Muscular system
1/123
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BIO 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
In general, oxygen debt develops as a result of ______
strenuous exercise
define muscle tone
state of partial contraction of muscles while at rest
in what types of muscle are the myofilaments arranged into sarcomeres?
cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle
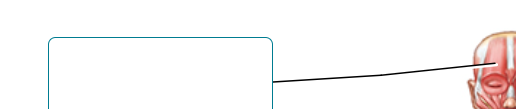
Label
frontalis
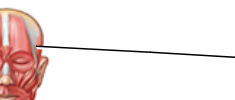
Label
temporalis

Label
Orbicularis Oris
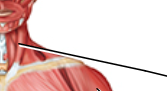
Label
Sternocleidomastoid
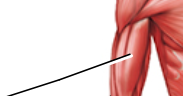
Label
biceps brachii
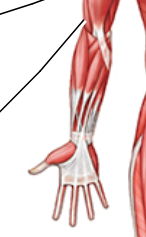
Label
Brachialis
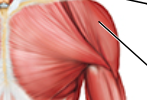
Label
deltoid
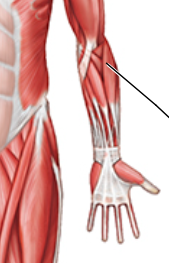
Label
Brachioradialis
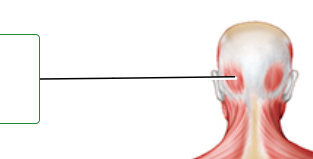
label
Occipitalis
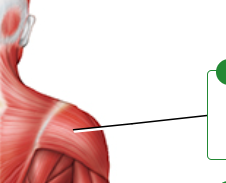
label
deltoid
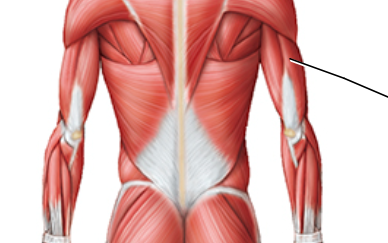
label
triceps brachii
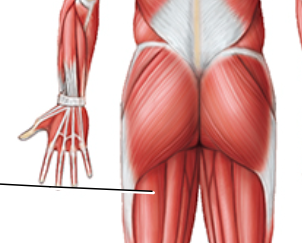
label
Biceps femoris
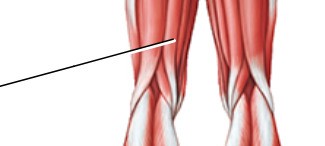
label
semitendinous
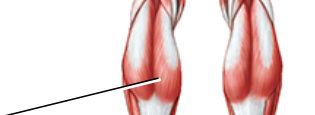
Label
Gastrocnemius
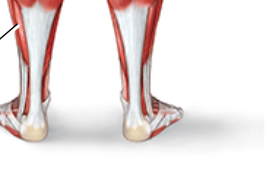
soleus
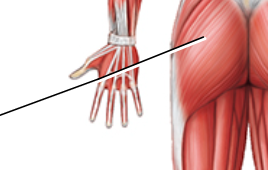
label
Gluteus Maximus
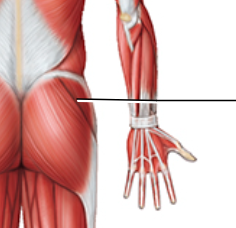
Label
Guteus medius
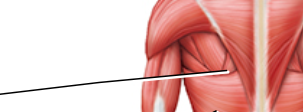
label
infraspinatus
Label
Latissimus dorsi
label
Rhomboid
label
trapezius
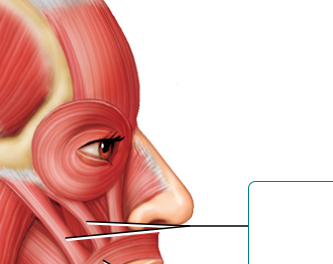
Label
zygomaticus
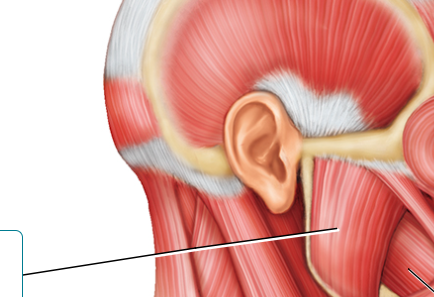
label
masseter
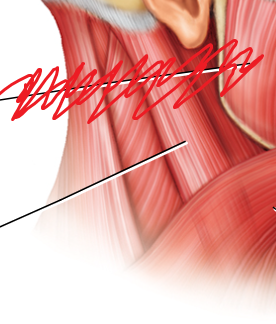
label
sternocleidomastoid
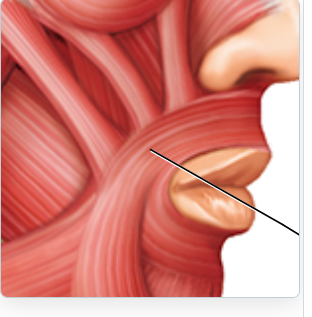
label
orbicularis oris
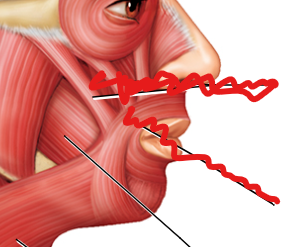
label
buccinator
label
platysma
Muscle contractions that generate less force than the resistance and result in lengthening of the muscle are called ___ contractions
eccentric contractions
which muscle is the prime mover of the shoulder abduction (abduction of the arm)?
deltoid
what word segment means “muscle”?
myo-
name the organelles that store neurotransmitter molecules within the distal end of a motor neuron axon
synaptic vesicles
what generates the force that shortens the sacromeres to bring about muscle contraction
Myosin cross-bridges pulling on the actin filaments
at neuromuscular junctions, acetylcholine binds to__
receptors in the muscle fiber membrane
when a muscle fiber stimulated at a high enough frequency that it doesn’t have time to relax, the forces of the individual twitches combine to cause stronger contractions. what is this process called?
summation
what is the name between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber at the neuromuscular junction?
synaptic cleft
muscles with attachment points on the pelvis girdle and on the femur will cause what type of movement?
movement of the thigh
when describing the roles of muscles involved in a movement, what is the role of the antagonist?
to oppose the action
Thin filaments
Actin
Troponin
Tropomyosin
Thick filaments
Myosin
What type of chemical is released by neurons? These chemicals then bind to effector cells.
Neurotransmitters
the _____ are repeating units within muscle fibers that act as the functional units of muscle contraction
sarcomeres
Within myofibrils, the area between two successive Z lines is called a(n)
sarcomere
A neuromuscular junction is a synapse between Blank______ and Blank______.
a motor neuron; a muscle fiber
What are the three types of muscles found in the human body?
Skeletal
Cardiac
Smooth
What is the name of the space between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber at the neuromuscular junction?
Synaptic cleft
Due to their shape, muscle cells are also called muscle ____
fibers
When is lactic acid produced?
During anaerobic metabolism
In order to communicate with a target cell at a synapse, a neuron releases chemicals called
neurotransmitters
Prolonged or intense exercise can lead to a condition called muscle ___
, defined as the loss of a muscle's ability to contract.
muscle fatigue
How many myofibrils and sarcomeres are found in a muscle fiber?
Each muscle fiber contains many myofibrils, each made of many sarcomeres joined end to end.
Muscle contractions generate ______, which is important for the overall functioning of the body.
heat
A skeletal muscle will typically only contract when stimulated by its motor neuron at the
neuromuscular junction
For a typical muscle fiber in its optimal state, how many action potentials generated by a motor neuron must arrive at the neuromuscular junction to reach the threshold stimulus?
Typically, a single action potential is enough to bring the muscle fiber to the threshold.
The synaptic ____ is the gap between a motor neuron and the muscle fiber at a neuromuscular junction.
cleft
When the frequency of stimulation of a muscle fiber increases, eventually the individual twitches combine by the process of ___ which results in a sustained contraction.
summation
During high-intensity exercise, anaerobic metabolism results in the production of pyruvic acid, which is then converted to ____ acid.
lactic acid
Muscle fatigue is a condition described by ____ and is usually caused by prolonged use of a muscle.
the loss of a muscle's ability to contract
A motor neuron and the muscle fibers that it controls constitute a motor ___
unit
true or false - Muscles generate heat when they contract.
true
What type of contraction involves the development of tension but no change in length?
Isometric
If a muscle fiber is subjected to stronger and stronger electrical impulses, it will initially be unresponsive until a strong enough impulse is applied which causes it to contract. The level of electrical stimulation needed to stimulate contraction is called the
threshold stimulus
The cells of ____muscle are tapered, lack striations, and have a sarcoplasmic reticulum that is not very extensive.
smooth
Why does summation result in an increased force of contraction?
Individual twitches combine due to the high frequency of stimulation.
The product of glycolysis, pyruvic acid, is converted to ______ when oxygen is not available.
lactic acid
What is the name of the structures that connect cardiac muscle cells end-to-end, allowing muscle impulses to pass freely from one cell to another?
Intercalated disc
What is a motor unit composed of?
A single motor neuron
Several muscle fibers
What structures within cardiac muscle tissue allow the entire cardiac muscle network to contract in unison?
Intercalated discs
A muscle that is generating increased tension without changing its length is undergoing a(n) ____ conttraction
isometric
The end of a muscle that is fixed (relatively immovable) is called its
origin
characteristics of smooth muscle cells.
They are not striated.
Their sarcoplasmic reticula are not well developed.
They have a single nucleus.
When describing the roles of muscles in an action, what is the role of the agonist?
To cause an action
When the frequency of stimulation of a muscle fiber increases, eventually the individual twitches combine by the process of _____which results in a sustained contraction.
summation
Cardiac muscle cells are connected by cross-bands that include components of desmosomes and gap junctions. These cross-bands are called
intercalated discs.
Muscles can act in different ways during a particular movement. What is the role of the antagonist?
To oppose the action
Structures called _____ allow action potentials to pass rapidly between cardiac cells, causing the entire cardiac muscle to contract in unison.
intercalated discs
What is the term for muscles that assist a prime mover to cause movement?
Synergists
The point of attachment for a muscle that remains relatively stationary is its
origin
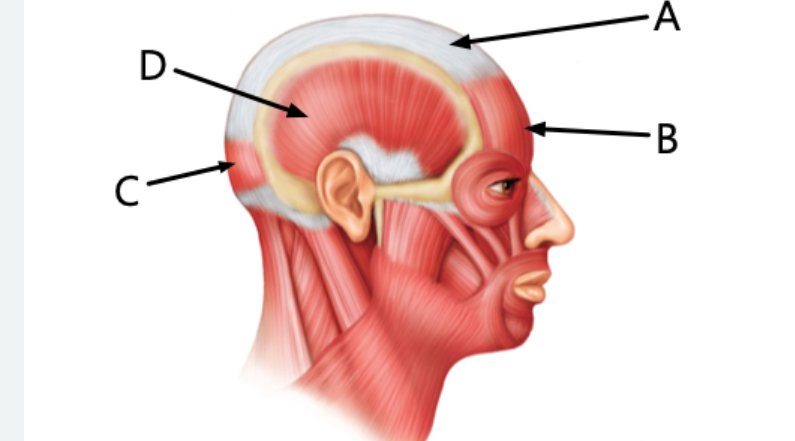
Label letter A
Epicranial aponeurosis
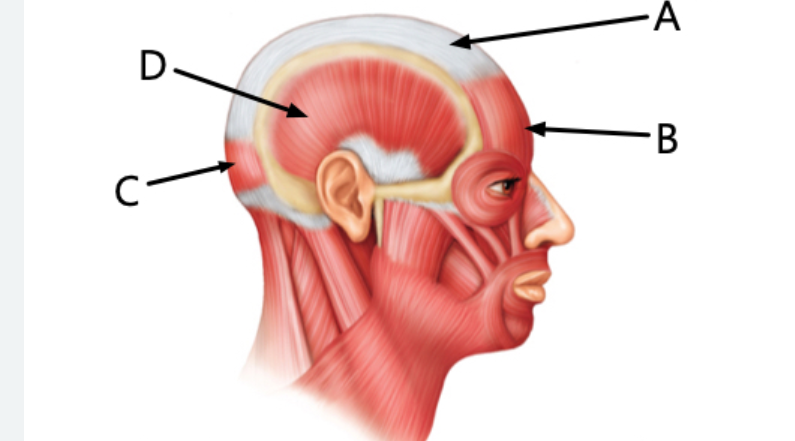
Label B
frontalis
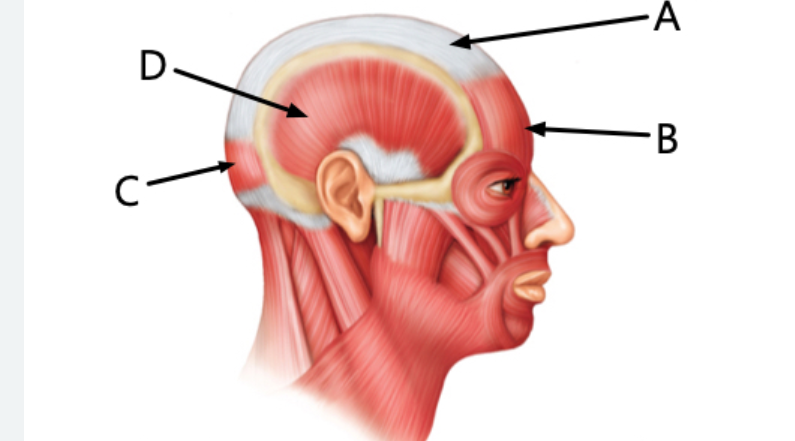
Label C
Occipitalis
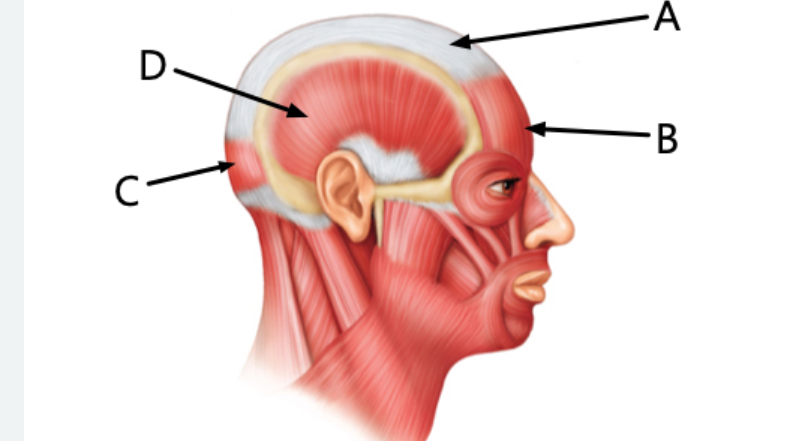
Label D
Temporalis
A muscle that functions to cause action is referred to as the
agonist
What is the action of the masseter?
It elevates mandible.
When a muscle fiber is stimulated at a high enough frequency that it doesn't have time to relax, the forces of the individual twitches combine. What is this process called?
Summation
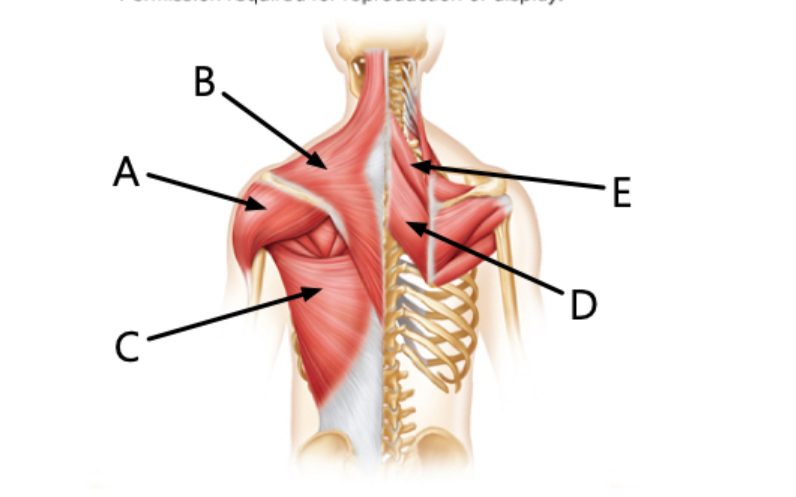
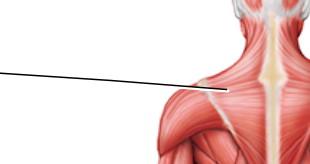
The latissimus dorsi muscle is indicated by the letter
C
A muscle that opposes the action at a joint is classified as a(n)
antagonist
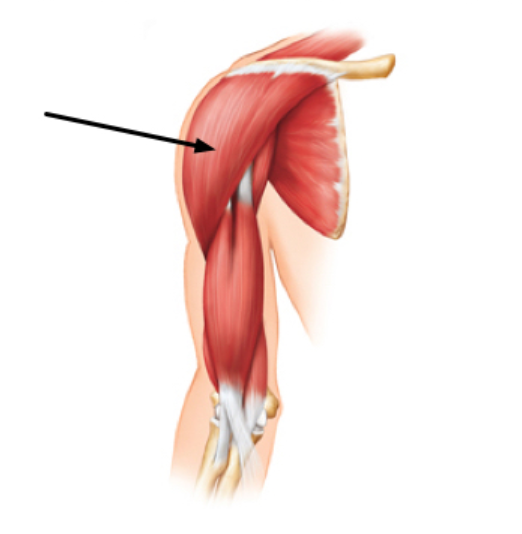
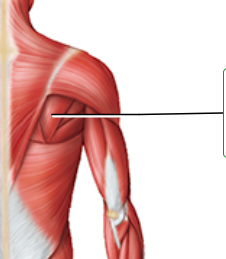
Which muscle of the anterior surface of the arm is indicated by the arrow?
Deltoid
Any muscle that assists the agonist during a movement is called a(n)
synergist
Muscles found on the______ surface of the humerus cause flexion of the forearm at the elbow.
anterior
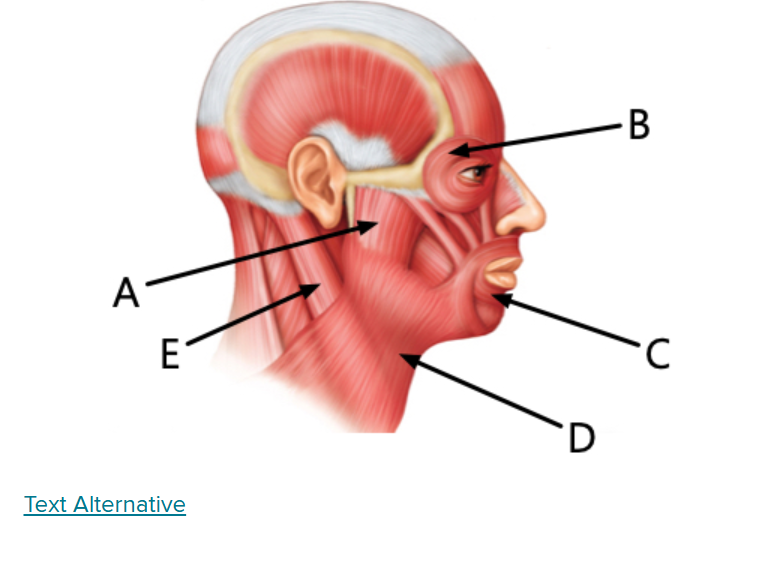
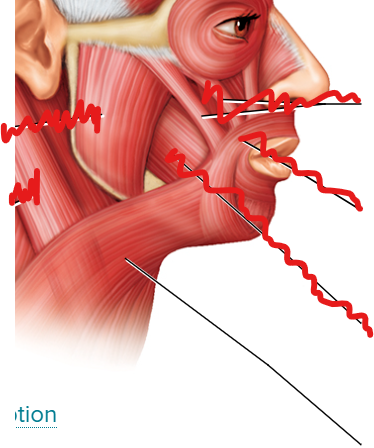
what is A
Masseter
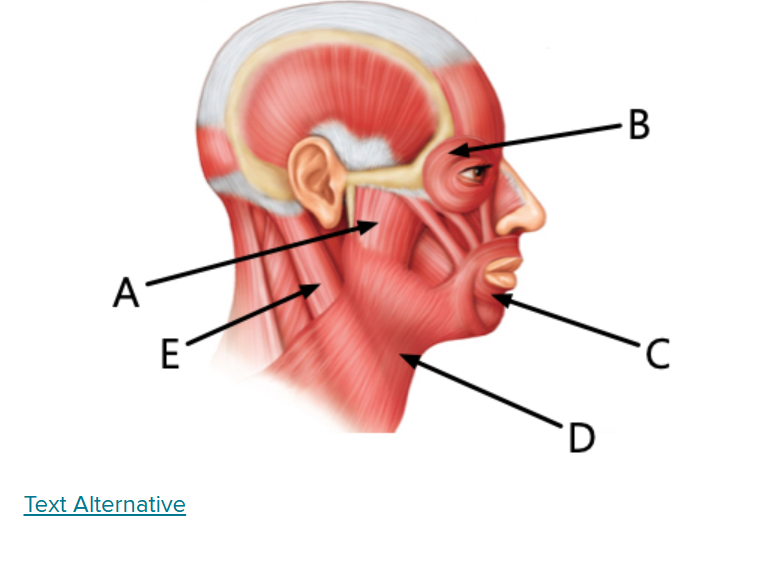
what is B
Orbicularis oculi
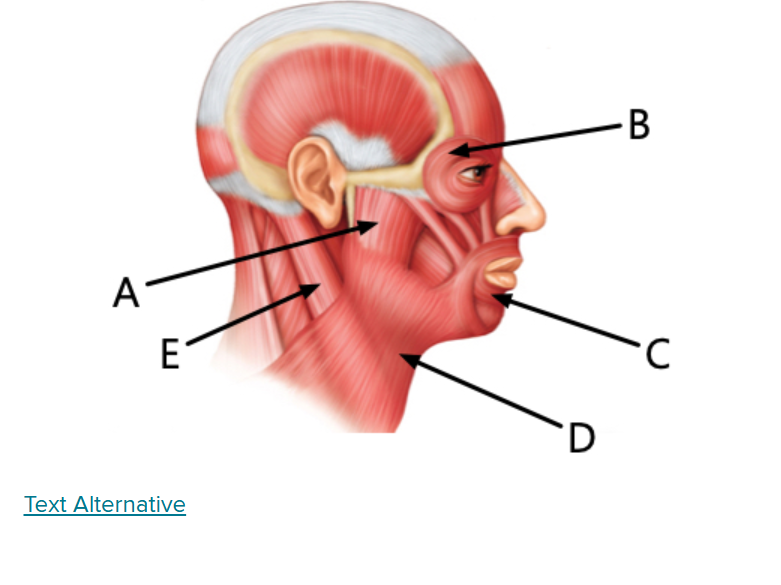
what is C
Orbicularis oris
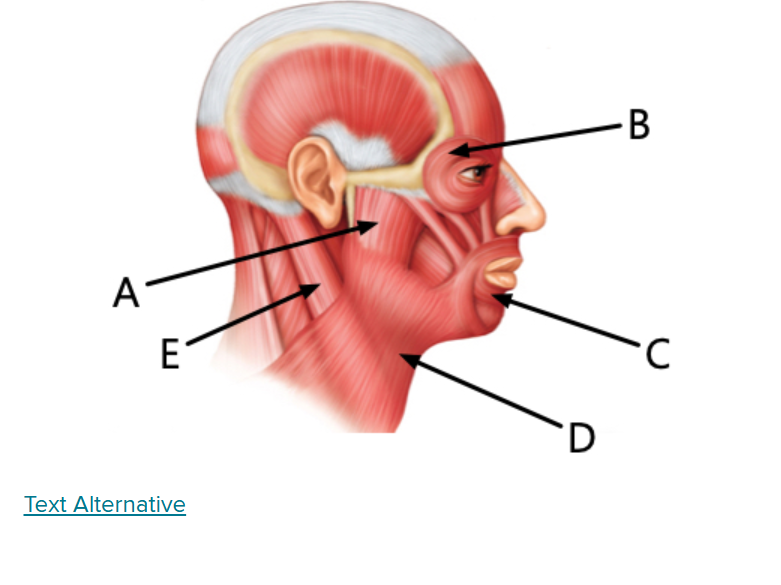
what is D
Platysma
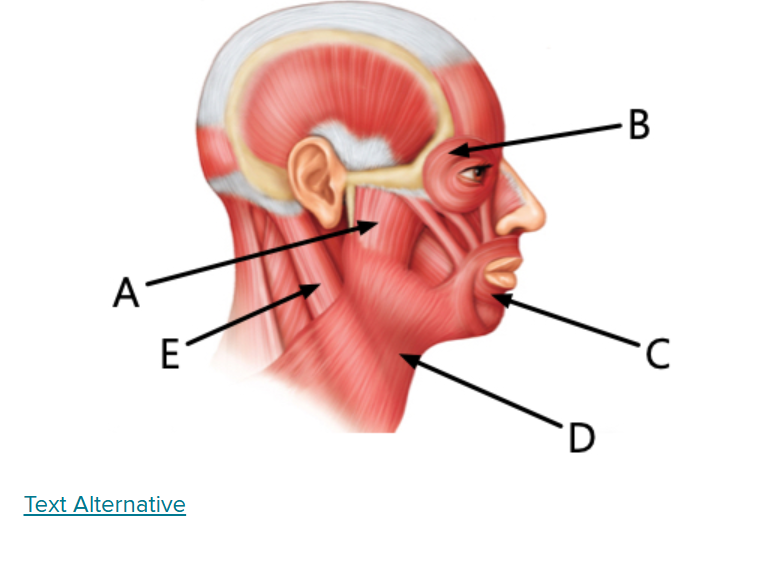
what is E
Sternocleidomastoid
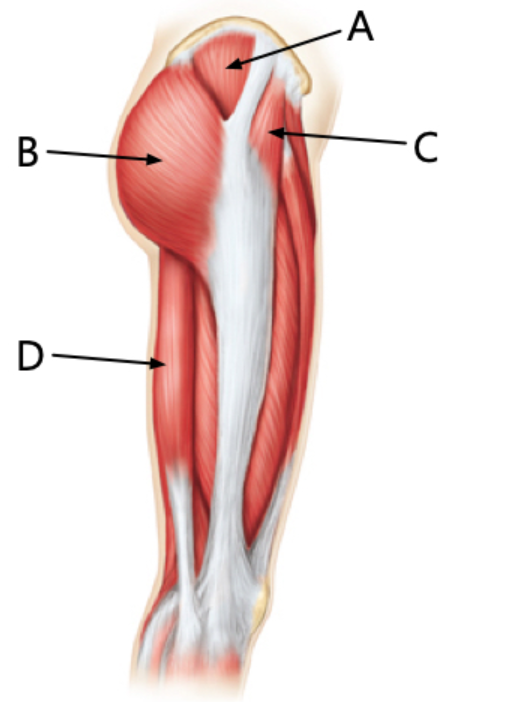
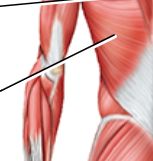
The gluteus maximus is indicated by the letter ___
. The gluteus medius is indicated by the letter
___
B & A
Which muscle elevates the mandible?
Masseter
Muscles of the ______ muscle group flex the knee and those of the ______ muscle group extend the knee.
hamstrings; quadriceps femoris