Chapter 13: Arthropods
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:37 PM on 10/31/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
1
New cards
Cuticle
Consists of outer, relatively think epicuticle and an inner, thicker procuticle, found in most protostomes
2
New cards
Class Diplopoda
-Millipedes
-Cylindrical bodies with 25-100 segments
-Four thoracic segmented bear one pair of legs
-Abdominal segments bear 2 pairs of legs
-typically herbivorous
-Cylindrical bodies with 25-100 segments
-Four thoracic segmented bear one pair of legs
-Abdominal segments bear 2 pairs of legs
-typically herbivorous
3
New cards
Exoskeleton
hardened cuticle that is secreted by underlying epidermis, must be molted (shed) in order to grow, contains chitin proteins
4
New cards
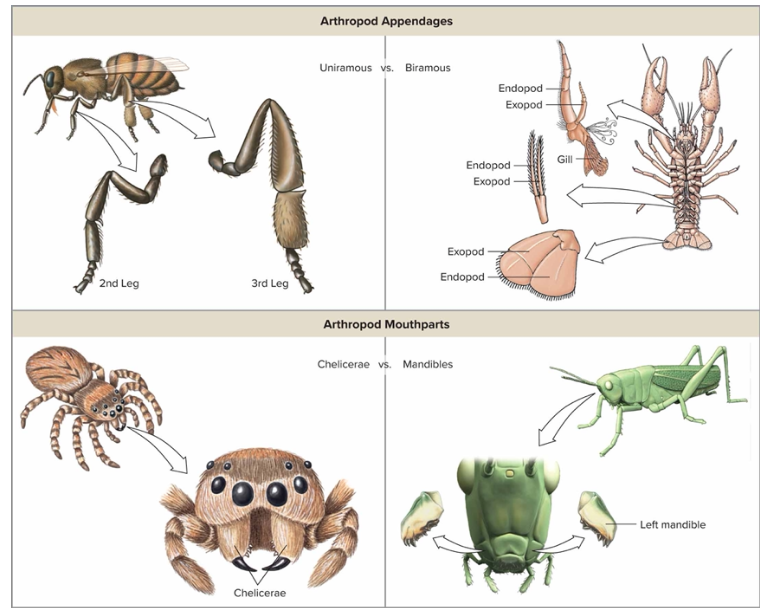
Appendages
uniramous (one tip legs)
Biramous (multiple tip legs)
Chelicerae (pinchers by mouth)
Mandibles (by mouth)
Biramous (multiple tip legs)
Chelicerae (pinchers by mouth)
Mandibles (by mouth)
5
New cards
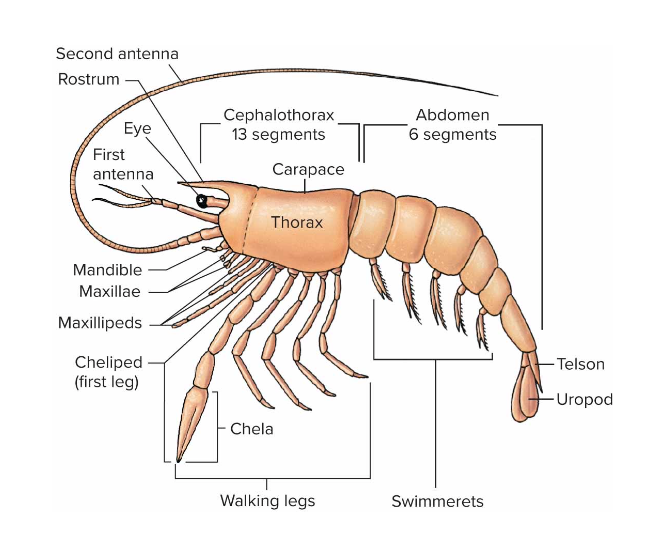
Subphylum Crustacea
-2 pairs of antennae
a pair of mandibles and -2 pairs of maxillae
one pair of appendages on each segment
-All appendages except perhaps first antennae care biramous
- Basal protopod, an outer branch called on exopod and an inner branch called endopod
a pair of mandibles and -2 pairs of maxillae
one pair of appendages on each segment
-All appendages except perhaps first antennae care biramous
- Basal protopod, an outer branch called on exopod and an inner branch called endopod
6
New cards
Crustacean Segmentation
-Primitive Crustaceans may have up to 60 segments, derived crustaceans have fewer
-Tagmata are usually head, thorax and abdomen
-Not homologous across taxa
-In most, one or more thoracic segments are fused with the head as a cephalothorax
-Dorsal covering is the carapace
- May cover most of body or just cephalothorax
-Tagmata are usually head, thorax and abdomen
-Not homologous across taxa
-In most, one or more thoracic segments are fused with the head as a cephalothorax
-Dorsal covering is the carapace
- May cover most of body or just cephalothorax
7
New cards
Crustacean Appendages
Have wide variety of walking legs, mouthparts, swimmerets from modification of the basic biramous appendages
-some have lost 1 branch and are uniramous
Crayfish
- 1st 3 pairs of thoracic appendages are celled maxillipeds
-5 pairs walking legs
- 1st pair of swimmerets in male called monopods used in copulation
-Uropods are last pairs of appendages used for backwards movements and protection for eggs or young on swimmerets
-some have lost 1 branch and are uniramous
Crayfish
- 1st 3 pairs of thoracic appendages are celled maxillipeds
-5 pairs walking legs
- 1st pair of swimmerets in male called monopods used in copulation
-Uropods are last pairs of appendages used for backwards movements and protection for eggs or young on swimmerets
8
New cards
Suspension feeders
generate water currents in order to feed
9
New cards
Predators
hunt for their food, consume larvae, worms, crustaceans, snails, and fishes
10
New cards
Scavengers
eat dead animals and plant matter, many have a two-part stomach
11
New cards
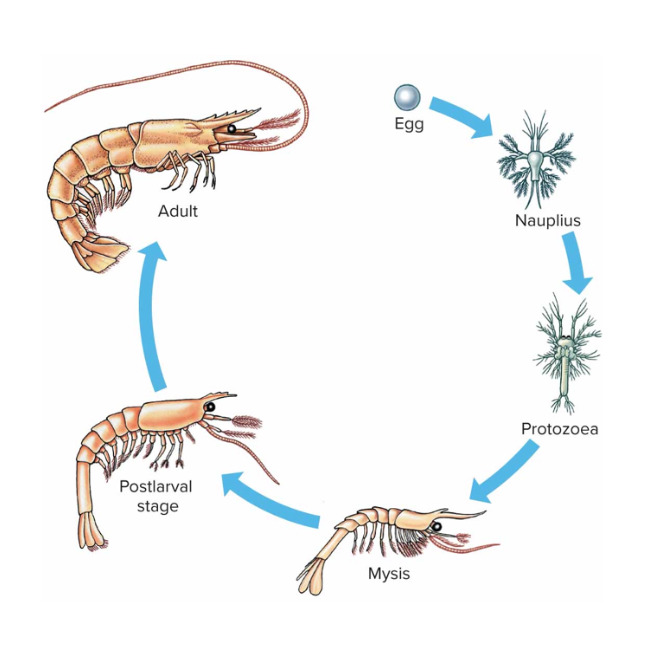
crustacean life cycle
Most crustaceans have separate sexes
Most crustaceans brood eggs in brood chambers, in eggs sacs attached to abdomen, or attached to abdominal appendages
Crayfishes develop directly without a larval form
Most crustaceans have a larva unlike the adult in form and undergo metamorphosis
Nauplius is a common larval form with unsegmented body, frontal eye, 3 pair of appendages
Most crustaceans brood eggs in brood chambers, in eggs sacs attached to abdomen, or attached to abdominal appendages
Crayfishes develop directly without a larval form
Most crustaceans have a larva unlike the adult in form and undergo metamorphosis
Nauplius is a common larval form with unsegmented body, frontal eye, 3 pair of appendages
12
New cards
Branchiopoda
3 orders are recognized
-Anostraca: includes fairy shrimp and brine shrimp
-Notostraca: includes tadpole shrimp
-Diplostraca: Includes water flea and clam shrimp
-Anostraca: includes fairy shrimp and brine shrimp
-Notostraca: includes tadpole shrimp
-Diplostraca: Includes water flea and clam shrimp
13
New cards
Brachiopod Anatomy
Flattened leaf-like legs serve as respiratory organs, assist in suspension feeding, and except for cladocerans, locomotion
Most are freshwater
Important component of freshwater zooplankton
Most are freshwater
Important component of freshwater zooplankton
14
New cards
Subclass Copepoda
roup of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic, some are benthic, a number of species have parasitic phases
15
New cards
Epicuticle
outer most layer of arthropods, made of protein and often lipids
16
New cards
Procuticle
Divided into exocuticle (secreted before a molt) and endocuticle (secreted after molting). Both layers contains chitin bound with proteins
17
New cards
Ecdysis
The process of molting ends in the shedding of skin
18
New cards
molting
necessary for an arthropod to increase in size, since exoskeleton does not grow
19
New cards
Segmentation
Typically each arthropod segment has a pair of jointed appendages
Arrangement is often modified with both segments and appendages specialized for a range of functions
Each section of an appendage functions as a hollow tube moved by muscles, which insert on the inside
Arrangement is often modified with both segments and appendages specialized for a range of functions
Each section of an appendage functions as a hollow tube moved by muscles, which insert on the inside
20
New cards
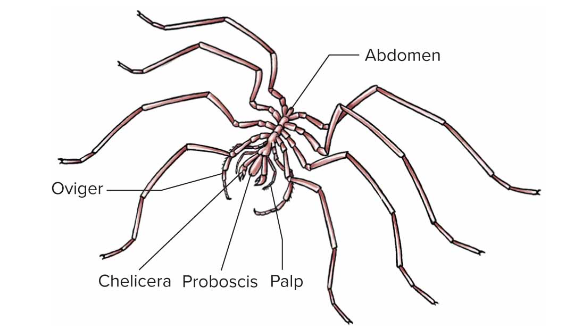
Class Pycnogonida
-sea spiders
-4 pairs of walking legs
-suctorial proboscis
-much reduced abdomen
-male use ovigers (pair of legs) to carry egg masses
-common in the waters
-4 pairs of walking legs
-suctorial proboscis
-much reduced abdomen
-male use ovigers (pair of legs) to carry egg masses
-common in the waters
21
New cards
Cephalothorax and abdomen are joined by?
Thin Pedicel
22
New cards
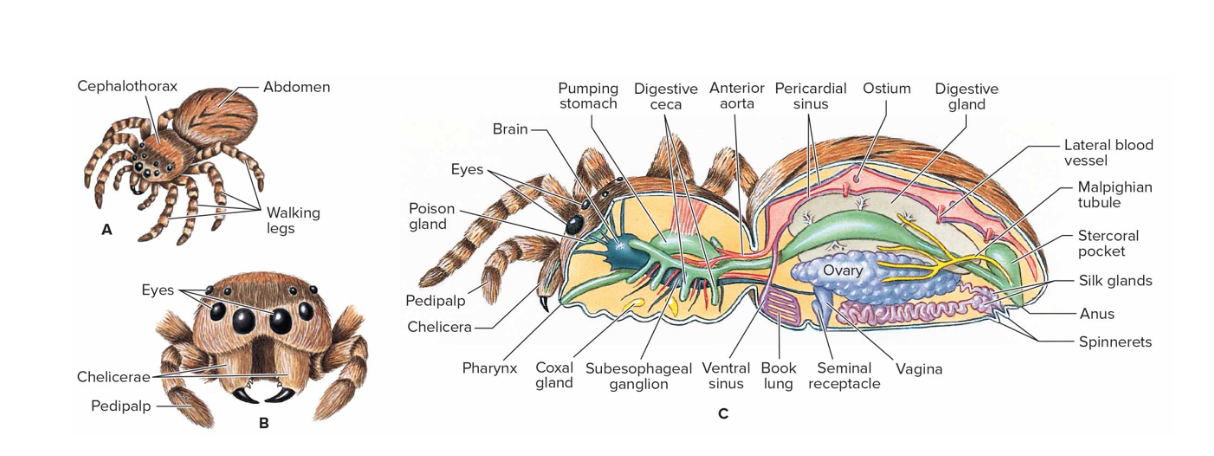
Class Arachnida
-over 100,000 species described
-spiders, scorpion, whip scorpions, ticks, mites, harvestmen, etc
-cephalothorax and abdomen
-spiders, scorpion, whip scorpions, ticks, mites, harvestmen, etc
-cephalothorax and abdomen
23
New cards
Order Araneae
-Spiders
-All predaceous
-chelicerae function as fangs
-web spinning to trap pray
-others are cryptic or stalk prey
-All predaceous
-chelicerae function as fangs
-web spinning to trap pray
-others are cryptic or stalk prey
24
New cards
Trilobite Fossil
-extinct for 250 million
-Abundant during Cambrian and Ordovician period
-Trilobed shaped body, pair of longitudinal grooves
Probably bottom dwellers and scavengers
-Abundant during Cambrian and Ordovician period
-Trilobed shaped body, pair of longitudinal grooves
Probably bottom dwellers and scavengers
25
New cards
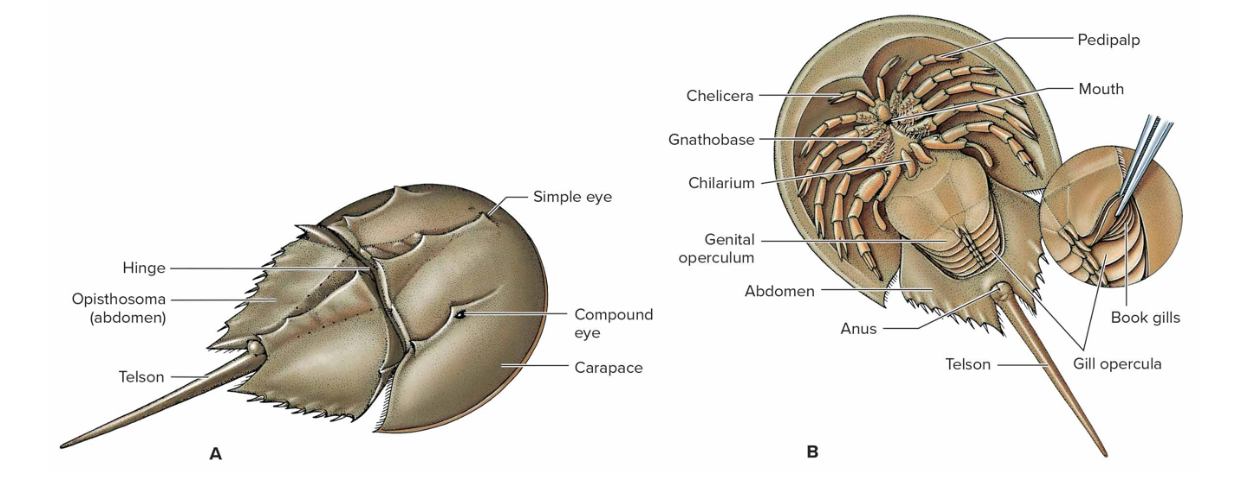
Class merostomata
Horseshoe Crab- looks like a crab but it closely related to spiders
- ancient marine group
-carapace, abdomen, telson
-their blue blood is harvested and used to test medicine
- ancient marine group
-carapace, abdomen, telson
-their blue blood is harvested and used to test medicine
26
New cards
Spiracles
opening on the outside of the arthropods that connects to the tracheae for breathing
27
New cards
Air piped directly to cells
Most land arthropods have a highly efficient tracheal system of air tubes, which deliver oxygen directly to tissues and cells
Tracheae are not present in aquatic arthropods, which breathe mainly by gills
Tracheae are not present in aquatic arthropods, which breathe mainly by gills
28
New cards
Pros and Cons of Arthropods
Pros: Important source of products
Cons: Cause many diseases and economic losses
Cons: Cause many diseases and economic losses
29
New cards
Order scorpionida
scorpions, females carry young on their back
30
New cards
Order Acari
ticks and mites that like to eat dead skin cells, common allergy to humans
31
New cards
Lyme disease
occurs when bitten by Ixodes pacificus (blacklegged tick) who are carriers of this disease, can be carried by any in the genus Ixodes
Opossums are vital in tick control
Opossums are vital in tick control
32
New cards
Class thecostraca
barnacles, very long penis that can inseminate females, slows ships
33
New cards
Order isopoda
terrestrial crustaceans, decomposers, rollie pollies, some are parasitic
34
New cards
Order euphausiacea
krill, major component of animals diets
35
New cards
Decapoda
crabs, have ten legs in total