MGCR 352: Chapter 6 Segmentation, Targeting, Positioning
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Market segmentation
separate prospective buyers into groups:
common needs
respond similarly to marketing
What does market segmentation mean
segmentation mean finding homogenous groupings
marketers have responded w different products for each grouping
what does segmentation mean
linking market needs to organizations marketing program
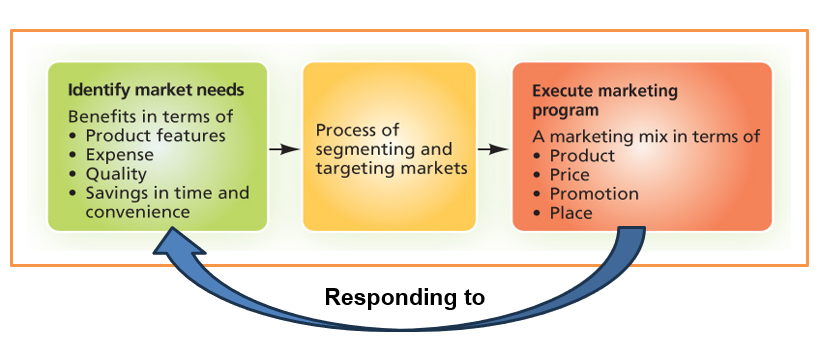
Differentiation
company positions its product or service as distinct from competitors
census metropolitan areas
geographic labour market areas having a population of 100k persons or more
What are the main product strategies used to segment markets?
One product for all segments – Same product, different marketing.
Multiple products for multiple segments – Tailored products for each group.
Segments of one (mass customization) – Personalized products at scale.
Unmet needs segmentation – New products for underserved groups.
Segmentation/Targeting Position Process
1) Strategy/Objectives
2) Segmentation bases
3) Evaluate segment attractiveness
4) select target market
5) identify and develop positioning strategy
Step 1: Establish overall strategy or objectives for segmentation
be consistent with mission statement
objectives are derived from mission/current state of capabilities
Step 2: Segmentation bases
Geographic
demographic
Psychographic
Behavioural
Geographic segmentation
divide market into separate geographic units
countries, regions, provinces, cities, neighbourhoods, climate
develop appropriate marketing program for each
Demographic segmentation
most common methods
divide market into groups based on (gender, age, ethnicity groups, etc)
census is a excellent source of segmentation data
Psychographic segmentation
how consumers describe and view themselves
self values
self concept
lifestyles
Behavioural Segmentation
benefits
usage rate
loyalty
occasion
Values, Attitude and Lifestyle
1) Values
2) Attitudes
3) Life style
qualitative methodology used to understand how consumers think and behave differently
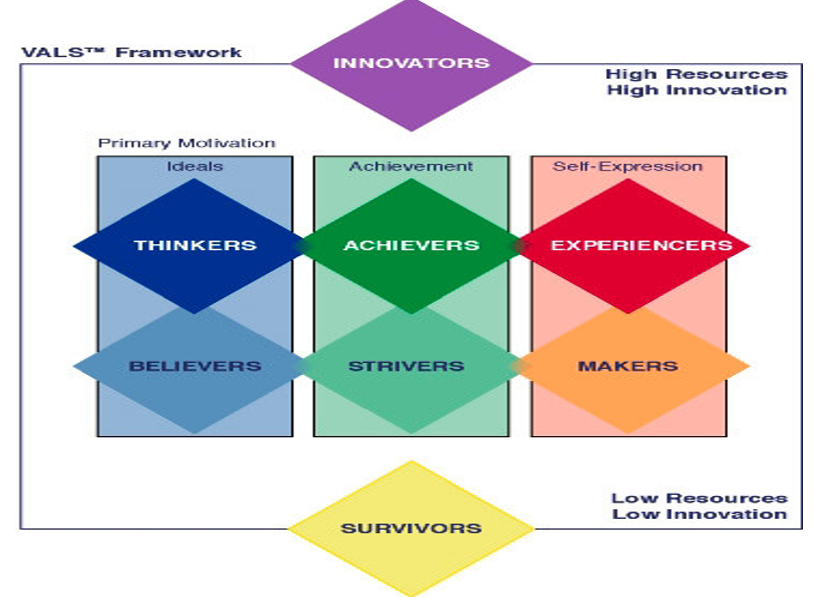
Val categories
innovators
thinkers
believers
achievers
strivers
experiencers
makers
survivors
what makes segment attractive
a) Identifiable
b)Reachable
c)Sustainable/Profitable
d)Responsive
a) Identifiable
firms must determine who is within market to design products/services to meet target markets
segments must be identifiable
b) Reachable
know products exists
understand what it can do
recognize how to buy
c) Customer Response
customers will:
react positively to firm’s offering
accept
move towards buying
d) substantial/profitable
sizes matters
too small, segment is insignificant n will not be profitable
growth potential is equally important
Step 4: Select Target Market
base on swot analysis
assess attractiveness of opportunity
consider organization’s competencies
Types of Targeting Strategies
undifferentiated
differentiated
concentrated
micromarketing
undifferentiated
mass marketing
provide same benefits for all
same strategy for all groups
Differentiated
targeting strategy
targets several market segments w different offerings for each
concentrated
fine targeting strategy
selects a single, primary target market
focuses on providing a product to fit specific market’s needs
micromarketing
one to one approach
form of segmentation that tailors product/service to suit an individual customers needs/
Step 5: Identify and develop positioning strategy
position your offerings in hearts/minds of customers by:
value
product attributes
benefits/symbolism
competition
market leadership
loyalty
product attributes
focus on attributes that are most important and varies by target markets
what are the two types of positioning against competition?
two basic options:
Position against a specific competitor’s product/services
position against an entire product classification
Positioning by Using Perceptual Mapping
1) determine consumers’ perceptions and evaluations in relation to competitors
2) identify the markets ideal points/size
3) identify competitors positions
4) determine consumer preferences
5) select the position
6) monitor the positioning strategy
Repositioning
refers to strategy in which marketers change a brand focus to target new markets
realign the brand’s core emphasis with changing market preferences