crystallography pt 1
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
151 Terms
what is an amorphous structure?
does it diffract X-rays?
no long range structure
doesn’t diffract
what is a crystal structure? (how are atoms organised)
atoms organised in a regular, 3D structure
why is diamond used in IR spec?
it is transparent to IR
high electrical resistance but good heat conductivity
what is a symmetry operation?
an operation that can be performed to give no change in the appearance of an object
what are the 3 types of symmetry operations?
rotation
reflection
inversion
what is a 1-fold rotation axis?
identical after a 360 degree rotation
what is a 2-fold rotation axis?
appears identical after a rotation of 180
what is a 3-fold rotation axis?
object appears identical after a 120 degree rotation
what is a 4 fold rotation axis?
object appears identical after a 90 degree rotation
what is a 6 fold rotation axis?
object appears identical after a 60 degree rotation
how do inversion symmetry lines work?
lines drawn all points on the object through centre of the object
lengths are equidistant
when lines are connected, the object is reproduced inverted from its original appearance
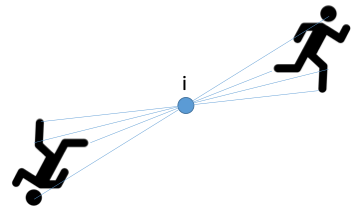
what is a lattice?
infinite regular arrangement of points
each has identical surroundings
what are lattice points?
points having identical surroundings in the crystal
what is a unit cell?
building block of the lattice
unit cell is parallelepiped or parallelogram with lattice points at its vertices, when translated in all directions create the lattice
what is a motif?
information on the pattern
what is a unit cell containing 1 lattice point called?
a primitive unit cell
how is a unit cell chosen?
possess same symmetry as crystal structure
it should contain smallest number of lattice points
what are the 5 unit cells for 2D lattices?
square
hexagonal
rectangular
centred rectangular
oblique
what do the a and b axes look like?
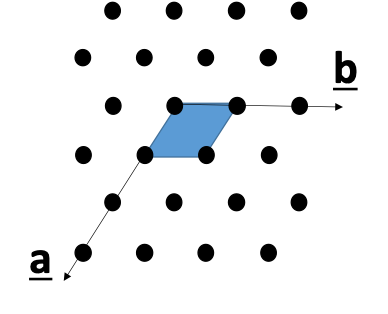
how are directions written?
square brackets
line above for negative
simplify to smallest integers
how are miller indices determined?
find intercepts along axes (a and b)
specify intercepts as fractional coordinates
take reciprocals
multiply to make integers
what are miller indices when lines do not cut the axis?
cuts at infinity so gives miller index of 0
are miller indices simplified to smallest integer value?
no miller indices are not simplified to be smaller
what is d?
the shortest distance between the lattice lines (perpendicular)
what do the most stable crystal lattices have?
highest density of atoms = lower energy
low indices
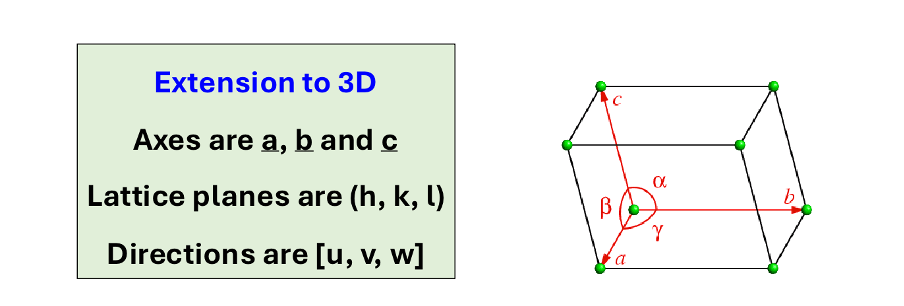
what are the axes, lattice planes and directions?
what does a small miller index mean?
the more nearly parallel the plane is to the axis
what does a large miller index mean?
the more nearly perpendicular a plane is to the axis
how does multiplying/dividing a miller index affect the orientation of the plane?
no effect
what is the fraction of a corner?
1/8
what is the fraction of an edge?
1/4
what is the fraction of a face?
1/2
which shapes are orthogonal
cubic, tetragonal and orthorhombic
equation if a direction lies on a plane?
hu + kv + lw = 0
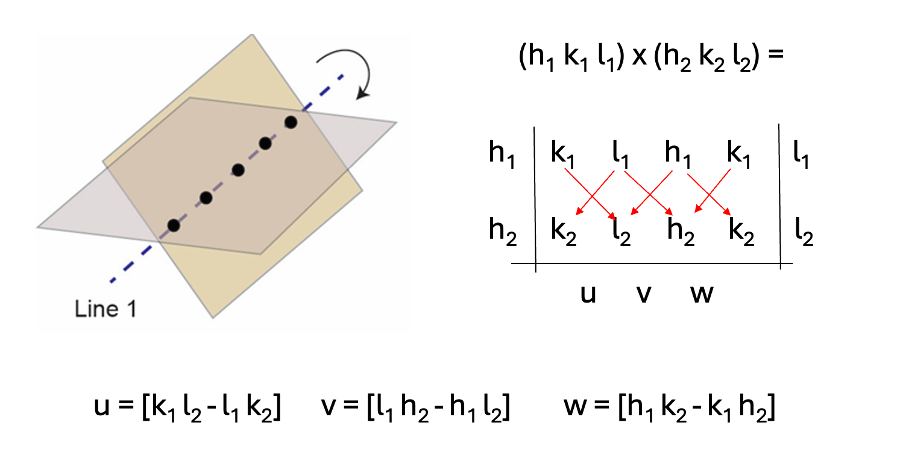
how to work out the common axis of two planes? what is this called?
zone axis
taking the cross product of the planes
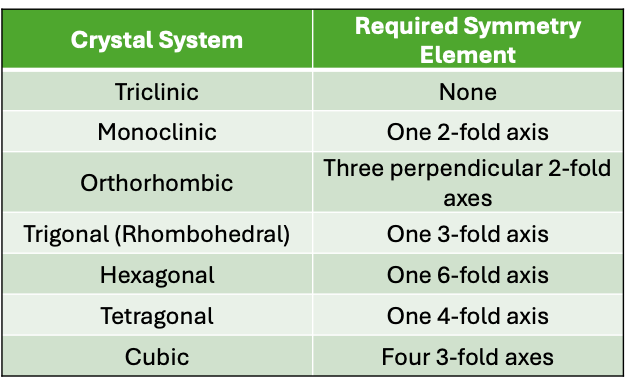
what are the seven 3d crystal systems?
simple cubic
tetragonal
orthorhombic
rhombohedral
monocyclic
triclinic
hexagonal
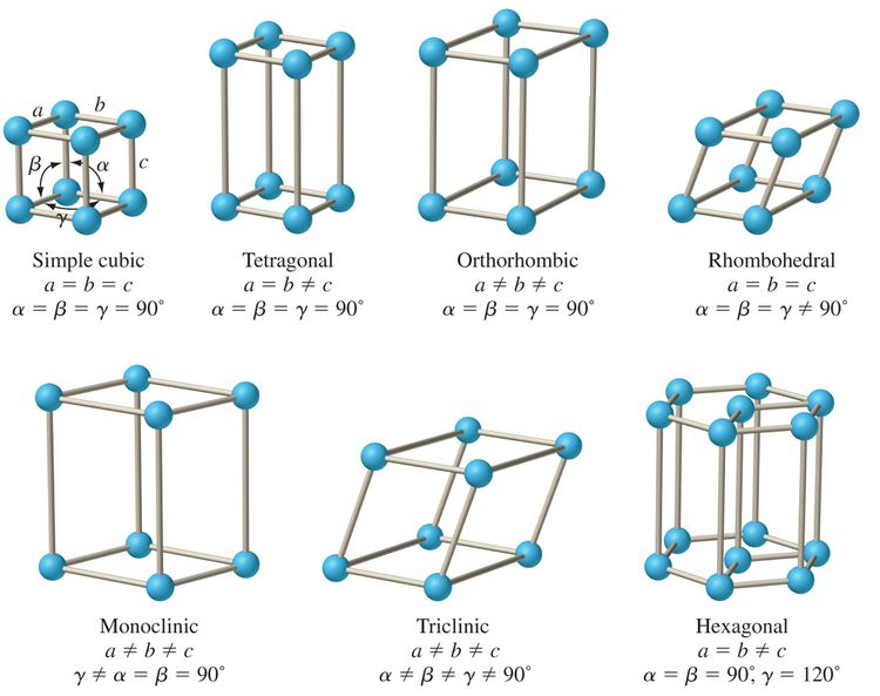
what is the abc and αβγ relationship for cubic?
a = b = c
α = β = γ = 90
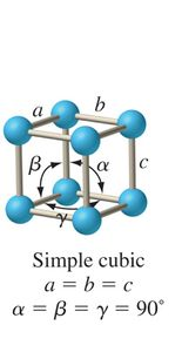
what is the abc and αβγ relationship for tetragonal?
a = b ≠ c
α = β = γ = 90
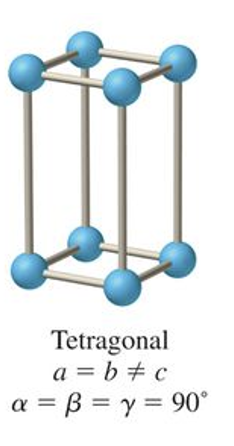
what is the abc and αβγ relationship for orthorhombic?
a ≠ b ≠ c
α = β = γ = 90
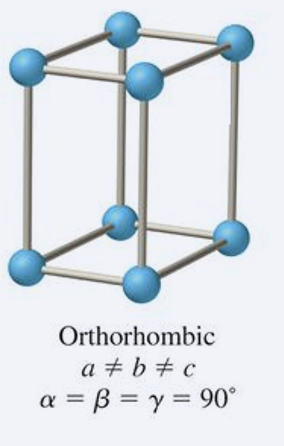
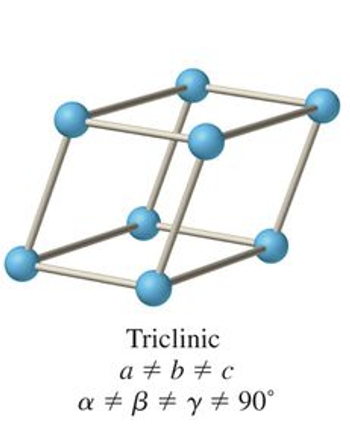
what is the abc and αβγ relationship for rhombohedral?
a = b = c
α = β = γ ≠ 90
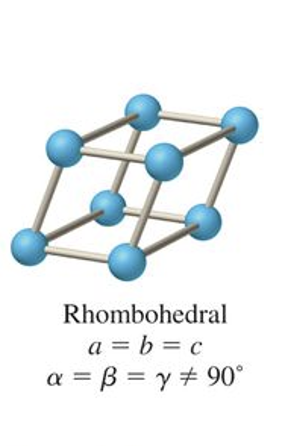
what is the abc and αβγ relationship for monoclinic?
a ≠ b ≠ c
γ ≠ α = β = 90
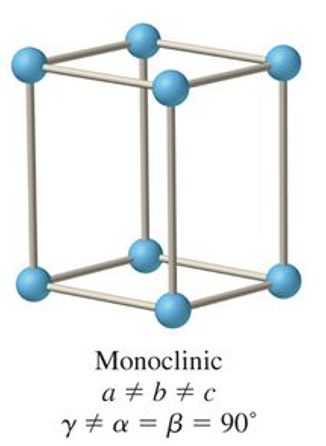
what is the abc and αβγ relationship for triclinic?
a ≠ b ≠ c
α ≠ β ≠ γ ≠ 90
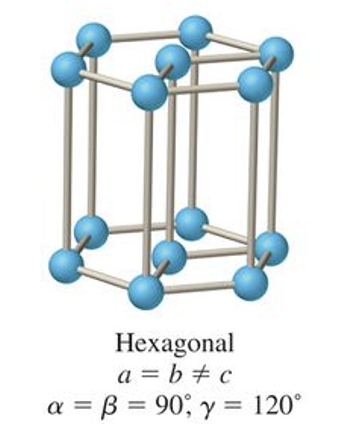
what is the abc and αβγ relationship for hexagonal?
a = b ≠ c
α = β = 90, γ = 120
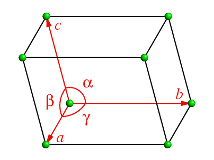
what sides are αβγ between?
α between b and c
β between a and c
γ between a and b
what are the axes of a b and c on a 3d diagram?
what are the symmetry elements for the 7 crystal systems? (triclinic, monoclinic, orthorhombic, trigonal/rhombohedral, hexagonal, tetragonal, cubic)
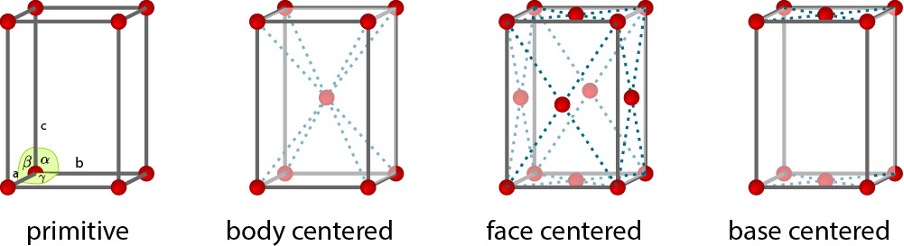
what are the 4 unit cell types?
primitive
body centred
face centred
base centred
why is there not 28 bravais lattices (4 unit cells x 7 crystal structures)?
how many are there?
there are only 14 because not all unit cells are consistent with the symmetry of the crystal systems
some give equivalent lattices
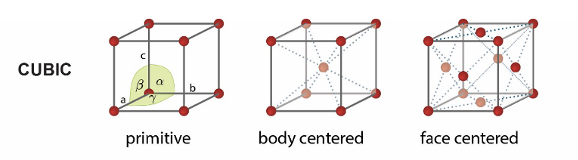
what are the 3 cubic unit cells?
primitive
body centred
face centred
what are the 4 orthorhombic unit cells?
primitive
body centred
face centred
base centred
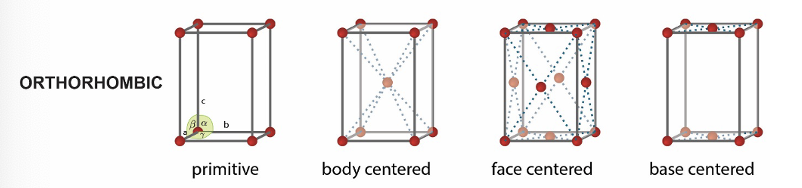
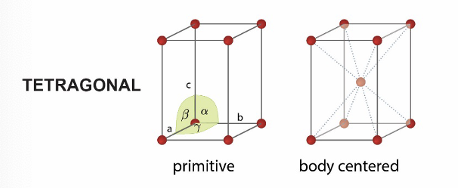
what are the 2 tetragonal unit cells?
primitive
body centred
what are the 2 monoclinic unit cells?
primitive
base centred

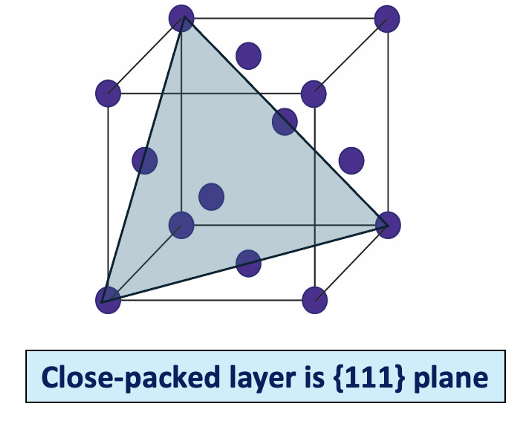
what are the two close packed structures?
hexagonal close packed
cubic close packed
what are the layers of HCP?
what is the coordination number?
ABABABAB
12
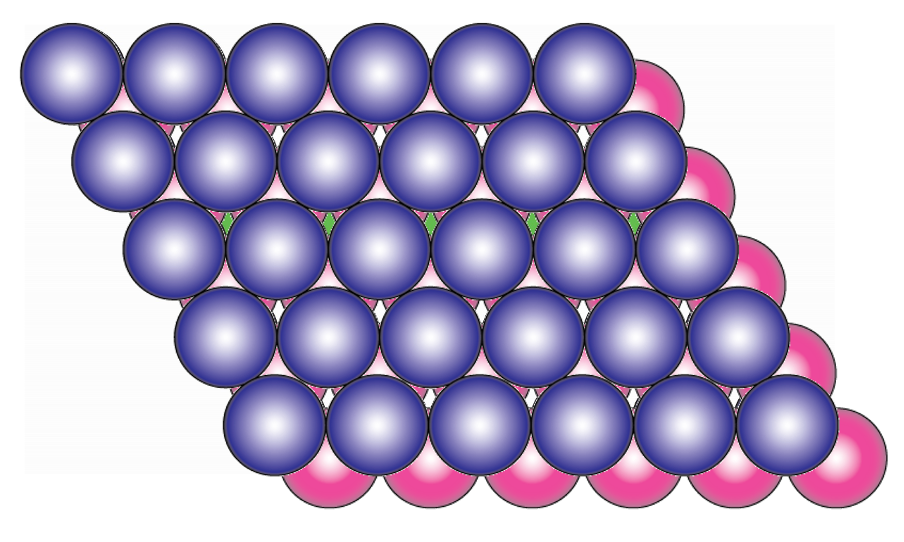
what is the 3d unit cell of HCP and projection view?
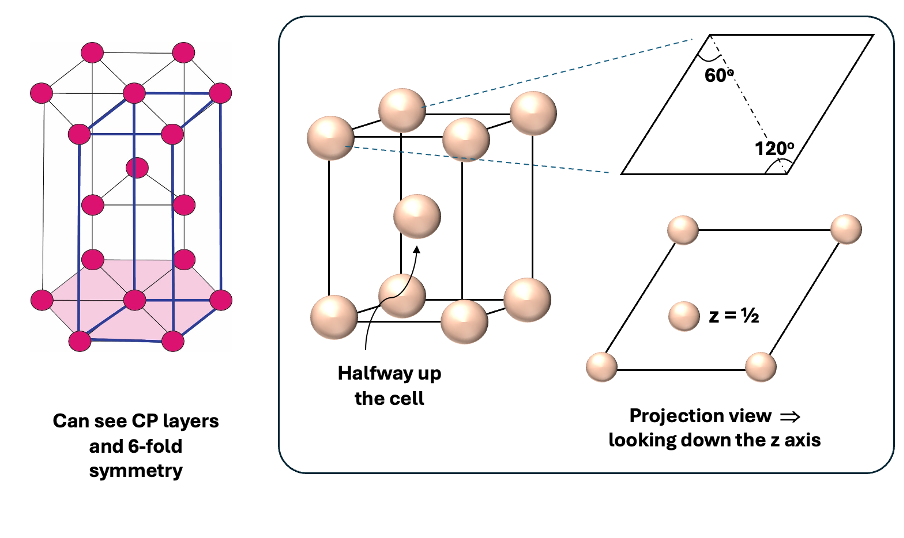
what are the layers of CCP?
what is the coordination number?
ABCABCABC
12
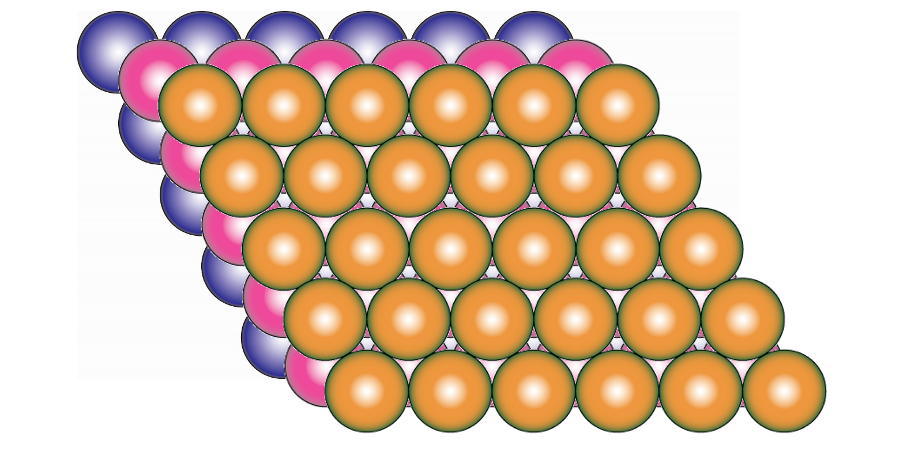
what is the close packed layer in FCC unit cell ?
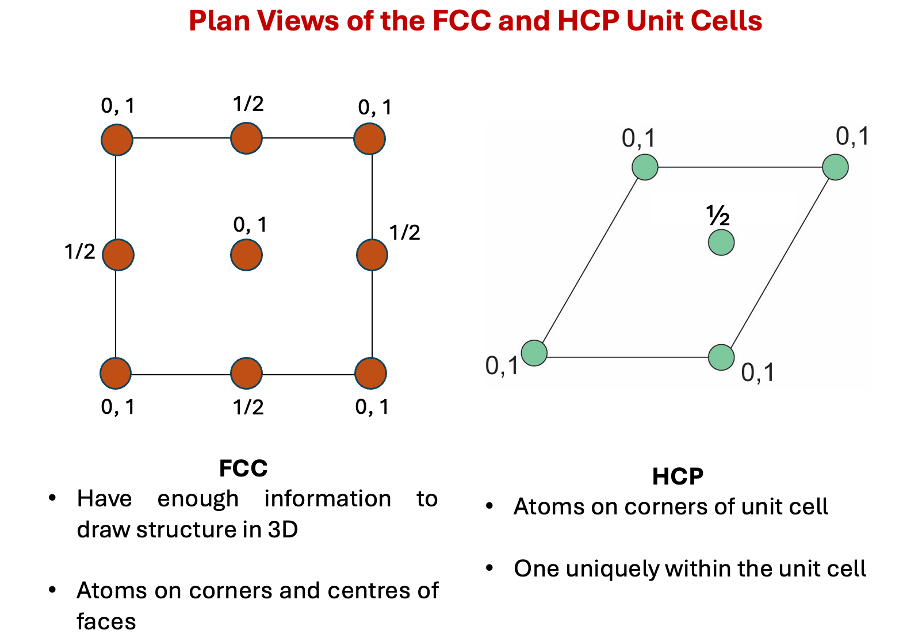
plan views of FCC vs HCP
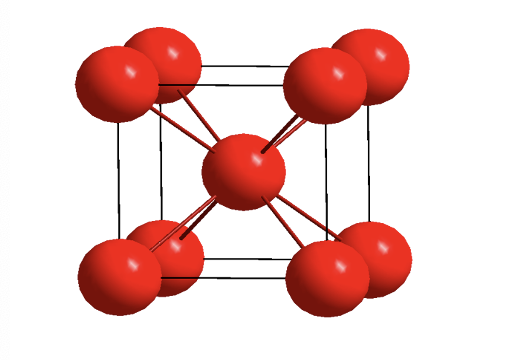
what is body centred cubic? what is the close packed direction?
what materials are BCC?
direction is diagonal along body centred cubic
alkali metals and some transition metals
what are the 2 types of interstices?
what are the shapes?
tetrahedral and octahedral
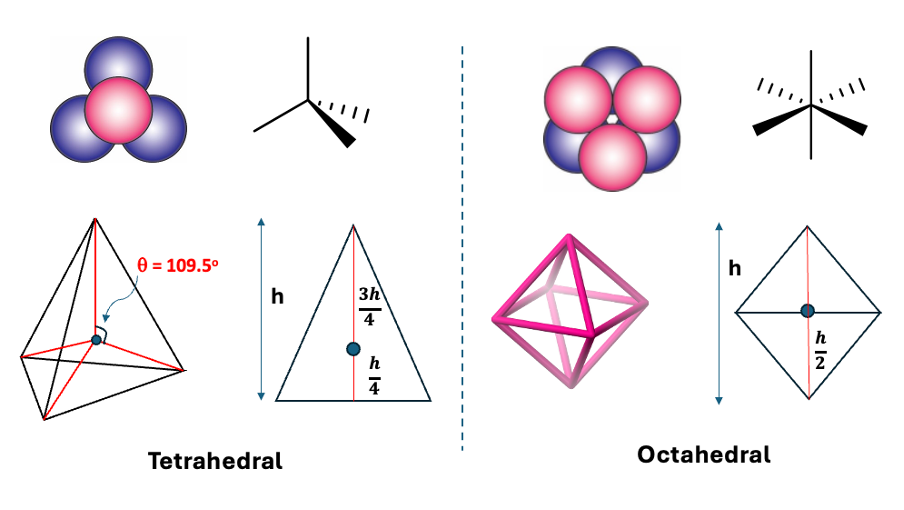
how many octahedral interstices are there in a HCP unit cell?
draw plan view
2 sites
how many tetrahedral interstices are there in a HCP unit cell?
draw plan view
2 inside, 8 on edge of unit cell (8 × ¼ =2)
= 4 total
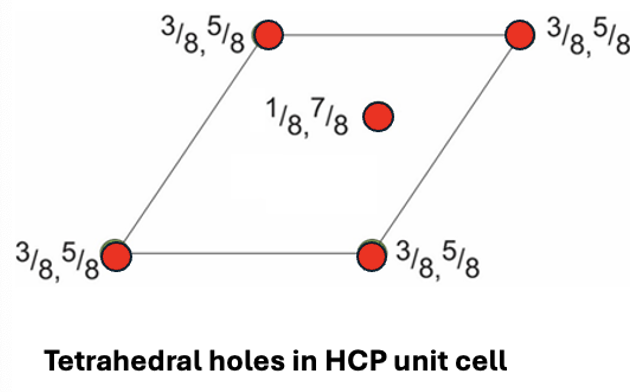
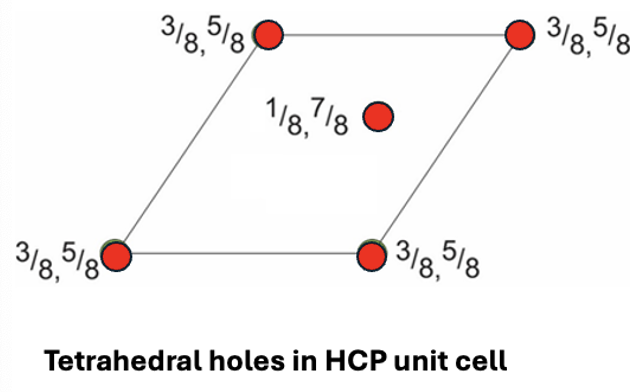
why is it unfavourable to fill both lattice points of tetrahedral interstitial sites of HCP?
3/8 and 5/8 are very close together, so little separation between ions = repulsion
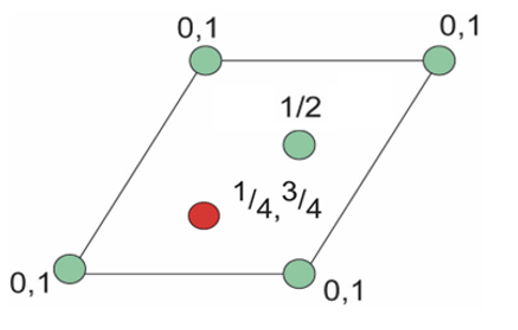
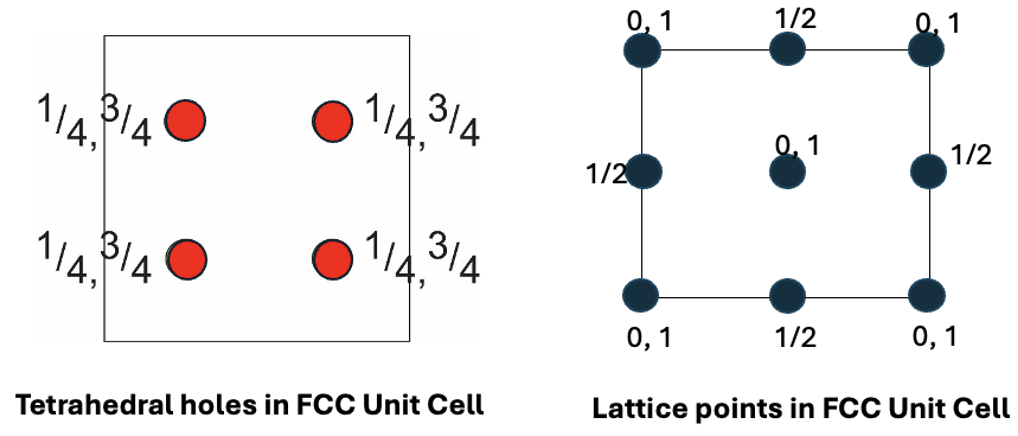
how many octahedral interstices are there in a FCC unit cell?
draw plan view
1 in centre
12 on edges (12 × ¼ = 3 )
= 4 in total
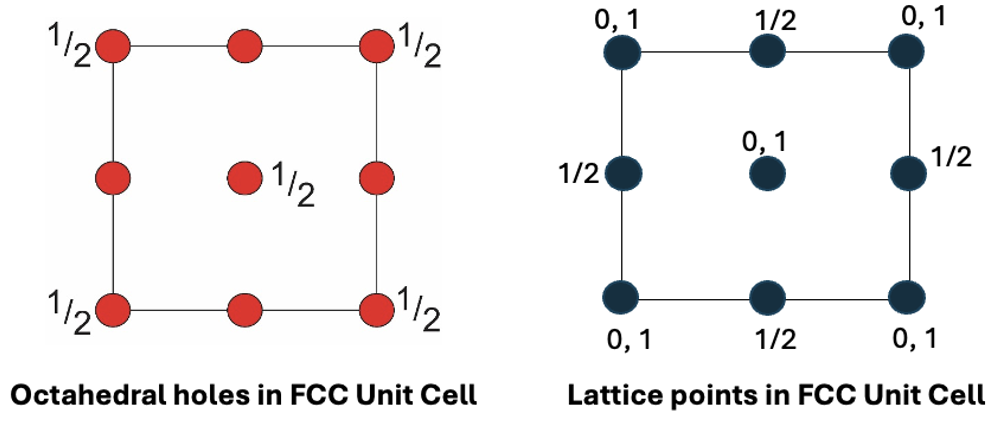
how many tetrahedral interstices are there in a FCC unit cell?
draw plan view
8 in unit cell
what are the rules in terms of HCP and FCC interstices numbers?
twice as many tetrahderal as close packed atoms
same number of octahedral as close packed atoms
how is NaCl made up?
CCP lattice of Cl- ions
Na+ fills octahedral interstices
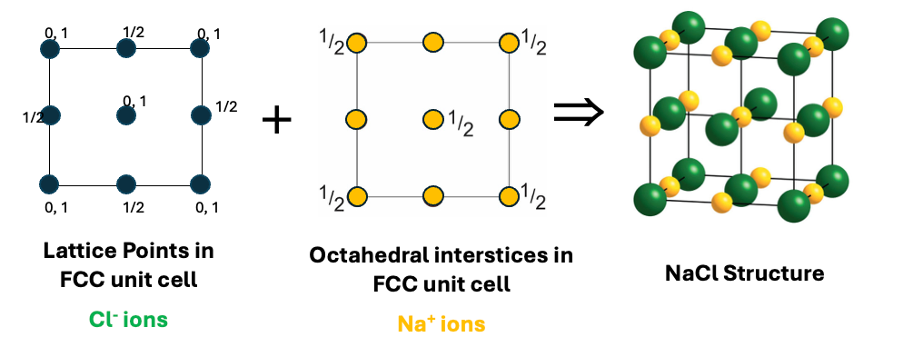
why do anions surround cations and cations surround anions?
to avoid electrostatic repulsion and the formation of areas of high charge density
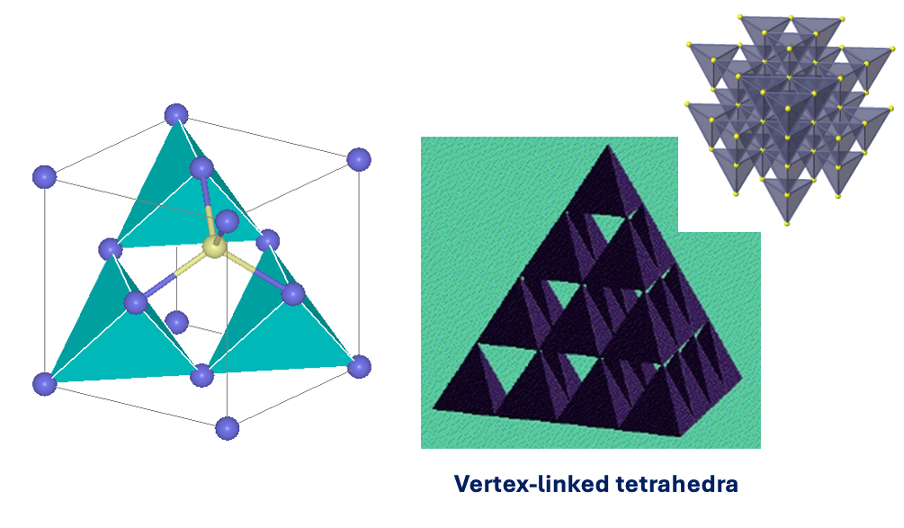
what are the three different types of polyhedra linking?
what are their relative stability?
when is this effect the largest?
vertex sharing > edge sharing > face sharing
effect largest for cations with high charge and low coordination number
why is edge and face sharing less stable than vertex?
brings ions at the centre of each polyhedron closer together = increasing electrostatic repulsions
how is NiAs made up?
As3- makes up HCP lattice
Ni3+ fills octahedral holes
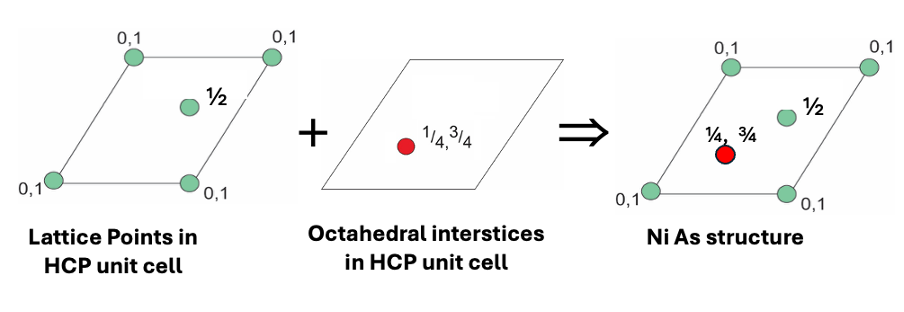
show the NiAs unit cells together to form 3D structure
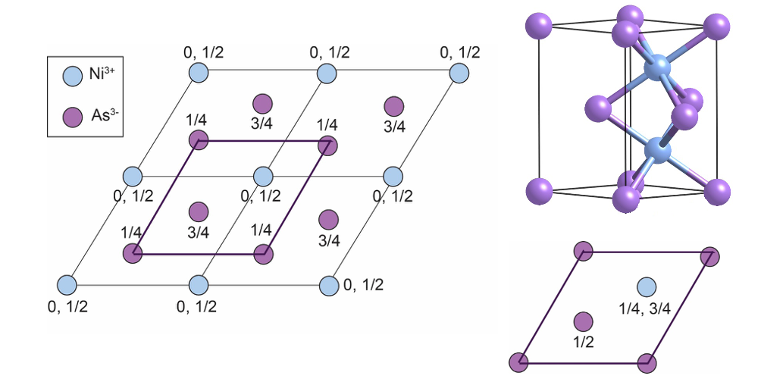
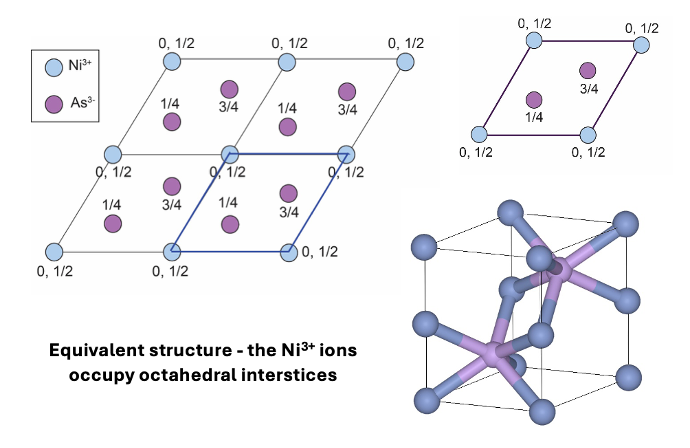
what is NiAs alternative unit cell?
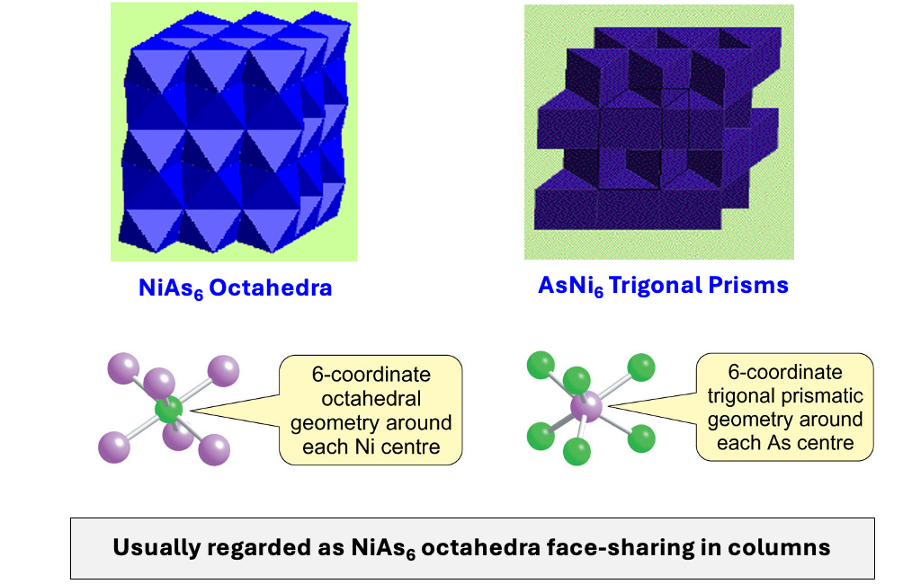
what is the polyhedron sharing in NiAs?
regarded as NiAs6 octahedral face sharing in columns
both 6 coordinate
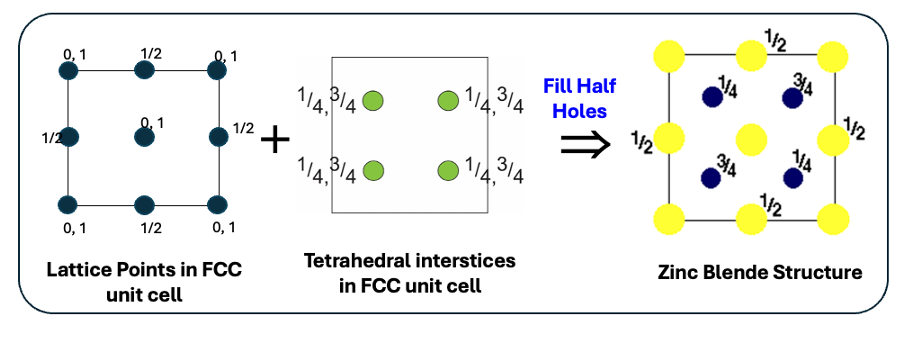
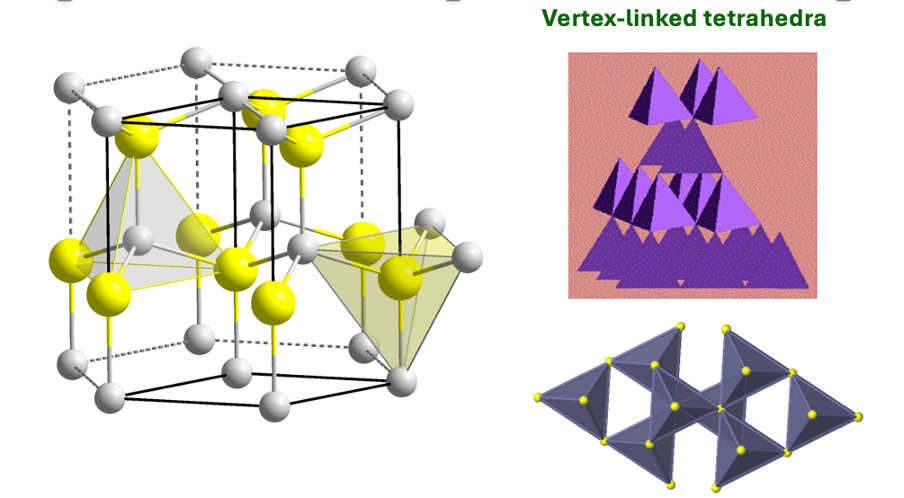
how is ZnS blende made up?
how are the interstices filled?
S2- ions in CCP lattice
half tetrahedral holes filled with Zn2+ ions
fill diagonal quarters then opposite diagonal ¾
what is 3D structure of ZnS blende?
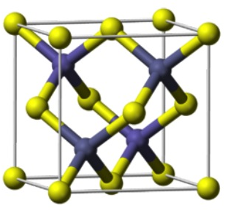
what are the coordination numbers for ZnS blende?
what is the polyhedron sharing?
both in tetrahedral environments = both 4 coordination
vertex linked tetrahedra
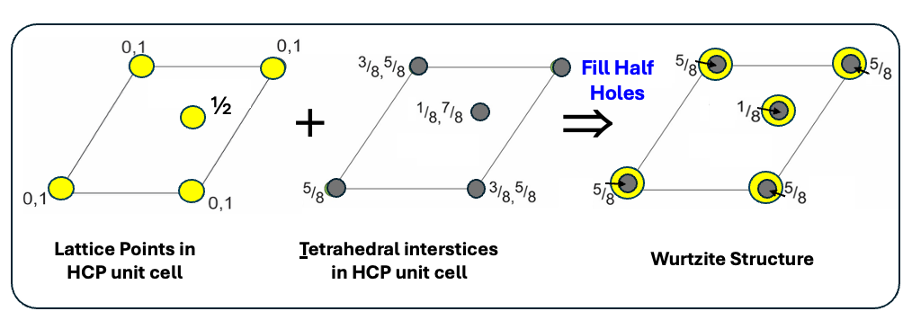
how is ZnS wurtzite made up?
HCP lattice of S2-
half tetrahedral holes filled by Zn2+
what is 3d structure of ZnS wurtzite?
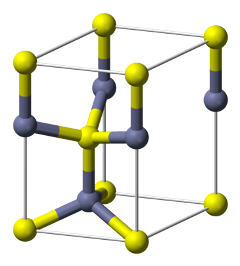
what is the coordination polyhedra for ZnS wurtzite?
both in tetrahedral environments = 4 coordinate
vertex linked tetrahedra
what is polymorphism?
why does it occur? transformation between structures?
when compounds of the same formula exhibit different crystal structures
occurs because crystallisation depends on both kinetics and thermodynamics.
may obtain a kinetic product if the barrier is lower than the thermodynamically favoured phase
transformation between structures is slow
what conditions can give one ZnS structure over the other?
changes in temperature or pressure
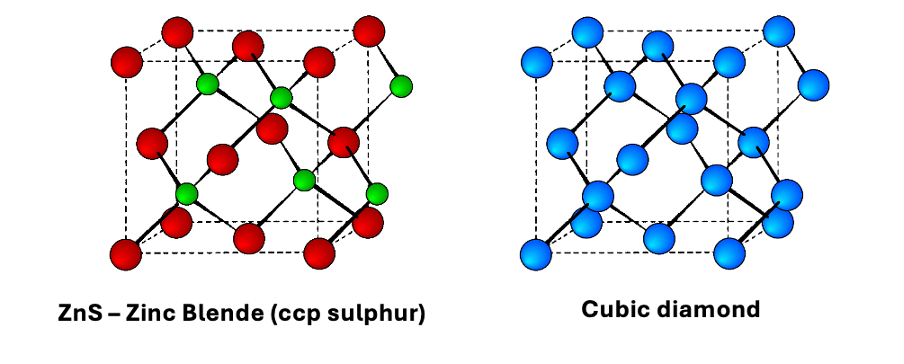
how can a cubic diamond structure be described?
how is this similar to ZnS blende structure?
described as FCC lattice where half the tetrahedral sites are filled
zinc blende = also two interpenetrating FCC lattices, with one offset ¼ of a cube along the cube diagonal
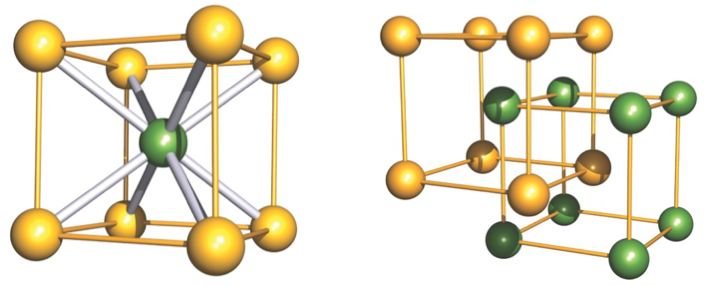
how is CsCl made up?
primitive cubic packing of Cl- ions
all cubic holes filled by Cs+ ions
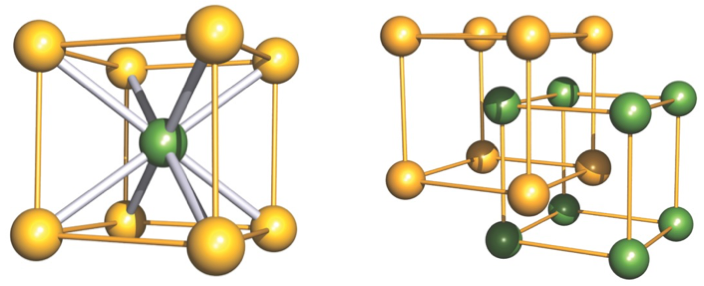
why is this not BCC?
what is it?
central atom differs from those at corners
BCC = all same atoms
two interpenetrating primitive cubic lattices
how is CaF2 (fluorite) made up?
CCP lattice of Ca2+
F- ions occupy tetrahedral holes
fluoride ions smaller so fill interstices
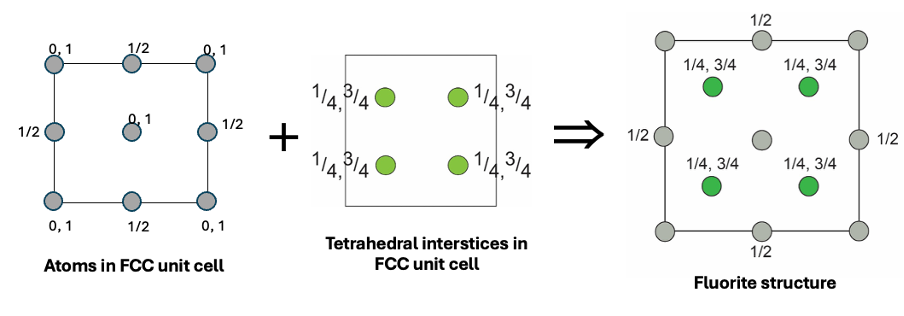
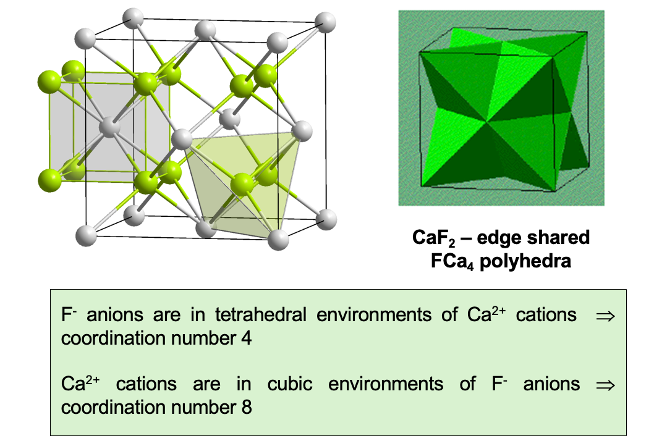
coordination polyhedra of CaF2
F- in tetrahedral environments of Ca2+ cations = coordination 4
Ca2+ in cubic environments of F- anions = coordination 8
edge sharing
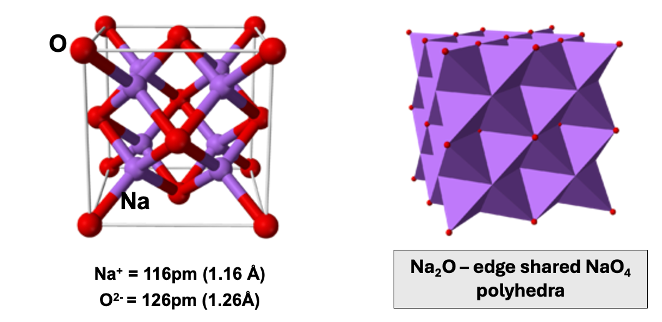
what is Na2O (anti fluorite) structure?
O2- anions in CCP lattice
Na+ cations in tetrahedral interstices
coordination polyhedra of Na2O (anti fluorite)
Na+ coordination 4
O2- coordination 8
edge sharing polyhedra
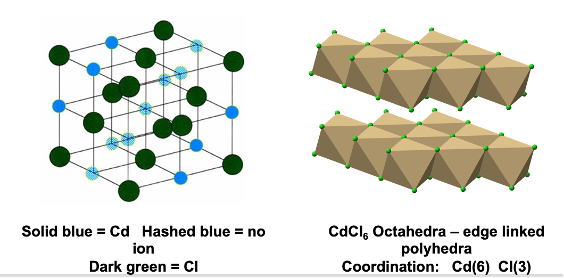
how is CdCl2 made up?
how is this similar to NaCl?
CCP lattice of Cl-
half octahedral holes filled by Cd2+, alternate layers
structure is identical to NaCl, but half cations removed as sheet
coordination polyhedra of CdCl2?
Cd coordination 6
Cl coordination of 3
edge sharing polyhedra
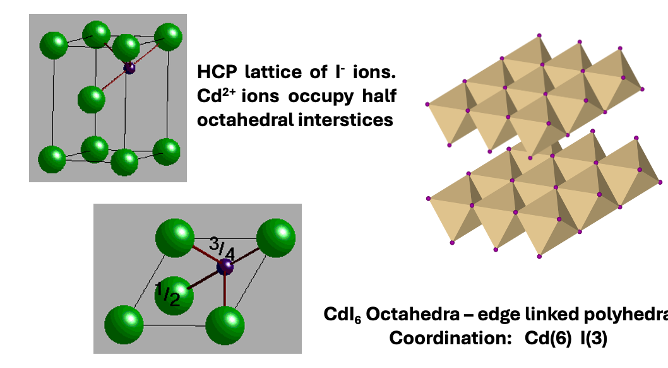
how is CdI2 made up?
HCP lattice of I- ions
half octahedral holes in HCP lattice filled by Cd2+
what is coordination polyhedra of CdI2?
Cd = 6
I = 3
edge linked polyhedra
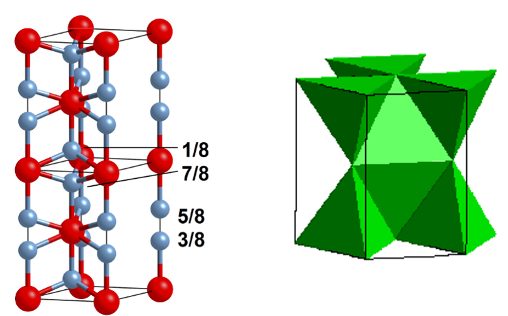
why is there no AX2 with tetrahedral holes in an HCP lattice?
this would involve face linking of tetrahedra = unfavourable as it brings ions at the centre of each polyhedron close together and increases electrostatic repulsions
what are the 3 factors that influence ionic structures?
electrostatics
polarisation
steric factors
how do electrostatics influence structure?
structure maximise favourable interactions (anion/cation)
minimise unfavourable interactions (anion/anion and cation/cation)
how does polarisation affect ionic structures?
ions are considered hard spheres
if there is a significant difference in the polarisability of cation and anion, this affects ion packing
how do steric factors affect ionic structures?
ionic compounds built by filling interstices of close packed array of ions
this is governed by the ratio of the size of ions = radius-ratio rules
what is polarisability?
what are the characteristics of polarisable ions?
the tendency of electron distribution in an ion to be influenced by other ions
ions tend to have low charges and large radii
how to work out polarisability?
polarisability ≈ r / n
ionic radius / charge