Clin Lab Final Blood and Urine
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
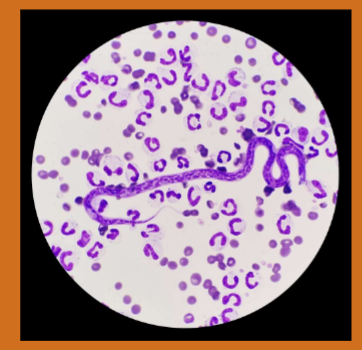
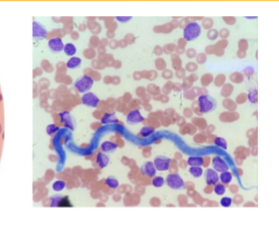
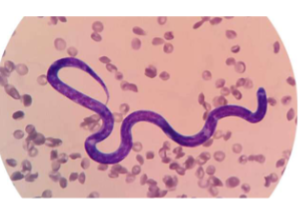
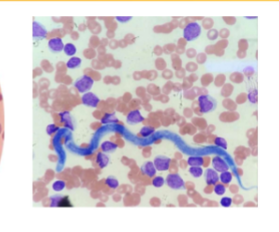
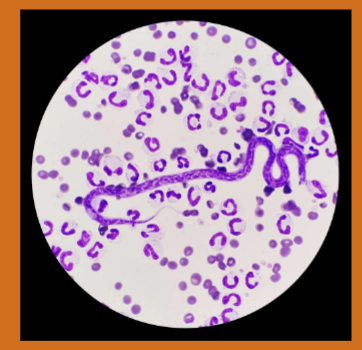
Dirofilaria immitis
Canine Heartworm
Prepatent period of Dirofilaria immitis
6 months
Where can you find Dirofilaria immitis
right ventricle and pulmonary artery
Infective stage of Dirofilaria immitis
L3
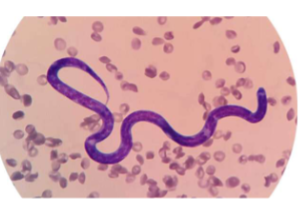
intermediate host of Dirofilaria immitis
mosquito
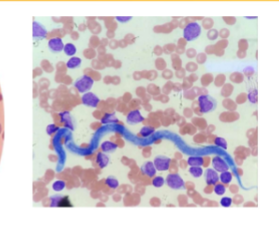
what can Dirofilaria immitis cause in dogs
right-sided congestive heart failure, fatal heart and liver failure, others are cough, ascites, and exercise intolerance
what can Dirofilaria immitis cause in cats
can be subclinical or have respiratory signs and vomiting; sudden death
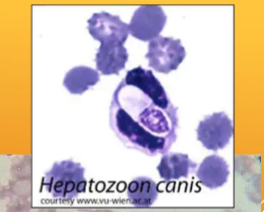
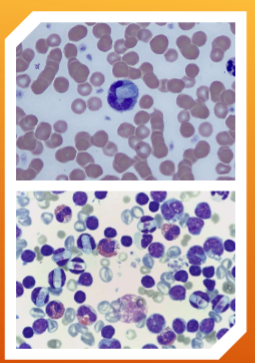
Hepatozoon spp.: H. canis and H. americanum
Hepatozoon
What species does Hepatozoon spp.: H. canis and H. americanum infect
dogs
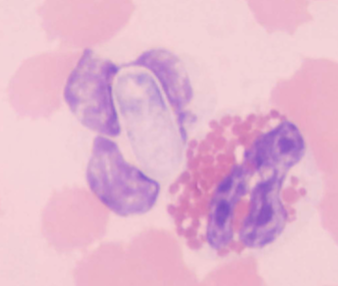
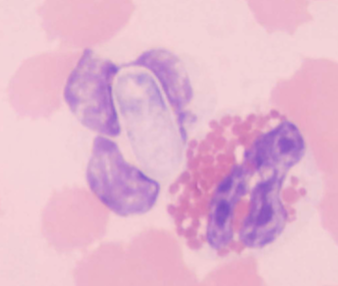
what is Hepatozoon spp.: H. canis and H. americanum spread by
ticks
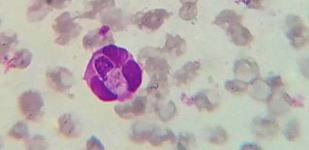
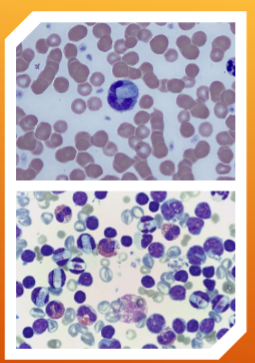
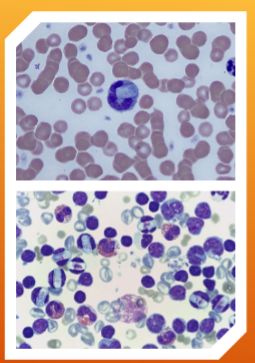
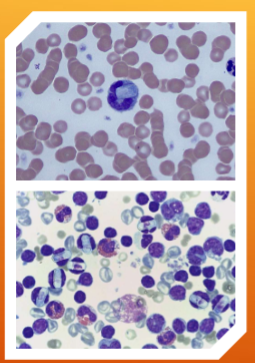
which of the species Hepatozoon spp.: H. canis and H. americanum is more pathogenic?
H. americanum
How do you identify Hepatozoon spp.: H. canis and H. americanum
INTRAcellular – malaria-like pill-shaped inclusions inside neutrophils and monocytes (WBCs)
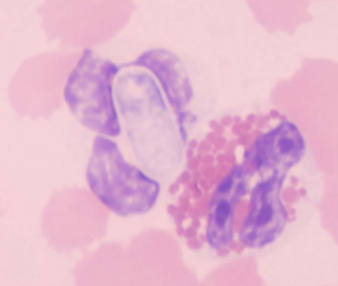
what are the 2 forms of Hepatozoon spp.: H. canis and H. americanum
Gamonts and Schizonts
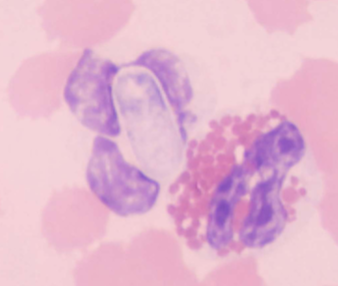
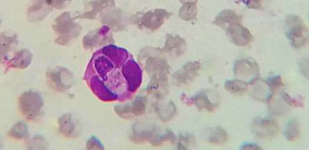
What does Hepatozoon spp.: H. canis and H. americanum cause
Subclinical to fever, depression, and bone disease
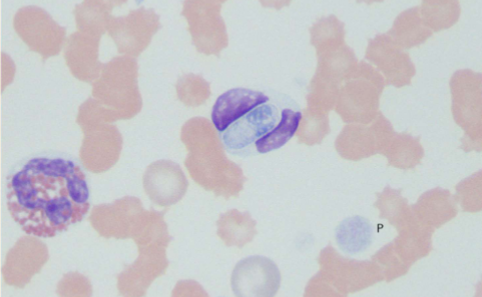
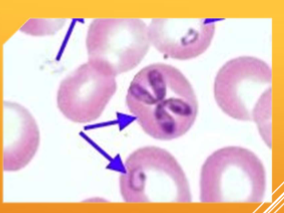
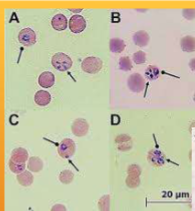
Babesia spp.: B. canis, B. gibsoni, B. bovis
Babesia/Canine piroplasm
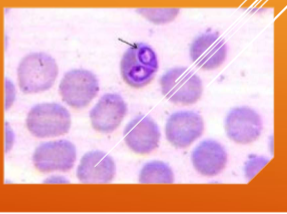
What species does Babesia spp.: B. canis, B. gibsoni, B. bovis infect
dogs and ruminants
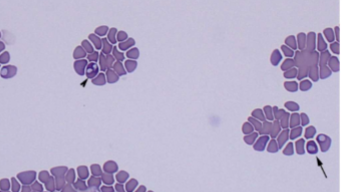
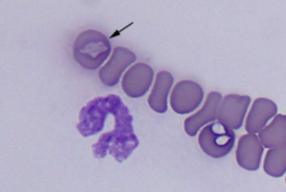
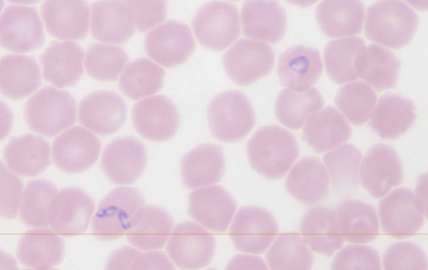
What spreads Babesia spp.: B. canis, B. gibsoni, B. bovis
ticks
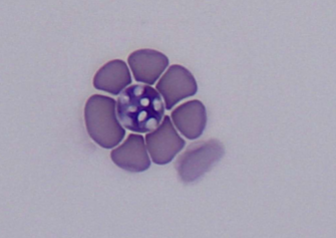
Out of the Babesia spp. which is more pathogenic?
B. gibsoni
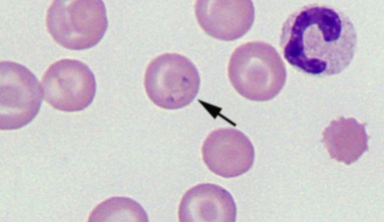
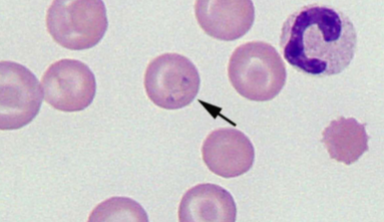
How do you identify Babesia spp.: B. canis, B. gibsoni, B. bovis
INTRAcellular - tiny basophilic, pear-shaped inclusions in RBCs; occurs in pairs that form an acute angle within the RBC
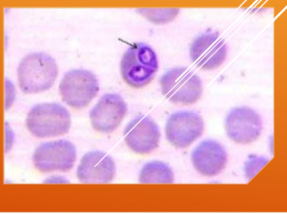
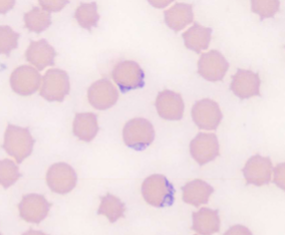
What does Babesia spp.: B. canis, B. gibsoni, B. bovis cause?
Causes damage by inflammation within the RBCs - anemia, hemolytic crisis, fever, icterus, splenomegaly, organ failure
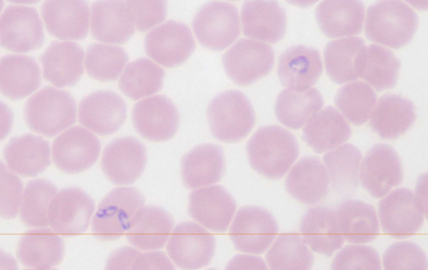
Theileria equi (formerly Babesia equi); Babesia caballi
equine piroplasms

What species does Theileria equi (formerly Babesia equi); Babesia caballi infect
horses
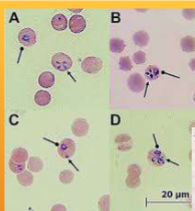
What spreads Theileria equi (formerly Babesia equi); Babesia caballi
ticks
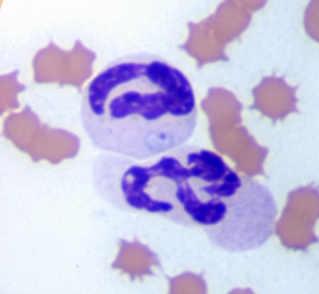
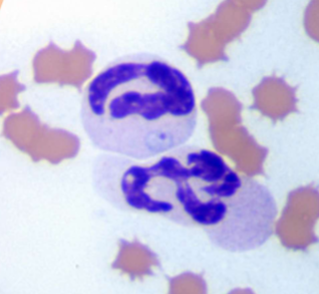
How does one identify Theileria equi (formerly Babesia equi); Babesia caballi
INTRAcellular – basophilic, pear-shaped throphozoites in RBCs, 4 organisms may be joined to give the effect of a Maltese cross

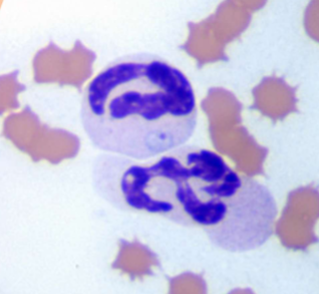
What does Theileria equi (formerly Babesia equi); Babesia caballi cause
Causes damage by inflammation within the RBCs - anemia, fever, depression, icterus, hemogloinuria, pale MM, weakness, enlarged spleen
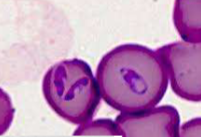
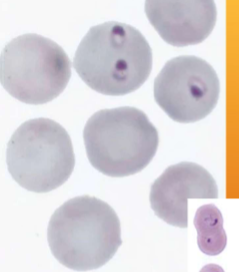
Cytauxzoon felis
Cytauxzoon
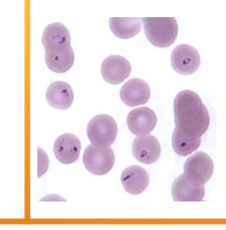
What species does Cytauxzoon felis infect
cats
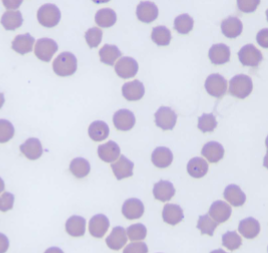
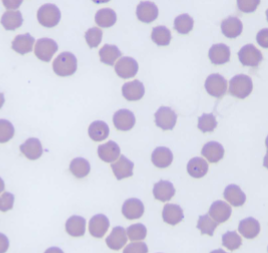
What spreads Cytauxzoon felis
ticks
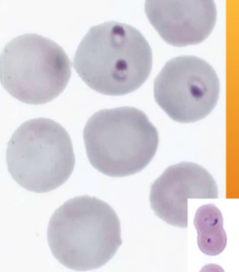
How do you identify Cytauxzoon felis
INTRAcellular – small “engagement ring” inclusions in RBCs, referred to as a “bejeweled ring” shape
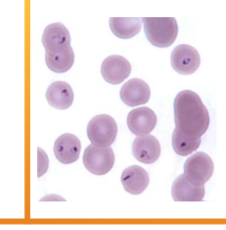
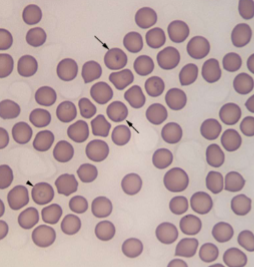
What does Cytauxzoon felis cause
Causes damage by inflammation within the RBCs - anemia, fever, icterus, enlarged spleen and liver; usually fatal
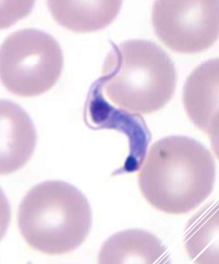
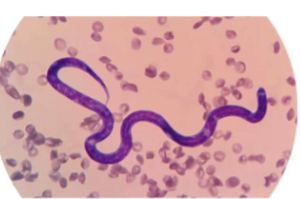
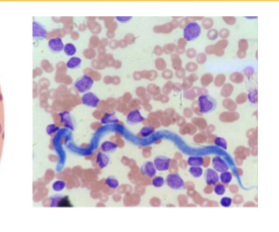
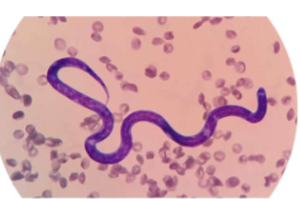
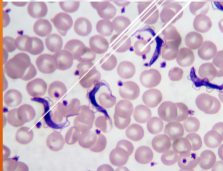
Trypanosoma cruzi
Trypanosome
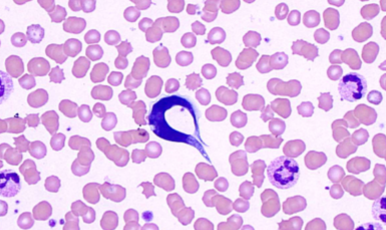
What does Trypanosoma cruzi infect
humans and dogs
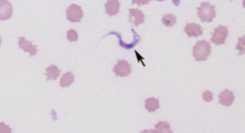
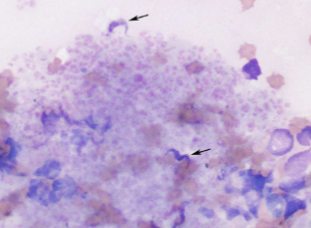
What spreads Trypanosoma cruzi
reduviid bugs aka kissing bugs
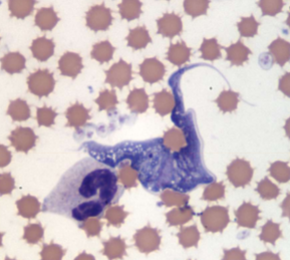
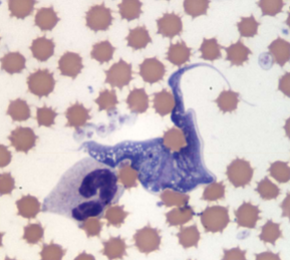
What does Trypanosoma cruzi cause
Causes Chagas disease; Highly pathogenic: fever, lethargy, muscle aches, headaches, vomiting, rash, enlarged lymph nodes → chronic cardiac issues, megaesophagus, megacolon
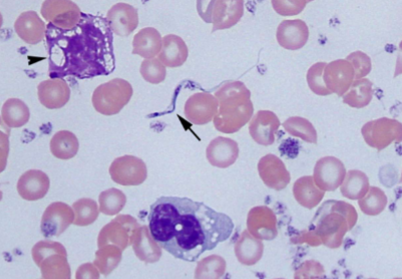
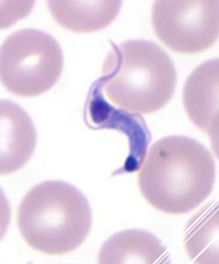
how do you ID Trypanosoma cruzi
EXTRAcellular - banana-shaped with a thin, whip-like tail (flagellum) used for “swimming”
Klossiella equi
klossiella
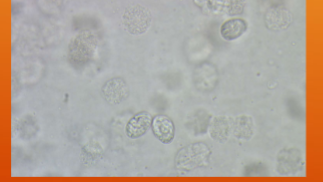
what does Klossiella equi infect
horses
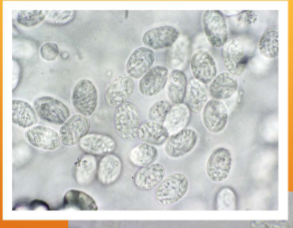
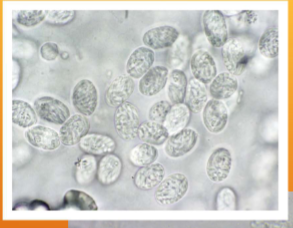
Where in the host does Klossiella equi live?
kidneys
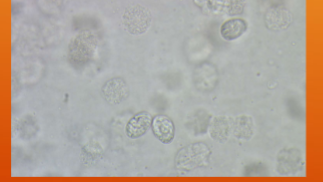
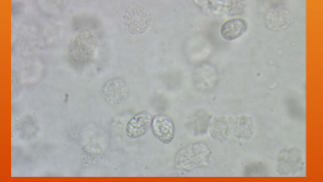
What does Klossiella equi cause?
Non-pathogenic coccidian; can cause kidney inflammation in immune-compromised
horses or with heavy loads
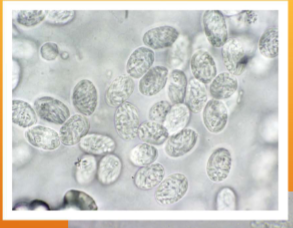
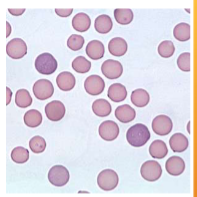
Mycoplasma haemofelis
Feline Infectious Anemia (FIA)/Hemobartonellosis
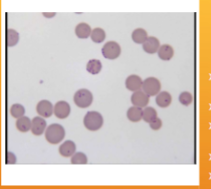
How does one ID Mycoplasma haemofelis
INTRAcellular parasitic bacterium – cannot live outside red blood cells; Appears as coccoid, rod-shaped, or ringlike bacteria on RBCs, usually on the periphery
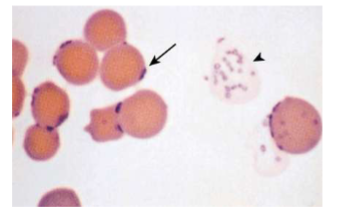
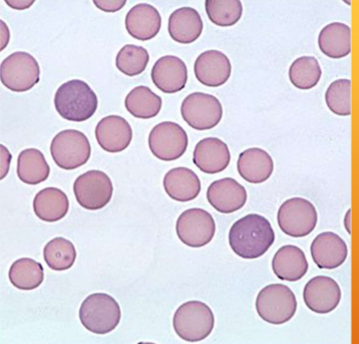
what does Mycoplasma haemofelis cause
Infected blood cells are destroyed, causing progressive anemia and associated signs and symptoms (lethargy, pale MMs, death)
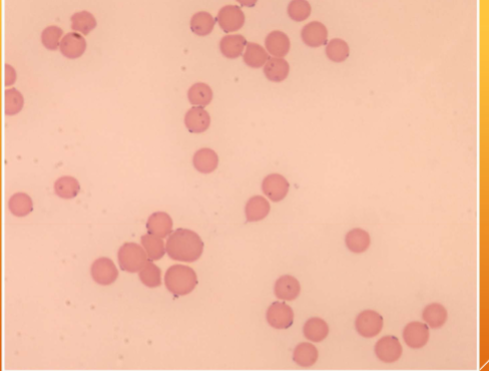
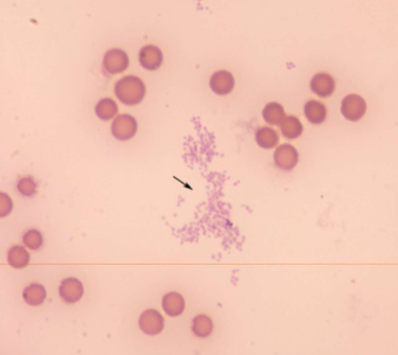
how is Mycoplasma haemofelis transmitted
from queen to kitten although it is unclear how
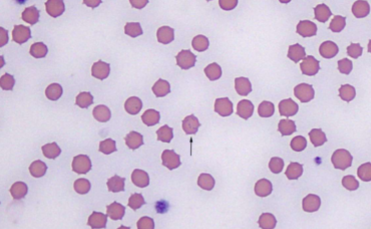
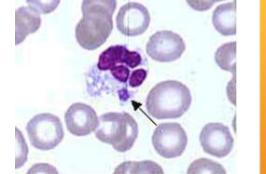
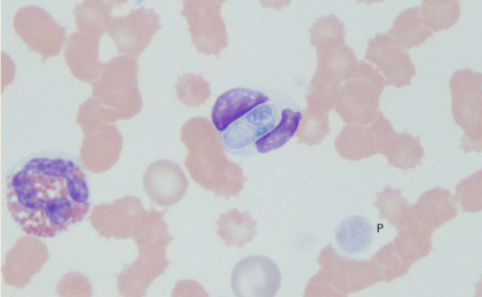
Ehrlichia spp.; E. canis/E. ewingii
Ehrlichia
what species does Ehrlichia spp.; E. canis/E. ewingii infect
dogs
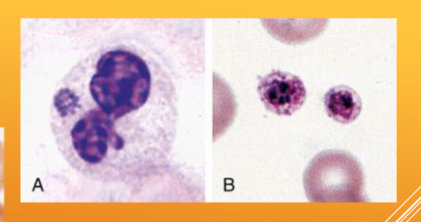
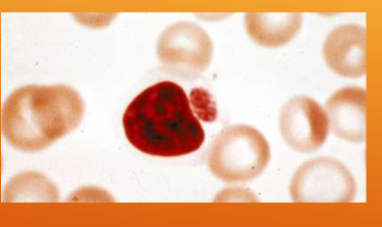
what is Ehrlichia spp.; E. canis/E. ewingii spread by
ticks
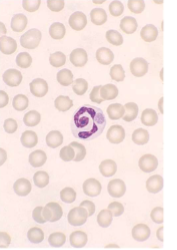
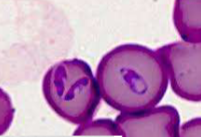
how would you ID Ehrlichia spp.; E. canis/E. ewingii
WBC inclusions – small clusters (morulae) in the cytoplasm very rarely present on blood smear
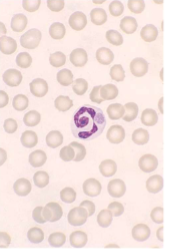
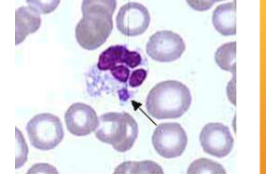
what does Ehrlichia spp.; E. canis/E. ewingii cause
canine granulocytic ehrlichiosis; Fever, lethargy, anemia, joint pain, weight loss, swollen lymph nodes
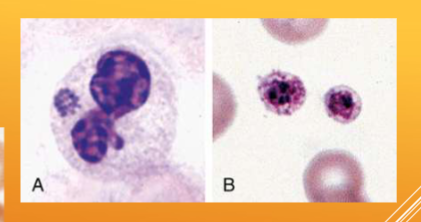
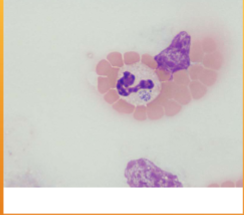
Anaplasma spp.; A. phagocytophilum/A. platys
(formerly Ehrlichia platys)
Anaplasmosis
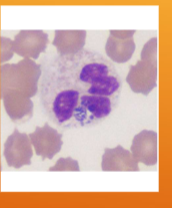
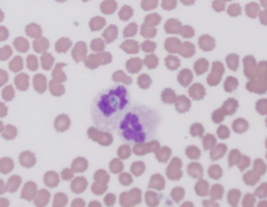
what species does Anaplasma spp.; A. phagocytophilum/A. platys infect
dogs and horses
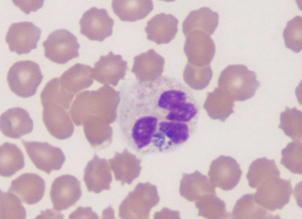
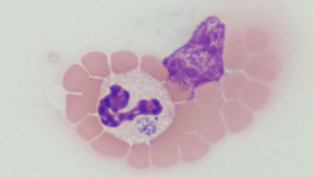
what spreads Anaplasma spp.; A. phagocytophilum/A. platys
ticks
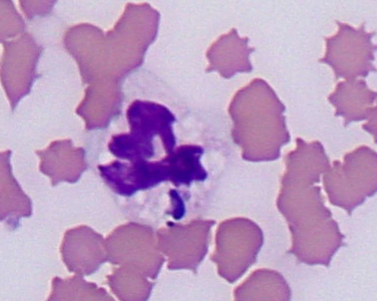
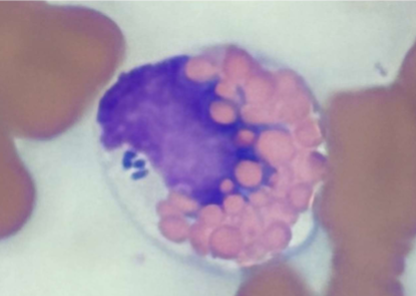
what does A. phagocytophilum cause
causes granulocytotropic anaplasmosis (WBCs); Fever, muscle pain, fatigue, nausea, joint pain, lameness, vomiting, bleeding disorders
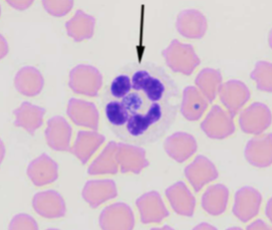
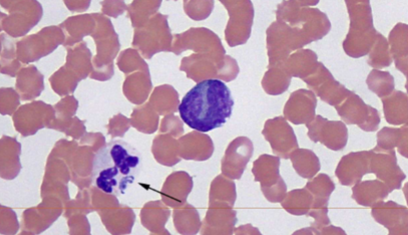
what does A. platys cause
causes thrombocytotrophic ehrlichiosis (platelets); Fever, anorexia, lethargy, swollen lymph nodes, thrombocytopenia
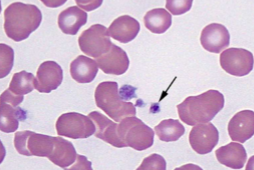
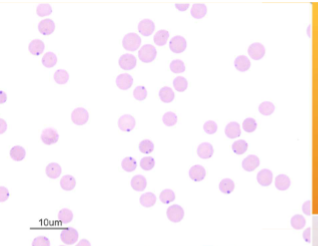
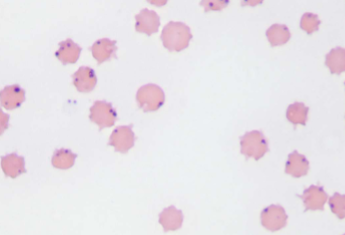
Anaplasma spp.; A. marginale
Anaplasmosis
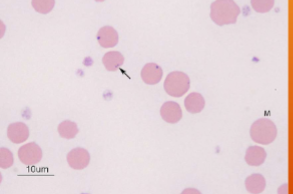
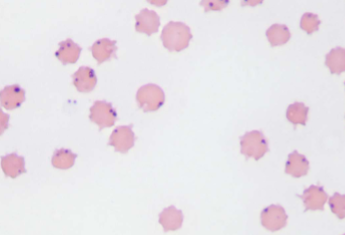
what does Anaplasma spp.; A. marginale infect
cattle and other ruminants
what transmits Anaplasma spp.; A. marginale
ticks
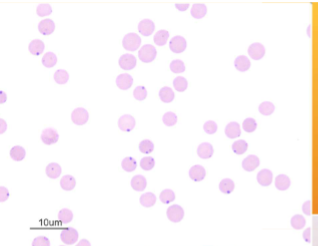
how would you ID Anaplasma spp.; A. marginale
INTRAcellular - small, dark-staining cocci at the margin of the RBCs, and it must be differentiated from Howell-Jolly bodies, because their sizes are similar
Borrelia burgdorferi
Lyme disease, Borreliosis
what species does Borrelia burgdorferi infect?
humans, dogs, and sometimes cats
what spreads Borrelia burgdorferi
ticks
what does Borrelia burgdorferi cause
Gram-negative spirochete bacteria that causes symptoms of joint pain and swelling, shifting-leg lameness, lethargy, fever, anorexia, and kidney disease (43% increased risk of CKD); classic “bullseye'“ rash
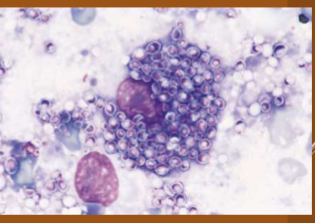
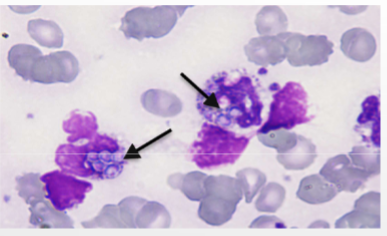
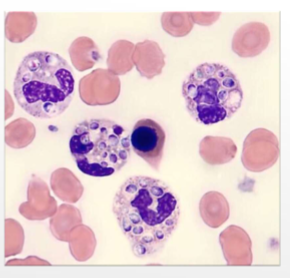
Histoplasma capsulatum
Histoplasmosis
what does Histoplasma capsulatum infect
dogs, cats, and humans
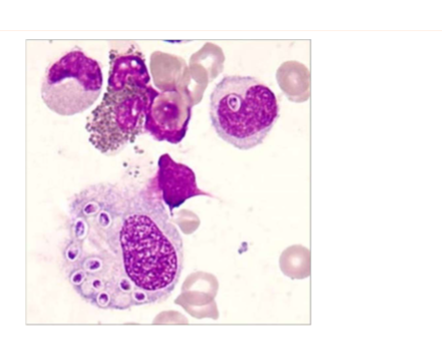
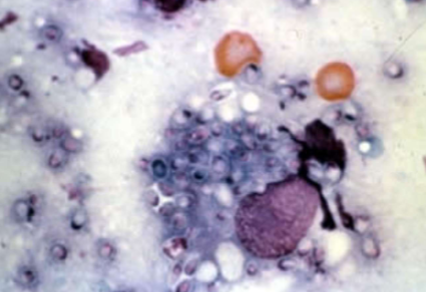
what does Histoplasma capsulatum cause
Fever, lethargy, weight loss, diarrhea, loss of appetite, coughing and labored or rapid breathing, eye infections, such as chorioretinitis or retinal detachment, pain or lameness in the joints
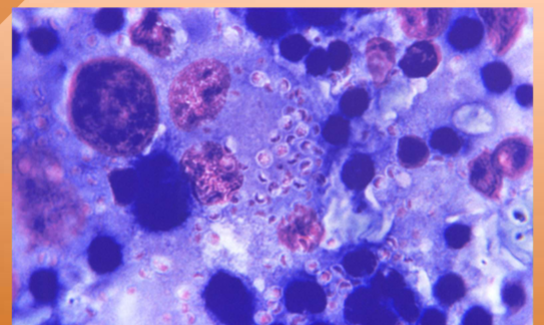
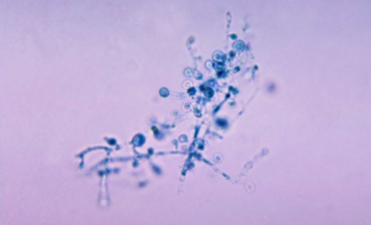
Blastomyces dermatitidis
Blastomycosis/Blasto
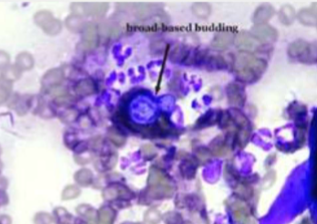
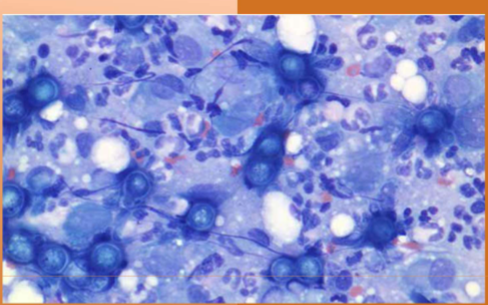
Where is Blastomyces dermatitidis found
found in regions of na: ohio river valley, missouri, mississippi, mid-atlantic states, pacific northwest, and canada
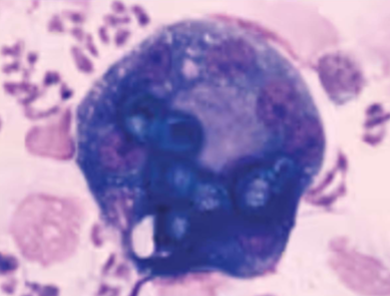
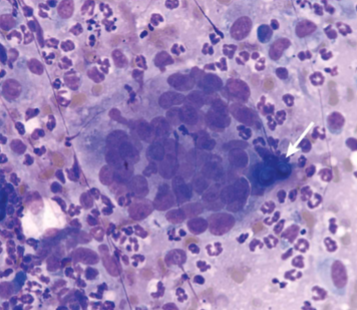
what does Blastomyces dermatitidis infect
dogs and humans
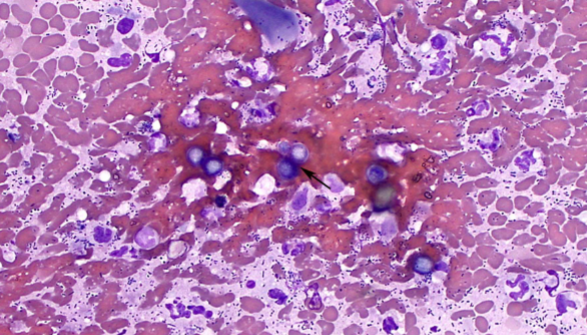
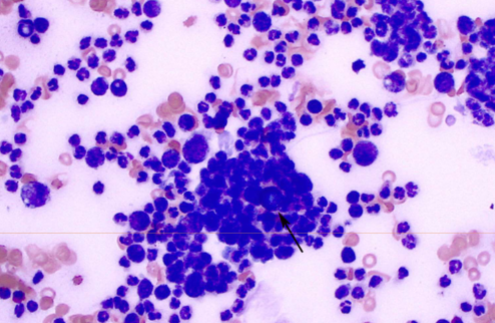
symptoms of Blastomyces dermatitidis
Fever, lethargy, weight loss, diarrhea, loss of appetite,
coughing and labored or rapid breathing, pain or
lameness in the joints, skin lesions, eye swelling
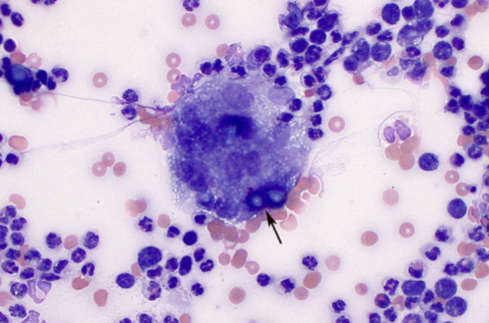
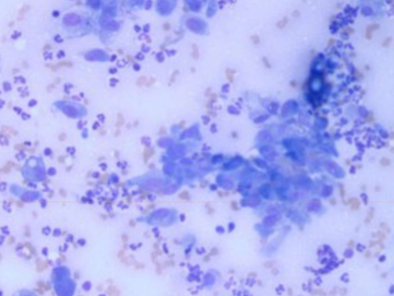
is Blastomyces dermatitidis zoonotic
nah
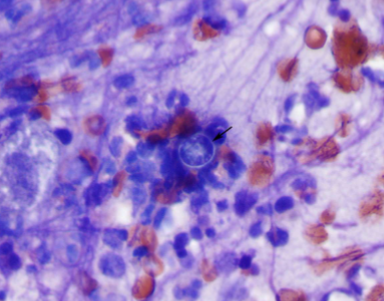
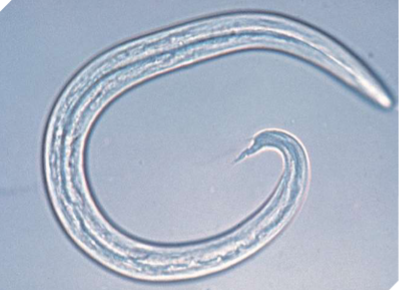
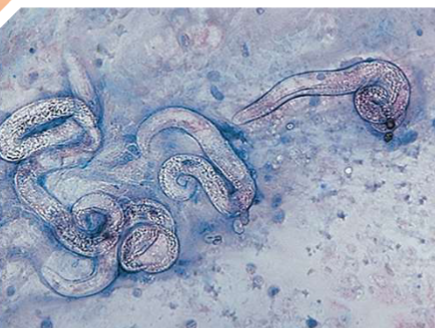
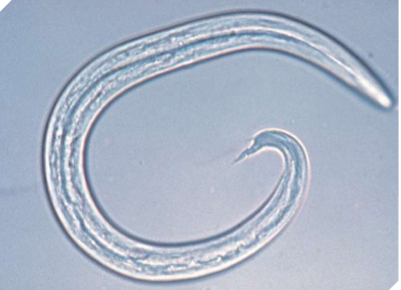
Aelurostrongylus abstrusus
feline lungworm
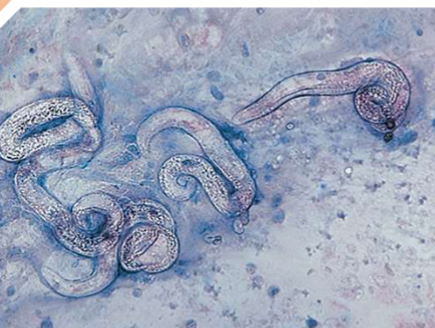
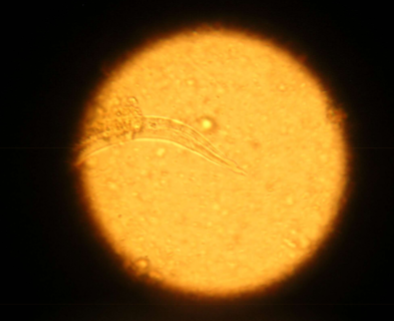
what does Aelurostrongylus abstrusus infect
cats
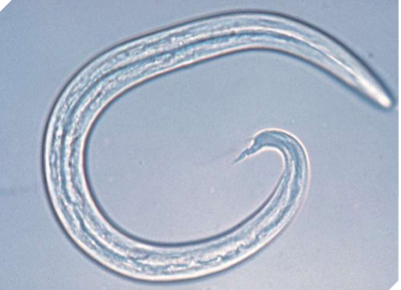
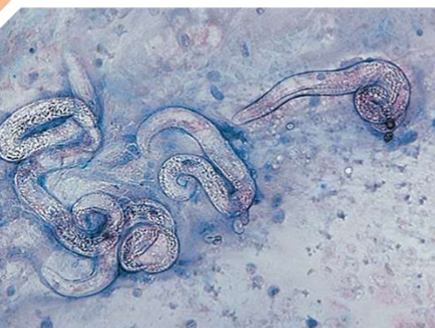
where is Aelurostrongylus abstrusus located in host
respiratory bronchioles
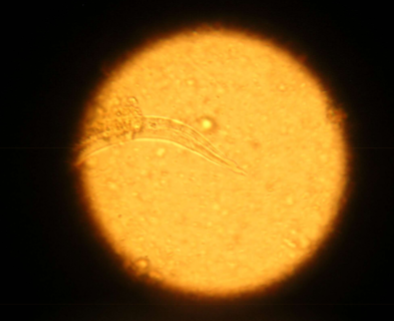
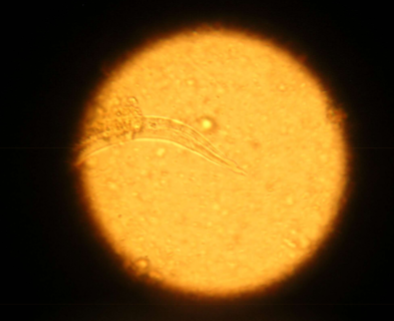
what techniques can you use to diagnose Aelurostrongylus abstrusus
fecal float and baermann technique (b is more reliable)
is Aelurostrongylus abstrusus zoonotic
no
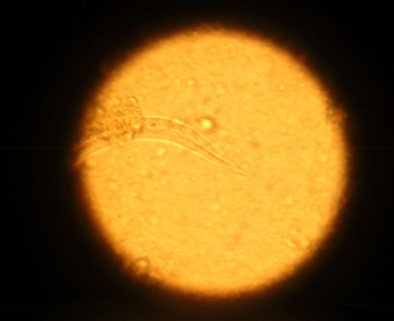
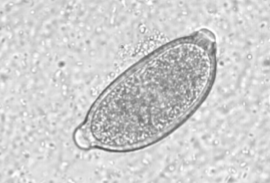
Eucoleus aerophilus
Capillarid lungworm of dogs and cats

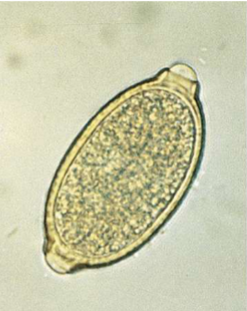
where is Eucoleus aerophilus located in host
adults are located in bronchi and trachea
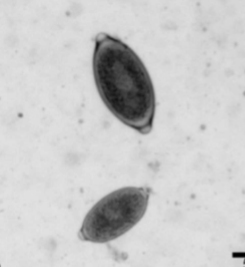
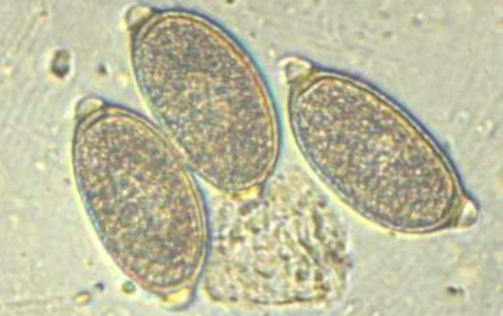
is Eucoleus aerophilus zoonotic
yes
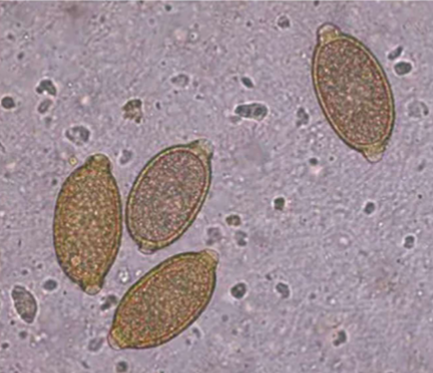
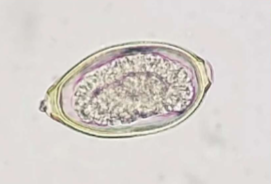
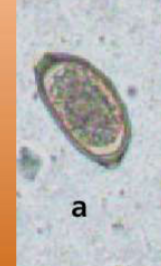
Eucoleus böehmi
Respiratory capillarid of dogs
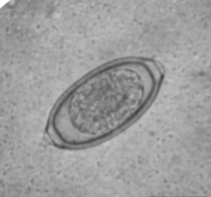
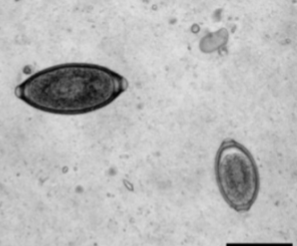
where is Eucoleus böehmi located in host
adults are located in nasal cavities and sinuses
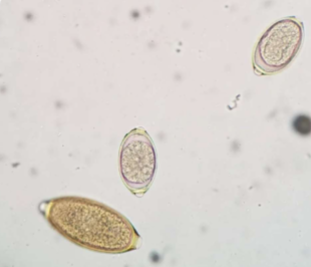
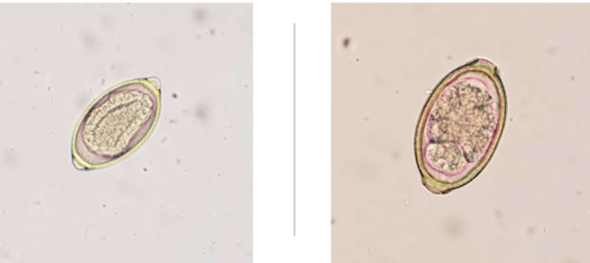
are Eucoleus böehmi zoonotic
nope
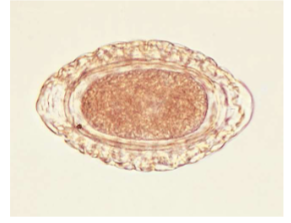
Dioctophyma renale
“giant kidney worm” of dogs, mink, raccoons, and humans
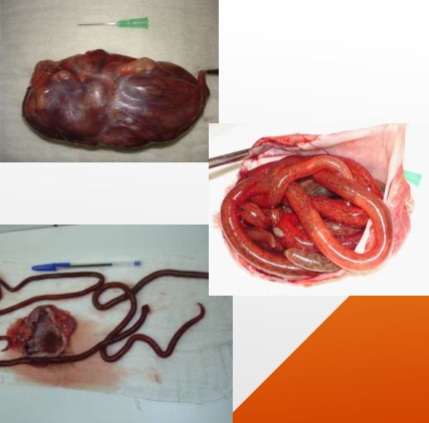
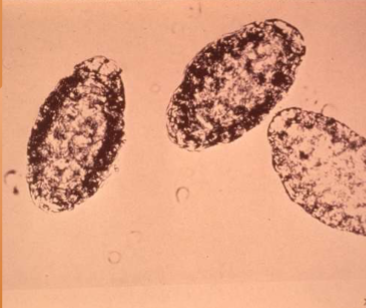
where does Dioctophyma renale live in the body of host
infects the right kidney.
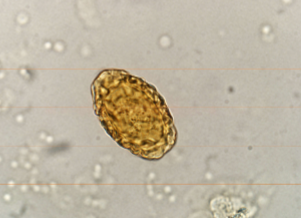
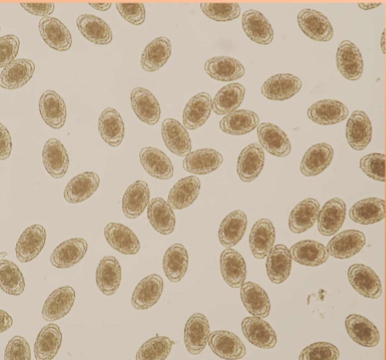
symptoms of Dioctophyma renale
kidney/abdominal pain, enlargement, hematuria, proteinuria, lethargy, weight loss, can destroy entire contents of kidney, just leaving a “shell”
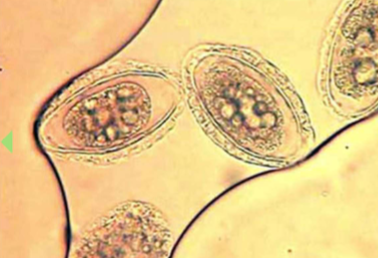
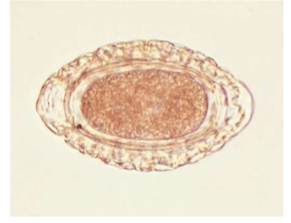
what lifecycle does Dioctophyma renale have
indirect with 2 aquatic intermediate hosts (worm and frog or fish)
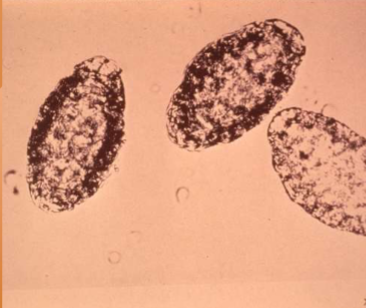
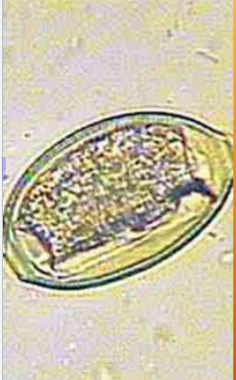
Pearsonema plica/ Pearsonema feliscati
bladder worm of dogs, foxes, and cats
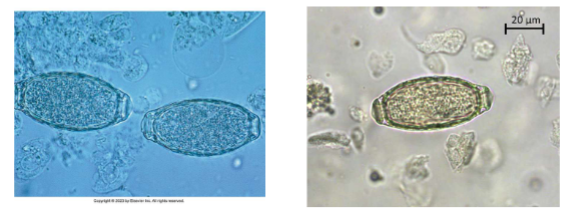
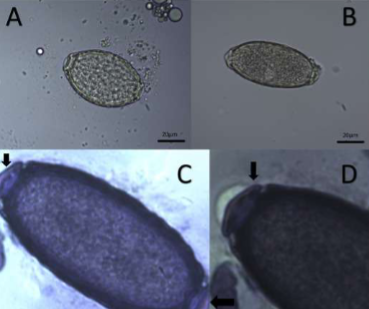
what lifecycle does Pearsonema plica/ Pearsonema feliscati have
indirect; earthworm is the intermediate host
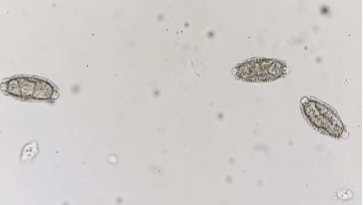
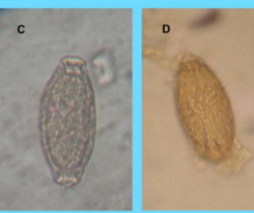
symptoms of Pearsonema plica/ Pearsonema feliscati
usually asymptomatic, but can cause blood in urine, irritated bladder
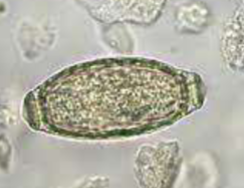
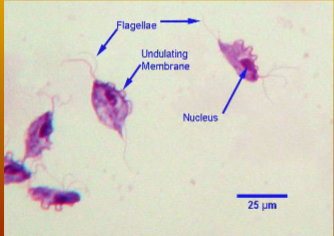
where does Tritrichomonas spp. in the dog and cat host
the intestine or urogenital tract of dogs and cats
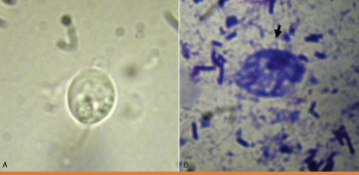
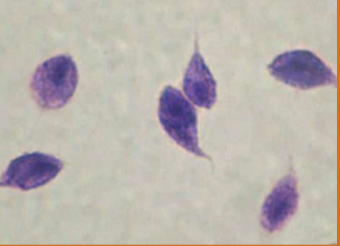
what can Tritrichomonas spp cause
chronic diarrhea sometimes intermittent for years; mucoid, bloody, frequent urinating in small amounts, licking genital area
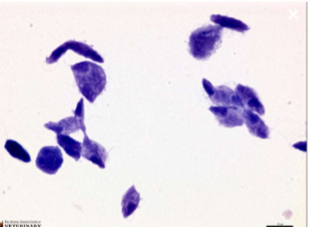
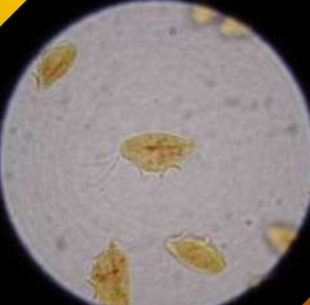
where does Tritrichomonas spp live in a cattle host
the genital tract.
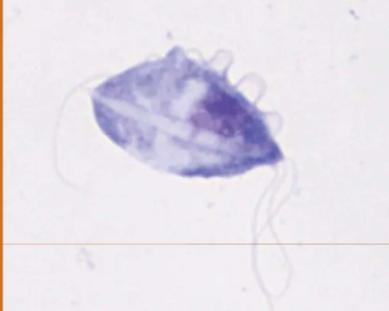
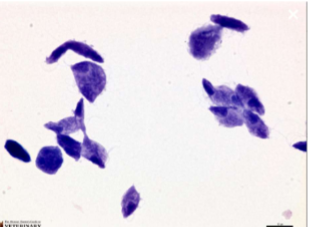
how can Tritrichomonas spp be transmitted (in cattle)
sexually transmitted
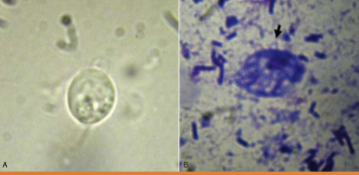
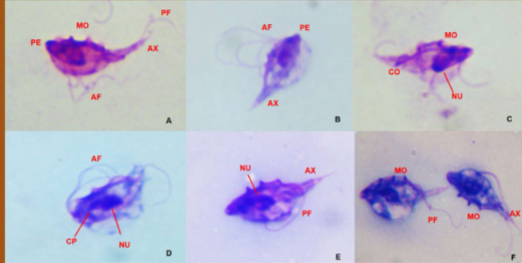
what can Tritrichomonas spp cause in cattle
can cause abortion in cattle and thus herd/economic losses
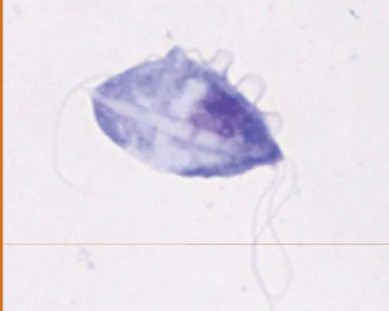
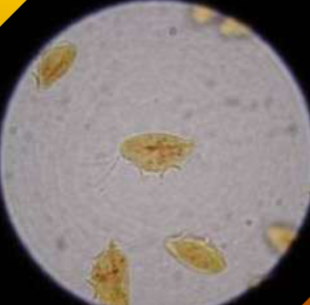
symptoms of Tritrichomonas spp in cattle
bulls are asymptomatic carriers that infect the cows
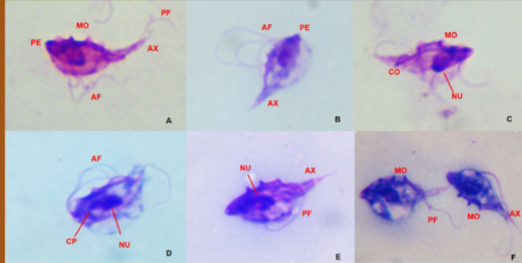
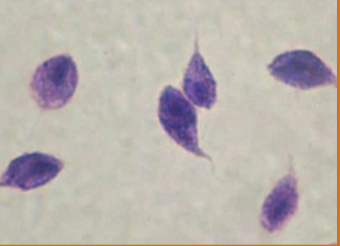
does Tritrichomonas spp have a cyst stage
no, it have a pseudocysts form
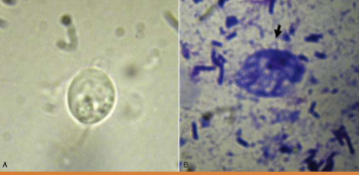
Leptospira interrogans
leptospirosis, lepto
what shape of bacteria is Leptospira interrogans
helical or spirochaete
how is Leptospira interrogans spread
by mostly rodents to dogs and wild animals to humans
how is Leptospira interrogans transmitted
by the urine of an infected animal and is contagious as long as the urine is STILL MOIST
what parts of the body does Leptospira interrogans invade
many body tissues and organs; kidneys, liver, lungs, brain
how can Leptospira interrogans enter the body
through a BREAK in the skin or mucous membranes including eyes and nose