Filtering - microbe growth control
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
How does filtration control microbial growth?
Physical removal of microbes. Nylon/Teflon filters w/ a spore size of 0.2 or 0.45 um. Viruses can be removed from liquids by ultrafiltration methods (reducing pore size 10 to 100 nm).
Problems with filtration as a microbial control method
Large particles clog filters, viscous liquids don’t filter well, ultrafiltration requires high pressure
What are the ideal conditions for using filtration to remove particles from liquids and gasses
0.2 um pore size common for sterilization. Ideal when material is heat or radiation sensitive
What is the purpose of using varying pore sizes for filtration?
Separation or distinguishing organisms. E.g., retrieving small cells from mixture of large cells.
What is a depth filter?
Fibrous sheet or mat (randomly overlapping fibers of different substances). E.g., paper, glass, cotton (“filter paper”).
What is a depth filter used for?
As a “pre-filter” for filtration. Removes suspended particles in a “trapping action”
Conventional membrane filter
Used for routine sterilization. Polymer filter (0.45 or 0.22 um). Cellulose acetate or cellulose nitrate
What is the pore diameter for conventional membrane filters?
Variable during production. “Sieve” like acton
Nucleopore filters
Thin polycarbonate film (~10 um thick). Radiation damage, cracks enlarged by chem “etching”. Consistent pore spize.
What are nucleospore filters useful for?
Filtered material as a single surface plane.
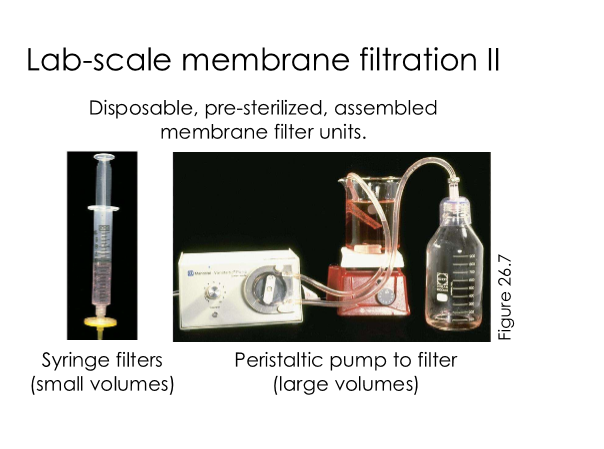
Disposable, pre-sterilized, assembled membrane filter units for small & large volumes
Syringe filters for small volumes, peristatic pump to filter large volumes
Temperature manipulation to control microbe growth (heat)
Heat denatures proteins and nucleic acids. 100C kills most microbes quickly.
Filtrations for sterilizing liquids and gases
Effective. Cells are removed based on size vs destroyed, but don’t remove virus-sized particles. Membrane filters are commonly used to sterilize solutions or growth media.