Heme Metabolism and Disorders
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
bilirubin
human adults form 250-350mg of ____ per day, a toxic waste product from the breakdown of heme that must be eliminated by hepatocytes
hemoglobin
human adults turn over approximately 6g of ______ daily
iron (Fe) → recycled
heme → bilirubin (toxic waste product)
globin chains → amino acids (recycled)
biliverdin
1.RBCs removed from circulation by spleen, heme librated from hemoglobin
2.heme oxygenase converts heme into _____ (green tetrapyrrolic bile pigment)
gives the greenish color to healing bruises (ecchymosis/hematoma)
Bilirubin normal metabolism
unconjugated
Biliverdin reductase converts biliverdin → ________ bilirubin (indirect bilirubin) which is transported to the liver and bound to albumin
*not water soluble!
bile
1.in the liver, bilirubin-UDP-glucuronosyl transferase converts unconjugated bilirubin → conjugated bilirubin (direct bilirubin) with addition of glucuronic acid
2.Conjugated bilirubin is incorporated into _____, secreted into GI tract to ingest fatty foods → excreted in the stool
*water soluble
urobilinogen
In the terminal ilium and colon bacteria reduce some bilirubin to ______ (colorless), which is oxidized to urobilin and excreted in stool
porphyria (general)
Etiology
-caused by alterations in the eight enzymes of heme biosynthesis
-requires a genetic mutation + environmental insult
Pathophysiology
-porphyrinogens spontaneously oxidize to the inactive form (porphyrin) which increases levels in plasma, urine, stool, skin
Clinical Presentation: cutaneous (photosensitivity) or acute (neurovisceral)
porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT)
Epidemiology/Risk Factors
-most common porphyria overall, most common cutaneous porphyria
-usually adults, seen with liver disease due to changes iron metabolism
Etiology
-Deficient activity of fifth enzyme (UROD) of heme biosynthesis, an acquired inhibition
porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT)
Pathophysiology
-Porphyrins that accumulate are transported to skin, cause phytotoxic damage with exposure to light
Clinical Presentation
-chronic, blistering cutaneous photosensitivity and scarring of skin
Evaluation
-Total porphyrins (plasma or urine)
porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT)
Which disorder of heme metabolism presents in adults with chronic, blistering cutaneous photosensitivity and scarring of skin?
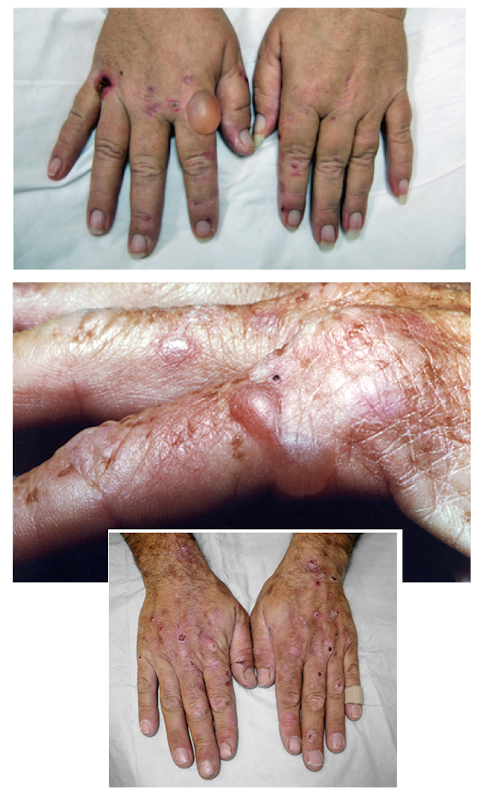
acute intermittent porphyria (AIP)
Epidemiology/Risk Factors
-second most common porphyria
-most common acute porphyria worldwide
-usually adults, N. European (Sweden)
Etiology
-Deficient activity of third enzyme (PBGD/HMBS) of heme biosynthesis due to genetic mutation + insult (increasing demand for heme production)
acute intermittent porphyria (AIP)
Pathophysiology
-Porphobilinogen (PBG) accumulates → neurotoxic effects
Clinical Presentation
1.abdominal pain (85-90%)
2. peripheral neuropathy
3. neuropsychiatric changes
Evaluation
-urine porphobilinogen (PBG)
-total porphyrins (plasma or urine)
acute intermittent porphyria (AIP)
Which disorder of heme metabolism presents with a triad of:
1.abdominal pain (85-90%)
2. peripheral neuropathy
3. neuropsychiatric changes
erythropoietic porphyria (EEP)
Epidemiology/Risk Factors
-third most common porphyria overall
-typically kids, an inherited condition (family history)
Etiology
-deficiency of the eighth enzyme (FECH) last enzyme of heme biosynthesis
erythropoietic porphyria (EEP)
Pathophysiology
-Protoporphyrin IX accumulates in bone marrow, erythrocytes, plasma
→bound to hemoglobin, light irradiation may promote release from erythrocytes
Clinical Presentation
-acute, painful non-blistering photosensitivity (typically kids/young adults)
Evaluation
-total erythrocyte porphyrins
erythropoietic porphyria (EEP)
Which disorder of heme metabolism presents with acute, painful non-blistering photosensitivity (typically kids/young adults)?
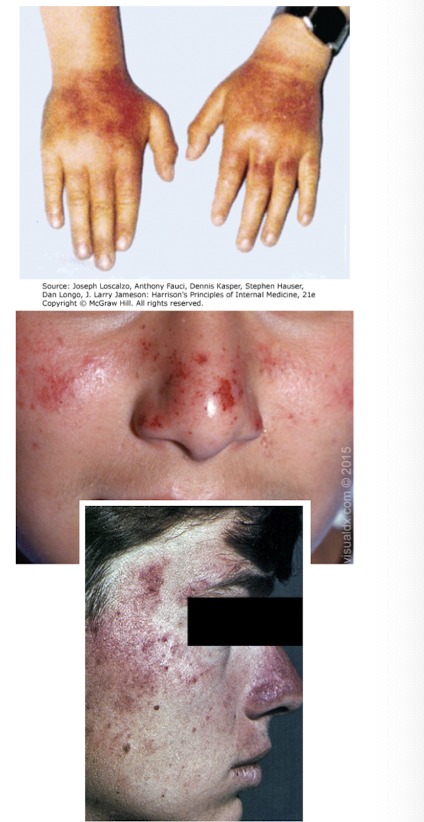
lead poisoning
Epidemiology/Risk Factors
-exposure is worse for kids (more vulnerable)
-occupational exposure (adults)
-low-income countries gasoline/industrialized uses of lead
Etiology
-ingestion of chips/dust from lead paint
-contaminated soil from gasoline emissions
→Inhalation: 30-50% retained in lungs
→Ingestion: 70% absorbed (kids), 20% (adults)
lead poisoning
In the US, highest among urban children who live in deteriorating housing built before 1970s
→ black children have statically higher risk, as well as refugee children and foster care
25 years
What is the half life for lead in mineralizing tissues (bone) and 70% of the total body burden for children?
two years
Children younger than ____ of age retain approximately 50% of absorbed lead
Half-Life:
Blood: 28-26 days
Soft tissue: 40 days
Mineralizing tissues >25 years
lead poisoning
Pathophysiology
-affects nervous system (neurocognitive deficits, hearing loss, peripheral neuropathy)
-heme biosynthesis, renal system, cardiovascular system
Clinical Presentation
-lead line deposits in gums
-skeletal lines in bones
-lead flecks in abdomen
Evaluation
-test blood lead level (BLL) via capillary (finger-stick) or venous
lead poisoning
Which condition affects heme biosynthesis interfering with the maturation of the cytoplasm, and in severe cases can observe coarse basophilic stippling of RBCs under the microscope?
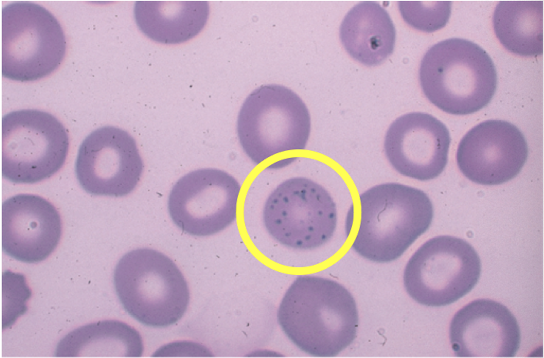
lead poisoning
Which disorder of heme metabolism presents with neurocognitive deficits, hearing loss, peripheral neuropathies and the findings pictured (typically kids/adults with occupational exposure)?
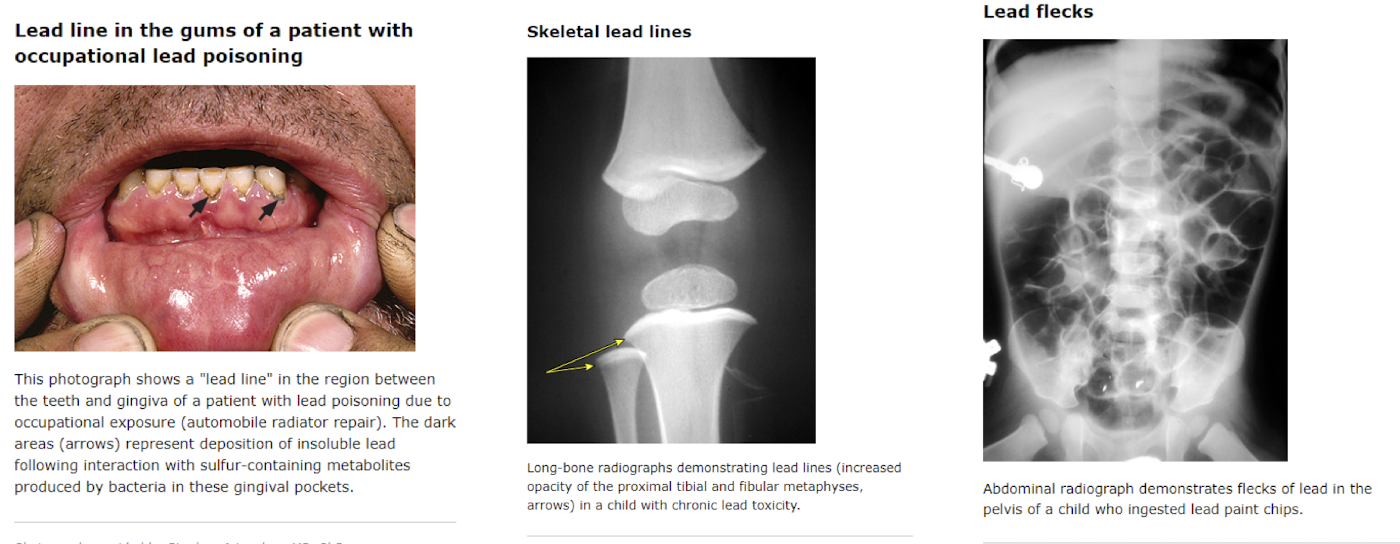
lead poisoning
Primary Prevention
No safe or nontoxic blood level exists, screening recommendations are targeted for young children (between 12-24 months) at increased risk of exposure