Liver, Gallbladder, and Pancreas Pathophysiology (no neoplasms)
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Toxic liver injury
What diagnosis is best associated with massive hepatocellular necrosis 2 days following onset of symptoms in an otherwise healthy individual?
Alcoholic hepatitis (steatofibrosis)
What diagnosis is best associated with Mallory-Denk bodies and neutrophils?
Acute viral hepatitis
What diagnosis is best associated with acidophil/Councilman bodies and lymphocytes?
Chronic viral hepatitis
What diagnosis is best associated with piecemeal necrosis (aka interface hepatitis) and lymphocytes?
Autoimmune hepatitis
What diagnosis is best associated with piecemeal necrosis (aka interface hepatitis) and plasma cells?
Cirrhosis
What diagnosis is best associated with fibrosis, regenerative nodules, and disruption of normal architecture?
Reye syndrome
What diagnosis is best associated with hepatic dysfunction and marked microvesicular steatosis WITHOUT OVER NECROSIS?
Neonatal hepatitis
What diagnosis is best associated with giant cell transformation of hepatocytes?
Obstructive gallstone in cystic duct
Waxing/waning RUQ pain described as a "biliary colic" without jaundice is most likely:
PBC
What diagnosis is best associated with florid duct lesions with granulomas of INTRAhepatic bile ducts?
Portal lymphocytes and histiocytes with bile duct injury
Describe a "florid duct lesion"
Ascending cholangitis
What diagnosis is best associated with intraluminal neutrophils in bile ducts?
PSC
What diagnosis is best associated with onion-skin fibrosis around bile ducts?
Large bile duct obstruction (bonus: bile duct stricture post-surgery)
What diagnosis is best associated with ductular reactions, portal tract edema w/ neutrophils, and conjugated hyperbilirubinemia? (Bonus: provide an example)
Acute calculous cholecystitis (bonus: US)
What diagnosis is best associated with a thick gallbladder wall with presence of cholesterol stones? (Bonus: what imaging modality would be best to see these types of stones?)
Acute acalculous cholecystitis (bonus: ICU)
What diagnosis is best associated with a thin gallbladder wall with gangrene? (Bonus: in what setting would you most likely find these patients?)
Portal vein, hepatic artery, bile duct
What 3 structures compose the portal tract/portal triad?
Sinusoids
Where does oxygenated and deoxygenated blood mix in the liver?
Kupffer cells
What cells act as the macrophages in the liver?
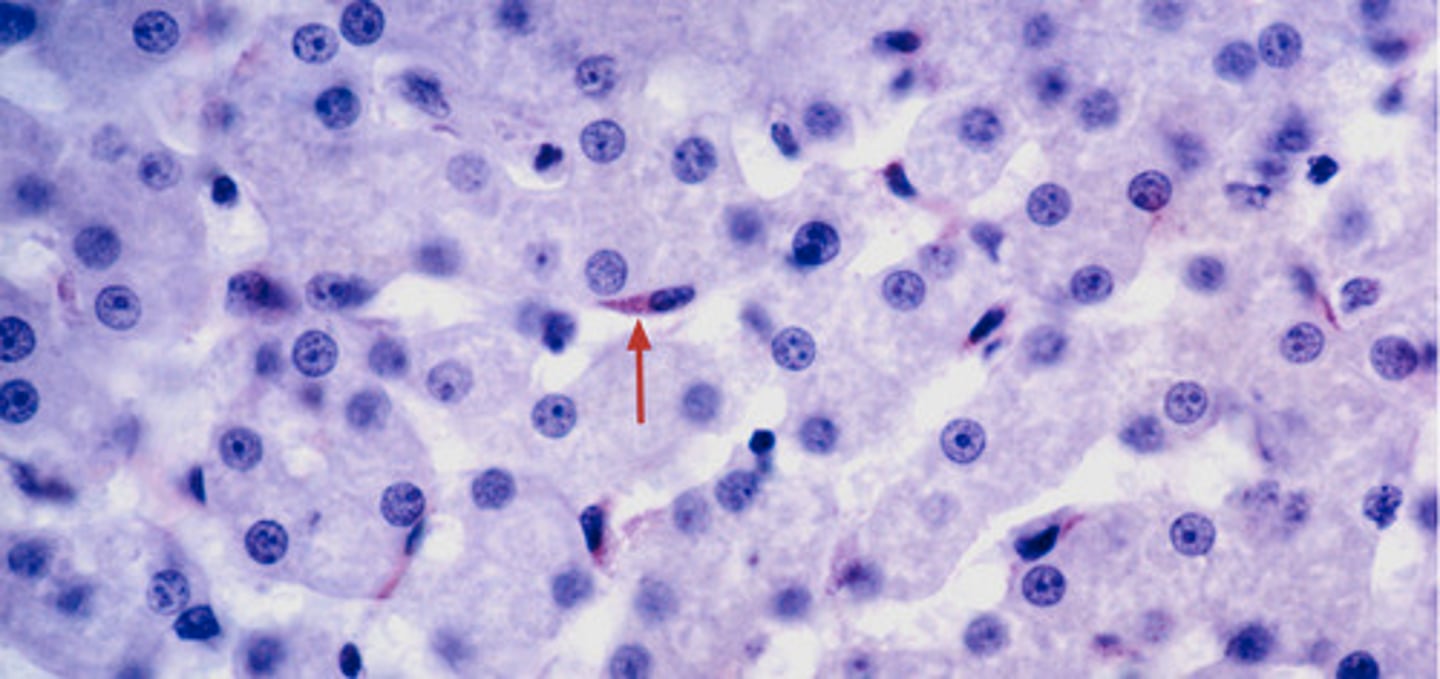
Stellate cells
What cells store vitamin A in the liver?
Stellate cells
What cells induce the fibrosis seen in cirrhosis?
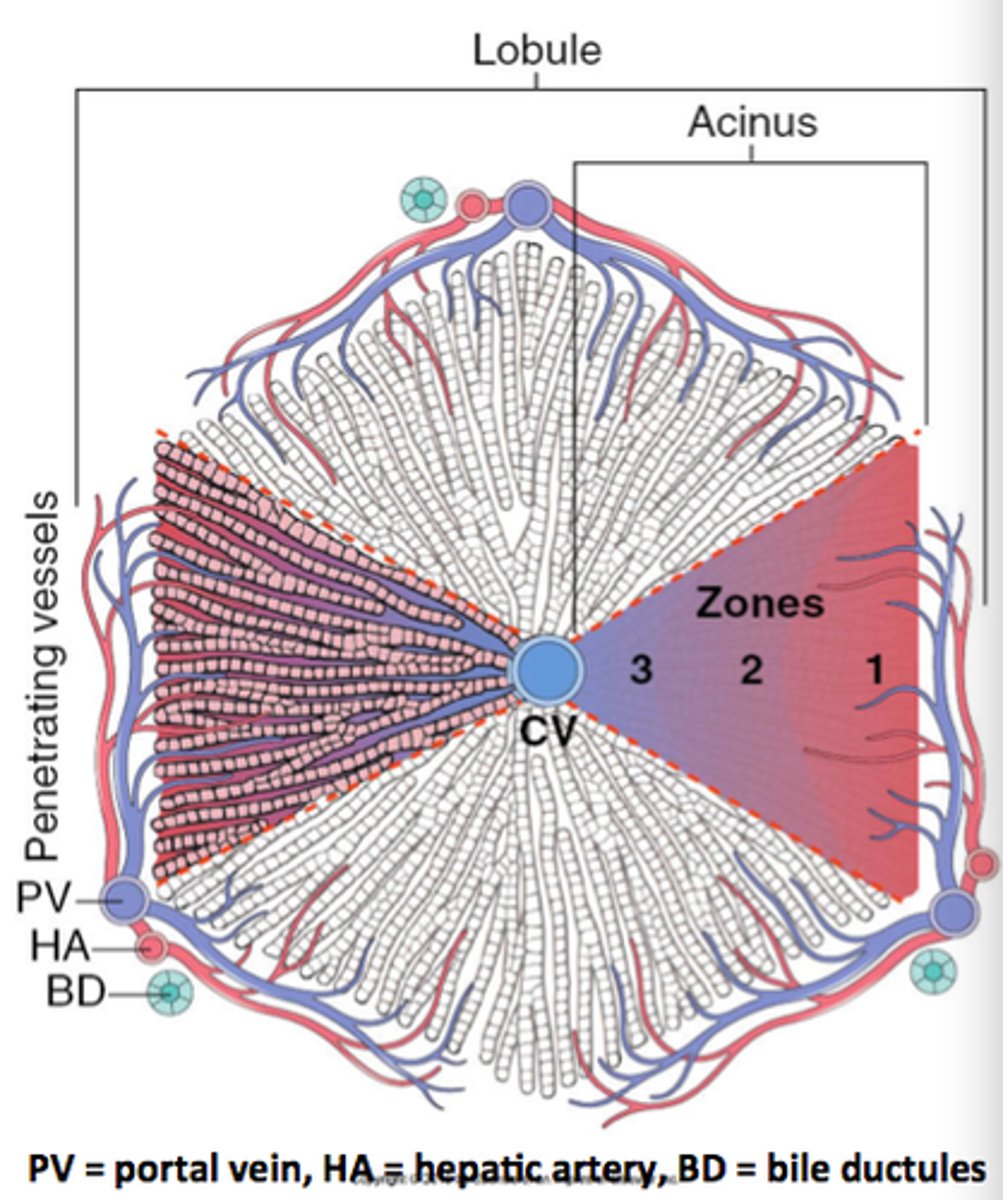
Zone 3, least O2
What zone is most susceptible to injury? Why?
ALT, AST, LDH
Which lab tests evaluate hepatocyte integrity?
Ammonia
What lab test best supports a diagnosis of hepatic encephalopathy in a patient with asterixis and coagulopathy?
Bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, GGT
Which lab tests evaluate the biliary tract?
Albumin, coagulation factors, ammonia
Which labs tests evaluate hepatocyte function?
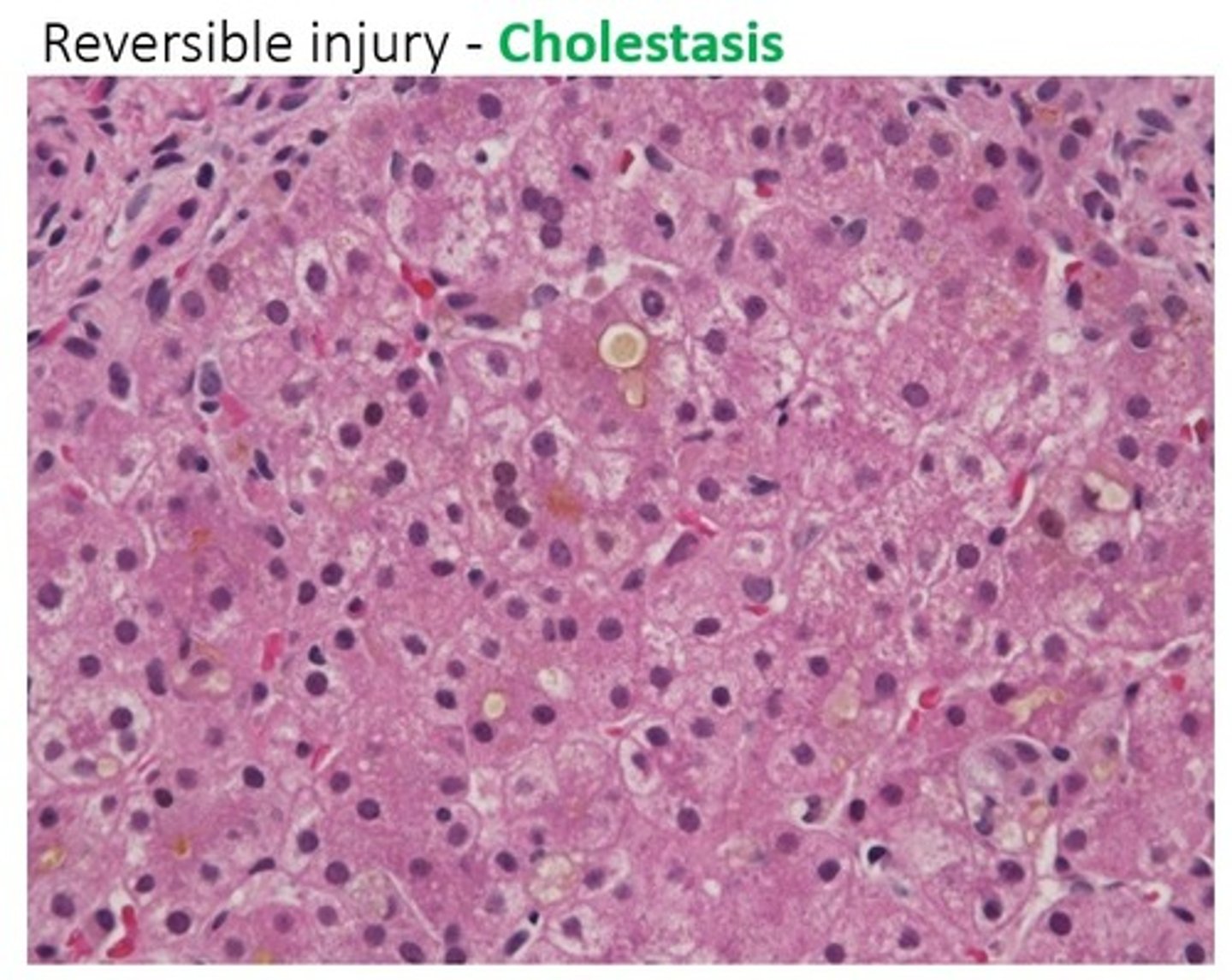
Feathery degeneration
What pattern of injury is seen with cholestasis, such as 2/2 bile stone obstruction?
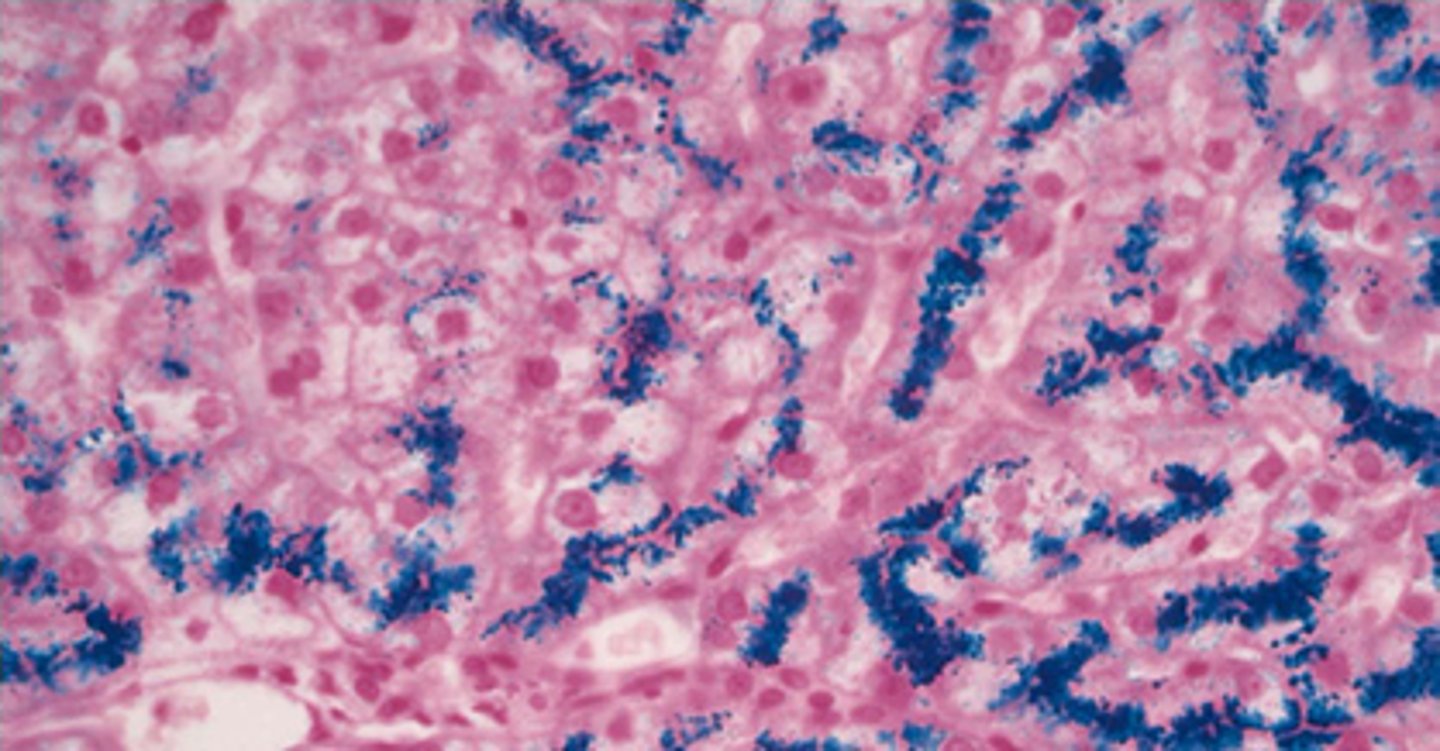
Hemochromatosis, iron
If this is a prussian blue stain of the liver, what is the diagnosis? What is all the blue?
Left gastric and azygous veins
What is the porto-systemic shunt associated with esophageal varices?
Paraumbilical and epigastric veins
What is the porto-systemic shunt associated with caput medusa?
Super rectal and middle/inferior rectal veins
What is the porto-systemic shunt associated with rectal varices/hemorrhoids?
Increased resistance to hepatic blood flow (aka portal HTN)
What mechanism directly contributes to the development of ascites in cirrhosis?
Hyperestrogenism
What mechanism directly contributes to the development of palmar erythema, spider angiomas, testicular atrophy, and gynecomastia in cirrhosis?
Nothing, hepatorenal syndrome caused by decreased perfusion (pre-renal)
A patient with cirrhosis develops oliguria, elevated BUN, and elevated creatinine. What would you expect to renal biopsy? Why?
Gilbert syndrome, none
An 18 year old male presents with jaundice, onset x2 weeks. No symptoms. Brother has similar episodes. Bilirubin is elevated, mostly unconjugated. Normal transaminases, normal alk phos, urine normal. Best diagnosis? Treatment?
Lymphocytes
What cell dominates in acute viral hepatitis?
Chronic HBV
What diagnosis is characterized by "ground glass" hepatocytes?
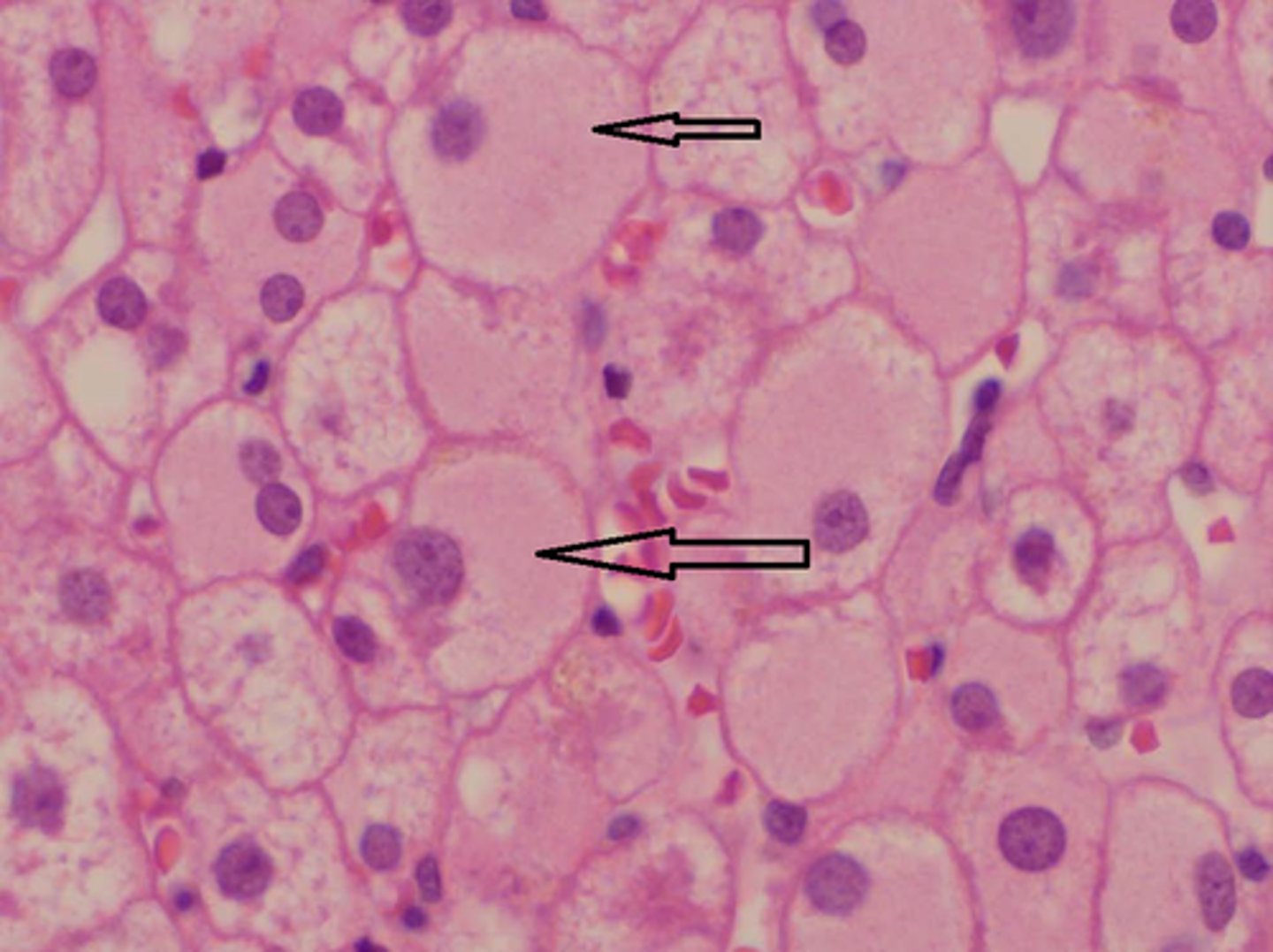
Cholestasis
Accumulation of bile pigment in Kupffer cells is consistent with:
Fecal-oral
How is Hep A transmitted?
2-4 weeks, second half of incubation before symptoms
What is the incubation for Hep A? When is it most infectious?
Presence of Hep B (either coinfection at same time or superinfection of already present HBV)
What does Hepatitis D require for infection?
Parenteral AND vertical
How is hepatitis B transmitted?
Hepatitis B
Which hepatitis virus is the only one that is NOT an RNA virus?
HDV superinfection of chronic HBV
Which hepatitis virus has the highest chance for causing fulminant hepatocyte necrosis?
Hepatitis E
Which hepatitis virus causes a high mortality rate in pregnant women?
No proofreading in RNA polymerase means more mutations
Why is hepatitis C likely to cause chronic disease?
Type 2 autoimmune hepatitis
What diagnosis is best associated with elevated IgG and positive ALKM-1/ALC-1?
Type 1 autoimmune hepatitis
What diagnosis is best associated with elevated IgG and positive ANA/SMA/AAA?
Cytoplasmic intermediate filaments (keratin)
What are Mallory-Denk bodies?
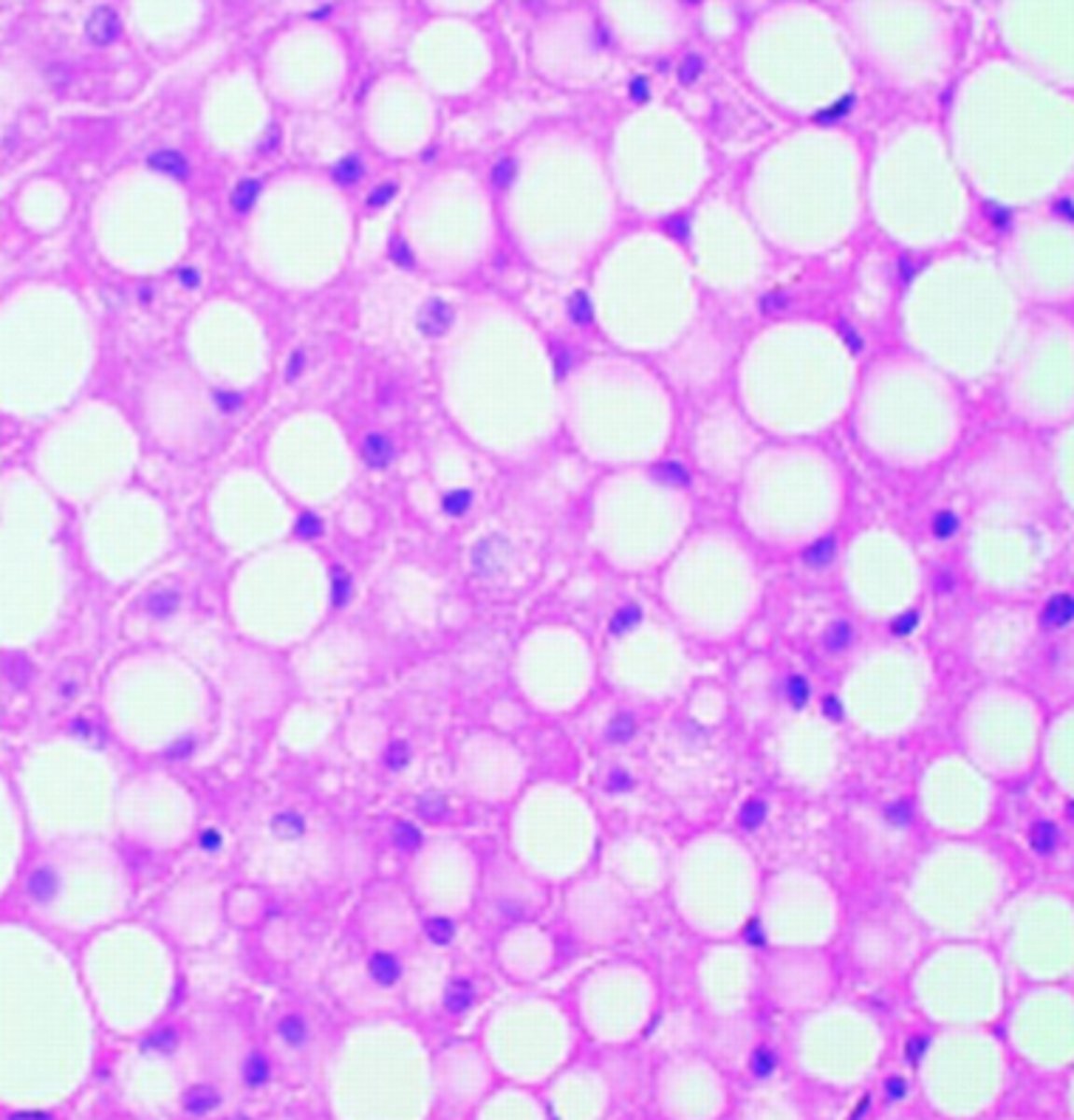
Steatosis
Diagnosis?
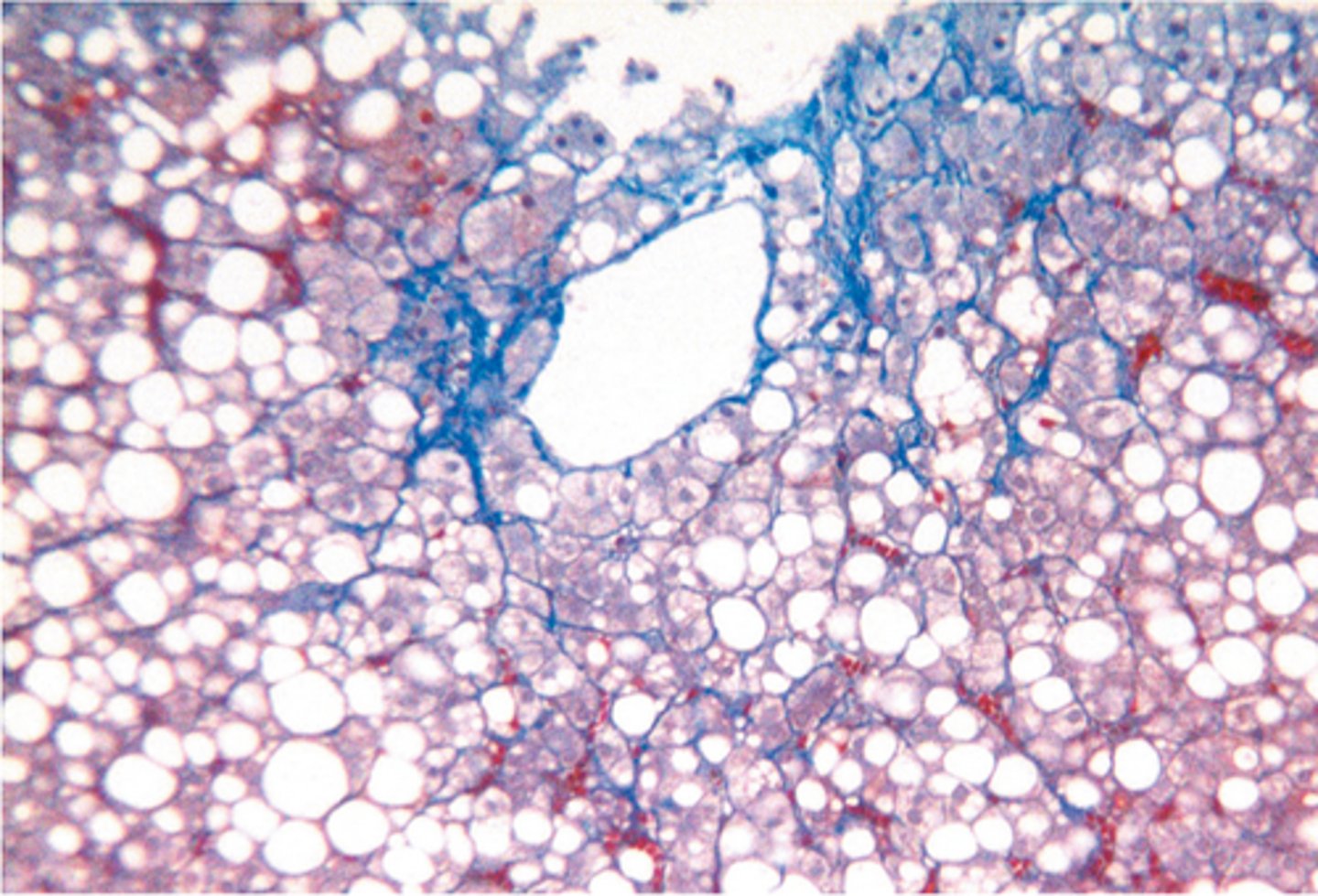
Steatofibrosis
Diagnosis?
Hepatocytes
In hereditary hemochromatosis, excess iron is stored in the:
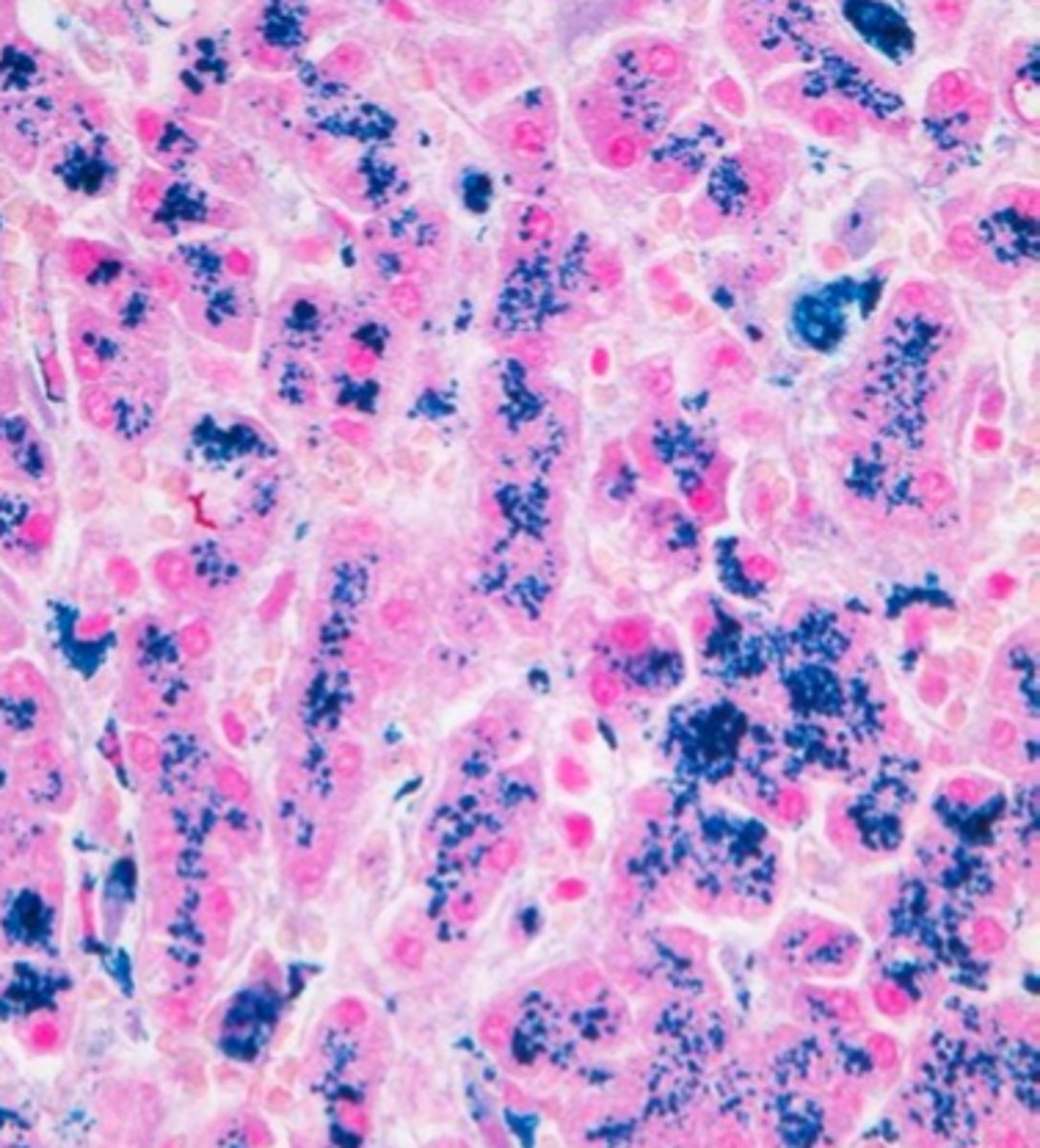
Kupffer cells
In secondary hemosiderosis, excess iron is stored in the:
HFE mutation causes low hepcidin and unregulated iron absorption
What causes hemochromatosis?
Low ceruloplasmia, high urine copper
What labs would you expect associated with Wilson's disease?
Basal ganglia
In addition to the liver, the copper in Wilson's disease is also toxic to the:
Alpha 1 AT deficiency
PAS + globules on liver biopsy in a patient with panacinar emphysema suggests:
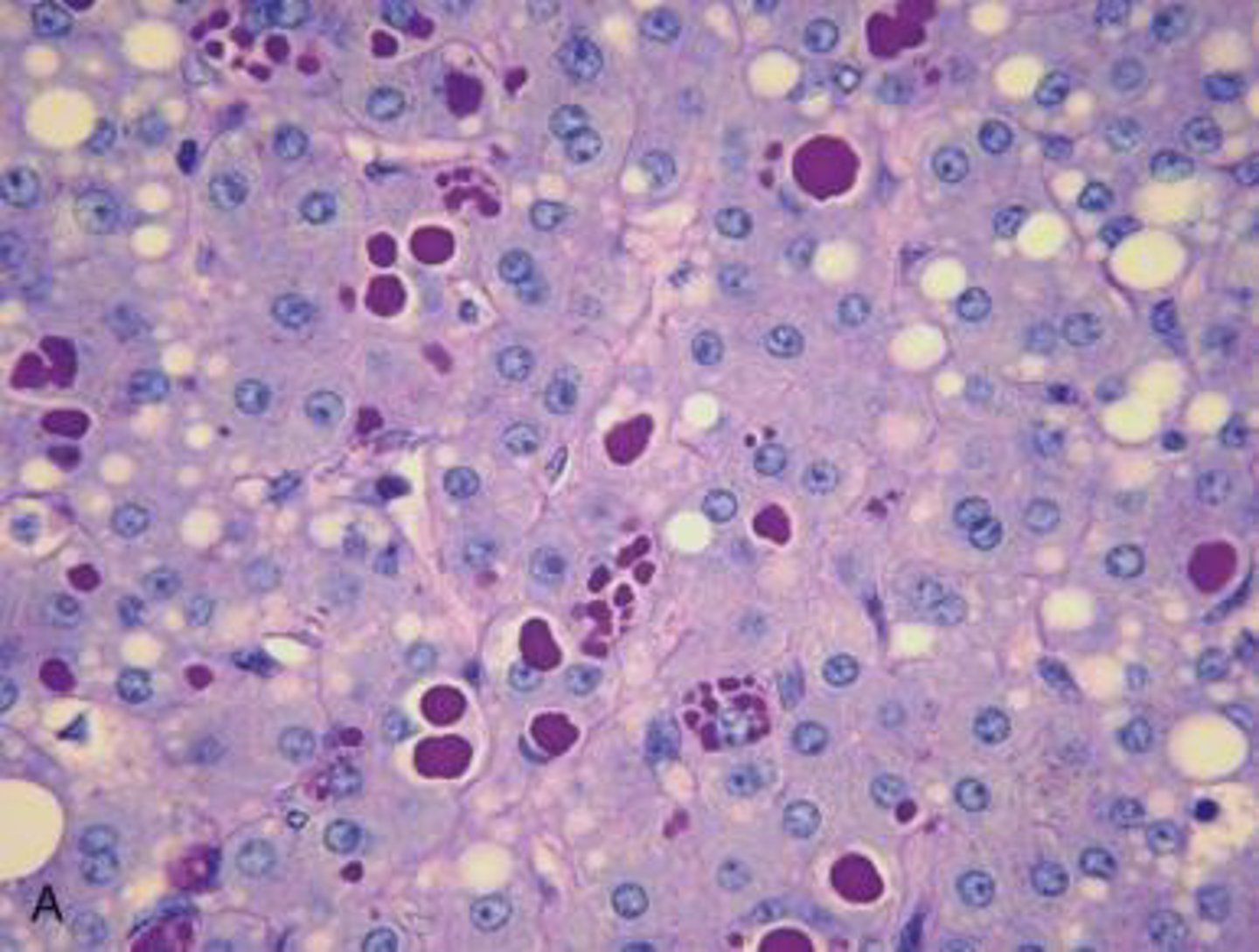
After 6 months if chronic (otherwise, many acute will resolve)
When should a patient with Hepatitis B get a liver biopsy?
Serial AFP and serial US
How should HCC screening be performed?
Autoimmune hepatitis, steroids
A 35 year old woman presents with fever, fatigue, and icterus. Bili is elevated, neg viral hepatitis serology, negative AMA. Liver biopsy shows parenchymal and periportal lymphocytes and many plasma cells. Diagnosis? Treatment?
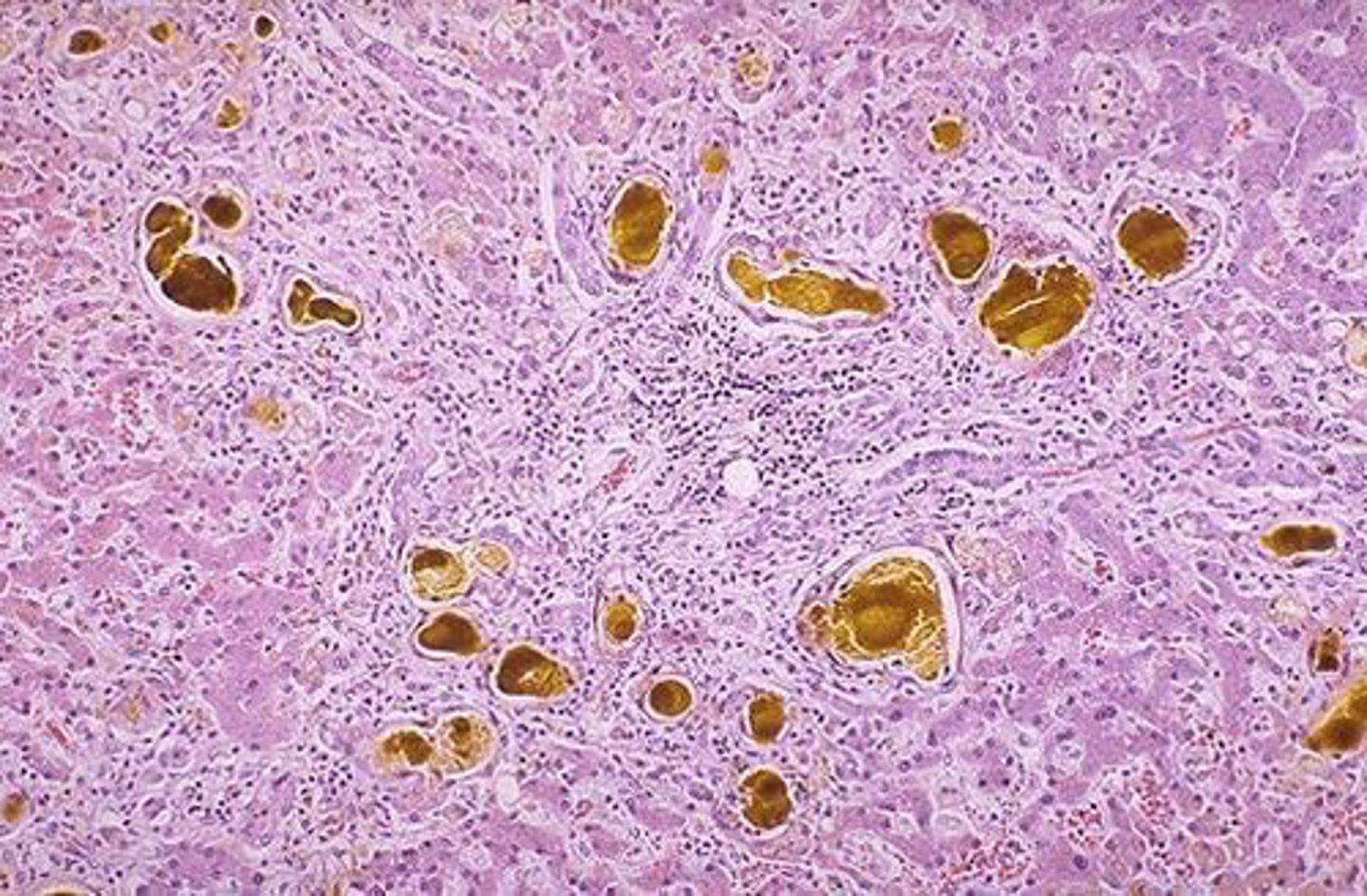
Hemochromatosis (Bonus: Restrictive/dilated cardiomyopathy and HCC)
A 50 year old man has diabetes mellitus and progressive skin hyperpigmentation. His father died of liver disease. Biopsy shows blue granules in hepatocytes on Prussian blue stain. Diagnosis? (Bonus: What else is he at risk for?)
Extrahepatic cholelithiasis (gallstones), pancreatic head cancer, stricture post-biliary surgery
What are possible causes of large bile duct obstruction in adults?
Biliary atresia, cystic fibrosis, choledochal cyst
What are possible causes of large bile duct obstruction in children?
<2 weeks
Physiologic jaundice of the newborn lasts:
Hepatic artery (high O2) and portal vein (low O2)
The liver receives blood from both:
Portal vein thrombus, schistosomes
Impaired "inflow" to the liver may occur from:
Budd-Chiari syndrome (hepatic vein thrombosis), centrilobular necrosis and hemorrhage
A pregnant patient presents with painful hepatomegaly, ascites, and RUQ pain. She is a smoker, takes OCPs even though they clearly didn't work, and also has polycythemia vera. Life is tough for her. What is the diagnosis? What would you expect on liver biopsy?
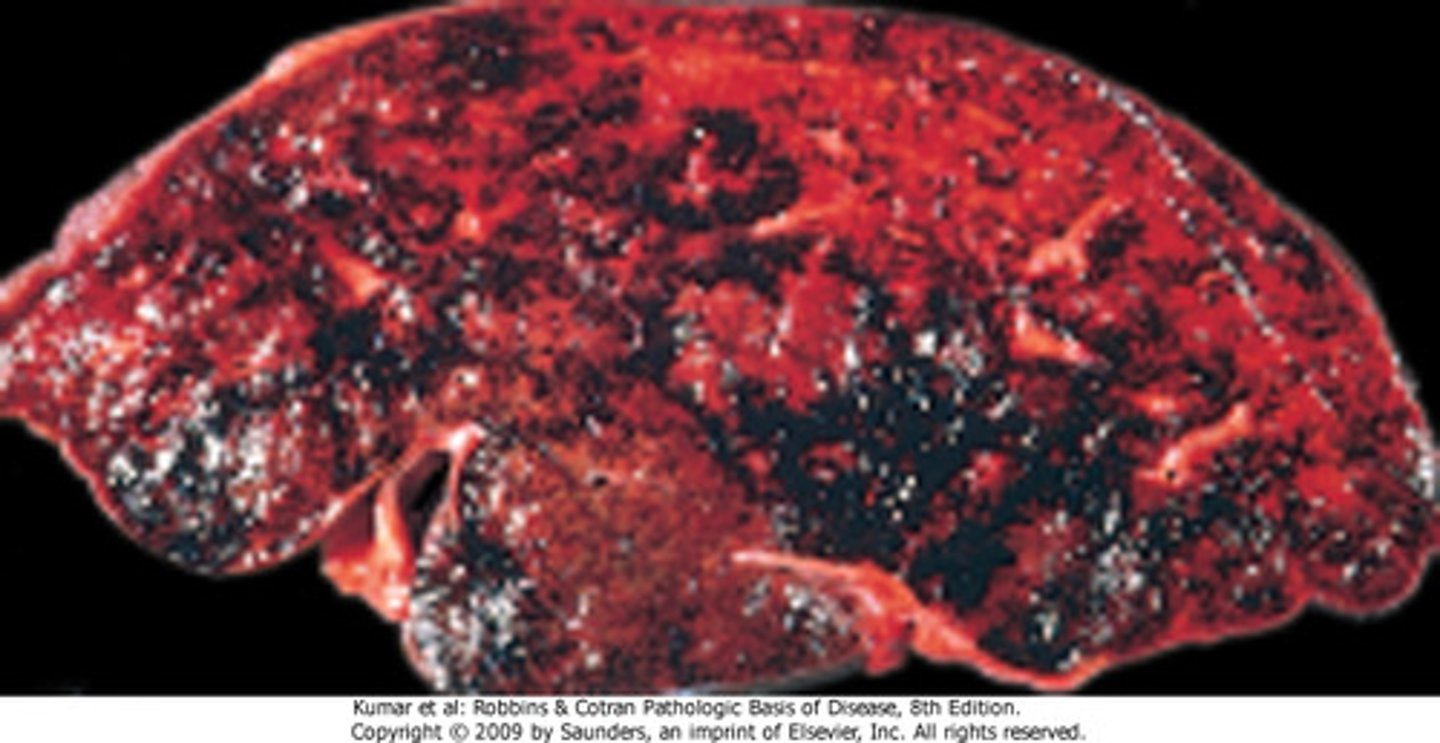
Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome
A patient undergoes a bone marrow transplant and is undergoing chemotherapy because life isn't fair. He drinks a lot of bush tea from Jamaica. What diagnosis might be associated with these risk factors?
Nutmeg liver
Acute passive congestion of the liver with centrilobular hemorrhagic necrosis secondary to right heart failure is also called:
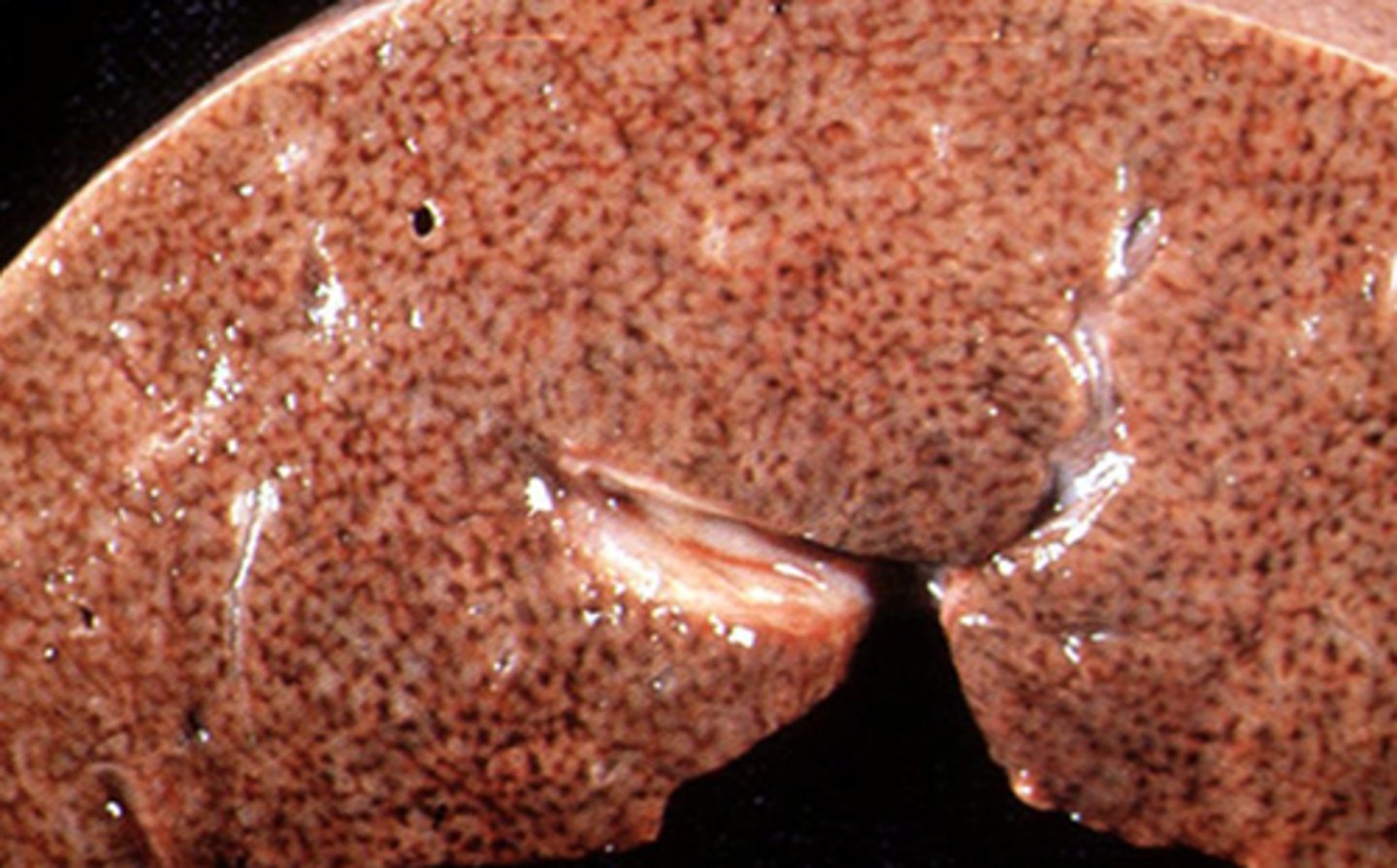
3rd trimester, delivery
When does acute fatty liver of pregnancy present itself? What is the treatment?
Radiolucent
Cholesterol gallstones are ________, meaning they don't show up on x-ray
Hypersecretion of cholesterol and supersaturation of bile salts and lecithins
What is the pathophysiology of cholesterol gallstones?
Outpouching of gallbladder mucosa into muscularis (pseudodiverticulum), chronic cholecystitis
What is a Rokitansky-Aschoff sinus? What condition is it characteristic of?
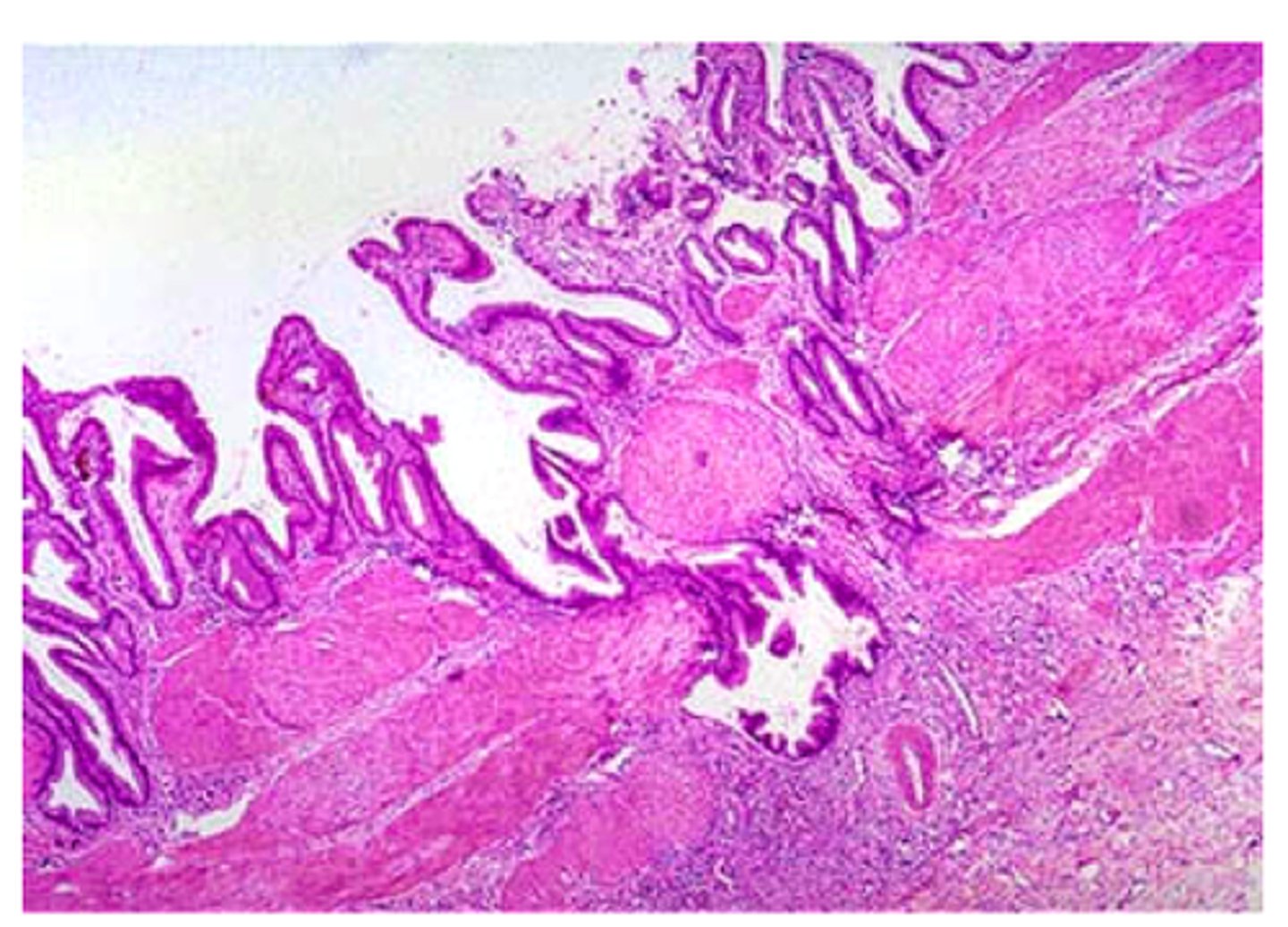
Ducts, bicarb
Secretin triggers the _____________ of the pancreas to secrete ___________
Acinar cells, lipase/amylase
CCK triggers the ____________ of the pancreas to secrete ________
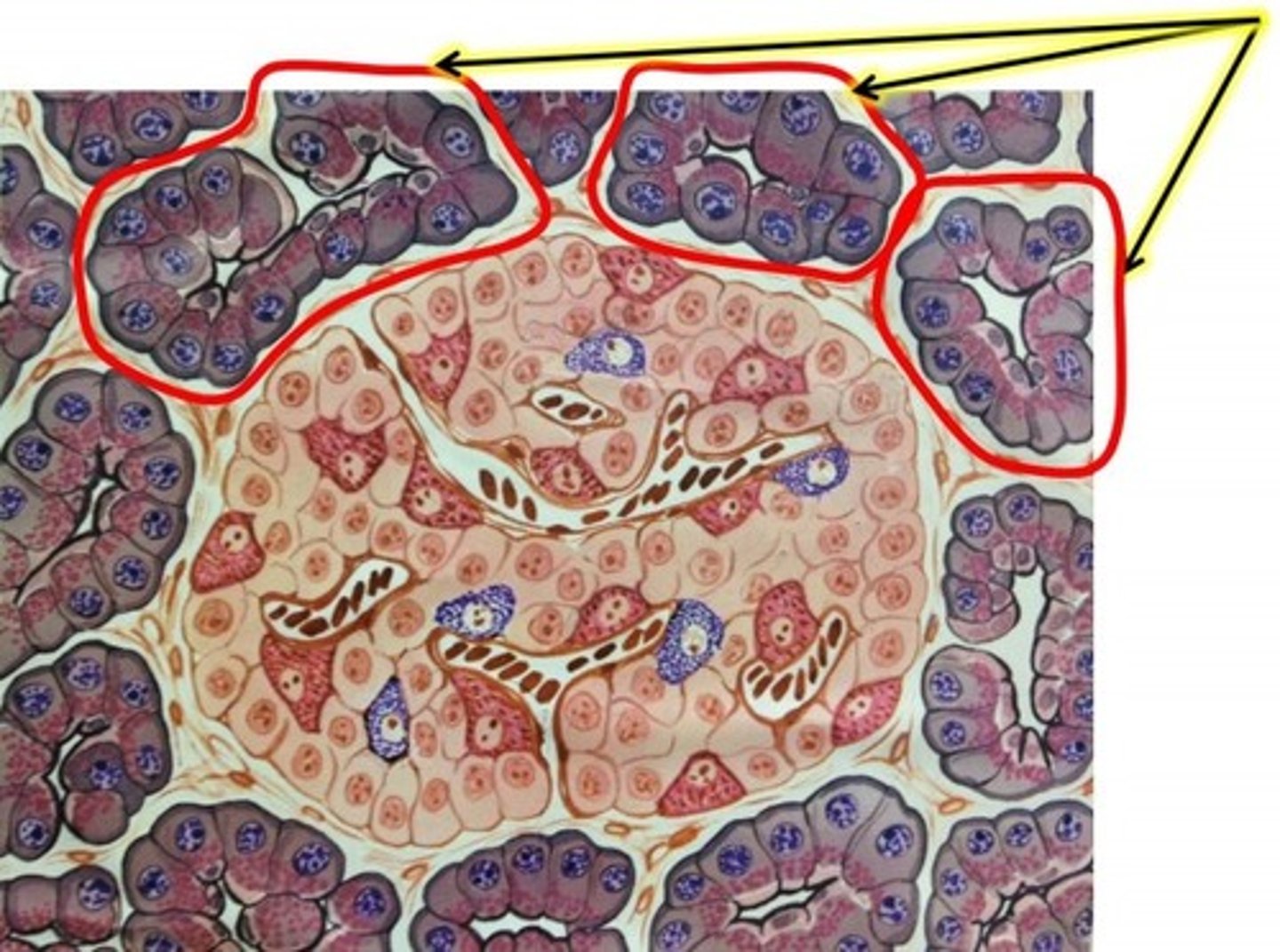
Proenzymes in zymogen granules, must be activated by trypsin, which itself has to be activated in the duodenum
Why doesn't the pancreas digest itself under normal conditions if the acinar cells secrete digestive enzymes like amylase and lipase?
Alcoholism and gallstones
The top two causes of acute pancreatitis are:
Lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis
Autoimmune pancreatitis is also called:
Pseudocysts (no epithelium, filled w/ enzymes)
Both acute and chronic pancreatitis can be complicated by formation of:
Diabetes, malabsorption, chronic pain
Chronic pancreatitis may destroy acinar cells, then islets, leading to:
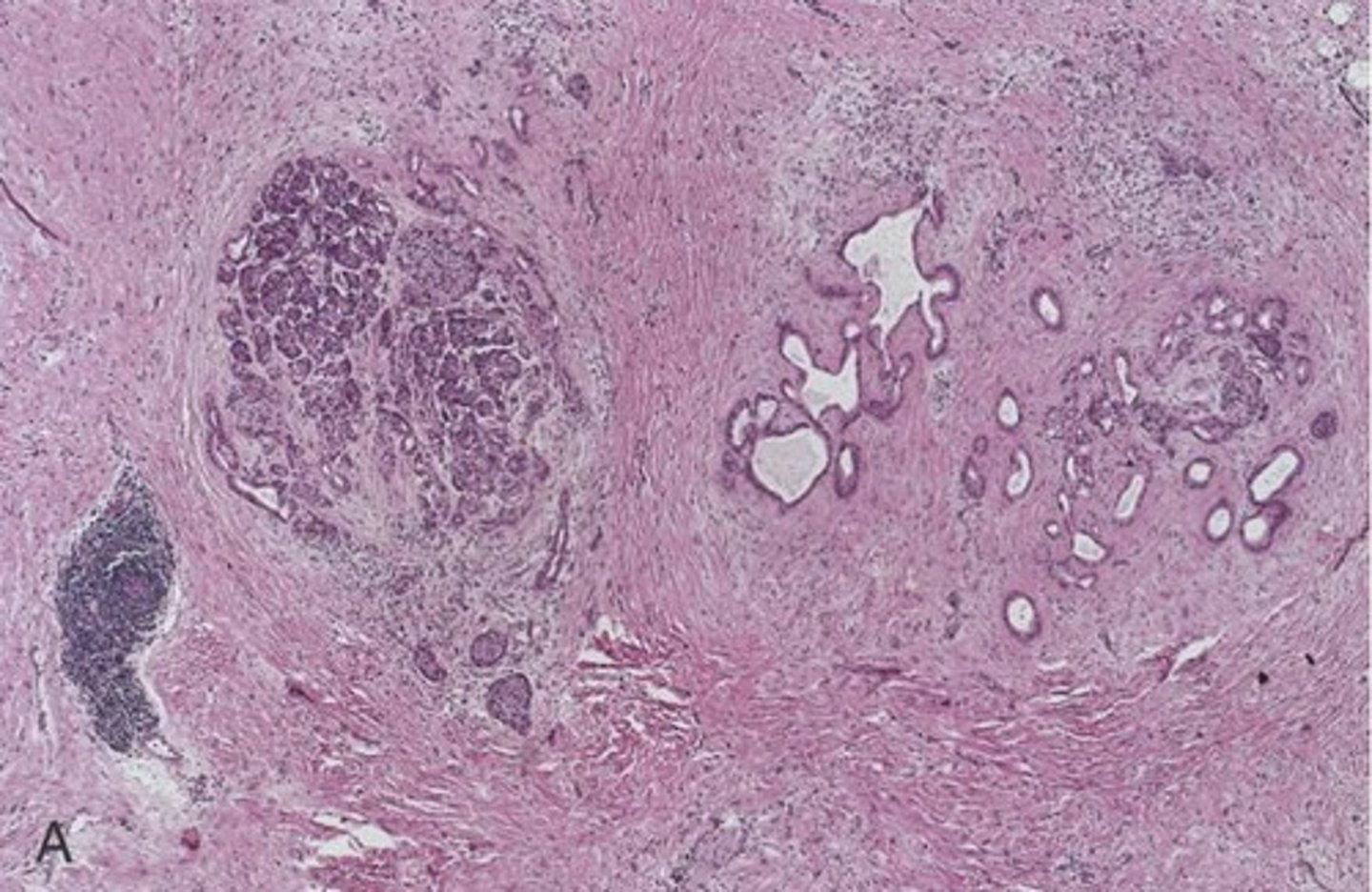
Fat necrosis/saponification
Acute pancreatitis is characterized by:
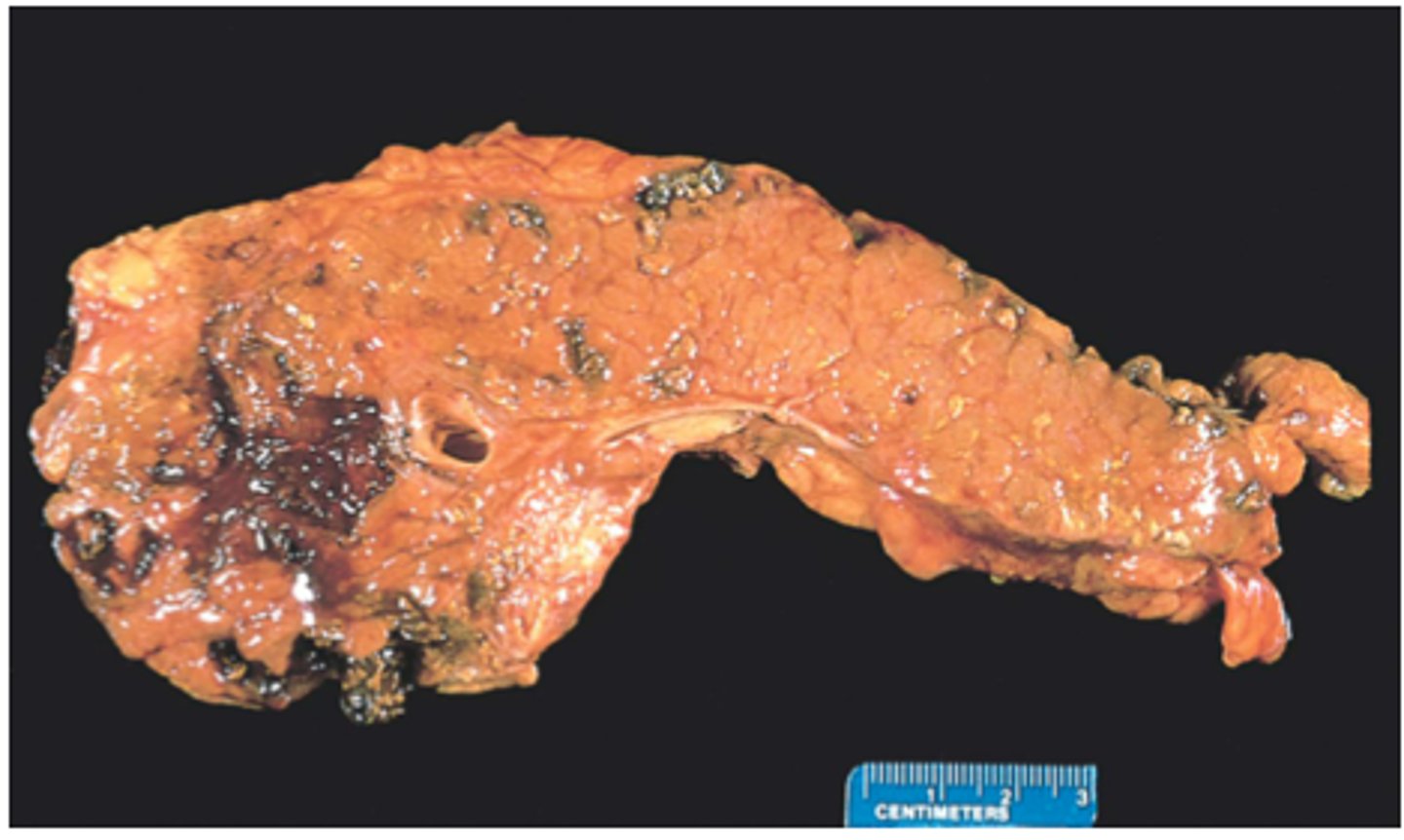
Ductopenia and regenerative nodules (biliary cirrhosis)
Late-stage/advanced PBC may show:
Pyogenic liver abscess (bonus: bacteria spread from appendix to liver via portal vein, must be drained)
A 50 year old alcoholic presents with RUQ pain, fever, and tender hepatomegaly. He had an appendectomy 2 weeks ago. LFTs normal on labs today. Viral serology negative. US shows 4cm liver mass. Diagnosis? (Bonus: Explain pathogenesis and treatment)
Drugs, ischemia, ERCP
Other than alcohol and gallstones, acute pancreatitis may be caused by:
Amylase (shows up first, then lipase)
You are treating a patient admitted to the hospital for acute pancreatitis. At the ED last night, his amylase and lipase were both very elevated. What lab should you check to see if any acute pancreatic injury is still ongoing?