[L1] Current Resistance and Electromotive Force
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
current (i)
it is any motion of charge from one region to another
no current
when the motion of electron is random, there is ____ current
current
this requires net flow of charge in one direction
electric field
current is supplemented by ____, where it helps move electrons in a singular path
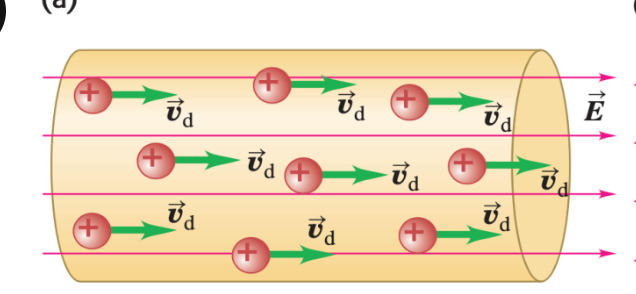
conventional current
this is treated as a flow of positive charges, regardless of whether the three charges in the conductor are positive, negative, or both
positive charges
conventional current is treated as a flow of ____, regardless of whether the three charges in the conductor are positive, negative, or both
current (it would still follow conventional current flow)
in a metallic conductor, the moving charges are electrons, but the ____ still points in the direction positive charges would flow
current
the direction in which there is a flow of positive charge
positive charge flow
we describe currents as though they consisted entirely of ____, even in cases in which we know that the actual current is due to electrons
conventional current
we describe currents as though they consisted entirely of positive charge flow, even in cases in which we know that the actual current is due to electrons. this is called ____
current (positive charge flow) is along direction of electric field
the main description of conventional current
current
it is the time rate of charge transfer through the cross-sectional area A
charge transfer, cross-sectional area
current is the time rate of ____ through the ____
scalar
current is a ____ quantity
the same
the current is in ____ direction as electric field whether the moving charges are positive or negative
ampere
the si unit for current
ampere (current)
defined to be one coulomb per second (C/s)
resistance
it is a measure of the opposition to current flow
ohm
si unit for resistance
resistivity (p)
it is a measure of the resistance of a given size of a specific material to electrical conduction
resistance, given size
resistivity is a measure of the ____ of a ____ of a specific material to electrical conduction
ohm * meter
unit for resistivity
directly proportional
resistance of an object is ____ to its length
inversely proportional
resistance of an object is ____ to its cross-sectional area
conductivity
it is the reciprocal of resistivity
resistivity
conductivity is the reciprocal of ____
(ohm * m)^-1
the unit for conductivity
larger
good conductors of electricity have ____ conductivity than insulators
low
a material with a ____ resistance has high conductivity
resistor
a circuit device made to have a specific value of resistance between its ends
resistance
resistor is a circuit device made to have a specific value of ____ between its ends
cylindrical, a few millimeters
individual resistors used in electronic circuitry are often ____, ____ in diameter in length, with wires coming out of the ends
3 or 4
the resistance of a resistor may be marked with a standard code using ____ bands near one end (how many)
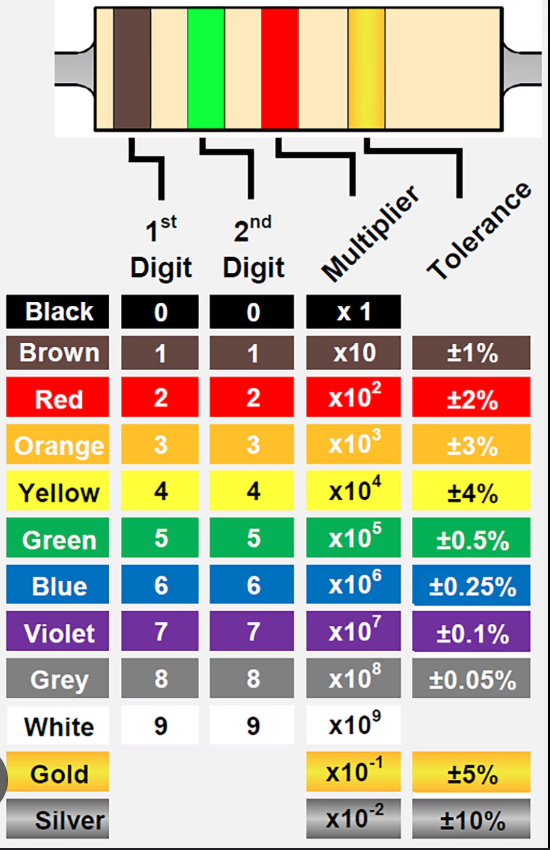
refer to chart
enumerate the color code for resistors
digits
the first two bands of a resistor are ____
multiplier
the third band on a resistor is ____
tolerance
the fourth band on a resistor is ____
voltage
this is the potential energy per coulomb of charge available to electrons moving between terminals
voltage
this provides the “electric pressure” to move electrons between the terminals in a circuit
potential difference
there must be a large ____ between the ends of a long wire in order to cause a substantial electric current through the wire
there is no charge flow
if the ends of a conductor are at the same electric potential, then ____
charge flows from one end to another
if the ends of a conductor are at different electric potentials, then ____
ohm’s law
this states that electric current is proportional to voltage and inversely proportional to resistance
directly proportional
ohm’s law states that electric current is ____ to voltage
inversely proportional
ohm’s lae states that electric current is ____ to resistance
ohmic materials
materials that obey ohm’s law are called ____
linear
for ohmic material, the current-voltage graph is ____
I/R
for ohmic material, the slope is ____
nonlinear
for nonohmic material, the current-voltage graph is ____
voltage
this produces electric current
resistance
this opposes electric current
dc circuits (direct current)
these are characterized by current whose direction does not change
ac circuits (alternating current)
these are characterized by alternating current in which it oscillates back and forth
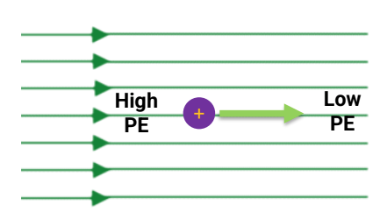
along the electric field. PE decreases
what is the natural flow of positive charges in an electric field? what will happen to its potential energy
electromotive force
the influence that makes current flow from lower to higher potential
lower to higher potential
electromotive force is the influence that makes current flow from ____ to ____
energy-per-unit charge quantity, just like epe
electromotive force is a poor term. it is not a force, but a ____ quantity
volt (same as epe)
the si unit for electromotive force
the same at the end of the round trip as at the beginning
if a charge q goes around a complete circuit and returns to its starting point, the potential energy must be ____
decrease
there is always a ____ in potential energy when charges move through an ordinary conducting material with resistance, so there must be some part of the circuit in which the potential energy increases
electromotive force
there is always a decrease in potential energy when charges move through an ordinary conducting material with resistance, so there must be some part of the circuit in which the potential energy increases. this is called
electric potential energy
sources of emfs (batteries, generators, etc.) convert energy of some form into ____ and transfer it into the circuit to which the device is connected
the same (because charge is conserved and it cannot accumulate in circuit devices)
current is ____ at every point in a simple loop
low
having a conductor with large area and shorter length will result into a ___ resistance to charge flow