C4.1 Populations & Communities (18)
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
C4.1.1+4+10
population = group of organisms of same species, same area, time (inc. by birth/immigration, dec. by death/emigration)
community = group of populations living tog./interacting in same area (plants, animals, fungi, bacteria)
interact w/ habitat to form ecosystem where each species occupies niche
motile species size → capture-mark-release-recapture
M = no. of individuals captured in defined area, marked, released
N = no. of individuals recaptured after set time
R = no. of marked individuals in recaptured sample
lincoln index for population estimate: M x (N/R)
assumptions: random sampling, marked individuals randomly distributed, marking individuals will not influence mortality/natality of population, marking remains visible, population size doesn’t sig. change between periods of capture
C4.1.2–3 Estimation of population size by random sampling +
populations fluid + change (some impractical to count)
diff. between estimate + true size = sampling error
random sampling → sampling point positions randomly selected to avoid bias (e.g. establishing grid + randomly picking coords)
systematic sampling → sampling point positions at fixed intervals in target area (allows for investigation of effects of environmental factors on species distribution via transect)
population size/distribution of non-motile species → quadrat sampling
quadrat (rectangular frame) placed inside defined area (randomly/transect), no. of species counted/estimated via % coverage
repeat many times to find mean + SD
C4.1.5–6 Carrying Capacity + Negative feedback control of Population size by density-dependent factors
carrying capacity = max. no. of individuals in species that environ. can support
species w/ high growth/low survivability fluctuate markedly around CC (r)
low growth/high survivability have more stable levels at CC (k)
populations oscillate around this, not static value but influenced by a/biotic factors
population size impacted by density-dependent factors pushing them back to CC
higher density → more competition, low-density → grow more
- feedback loop (inc. pop. density → reduced size bc of these factors)
Predation, Access to habitats, Nutrient supply, Diseases, Accumulation of waste
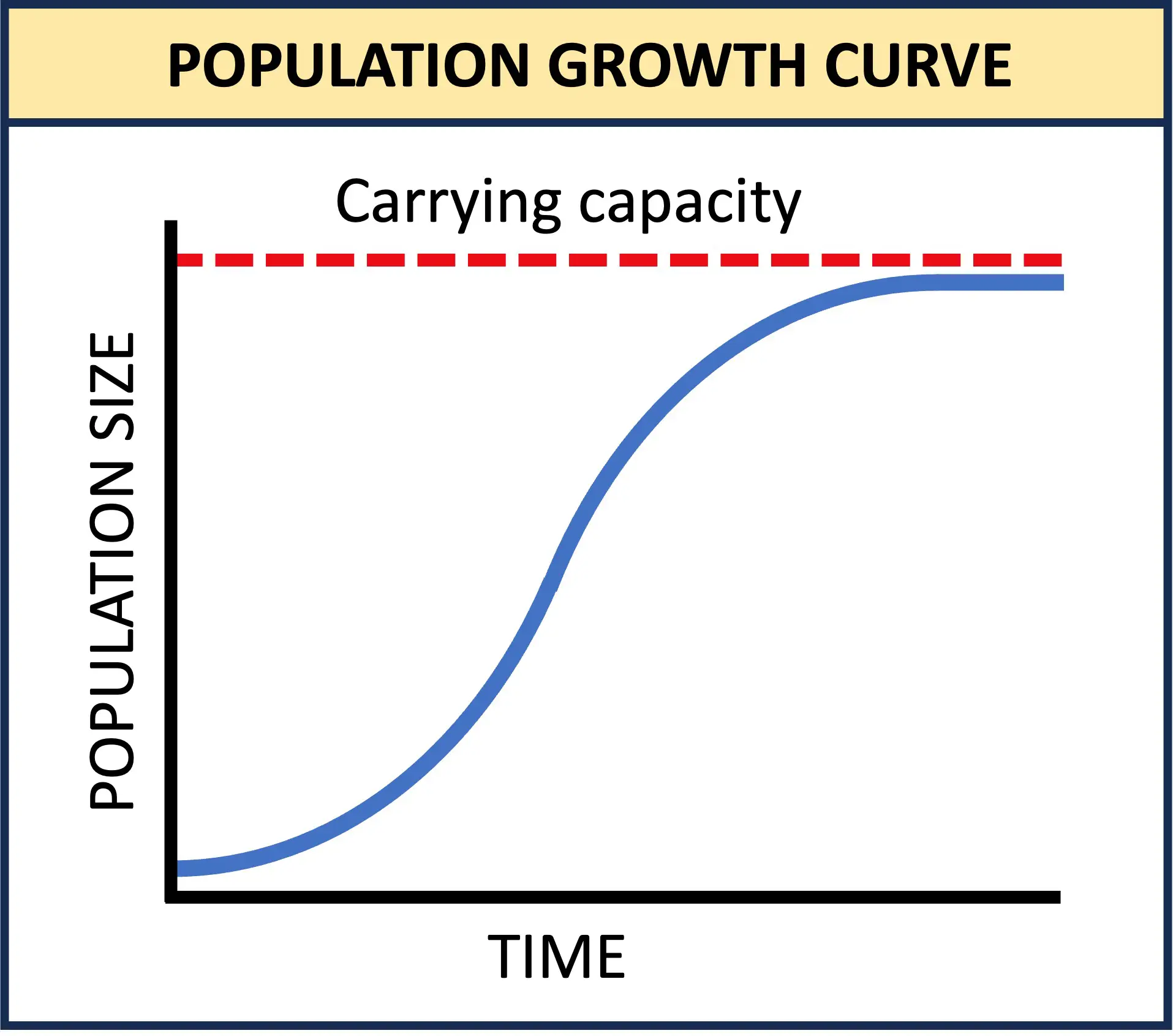
C4.1.7–8 Population growth curves + modelling
stable populations → S-shaped curve
exponential → initially slow, numbers accumulate + rapid inc., mortality low bc abundant resources + min. environmental resistance
transitional → resources become limited as population grows → competition. natality dec., mortality inc., slower growth
plateau phase) → mortality = natality, population growth static. reaches carrying capacity of environment, limiting factors keep it stable (oscillate around carrying capacity)
modelled using simple organisms in lab (yeast, duckweed) bc small, low requirements, rapid repro.
yeast growth measured growing in broth culture + measuring turbidity (cloudiness)
duckweed in petri dish w/ liquid fertiliser + light source
C4.1.9+11
intraspecific interactions = cooperation (+/+) + competition (+/-)
cooperation = pack animals hunt tog. to feed, insects work tog. to build nests + find food
competition = woodland trees competing for light/water/mineral access, territorial animals defending their space, M mating w/ F
herbivory (+/+ e.g. bee/pollen or +/- e.g. cow/grass)
predation (+/-) e.g. owl/mice, lion/zebra, wolf/deer
interspecific competition (+/-) direct e.g. territory/indirect e.g. depleting resource
lions/hyenas, beech/pine
symbiotic relationships = 2 species interact closely long-term
mutualism (+/+), commensalism e.g. barnacle/whale (+/0), parasitism e.g. tick/canine (+/-)
pathogenicity = infectionism micro-org live inside host, cause disease
bacteria causing TB in animals
C4.1.12–13 Mutualism + Invasive Species
root nodules (legumes gain nitrates/rhizobacterium gain carbs)
mycorrhizae in orchids (fungus connects to plant roots + inc. SA for abs., plant gives nutrients)
zooxanthellae in polyps (zooxanthellae photosynthesis for nutrients for polyp/polyp’s CaCO3 exoskeleton provides shelter)
endemic → native, alien → transferred
if alien has - effect on existing chains → invasive
normally have large fundamental niche, repro. rapidly, lack predator, have features suited to new environ.
red fox introduced to australia by european colonisation → apex predator that has common diet + niche w/ native quoll (size declined sig.)
C4.1.14–15
comparative distribution of species indicates their relationship type
inter. comp. indicated if 1 is more successful in another’s absence
lab experiments under controlled conditions by measuring DV when both species present/isolated
field manipulation via selective removal of species to determine its impact on the other in natural environment
field observations where random sampling sites assessed (quadrats) for presence/absence of each species
quadrat sampling → chi-squared test
if found in same habitat → + association e.g. predator-prey
if don’t occur in same habitat → - association e.g. inter. comp.
C4.1.16
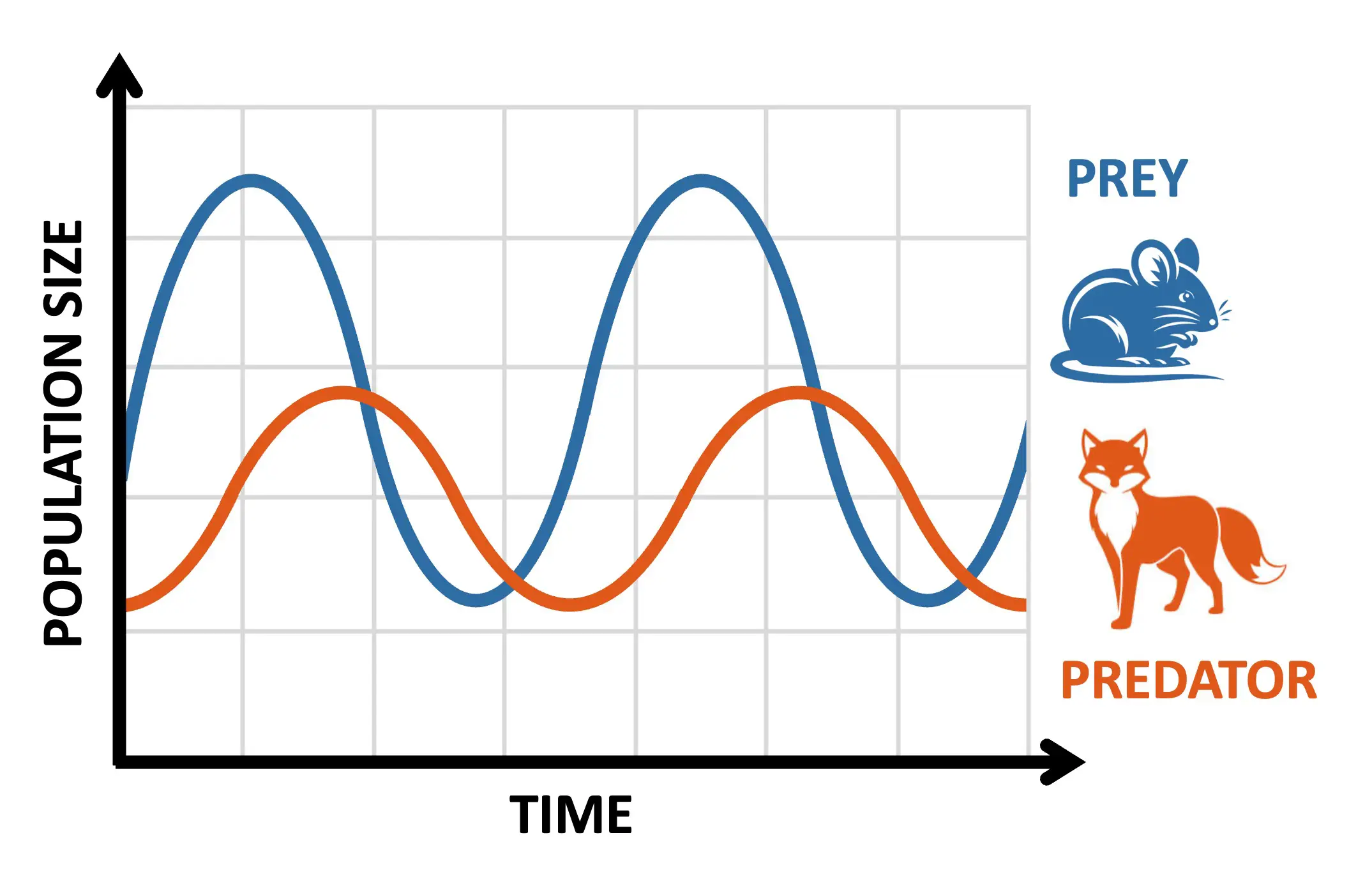
predator-prey dynamic means their populations lvls intertwined
= density-dependent population control mechanism
but most may not show clearly bc predators have multiple food sources, prey have multiple predators
prey drops → predator drops after bc more competition
prey rises → predator inc. bc over-abundant food source
C4.1.17–18
top-down control → higher trophic lvls exert pressure to control ecosystem’s pop. dynamics e.g. keystone species to prevent monopoly
oscillating trophic cascade (- ← + ← -)
consumer suppresses food source abundance / alters competitor's behaviour to impact lower trophic levels
bottom-up control → pressures applied to lower trophic lvls e.g. plants limited by light intensity. to impact abundance of animals at higher trophic levels by restricting E supply
- → - → -
(one more likely to dominate, can switch)
organisms can exert control over other species by releasing chemicals
allelopathy → releases chem. that influence growth/survival/repro. (+/-)
e.g. garlic mustard plant reduces germination + root growth of other species
antibiotics → releases chemicals that neg. affect bacteria by targeting prokaryotic-specific features (inhibit growth/kill it)
e.g. penicillium releases penicillin, preventing bacteria cell wall formation