IUPUI N261 - The Nervous System (The Brain and Spinal Cord)
1/196
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
197 Terms
Where is most of the neural tissue in our body found?
in the brain (95% of neural tissue)
neurocoel
hollow neural tube with a fluid-filled internal cavity
ventricles
enlarged chambers
primary brain vesicles
Prosencephalon (forebrain)
Mesencephalon (midbrain)
Rhombencephalon (hindbrain)
posencephalon
forebrain
mesencephalon
midbrain
rhombencephalon
hindbrain
What are the secondary brain vesicles?
subdivisions of the prosencephalon and the rhombencephalon
What are the two subdivisions of the prosencephalon?
telencephalon and the diencephalon
What are the two subdivisions of the rhombencephalon?
metencephalon and myelencephalon
telencephalon
cerebrum. possesses the paired cerebral hemispheres that dominate the superior and lateral surfaces of the adult brain.
diencephalon
thalamus and hypothalamus. has a roof (epithalamus), walls (left and right thalamus) and floor (hypothalamus). optic vesicles extend laterally from the sides.
metencephalon
pons and cerebellum. closest to mesencephalon
myelencephalon
medulla oblongata. closest to spinal cord
brainstem
contains important processing centers that relay information to and from the cerebrum or cerebellum
medulla oblongata
connects brainstem to the spinal cord. relays sensory information to the thalamus and other centers within brainstem. contains major centers regulating autonomic functions
pons
superior to the medulla. connects cerebellum to the brainstem. controls somatic and visceral motor functions
epithalamus
contains pineal gland
thalamus
relays messages between lower brain centers and cerebral cortex
hypothalamus
visceral control center. contains centers for emotions, autonomic nervous system function, and hormone production. link between nervous and endocrine systems
pituitary gland
endocrine gland at the base of the brain
hypophysis
narrow stalk that connects the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland
cerebellum
second largest part of the brain. automatically adjusts motor activities based on sensory information and memories of learned movements
cerebrum
largest part of the brain. conscious thought processes, intellectual functions, memory storage and retrieval, and complex motor patterns originate here
cerebral hemispheres
right and left sides of cerebrum
longitudinal fissure
separates cerebral hemispheres
sulci
folds in the brain
gyri
ridges of the brain
cortex
outermost covering of the brain consisting of densely packed neurons, responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input
How many ventricles are present in the adult brain?
four
What fills and lines each ventricle of the brain?
they are filled with cerebrospinal fluid and lined by ependymal cells
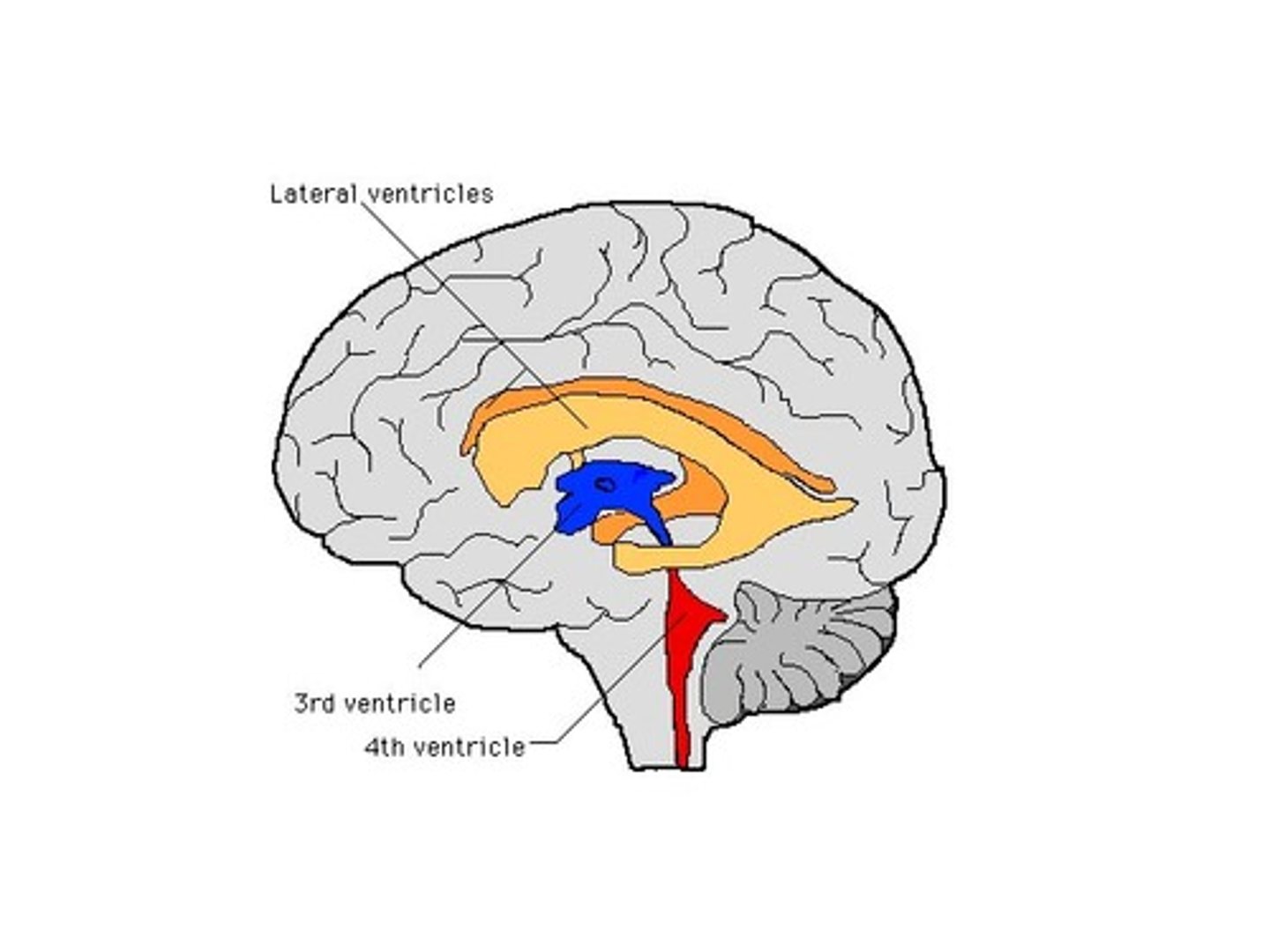
lateral ventricles
a set of paired ventricles lying within the cerebral hemispheres.
septum pellucidum
thin membrane that separates lateral ventricles
What is the structure of the lateral ventricles of the brain?
body, anterior horn, posterior horn, inferior horn. body lies within parietal lobe, anterior horn extends into frontal lobe. posterior horn projects into occipital lobe. inferior horn curves laterally within temporal lobe
interventricular foramen
connects lateral ventricles to third ventricle
third ventricle
the ventricle located in the center of the diencephalon
cerebral aqueduct
connects the third and fourth ventricles
fourth ventricle
the ventricle located between the cerebellum and the dorsal pons, in the center of the metencephalon
What five things are involved in protection, support, and nourishment of the brain?
bones of the skull, cranial meninges, blood brain barrier, cerebrospinal fluid, rich blood supply
cranial meninges
protect the brain by acting as shock absorbers, preventing contact with the skull bones. continuous with the spinal meninges with the same three layers.
dura mater
Outermost layer of the meninges
periosteal cranial dura
fused to periosteum lining the cranial bones.
meningeal cranial dura
innermost layer of the dura mater
dural sinuses
spaces that collect blood that has circulated through the brain
In what four locations does the dura fold and extend deep into the brain?
falx cerebri, tentorium cereblli, falx cerebelli, diaphragma sellae
falx cerebri
found between cerebral hemispheres in the longitudinal fissure. attaches to the crista galli and interior occipital crest and tentorium cerebelli.
superior and inferior sagittal sinuses
lie within falx cerebri dura folds
tentorium cerebelli
supports and protects the two occipital lobes of the cerebrum. separates cerebellar hemispheres from cerebrum.
transverse sinus
lies within the tentorium cerebelli
falx cerebelli
divides the two cerebellar hemispheres along the midsagittal line inferior to the tentorium cerebelli
diaphragma sellae
small segment of dura mater lining the sella turcica of the sphenoid. anchors dura mater to the sphenoid and surrounds base of pituitary gland
arachnoid amter
delicate membrane covering the brain between surperficial dura matera and deeper pia mater.
subdural space
separates the dura mater from the arachnoid mater
subarachnoid space
delicate, weblike meshwork of collagen and elastic fibers linking the arachnoid mater to the underlying pia mater
arachnoid granulations
extensions of the arachnoid mater that allow excess CSF to be absorbed by the dural sinuses.
cranial arachnoid mater
acts as roof over the cranial blood vessels, and underlying pia mater forms a floor
arachnoid trabeculae
supports cerebral arteries and veins. surrounded by CSF
pia mater
tightly attached to the surface of contours of the brain, sticking to its contours and lining the sulci. anchored to the surface of the brain by the processes fo astrocytes. highly vascular
blood brain barrier
a filtering mechanism of the capillaries that carry blood to the brain and spinal cord tissue, blocking the passage of certain substances.
In what four regions of the brain is the blood brain barrier notably different?
portions of the hypothalamus, where capillary endothelium has increased permeability. capillaries in the pineal gland, which is increasingly permeable. capillaries at a choroid plexus, the site of CSF production for maintenance of blood-CSF barrier. capillaries in the posterior lobe of pituitary gland.
endothelial transport across BBB
selective and directional.
What are the main functions of cerebrospinal fluid?
preventing contact between delicate neural structures and surrounding bones. supporting the brain. transporting nutrients, chemicals, and wastes, except at the choroid plexus where the ependymal lining is freely permeable.
Where is CSF formed?
choroid plexuses in all ventricles of the brain. capillaries are fenestrated and highly permeable, but large, highly specialized ependymal cells cover them. choroid plexus also removes waste from CSF and fine tune its composition
lateral apertures
pair of openings from the fourth ventricle to the subarachnoid space on either side and between the medulla and cerebellum
median aperture
an opening in the roof of the fourth ventricle that connects to the subarachnoid space
How does CSF reenter circulation?
through the arachnoid granulations
How are energy demands in the brain met?
extensive vascular supply
cerebrovascular diseases
circulatory disorders that interfere with the normal blood supply to the brain
cerebrovascular accident (CVA)
stroke. occurs when the blood supply to a portion of the brain is shut off. affected neurons begin to die in a matter of minutes
all communication between the brain and spinal cord involves tracts ascending or descending through what?
the medulla oblongata
What are the three groups of nuclei in the medulla oblongata?
relay stations and processing centers, nuclei of cranial nerves, autonomic nuclei
gracile nucleus
relay somatic sensory information to the thalamus
cuneate nucleus
fine touch and proprioception of the upper body
solitary nucleus
receives visceral sensory information that reaches the CNS from the spinal nerves and cranial nerves
olivary nuclei
relay information from spinal cord, cerebral cortex, diencephalon, and brainstem to the cerebellar cortex.
olives
prominent bulges formed by the bulk of olivary nuclei that occur along the ventrolateral surface of the medulla oblongata.
reflex centers
receive input from cranial nerves, the cerebral cortex, diencephalon, and brainstem, and their output adjusts the activities of one or more peripheral systems
What are the major reflex centers?
cardiovascular centers and respiratory rhythmicity centers,
cardiovascular centers
adjust heart rate, strength of cardiac contractions, and the flow of blood through peripheral tissues. divided into cardiac and vasomotor centers.
respiratory rhythmicity centers
set basic pace for breathing. inputs from apneustic and pneumotaxic centers within the pons regulate their activity
What is contained in the pons?
sensory and motor nuclei for four cranial nerves, nuclei regulating the involuntary control of respiration, nuclei that process and relay cerebellar commands, and ascending, descending, transverse tracts
What is contained in the white matter of the pons?
ascending and descending tracts (interconnect other portions of the CNS), and transverse fibers (interconnect cerebellar hemispheres, interconnect pontine nuclei with the cerebellar hemispheres on the contralateral side)
What is contained in the gray matter of the pons?
respiratory centers (modify output of respiratory centers in the medulla oblongata), reticular formation (automatic processing of incoming sensations and outgoing motor commands), and other nuclei/centers (nuclei associated with four cranial nerves and the cerebellum)
tectum
the surface posterior to the cerebral aqueduct
corpora quadrigemina
located in the midbrain; contains reflex centers for vision and auditory reflexes.
superior collicui
receive visual input from the lateral geniculate of the thalamus on the ipsilateral side
inferior colliculi
receive auditory input from the nuclei in the medulla oblongata; some of this information is forwarded to the medial geniculate on the ipsilateral side
red nucleus
a large nucleus of the midbrain that receives inputs from the cerebellum and motor cortex and sends axons to motor neurons in the spinal cord.
substantia nigra
lateral to the red nucleus. regulates motor output of the basal nuclei
cerebral peduncles
nerve fiber bundles on the ventrolateral surfaces of the midbrain. ascending fibers synapse in the thalamic nuclei and descending fibers of corticospinal pathway carrying voluntary motor commands from the primary cortex of each cerebral hemisphere
pineal gland
endocrine structure that secretes melatonin.
melatonin
regulates day/night cycles, and some effects on reproductive function
Where is most of the nervous tissue of the diencephalon concentrated?
in left and right thalamus
thalamic nuclei
provide integration and relay centers for sensory and motor pathway
What nerves synapse in the thalamic nuclei?
all ascending sensory information from the spinal cord and cranial nerves
How do the thalami act as information filters?
by processing all of the incoming sensory information and then passing on only a small portion to the cerebrum or brainstem.
What separates the two thalami?
the third ventricle
interthalamic adhesion
medial projection of gray matter that extends into the ventricle from the thalamus on either side.
What forms the lateral border of each thalamus?
fibers of the internal capsule
What are the five major groups of thalamic nuclei?
anterior, medial, ventral, posterior, lateral