week 3 - Probability
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
what is probability?
this is a measure on a sliding scale from 0 (impossible) to 1 (certain)
what is the classical approach?
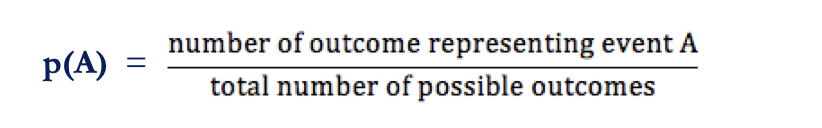
what is a mutually exclusive event?
two or more events cannot happen at the same time
what is a mutually exhaustive event?
they represent all possible occurrences eg when tossing a coin, it is going to land on either heads or tails so all outcomes have been exhuasted
formula for both mutually exclusive and exhaustive?
p(A) + p(B) + p(C) = 1
A, B and C are mutually exclusive and exhaustive → not just limited to 3 outcomes eg obtaining a first, 2.1, 2.2, 3rd or fail
what is complementary events and the formula?
how is it sometimes written?
set of outcomes not belonging to an event is called the complement of event
formula: P(event A NOT occuring) = 1 - P(A)
eg p(raining) = 1 - p(not raining)
sometimes written as p(A’)
what is the Addition Laws (OR rule)
this is the probability of either one event OR another occuring
if events are mutually exclusive, the formula is:
p(A+B) = P(A) + P(B)
if events are non mutually exclusive, the formula is:
how can it also be written?
P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A or B)

what is the multiplication laws (and rule)
how can it also be wrriten?
tf events are independent ie the result of one event does not affect result of event 2) then: P(A and B) = P(A) X P(B)
if events are dependent onie the result of one depends on the result of the other) then: P(A and B)= P(A) X P(B|A)
where P(B|A) means P(B) given that A happened

how do u calculate expected value
expected value = everything (Probability of outcome X financial result of outcome)