Local Anesthetics
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Local anesthetics (LAs) block __________ channels to inhibit pain transmission.
voltage-gated sodium (Na⁺)
They prevent the neuron from reaching __________, which stops action potential propagation.
depolarization
The local anesthetic must be in the __________ form to cross the membrane and enter the neuron.
unionized
Once inside, the drug becomes __________ and binds to the sodium channel from the cytoplasmic side.
ionized
Esters contain a __________ linkage, while amides contain a __________ linkage.
–COO–; –CONH–
__________ local anesthetics are more stable and longer-acting due to hydrolysis resistance.
amide
__________ are hydrolyzed more rapidly by plasma esterases.
esters
Esters tend to form __________, a metabolite that can cause allergic reactions.
para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA)
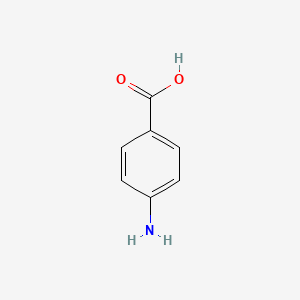
Benzocaine is an __________ with a very low pKa, making it mostly __________ at physiological pH.
ester, unionized
Because of its low water solubility, benzocaine is used __________.
topically
Benzocaine can cause __________ due to aromatic amine oxidation.
methemoglobinemia
Procaine is an ester with an added __________ group, improving water solubility.
ionizable amine
Procaine is hydrolyzed to PABA and has a __________ duration of action.
short
Lidocaine is an __________ local anesthetic with a longer duration and better solubility.
amide
A common use for lidocaine is in __________ procedures.
dental and minor surgical
The basic SAR for local anesthetics includes three parts:
→ __________ ring, __________ chain, __________ amine
aromatic; intermediate (ester/amide); hydrophilic
The aromatic ring increases __________ and enhances potency.
lipophilicity
Electron-donating groups on the aromatic ring (e.g., –NH₂, –OCH₃) tend to __________ potency.
increase
A branched or bulky intermediate chain hinders __________ and increases duration.
hydrolysis
A tertiary amine at the hydrophilic end allows for __________ formation.
salt
Ester LAs are metabolized by __________ in the blood.
plasma esterases
Amide LAs are metabolized in the liver by __________ enzymes.
CYP450
One toxic metabolite of lidocaine is __________, which can contribute to methemoglobinemia.
2,6-dimethylanilinea
Methemoglobinemia is caused by oxidation of Fe²⁺ to __________ in hemoglobin.
Fe³⁺
Symptoms of methemoglobinemia include cyanosis and poor oxygen delivery, even with normal __________ levels.
oxygen saturation (SpO₂)
Combining LAs with __________ prolongs duration by causing vasoconstriction.
epinephrine
Excessive vasoconstriction from EPI can lead to __________ if used in end-artery areas.
tissue necrosis
Local anesthetics should be avoided in areas like __________ and __________ due to poor blood flow.
fingers; toes (also acceptable: ears, nose)
Risk factors for methemoglobinemia include age under __________, anemia, G6PD deficiency, and prolonged use.
2 years
__________ is an ester local anesthetic that’s 10–50× more potent than procaine.
Tetracaine
__________ is a long-acting amide anesthetic with high cardiotoxicity risk.
Bupivacaine
__________ is a dental amide anesthetic that contains sodium metabisulfite, which may trigger allergies.
Articaine
__________ is a topical ester anesthetic with low solubility and is not injectable.
Benzocaine
__________ is an amide anesthetic commonly used with rapid onset and short duration.
Mepivacaine
Amides tend to have longer action due to their __________ to hydrolysis.
resistance
LAs with lower pKa values have a __________ onset of action.
faster
LAs with higher lipid solubility have __________ potency and longer duration.
greater
EPI increases local anesthetic duration by activating __________ receptors.
alpha-1 adrenergic
Allergic reactions from ester LAs may cross-react with __________ antibiotics due to PABA similarity.
sulfa