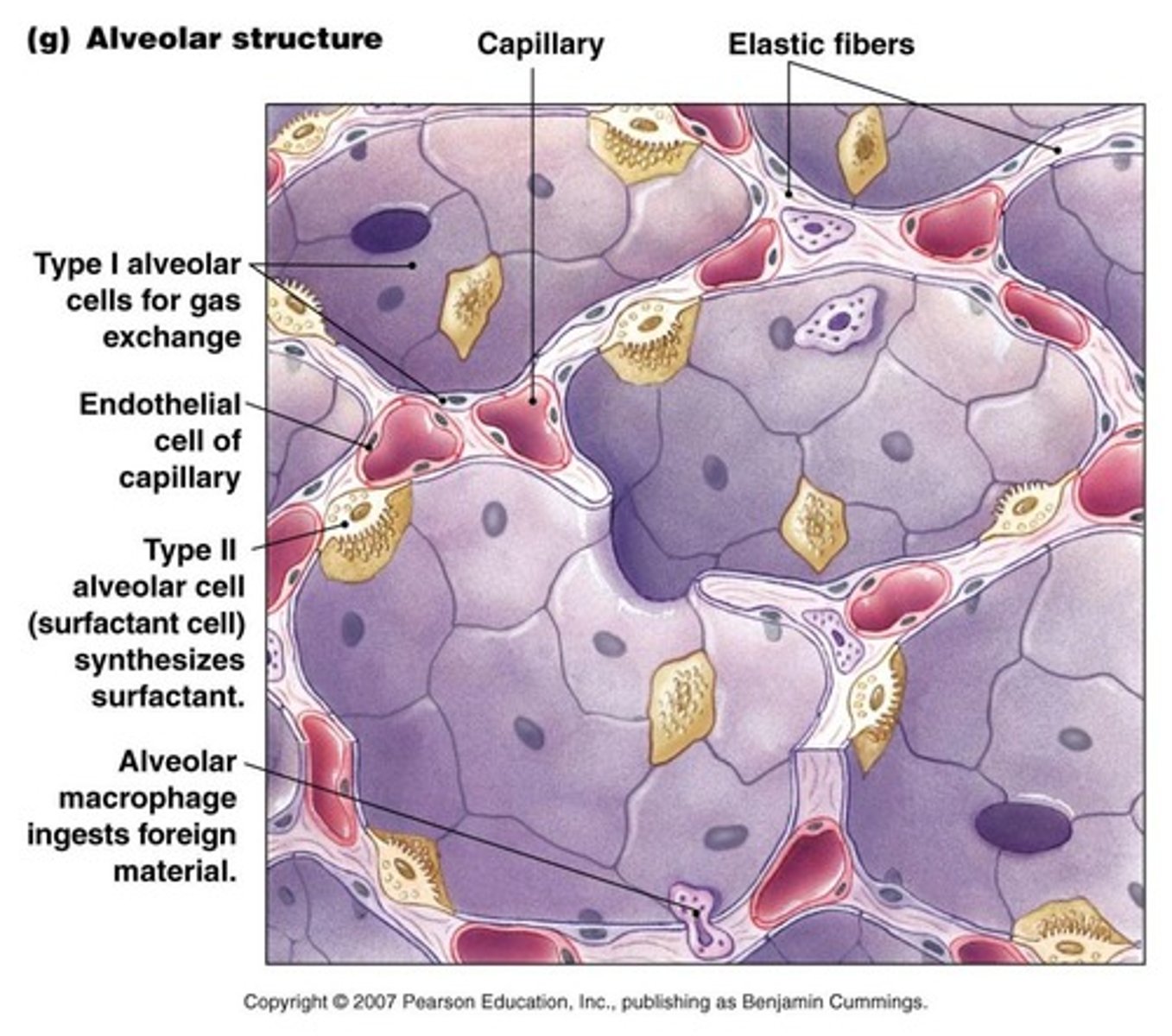
What is the primary function of alveoli?
To facilitate gas exchange between the air and the blood.
What are the two types of respiration mentioned?
Aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration.
What is the role of surfactant in the alveoli?
To reduce surface tension and prevent alveolar collapse.
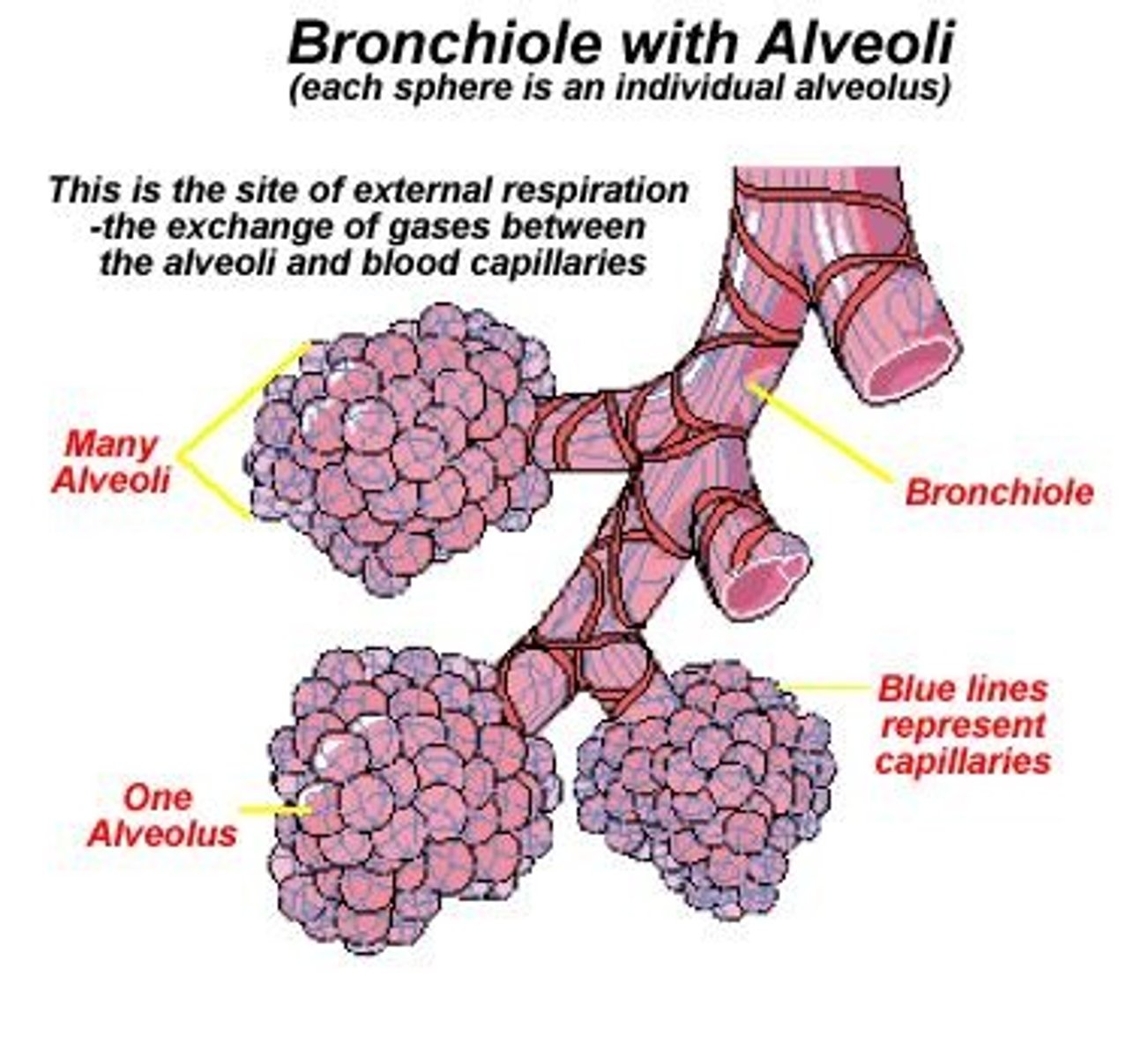
What is the process of ventilation?
The movement of air into and out of the lungs.
What is bulk flow in the context of the respiratory system?
The movement of air and gases across surfaces and through the circulatory system.
How does the body eliminate unwanted CO2 and H+?
Through the binding of H+ to hemoglobin, forming Hb.H.
What is the chloride shift in red blood cells?
The exchange of bicarbonate (HCO3-) with chloride (Cl-) to maintain ionic balance.
What are the local control mechanisms for respiration?
Bronchiole smooth muscle response to PCO2 and blood flow adjustments in capillaries.
What part of the brain controls voluntary respiration?
The cerebral cortex.
What are the two centers in the medulla oblongata that regulate involuntary breathing?
The Dorsal Respiratory Group (DRG) and the Ventral Respiratory Group (VRG).
What triggers peripheral chemoreceptors?
A decrease in pH or PO2 of the blood.
What is hypercapnia?
An increase in carbon dioxide (CO2) levels in the blood.
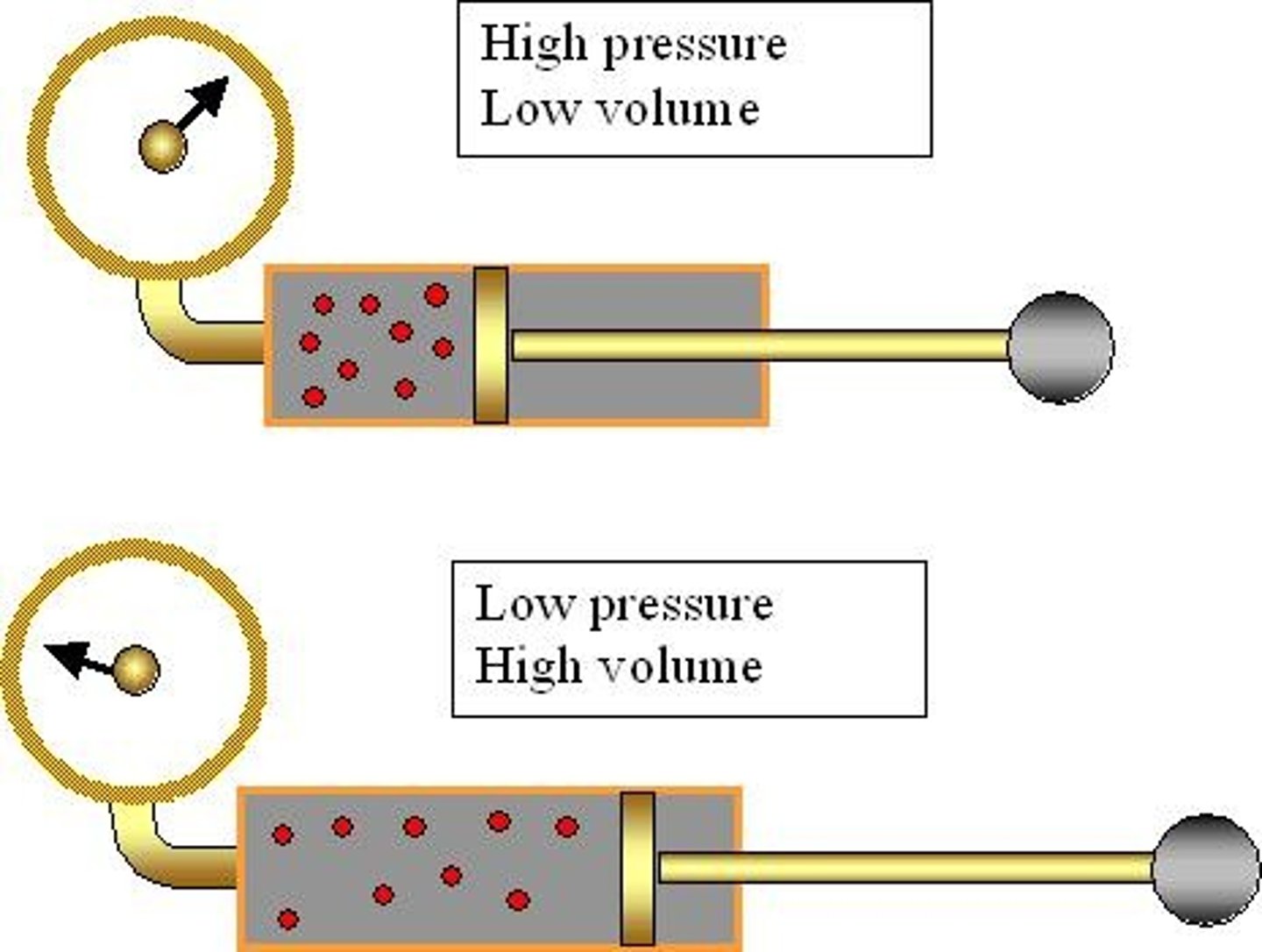
What is the effect of Boyle's law on pressure and volume?
Pressure is inversely proportional to volume; as volume increases, pressure decreases.
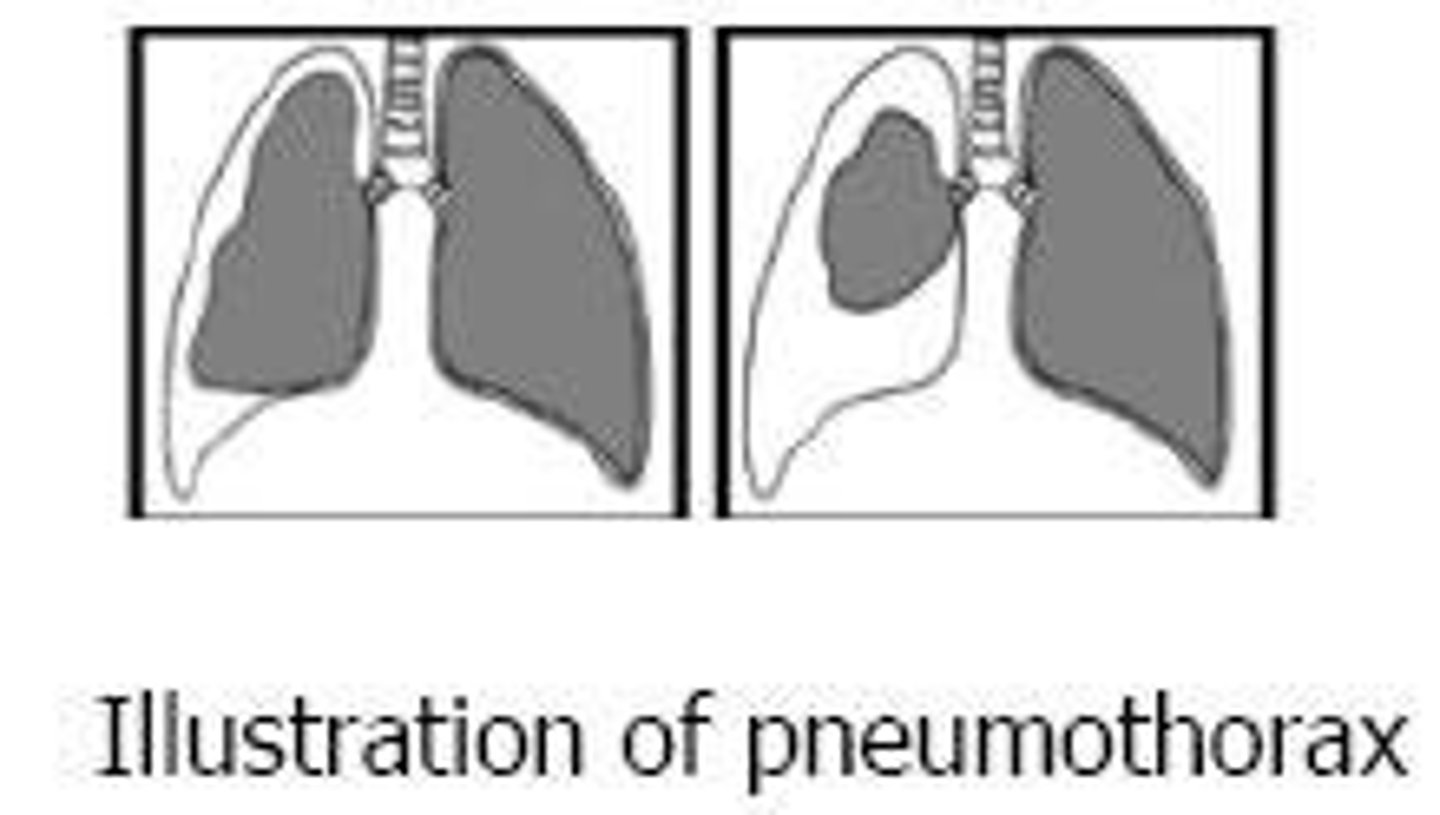
What condition occurs when air enters the pleural space?
Pneumothorax.
What happens to the lungs during atelectasis?
The lungs collapse due to a lack of air.
What reflex prevents overexpansion of the lungs?
The inflation reflex, which inhibits expiratory centers and stimulates inspiratory centers.
What is the primary factor that drives air movement during breathing?
The difference in air pressure, moving from higher to lower pressure.
What is the role of mitochondria in respiration?
They are the sites of aerobic respiration, producing energy for the body.
What is lactic acid associated with?
Anaerobic respiration, which occurs when oxygen is scarce.
What happens to blood flow in capillaries when PO2 is low?
Blood flow is shunted away from areas with low PO2.