Circulatory System Quiz
1/106
Earn XP
Description and Tags
01/07/2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
What is the circulatory system made of?
heart, arteries, veins, capillaries
Functions of the circulatory system
transport blood → carries O2 and CO2, nutrients, wastes, hormones, enzymes antibodies, heat
how many chambers in the heart
4
Cardiac muscles beat on their own. What is it called?
myogenic
Where is the eart found
middle of the chest
Fluid the protects the heart
pericardium
how does pericardium protect the heart
shock absorber
what is heat shielded by?
breast bone, sternum, ribcage
Does the right side pump oxygenated or deoxygenated blood? (and where to?)
deoxygenated, to the lungs
Does the left side pump oxygenated or deoxygenated blood? (and where to?)
oxygenated, the rest of the body
3 types of circulation
pulmonary, systemic, cardiac
pulmonary circulation
between the heart and the lungs
systemic circulation
between the heart and the rest of the body
cardiac circulation
within the heart
what are the upper and lower parts of the heart called?
upper- atria
lower- ventricles
how do the atria and ventricles work together?
atria squeeze blood into ventricles
are atria thin or thick walled? why?
thin walled (thin muscles), short distance → not much effort needed
what do the ventricles do/
pump blood away from the heart
Where do the left and right ventricles pump blood to? (are they thin/thick?)
right- to lungs (thinner)
left- the body (thicker)
what keeps the blood going in one direction/
valves
Where are the atrioventricular valves located/
between atria and ventricles
When do the AV valves close
when ventricles contract
AV valves full name
atrioventricular valves
What is the name for flaps of tissue in valves
cuspids
right vs left av valves (# of cuspids and name)
right- 3 tricuspid
left- 2 bicuspid
What holds cuspids from opening in reverse?
chordal tendinae
Semilunar valve (where, # of flaps)
between ventricles and arteries that take blood away, 3
what do the semilunar valves do?
open when ventricle contracts, then shut when it refills through suction
Do semilunar valves need chordae tendinae (why?)
no, suction does the job.
What sound does the closing of the av valves make?
lub
What sound does the closing of the semilunar valves make?
dub
what is the cardiac cycle
one heart beat
what happens during the cardiac cycle
two atria contract and two ventricles contract
What happens in systole
heart contracts- blood is squeezed out
what happens in diastole
heart relaxes- chamber fill with blood
Cardiac cycle is a full cycle …
of systole and diastole of the atria and then systole and diastole o the ventricles
What controls heart’s hearts tempo/rythm
Sinoatrial (SA) node and Atrioventricular (AV) node
What id the sinoatrial node?
bundle of nerves that initiates the heartbeat
another name of the sinoatrial node
pacemaker
What are the effects of the SA node impulses
atria contract and sends a shock to AV node
where is the SA node found
where superior vena cava enters the right atrium
What is the atrioventricular node
bundle of nerves
where is the atrioventricular node located
between right atrium and right ventricle
what does the AV node do?
impulse from SA node is sent to the bundle of HIS and then to purkinje fibers so the ventricle contract
electrocardiogram
tracks electrical impulses in the heart
What does the P wave mean on an electrocardiogram
atria contract
What does the QRS wave mean on an electrocardiogram
ventricles contract
What does the T wave mean on an electrocardiogram
ventricles relax
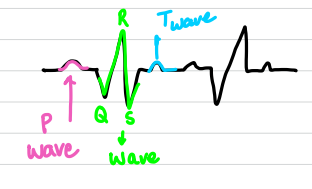
label the waves
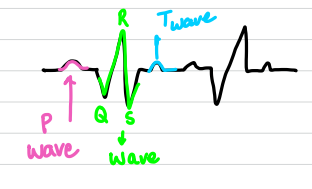
What is an electrocardiogram is used for
check heart rate, detect irregularities, detect damage to heart tissue after a heart attack
what is tachycardia
heart rate too fast
what is bradycardia
heartrate too slow
what is arrythmia
irregular heart rate
EVC
extra ventricular contractions
Stress test (why and what)
bc sometimes heart condition doesn't show till pushed to the limit, EKG is done on the treadmill/bike
what does a defibrillator do
stops the heart from continuously contracting → restarts the SA node → normal rhythm
Cardiac Output
the amount of blood pumped out of the left ventricle into the body in one minute
What does the cardiac output depend on?
stroke volume and heart rate
What is stroke volume
amount of blood pushed out each beat
avg stroke volume
70ml
what is heart rate
# of beats per minute
avg heart rate
72 beats per minute
cardiac output formula
stroke volume x heart rate
what does stroke volume depend on
strength of the heart: strong heart = more squeezed out with each beat
how does a strong heart affect heart rate
lower heart rate = not as many beats needed to circulate the blood
Blood flow through the body
(a circle)
heart
aorta
arteries
arterioles
capillaries
cells of the body
capillaries
venules
veins
arteries take blood to/away from the heart
away
arteries thick/thin walls?
thick
why do arteries have thick walls
withstand high blood pressure (blood is pushed into them
arteries can constrict and relax?
yes
Constriction of arteries
vasoconstriction
relaxation of arteries
vasodilation
what keeps arteries elastic ( + what happens with time?)
collagen.
aging = lose collagen = less elastic = high blood pressure
pulse
arteries contracting and relaxing
Aneurism
a bulge formed from weakening of the artery walls
what can cause weakening of the artery walls
age, genetics, chronic high blood pressure
what happens if an aneurism bursts
internal bleeding
arteriosclerosis
build up of plaque (fat and calcium) that narrows the diameter of the artery
Effects of arteriosclerosis
high blood pressure, blood doesnt get where it needs to → heart attack, stroke (brain)
how do you treat clots and arteriosclerosis
balloon angioplasty with stent, bypass surgery
arterioles
branch out from arteries
what do arterioles do
slow down blood
What is at the end of arterioles (+ purpose)
pre-capillary sphincters, control how much blood goes into capillaries
capillaries
thin vessels (1 cell thick)
what do capillaries do (+ examples)
diffuse metabolites to and from cells, co2 ←> O2 nutrients ←> wastes
total length of blood vessels
96,000km
how far away capillaries are
2-3 cells
Venules
drain things from capillaries into veins
veins (thickness)
thinner than arteries (low blood pressure)
can veins constrict/dilate
no
veins job
bring blood back to the heart
How do veins compete with gravity
skeletal muscle contractions push blood up and one way valves
Varicose veins (what and causes)
valves fail → blood pools → weighs down the vein → bulges and twists
age, genetics, standing for a long time, crossing legs
Blood pressure
pressure on walls of arteries by blood
what measures blood pressure
sphygmomanometer
Normal heart pressure ( + what each number stands for)
120 (systolic) / 80 (diastolic)
hypertension vs hypotension
high and low blood pressure
What affects blood pressure
Blood viscosity, volume, rate, elasticity of arteries, size of arteries
Blood viscosity ( + cause and effects)
how thick blood is
genetics
smoking → thickens
Alcohol → thins
Blood volume ( + cause and effects)
How much blood is in your body
dehydrated → blood pressure down\
Salty diet → blood pressure up
haemorrhage (bleeding) → blood pressure down