Chapter 8 & 9 - OChem 1
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Alkene Hydrohalogenation
The Pi bond is broken, and hydrogen and a halogen are added on each side of the bond. It will be a Markovnikov addition if the solvent is pure, and it will be an anti-Markovnikov addition if it is an impure solvent.
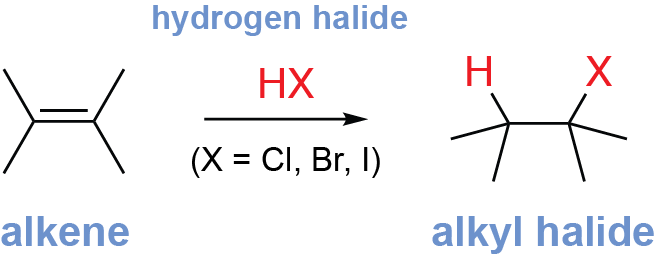
What reagent is used for alkene hydrohalogenation?
H-X (Cl, Br, I)
Is there a carbocation intermediate in alkene hydrohalogenation?
Yes, so it can possibly shift. Both enantiomers will form always if there is a chiral center.
Alkene acid-catalyzed hydration
The pi bond is broken and OH and H are added on each side of the bond. This is a Markovnikov addition
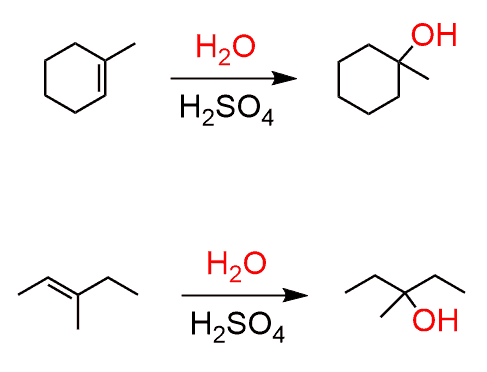
What are the reagents of alkene acid-catalyzed hydration?
H3O+ or [acid] + H2O
Can a carbocation intermediate form in alkene acid-catalyzed hydration?
Yes and rearrangement can occur. Forms both (2) enantiomers
What is special about there being a carbocation intermediate?
Both enantiomers can form in a racemic mixture, and the carbocation can move to a more stable position.
If a carbocation rearrangement can happen during alkene acid-catalyzed hydration...
It is considered an inefficient method, and oxymercuration-demercuration should be used instead because it doesn't form a carbocation rearrangement.
Alkene Oxymercuration-Demercuration.
Breaks the pi bond, and spreads H and OH across the bond. It is Markovnikov addition.
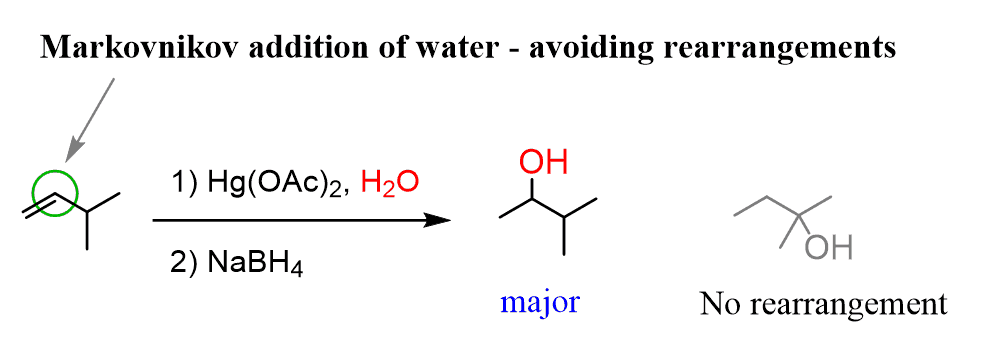
What are the reagents for alkene oxymercuration-demercuration?
1) Hg(OAc)2, H2O. 2) NaBH4
Does oxymercuration/demercuration form a carbocation?
No. If a chiral center is formed, either the enantiomer or diastereomer can be formed.
Alkene hydroboration-oxidation.
Breaks the pi-bond and adds H and OH across it. It is an anti-Markovnikov addition.
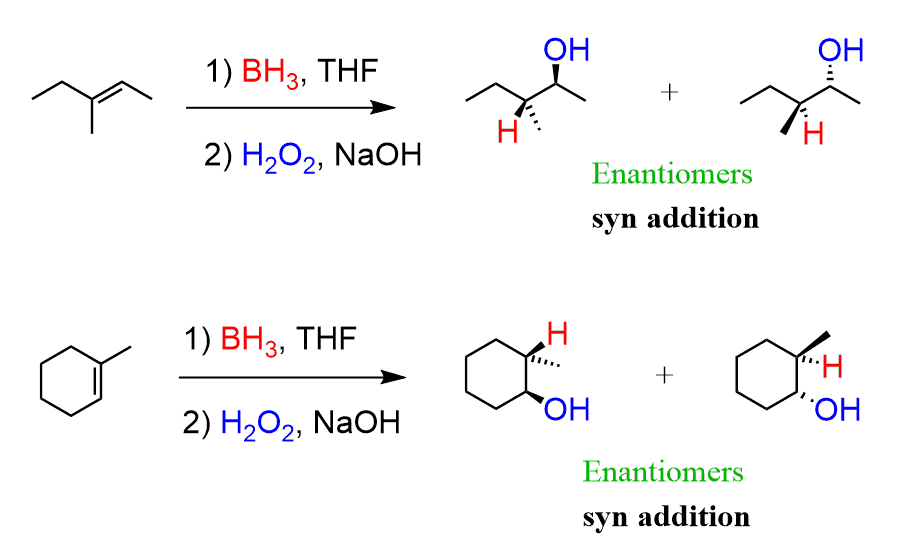
What are the reagents of alkene hydroboration oxidation hydration?
1) BH3 • THF 2) H2O2, NaOH
Does alkene hydroboration-oxidation-hydration form a carbocation intermediate?
No.
What is the stereochemistry for alkene hydroboration-oxidation-hydration?
If a chiral center is formed, both enantiomers will be formed. If two chiral centers are formed, then we will only get one pair of enantiomers. It is syn addition.
Alkene catalytic hydrogenation.
The pi bond is broken, and H2 is added across the bond in the presence of a metal catalyst.
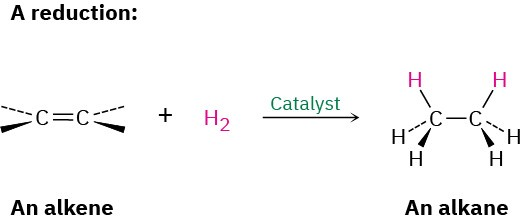
What are the reagents of alkene catalytic hydrogenation?
H2, Pt/Pd/Ni/Wilkinsonson’s catalyst (homogenous)
Does alkene catalytic hydrogenation form a carbocation intermediate?
No
What is the stereochemistry of alkene catalytic hydrogenation?
If one chiral center is formed, then both enantiomers are formed. If two chiral centers are formed, it will be syn addition. Meso compounds can also form if the product is symmetric.
Alkene halogenation.
The pi bond is broken, and Br2 or Cl2 are added across the bond.
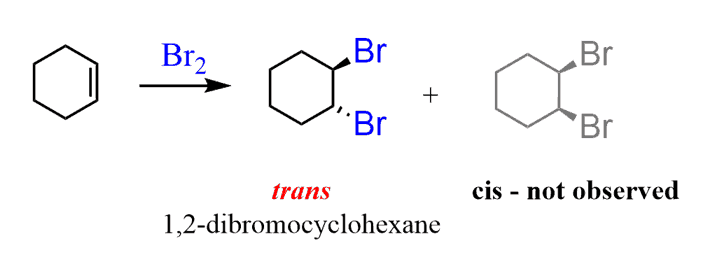
Does a carbocation intermediate form during alkene halogenation?
No.
What are the reagents of alkene halogenation?
Cl2 or Br2
What is the stereochemistry of alkene halogenation?
It proceeds via anti-addition.
Alkene halohydrin formation.
Pi bond is broken, and Br or Cl is added on one side of the bond, and OH is added on the other side. It is an Markovnikov addition, as in o-H will be added to the more substituted position.
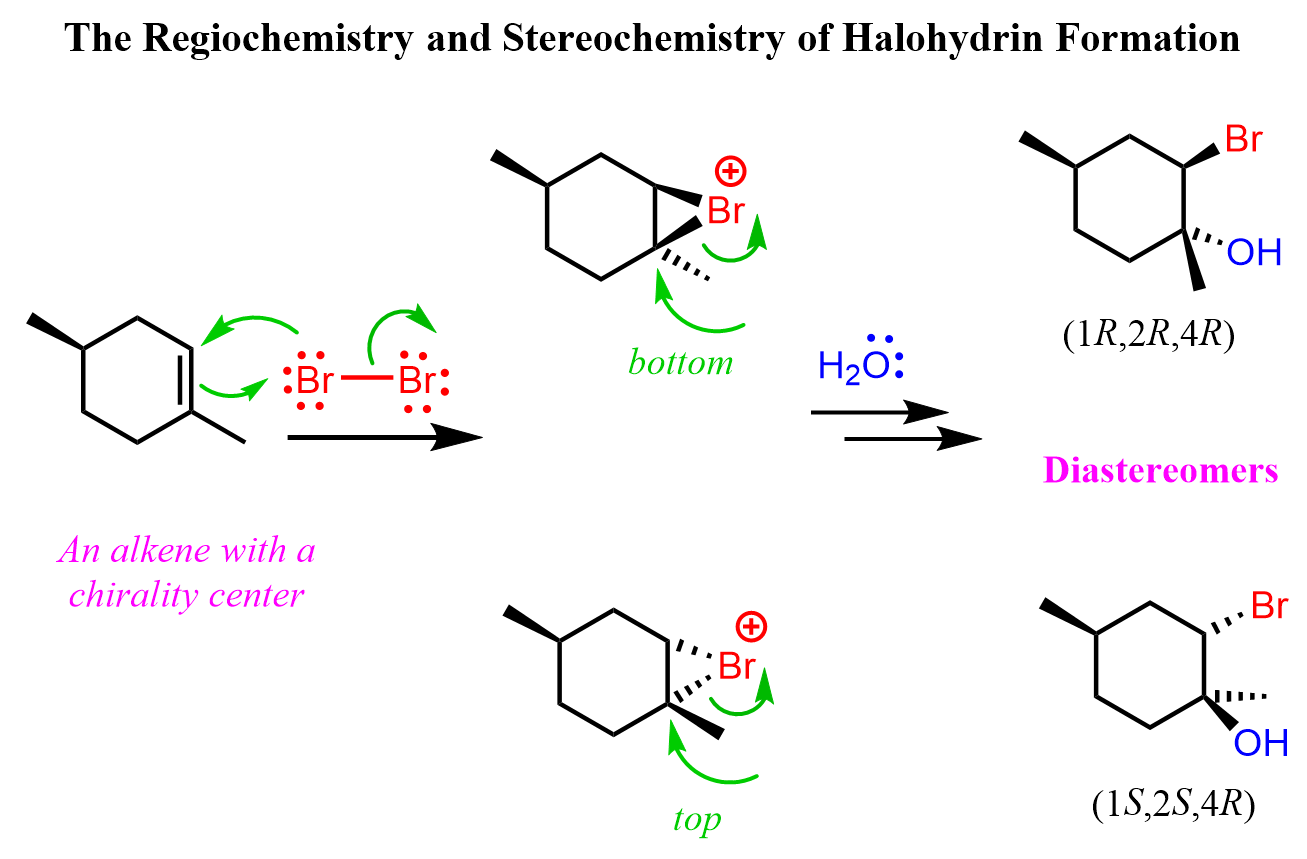
Does a carbocation on an intermediate form during a alkene halohydrin formation?
Yes, but it does not rearrange.
What are the reagents of alkene halohydrin formation?
Br2 or Cl2, H2O
What is the stereochemistry of alkene halohydrin formation?
Anti-addition & markovnikov to OH
Alkene dihydroxylation.
Pi bond is broken and an OH is added to each side of the bond.
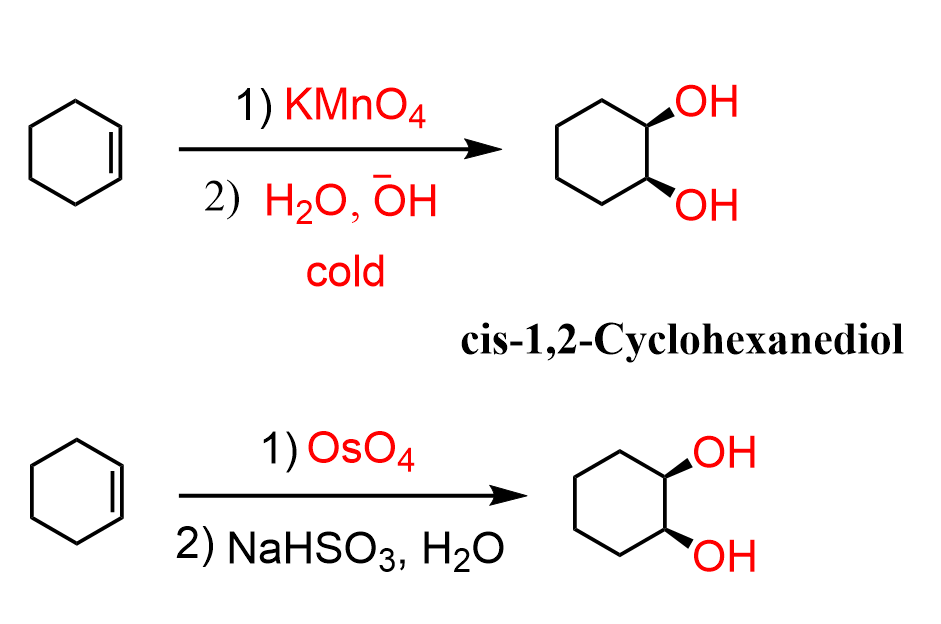
Alkene dihydroxylation reagents
For anti-addition dihydroxylation 1) RCO3H, 2) H3O+
For syn-addition dihydroxylation OsO4 & NaHSO3 or Na2SO3. Or Cold KMnO4 & NaOH
Alkene ozonolysis.
The compound is cleaved in half, leaving a double bond on each side. With oxygen added to each compound at that double bond.
What are the reagents for alkene ozonolysis?
1) O3, 2) DMS or Zn/H2O
Hydrohalogenation of alkynes.
Very similar to the process that happens with alkenes, except the bond is reduced to a double bond.
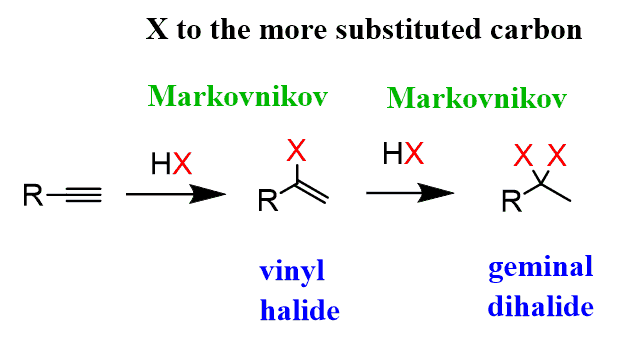
What are the reagents for alkyne hydrohalogenation?
HX to produce markovnikov addition and HX with ROOR to product anti-markovnikov
Is there a carbo-cation intermediate in the hydrohalogenation of alkynes?
Yes, and it can rearrange.
Alkyne acid-catalyzed hydration.
The triple bond is broken into a double bond, which forms a ketone. Markovnikov addition.
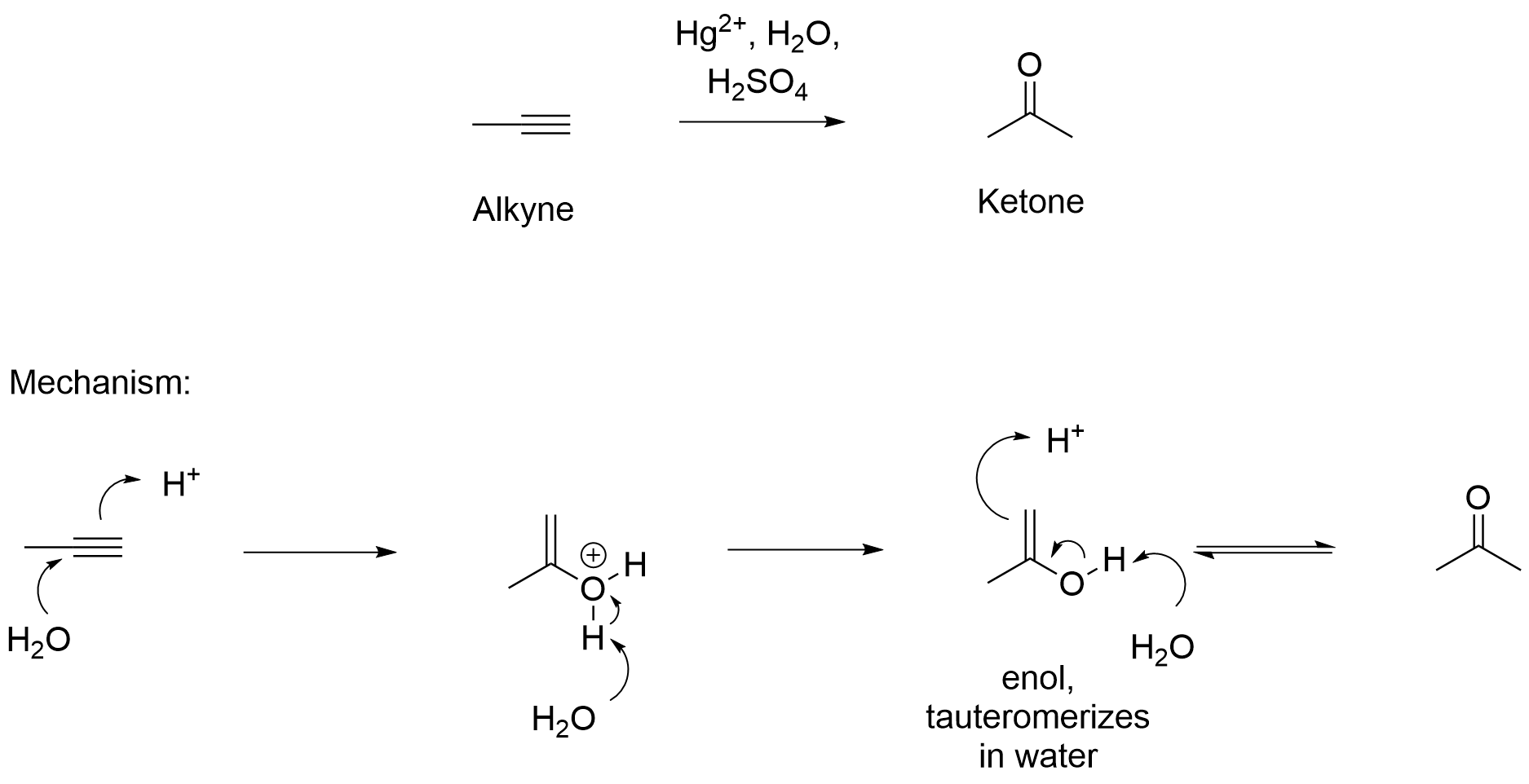
What are the reagents of alkyne acid-catalyzed hydration?
H2SO4, H2O, HgSO4
Alkyne hydroboration-oxidation.
Breakage of the triple bond into a double bond. It forms an anti-Markovnikov addition of an aldehyde, which is a double bond to an oxygen and a single to a hydrogen.
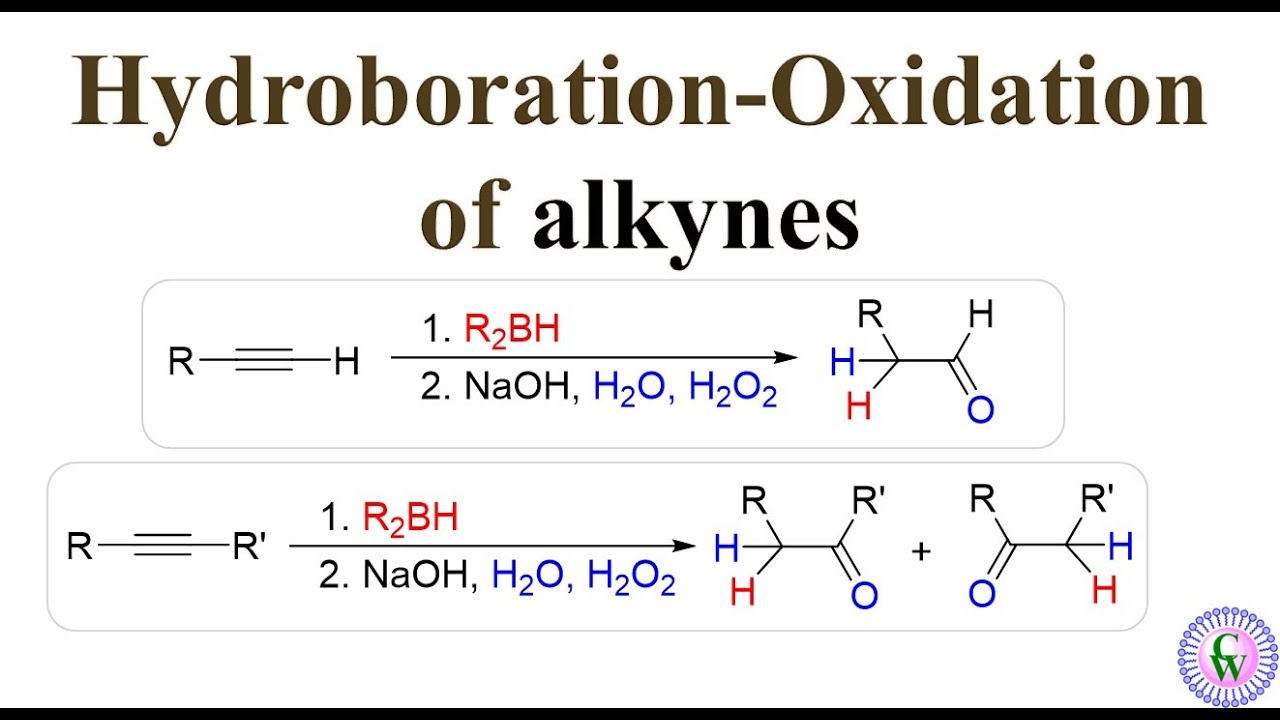
What are the reagents of alkyne hydroboration-oxidation?
1) R2BH or 9BBN, 2) H2O2
Is there a carbocation intermediate in alkyne hydroboration-oxidation?
No.
Alkyne halogenation.
Breaks the triple bond into a double bond and adds a halogen on each side.
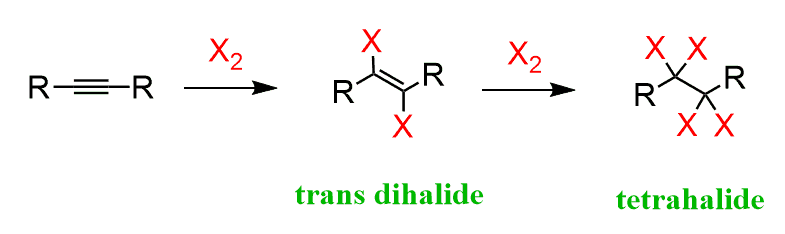
What are the reagents of alkyne halogenation?
X2, CCl4
What is special about alkyne halogenation?
If one equivalent of halogen is used, there is a mixture of major and minor products, with the E-isomer being the major.
Alkyne ozonolysis
Breaks the triple bond and does not cleave the molecule like with alkenes. It instead produces a double bond to oxygen and a single to OH (a carboxylic acid).
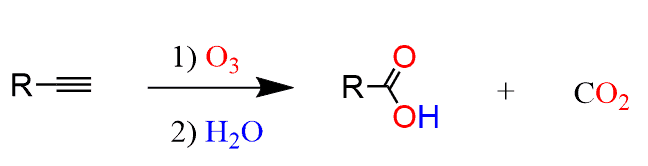
What are the reagents of ozonolysis of alkynes?
1) O3 2) H2O
What is special with ozonolysis of alkynes?
If a terminal alkyne is reacted, carbon dioxide is also produced.
Alkylation.
Increases the length of a carbon chain and can only be used on terminal alkynes.
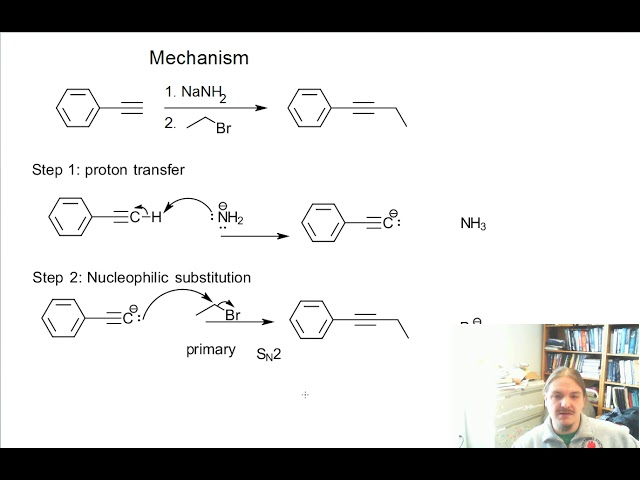
What are the reagents of alkylation?
1) NaNH2 2) R–X
Alkyne catalytic hydrogenation.
Triple bond is broken into either a double or single bond, and hydrogen is added to each side.
What are the reagents of alkyne catalytic hydrogenation?
To produce single (trans) = H2, Pt/Pd/Ni
To produce double (cis) = H2, Lindlar’s catalyst
To produce double (trans) = Na, NH3 (l)
Alkyne hydrohalogenation (2 equivalents).
Triple bond is broken into a single bond and two halogens are added to one side of the bond.
Alkyne halogenation (2 equivalents).
Triple bond is broken into a single bond with two halogens added to each side of the bond.
Reagent for alkyl hydrohalogenation (2 equivalents).
Xs HX
Reagent alkyne halogenation (2 equivalents).
Xs X2, CCl4
What are suitable reagents to create an alkyne from a dihalide using an E2 reaction?
2NaNH2, NH3
What reagent creates an epoxide from an alkene?
mCPBA