Chapter 13: Alkenes
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
whilst aliphatic alkenes have the general formula CnH2n, what kinds of alkenes DO NOT?
cyclic alkenes
alkenes with more than 1 double bond
for every carbon atom of a double, bond 3 are used in …
the other 1 is used in a …
sigma (σ) bonds
pi bond
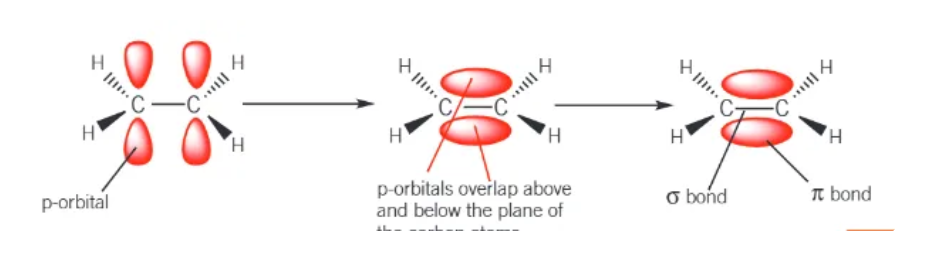
what is a pi bond?
the sideways overlap of 2 p-orbitals
where is the electron density of a pi bond?
concentrated above and below the line joining the nuclei of bonding atoms
draw the formation of pi bonds:
the shape around each of the carbon atoms in a double bond is:
trigonal planar
three regions of electron density
three regions repel as far as possible → bond angle is 120o
all atoms in the same plane
what is a stereoisomer?
An isomer with the same structural formula but a different arrangement of atoms in the space
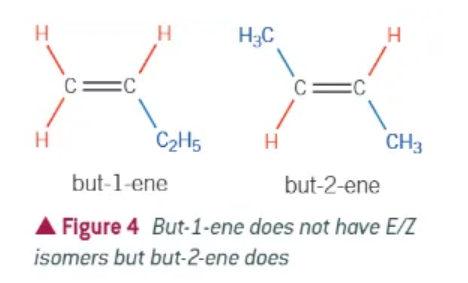
why does E/Z isomerism arise?
rotation around the double bond is restricted
groups attached to each carbon are therefore fixed relative to each other
why is a double bond’s rotation restricted?
the position of the ⫪ bond’s electron density is above + below the plane of the sigma bond
what 2 criteria both need to be filled out for E/Z isomerism?
carbon=carbon double bond
different groups attached to each carbon of the double bond
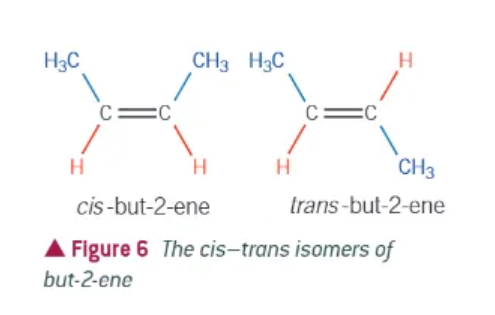
cis-trans isomerism:
special case of E/Z isomerism
one of the atoms on either side of the C=C bond is the same
Cahn-Ingold-Prelog nomenclature:
if the groups of higher priority are on the same side of the double bond, the compound is a Z isomer
if the groups of higher priority are diagonally placed across the double bond, the compound is an E isomer
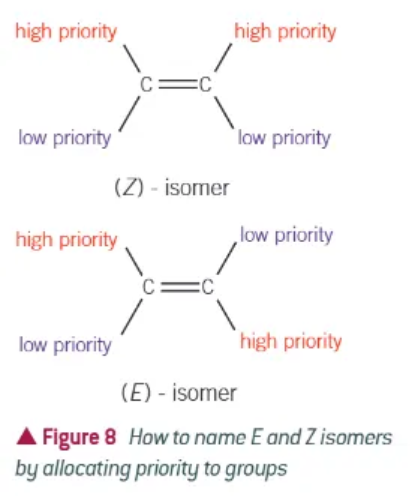
how do we decided what has the highest priority according to Cahn-Ingold-Prelog?
highest priority atom attached to the carbon has the largest atomic number.
if they are the same, you will need to find the first point of difference.
why are double bonds more reactive?
the concentration of electron density is above and below the plane of the sigma bond
being on the outside of the double bond, the pi electrons are more exposed than the electrons in the sigma bond
a pi bond readily breaks and alkenes undergo addition reactions relatively easily
calculating the enthalpy of a pi bond:

a C=C bond is…
a pi bond + a sigma bond
hydrogenation of alkenes:
alkene + hydrogen → (over nickel catalyst at 423K ) → alkane
addition reaction def.
2 molecules react together to make 1 product
halogenation of alkenes:
alkene + halogen → dihaloalkane
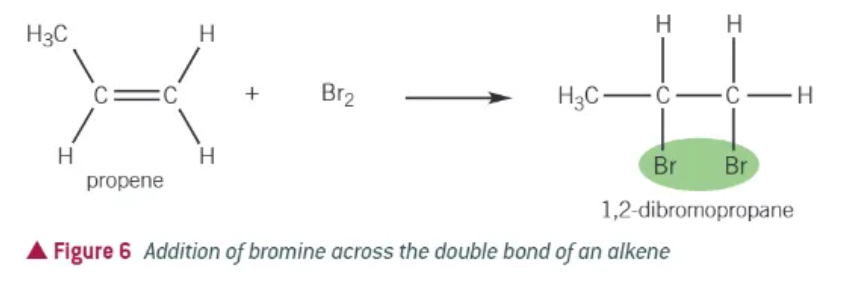
testing for unsaturation:
react with bromine water (orange solution)
positive result will turn colourless
any compound with a C=C will decolourise bromine water
addition reactions of alkenes + hydrogen halides:
alkene + gaseous hydrogen halide → haloalkane
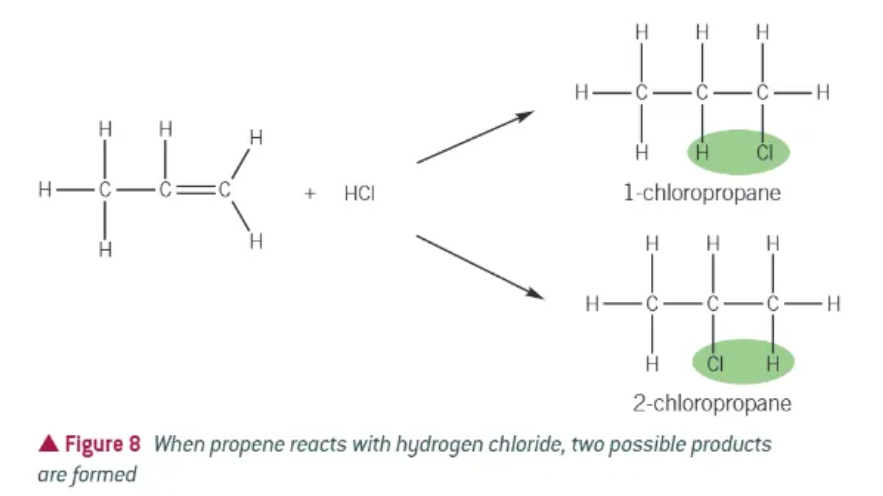
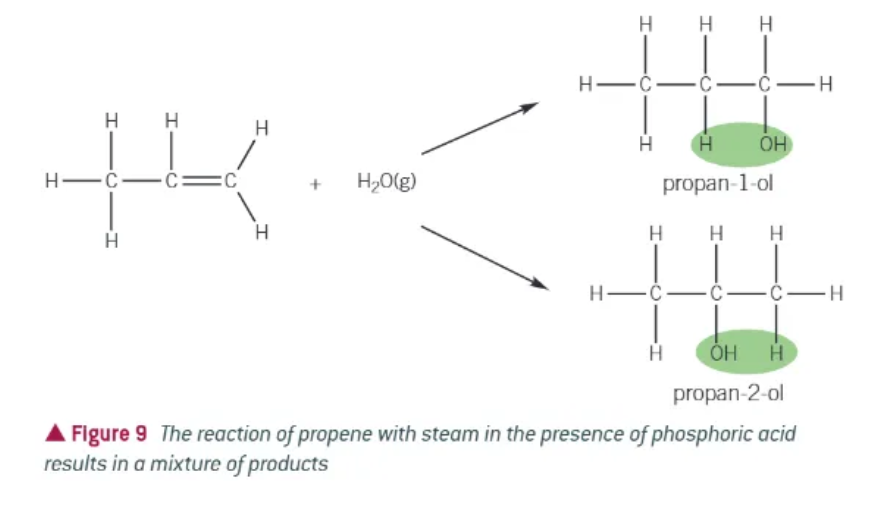
when an unsymmetrical alkene reacts with an unsymmetrical compound…
two products are possible
hydration reactions of alkenes:
alkenes + steam → (in the presence of a phosphoric acid catalyst, H3PO4) → alcohol