Overview of Special and General Senses
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Special Senses
Five senses excluding vision: taste, smell, hearing, equilibrium.
Taste
Special sense involving chemoreceptors on the tongue.
Smell
Special sense using chemoreceptors in the nasal cavity.
Hearing
Special sense involving mechanoreceptors in the ear.
Equilibrium
Sense of balance, detected by mechanoreceptors.
Photoreceptor
Receptor type for vision, sensitive to light.
Chemoreceptor
Receptor type for taste and smell stimuli.
Mechanoreceptor
Receptor type for hearing and equilibrium.
Nociceptor
Receptor for pain sensation.
Thermoreceptor
Receptor for temperature sensation.
Proprioceptor
Receptor for body position awareness.
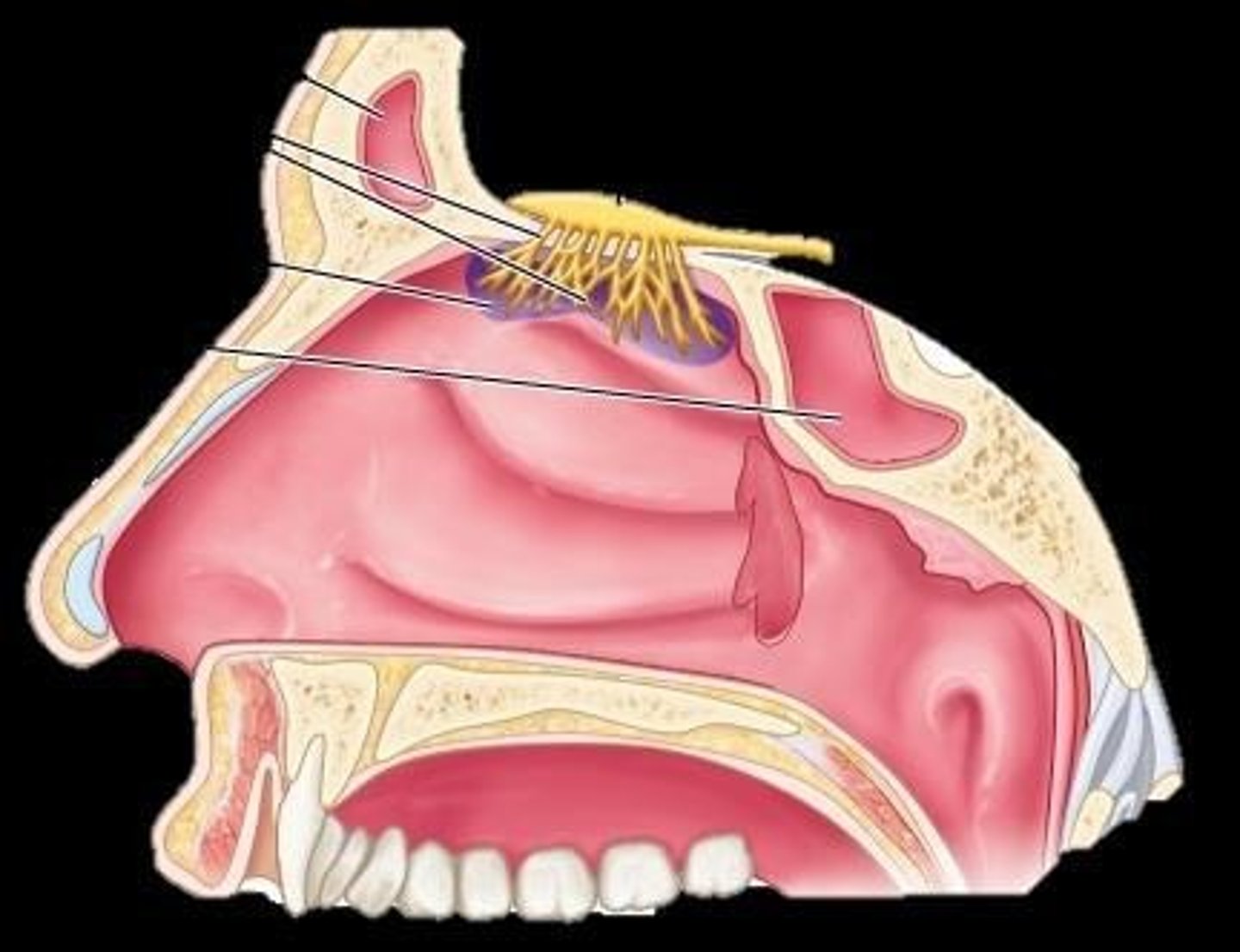
Olfactory Epithelium
Location of smell receptors in the nasal cavity.
Primary Olfactory Cortex
Brain area for conscious awareness of odors.
Taste Receptors
Located in taste buds on the tongue.
Cranial Nerve I
Olfactory nerve responsible for smell sensation.
Cranial Nerve VII
Facial nerve, innervates anterior tongue taste.
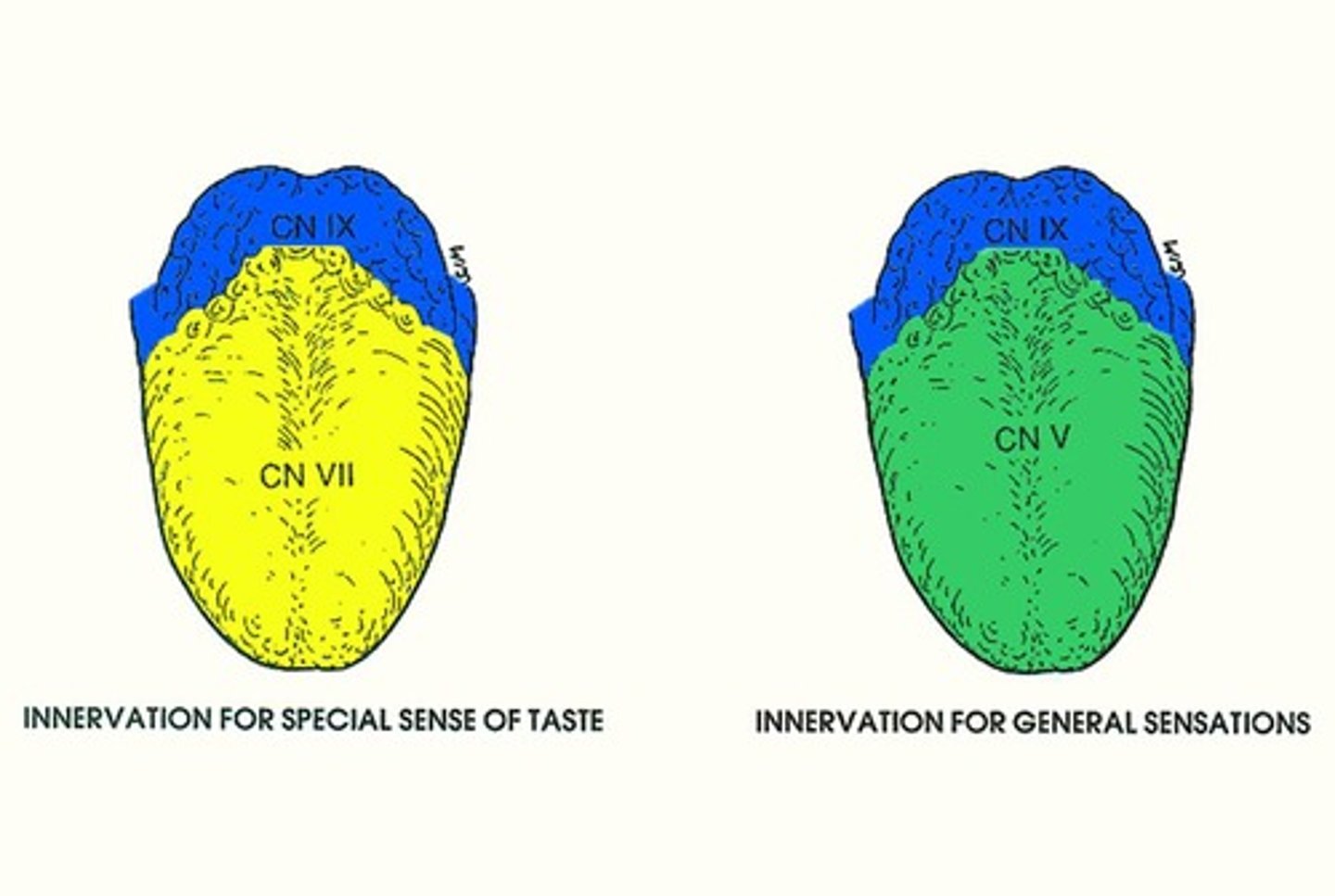
Cranial Nerve IX
Glossopharyngeal nerve, innervates posterior tongue taste.
Cranial Nerve V
Trigeminal nerve, general sensory for tongue.
Extrinsic Muscles of the Tongue
Muscles controlling tongue movement, innervated by CN XII.
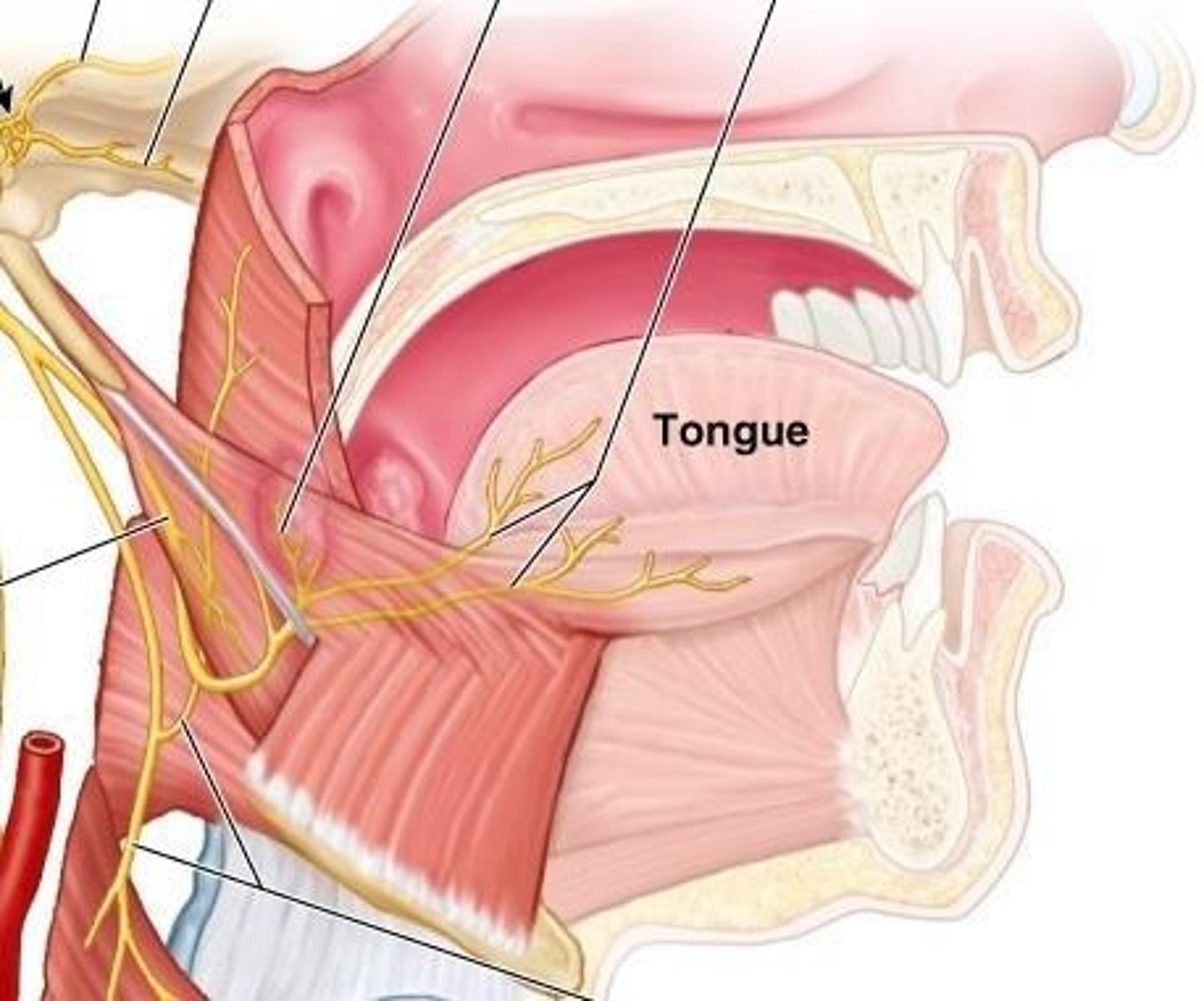
Genioglossus Muscle
Extrinsic muscle that protrudes the tongue.
Hyoglossus Muscle
Extrinsic muscle that depresses the tongue.
Styloglossus Muscle
Extrinsic muscle that retracts the tongue.
Auditory Ossicles
Malleus, incus, stapes amplify sound waves.
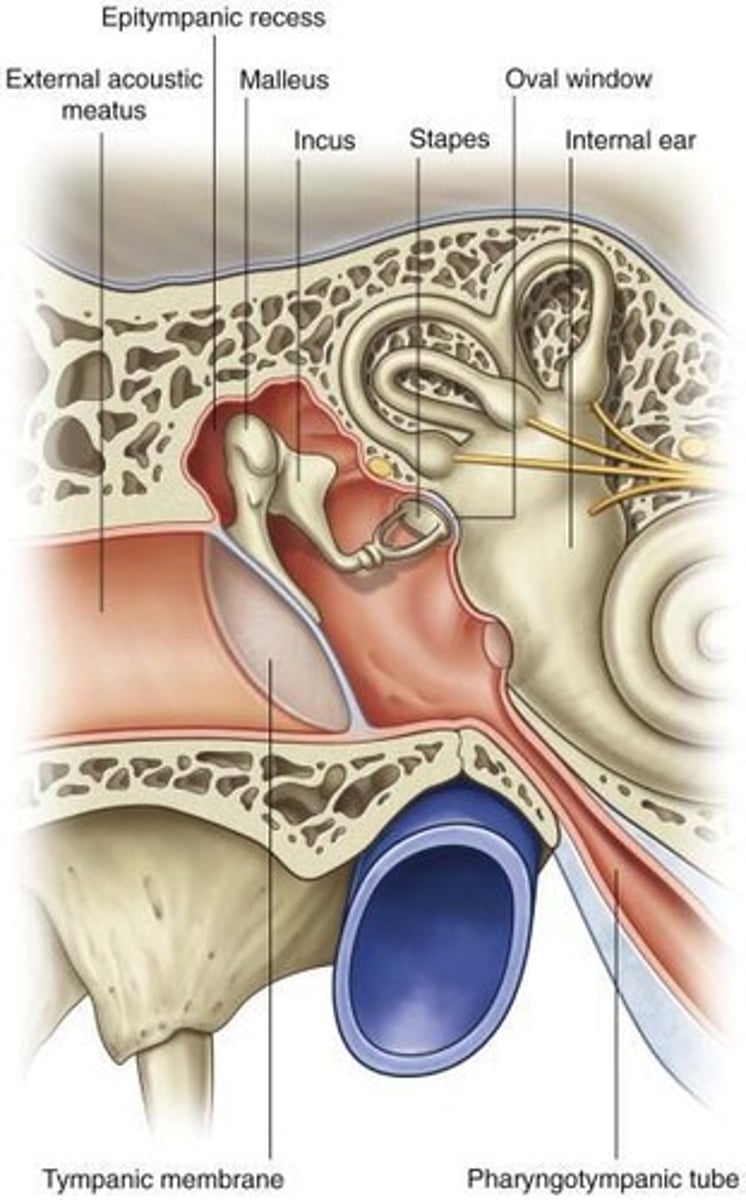
Cochlea
Internal ear structure for hearing.
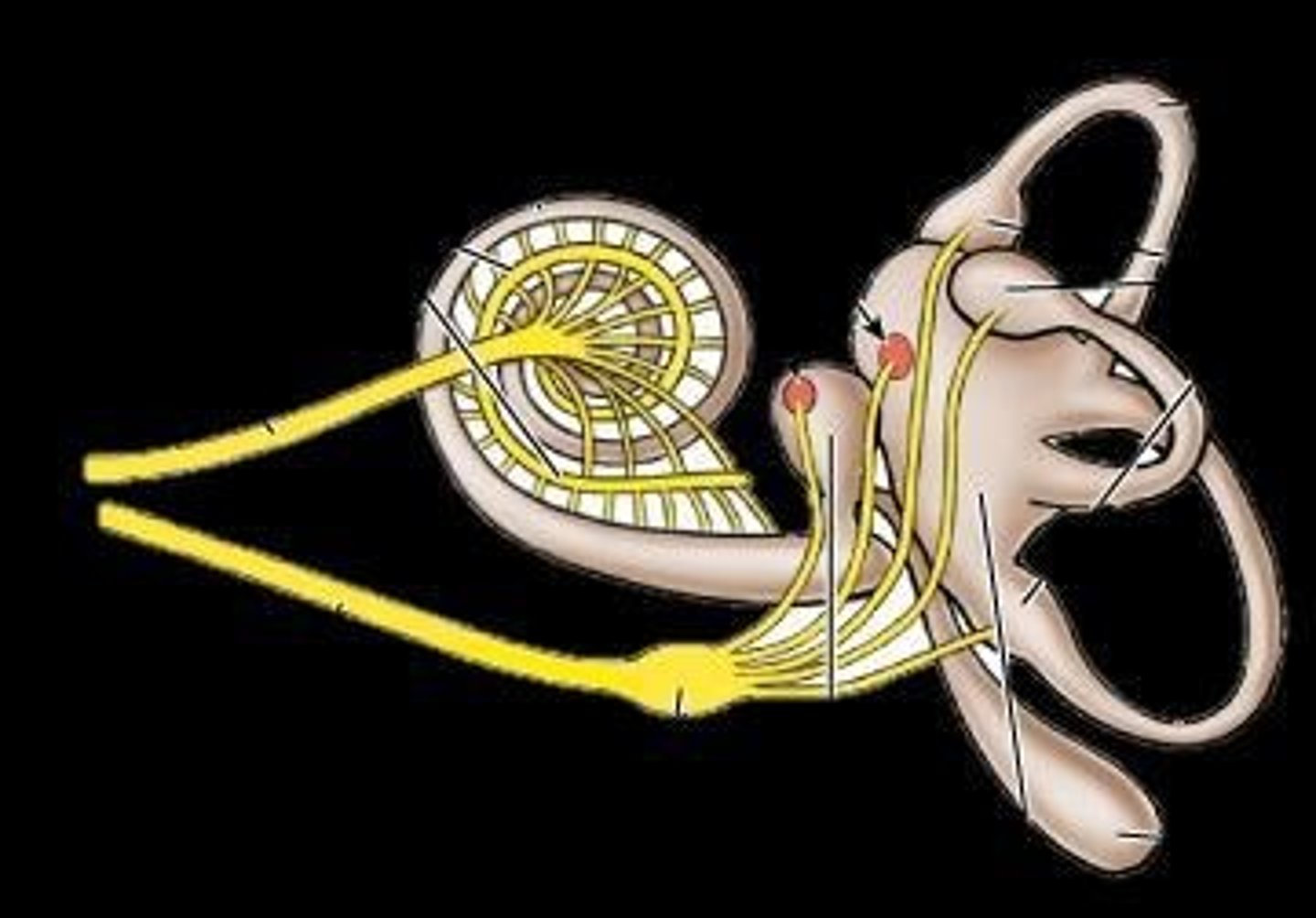
Semicircular Canals
Internal ear structures for balance and equilibrium.
Tympanic Membrane
Separates external and middle ear.
Round Window
Structure that dissipates pressure in the inner ear.